0% found this document useful (0 votes)
290 views9 pagesDeciles Calculation for Grouped Data
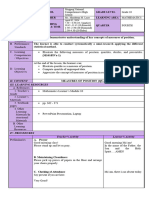
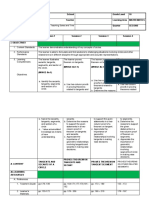
1. The document defines deciles as the nine score values that divide a distribution into 10 equal parts and are also the median of each part.
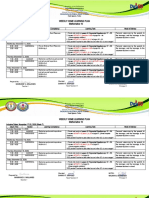
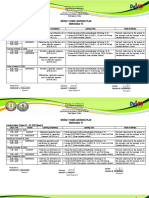
2. An equation is provided to calculate the deciles (Dk) of grouped data based on the lower boundary (LB) of each class, cumulative frequency (cf), class frequency (f), and class size (i).
3. Worked examples demonstrate applying the equation to a sample data set to find the third (D3) and fifth (D5) deciles. D3 is calculated to be 20.19 and D5 is calculated to be 31.75.
Uploaded by
maritope0404Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
290 views9 pagesDeciles Calculation for Grouped Data
1. The document defines deciles as the nine score values that divide a distribution into 10 equal parts and are also the median of each part.
2. An equation is provided to calculate the deciles (Dk) of grouped data based on the lower boundary (LB) of each class, cumulative frequency (cf), class frequency (f), and class size (i).
3. Worked examples demonstrate applying the equation to a sample data set to find the third (D3) and fifth (D5) deciles. D3 is calculated to be 20.19 and D5 is calculated to be 31.75.
Uploaded by
maritope0404Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Deciles
- Learning Competencies
- Understanding Deciles
- Deciles Formula
- Example Calculation