Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Submitted By: Ankit Timilsina Bipin Thakur Bishal Thapa
Uploaded by
deluxephantom5950 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views9 pagesThe document discusses the principles of reflection and refraction and how they apply to the behavior of light through lenses, prisms, mirrors and optical instruments. It covers how reflection occurs when light strikes a surface, refraction when light changes speed between mediums, and how lenses, prisms and mirrors manipulate light through converging, diverging and reflecting light rays. It emphasizes that understanding these ray optics principles is essential for designing optical instruments.
Original Description:
Original Title
Presentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the principles of reflection and refraction and how they apply to the behavior of light through lenses, prisms, mirrors and optical instruments. It covers how reflection occurs when light strikes a surface, refraction when light changes speed between mediums, and how lenses, prisms and mirrors manipulate light through converging, diverging and reflecting light rays. It emphasizes that understanding these ray optics principles is essential for designing optical instruments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views9 pagesProject Submitted By: Ankit Timilsina Bipin Thakur Bishal Thapa
Uploaded by
deluxephantom595The document discusses the principles of reflection and refraction and how they apply to the behavior of light through lenses, prisms, mirrors and optical instruments. It covers how reflection occurs when light strikes a surface, refraction when light changes speed between mediums, and how lenses, prisms and mirrors manipulate light through converging, diverging and reflecting light rays. It emphasizes that understanding these ray optics principles is essential for designing optical instruments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
' STUDY THE PRINCIPLES OF REFLECTION AND
REFRACTION AND ANALYZE THE BEHAVIOR OF
LIGHT THROUGH LENSES, PRISM AND
MIRRORS AND INVESTIGATE THE RAY OPTICS
PRINCIPLES IN OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS '
Project submitted by : Ankit Timilsina
Bipin Thakur
Bishal Thapa
Introduction
• Welcome to our presentation on the principles of reflection and
refraction in optics.
• Today, we'll delve into the fascinating behavior of light as it
interacts with various mediums, lenses, prisms, and mirrors.
Fig : Bending of light when
passing through a prism
Fig : Light rays converging when Fig : Convex mirror diverging
passing through a Convex Lens the parallel beam of light
Understanding
Reflection
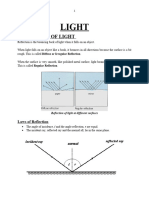
• Reflection is the bouncing back of light
when it strikes a surface.
• The angle of incidence is equal to the
angle of reflection, as described by the
law of reflection.
• Examples of reflection include mirrors,
polished metals, and still water surfaces.
Exploring
Refraction
• Refraction occurs when light passes from
one medium to another, causing it to
change direction.
• The change in direction is due to the
change in speed of light in different
mediums.
• Snell's law describes the relationship
between the angles of incidence and
refraction.
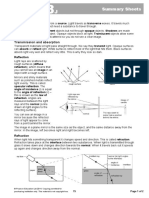
Behavior of light • Lenses are transparent objects that
refract light, focusing or dispersing it.
through Lenses
• Convex lenses converge light rays,
used in magnifying glasses and
cameras.
• Concave lenses diverge light rays,
used in correcting nearsightedness.
Fig (a) : Convex Lens Fig (b) : Concave Lens
Investigating Prism
Behavior
Prisms are optical devices that They are commonly used to
refract, reflect, and disperse light. separate white light into its
constituent colors (dispersion).
Fig : Refraction light
Prisms are crucial components in through glass prism
spectrometers and optical
instruments.
Analyzing Mirror
Properties
• Mirrors reflect light, producing images.
• Plane mirrors produce virtual images that
appear to be behind the mirror.
• Concave mirrors can produce real or
virtual images depending on the object's
position relative to the mirror.
• Convex mirrors always produce virtual,
diminished images.
Ray Optics Principles
in Optical Instruments
• Optical instruments, such as
microscopes, telescopes, and
binoculars, rely on ray optics
principles.
• They use lenses, mirrors, and
prisms to manipulate light for
magnification, focusing, and
image formation.
• Understanding ray optics is
essential for designing and
optimizing these instruments.
CONCLUSION
1. In conclusion, the principles of reflection and refraction govern the
behavior of light in various optical systems.
2. By studying these principles, we can design and understand the workings
of lenses, prisms, mirrors, and optical instruments.
3. Thank you for your attention. Let's keep exploring the wonders of optics
together.
You might also like
- Mirrors Form Images by Reflecting Light.: How Does Surface Affect Reflection?Document5 pagesMirrors Form Images by Reflecting Light.: How Does Surface Affect Reflection?Marlop CasicasNo ratings yet
- Refraction and Reflection of LightDocument9 pagesRefraction and Reflection of LightShenNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics by Kshitij Chandel (Physics)Document8 pagesRay Optics by Kshitij Chandel (Physics)Kshitij ChandelNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightArman Akram100% (1)
- Basic Optics For Photogrammetry: Janak Raj JoshiDocument32 pagesBasic Optics For Photogrammetry: Janak Raj JoshiAshish ChaliseNo ratings yet
- Application of Optical Instrument LeCtureDocument14 pagesApplication of Optical Instrument LeCtureNURSHAHADAH ISMAELNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - Light & OpticsDocument39 pagesLecture 13 - Light & OpticsPhilip Cedric DolorNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument9 pagesOpticsShrihari DholeNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorDocument6 pagesMirrors and Lenses: Ray Diagrams in A Plane MirrorLabeenaNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument25 pagesOpticsSam LoveNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 5Document29 pagesLecture 7 5mysaustine1No ratings yet
- Reflection and MirrorsDocument30 pagesReflection and MirrorsDavidis DotaroNo ratings yet
- LightDocument22 pagesLightPeerchand Chaudhary100% (1)
- Prepared By: Denzel G. Armelon Gen. ScienceDocument50 pagesPrepared By: Denzel G. Armelon Gen. ScienceJohn andre MarianoNo ratings yet
- Lights and MirrorsDocument17 pagesLights and MirrorsKDNo ratings yet
- Ch. 18 - Mirrors and LensesDocument28 pagesCh. 18 - Mirrors and LensesLunox NikolaiNo ratings yet
- Lights Mirrors and LensesDocument17 pagesLights Mirrors and LensesJusiah Mae Janolino Tabangan II100% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectDocument103 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectRishi Bhatia100% (1)
- Optics - Reflection, Refraction and LensesDocument46 pagesOptics - Reflection, Refraction and LensesBrianna Malcolm100% (1)
- Light MicrosDocument21 pagesLight MicrosSimranNo ratings yet
- Lens & MirrorDocument8 pagesLens & Mirrordivya singh100% (1)
- Introduction To Light (Notes)Document7 pagesIntroduction To Light (Notes)Shivang GuptaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 - Lights and Optics NotesDocument20 pagesAP Physics 2 - Lights and Optics Notes孙铭阳No ratings yet
- Light, Optics & ColourDocument38 pagesLight, Optics & ColourKrish ChopraNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light and Plane MirrorsDocument24 pagesReflection of Light and Plane MirrorsclarisseNo ratings yet
- Optics & Mirrors - Grade 10 (JP)Document12 pagesOptics & Mirrors - Grade 10 (JP)HotTornado XDNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Special Senses Part 2-VisionDocument16 pagesLecture 7 Special Senses Part 2-VisionMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document8 pagesOptics 1Stephson Micayee Da LastbornNo ratings yet
- Yamat, AngeloDocument21 pagesYamat, AngeloCAMILLE JOY PATUNGANNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument56 pagesOpticsahsan shahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedDocument40 pagesCHAPTER 7 Geometrical Optics UpdatedPriyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Name: Saksha Govind Ubale - Paper: - College Name: Icle'S Motilal Jhunjhunwala - Academic YearDocument12 pagesName: Saksha Govind Ubale - Paper: - College Name: Icle'S Motilal Jhunjhunwala - Academic YearPravin GoleNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument35 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesdeguzmanjannellegNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Week4Document19 pagesPhysics 2 Week4basurahangyujNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes - LightDocument10 pagesAdditional Notes - LightsidharthNo ratings yet
- Optics Egt22460Document14 pagesOptics Egt22460vimukthi gunasinghaNo ratings yet
- Light and OpticsDocument58 pagesLight and OpticsPARVEEN KAUR A/P MONHEN SINGH MoeNo ratings yet
- TelescopeDocument11 pagesTelescopeapi-279817487No ratings yet
- Print - Light WavesDocument22 pagesPrint - Light WavesantonellidejanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Light Handout 1Document3 pagesProperties of Light Handout 1hannah alexis agcolNo ratings yet
- Investigation 11 - Experience 3Document17 pagesInvestigation 11 - Experience 3weldeenytNo ratings yet
- Sample - Science NCERT SummaryDocument4 pagesSample - Science NCERT Summarysameer.61680No ratings yet
- Physics I Notes Chapter 14: Light, Reflection, and ColorDocument8 pagesPhysics I Notes Chapter 14: Light, Reflection, and ColorMinh PhamNo ratings yet
- Physics 122Document107 pagesPhysics 122stephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Light Gr.10Document5 pagesLight Gr.10Himayu RanpariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Optics 191 - TaggedDocument52 pagesChapter 5 Optics 191 - TaggedST4No ratings yet
- LightDocument12 pagesLightHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Torio, John Carl T. Science 10 q2 Week 6Document12 pagesTorio, John Carl T. Science 10 q2 Week 6carl twqeNo ratings yet
- Light and Mirror GRADE 10Document44 pagesLight and Mirror GRADE 10kimarie kinmon100% (1)
- Waves and Optics Finals ReviewerDocument8 pagesWaves and Optics Finals ReviewerJoshua QuimsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light Slides (Reflection)Document11 pagesChapter 5 Light Slides (Reflection)lutfiNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerniezlNo ratings yet
- Light PDFDocument5 pagesLight PDFAninda RoyNo ratings yet
- Wave and Optics DLPDocument8 pagesWave and Optics DLPlopezchinshin28No ratings yet
- Learning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Learning CompetenciesDocument13 pagesLearning Plan in Science 10: Unit Topic: Content Standard: Learning Competenciesakoaysijoy100% (1)
- Chapter Light-Reflection and RefractionDocument1 pageChapter Light-Reflection and RefractionVIDYA MNo ratings yet
- Physics: Nature of Light - Flat MirrorsDocument17 pagesPhysics: Nature of Light - Flat MirrorsReplayableNo ratings yet
- WP4 Light WavesDocument16 pagesWP4 Light Waveswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Light WaveDocument35 pagesLesson 5 - Light WaveElijah AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- UPVC CHECKLIST As ASTM 1748/BS 7413/ EN 12608: General NotesDocument2 pagesUPVC CHECKLIST As ASTM 1748/BS 7413/ EN 12608: General NotesAhmed DawodNo ratings yet
- NFRC 100-2010 E0a8Document108 pagesNFRC 100-2010 E0a8Ali KassidNo ratings yet
- Concentrating Solar CollectorsDocument10 pagesConcentrating Solar CollectorssureshlalNo ratings yet
- Model Posing GuideDocument2 pagesModel Posing GuideAndrei Mihail40% (5)
- CHAPTER 2 - Principles of Solar EnergyDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Principles of Solar EnergyNananq LalalalaNo ratings yet
- Strand Century Lighting 3413 8-Inch Fresnelite Spotlight Spec Sheet 6-77Document2 pagesStrand Century Lighting 3413 8-Inch Fresnelite Spotlight Spec Sheet 6-77Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Quotation For 50 W Semi Intergrated Solar Flood Light Make in IndiaDocument1 pageQuotation For 50 W Semi Intergrated Solar Flood Light Make in IndiaRama KrishnanNo ratings yet
- C20 3 4 Sem AEDocument92 pagesC20 3 4 Sem AEMohammed AyanNo ratings yet
- Comparison Data LED Lights Vs Incandescent & CFL BDocument7 pagesComparison Data LED Lights Vs Incandescent & CFL BidealparrotNo ratings yet
- Developing Manufacturing Capabilities To Support Local Content in Indonesia Solar PV IndustryDocument18 pagesDeveloping Manufacturing Capabilities To Support Local Content in Indonesia Solar PV IndustryAgus SupriyonoNo ratings yet
- Pentax mz-50 2Document36 pagesPentax mz-50 2andresbustosarayaNo ratings yet
- HalogensDocument29 pagesHalogensAvik Datta0% (1)
- 8J Summary SheetDocument2 pages8J Summary SheetScoop DoogNo ratings yet
- Rangematic 1000 ManualDocument4 pagesRangematic 1000 ManualPeter SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Westinghouse Feb. 1978 Large Lamp CatalogDocument52 pagesWestinghouse Feb. 1978 Large Lamp CatalogAlan Masters100% (1)
- Alc613003 enDocument1 pageAlc613003 enRuslan SlusarNo ratings yet
- Becuri Si Lampi - Lampi LED ScheiferDocument33 pagesBecuri Si Lampi - Lampi LED ScheiferGeoMarcNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION OF Lens, Mirror, RefractionDocument4 pagesSOLUTION OF Lens, Mirror, RefractionRumpa DasNo ratings yet
- Convex Concave Ray DiagramsDocument30 pagesConvex Concave Ray DiagramsDaniel RichardsNo ratings yet
- AVS BV Product CatalogDocument644 pagesAVS BV Product CatalogCRIS SEDANTONo ratings yet
- Solar Energy CollectorsDocument23 pagesSolar Energy CollectorsEric Cook100% (2)
- Compact Fluorescent LampDocument18 pagesCompact Fluorescent LampRoyalRajAcharyaNo ratings yet
- Microscope CouplersDocument22 pagesMicroscope CouplersITL200_UNo ratings yet
- 2023-07-Glass Proposal Data Center K2 - PT Woh Hup (Req) - Windy (Asahimas) - Revisi 2Document1 page2023-07-Glass Proposal Data Center K2 - PT Woh Hup (Req) - Windy (Asahimas) - Revisi 2figo zaliNo ratings yet
- Linhof Super Technika V 4x5 Instruction Manual 1969 - English LanguageDocument11 pagesLinhof Super Technika V 4x5 Instruction Manual 1969 - English LanguageTres BolasNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Physics ConcavemirrorDocument2 pagesHsslive XII Physics Concavemirroritsmeanandhan007No ratings yet
- Parts of A Compound MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A Compound MicroscopeKim Ashley BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Steel Window Framws QuotationDocument8 pagesSteel Window Framws QuotationAndrew MwambaNo ratings yet
- Solar TreeDocument19 pagesSolar TreeDP Technical ClassesNo ratings yet
- Solar Hybrid PVT System: Submitted By: Pravash Kumar RanaDocument12 pagesSolar Hybrid PVT System: Submitted By: Pravash Kumar RanaDev Kumar100% (1)