Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Bashkesite
Uploaded by
Edmir AsllaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Bashkesite
Uploaded by
Edmir AsllaniCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
BASHKSIT
1. BASHKSIT. KUPTIMET ELEMENTARE
Bashksia sht kuptim elementar n matematik.
Tek kuptimi i bashksis, sht me rndsi t dijm elementet (antart)
q prmban ajo.
Bashksit do ti shnojm me shkronjat A, B, C , D,...
Elementet e bashksive do ti shnojm me shkronjat a, b, c, d ,...
Nse elementi a i takon bashksis A, simbolikisht shnohet a A
(lexohet: a element i A s).
Nse elementi a nuk i takon bashksis A, simbolikisht shnohet a A
(lexohet: a nuk sht element i A s).
Zakonisht bashksit i prshkruajm me njrn nga mnyrat vijuese:
1) Duke prshkruar elementet, p.sh. bashksia {a, b, c, d } prbhet nga
elementet a, b, c, d .
2) Duke prshkruar vetit e elementeve me an t ndonj shprehje
p ( x ). P.sh. nse dshirojm t paraqesim bashksin e numrave
njshifror natyror kemi A = {x |1 x < 10, x }.
Bashksia t cils i takojn t gjitha elementet, prfshir edhe vetveten
quhet bashksi universale. Simbolikisht shnohet .
Bashksia q nuk ka asnj element quhet bashksi boshe. Simbolikisht
shnohet me .
Disa nga bashksit numerike:
N = {1, 2,3, 4,5,...} - bashksia e numrave natyror
Z = {... 2, 1,0,1, 2,...} - bashksia e numrave t plot
m
Q = | m, n Z , n 0 - bashksia e numrave racional
n
I = {x | x nuk mund t shkruhet si thyes}- bashksia e numrave
iracional
R = Q I - bashksia e numrave real
Shembulli 1. T paraqiten elementet e bashksive
a) A = {x | x N , 3 < x < 12} ,
b)
B = {x | x N , x ift, x < 15},
BASHKSIT
c)
C = {x | x N , x + 4 = 3}.
Zgjidhja.
a) A = {4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11}.
b) B = {2, 4,6,8,10,12,14}.
c) Meq zgjidhja e barazimit x + 4 = 3 sht x = 1 N prfundojm se
bashksia C nuk prmban asnj element. D.m.th. C = .
Shembulli 2. Jan dhn bashksit
X = {4, 2} , Y = {x | x 2 6 x + 8 = 0} ,
Z = {x | x N , xift, 1 < x < 5}.
Cila prej tyre sht e barabart me B = {2, 4}?
Zgjidhja.
Pr t caktuar elementet e bashksis Y zgjidhim barazimin kuadratik
x 2 6 x + 8 = 0 . Pas zgjidhjes merret x1 = 2, x2 = 4. Pra Y = {2, 4}.
sht e qart se Z = {2, 4}.
Pra, q t tri bashksit X , Y , Z jan t barabarta me bashksin {2, 4}.
Shembulli 3. Jan dhn bashksit:
X = {x | x 2 = 9 2 x = 4} , Y = {x | x x} ,
Z = {x | x Z , x + 8 = 8}. Cila prej tyre sht boshe?
Zgjidhja.
Lexuesi le t arsyetoj se bashksit X dhe Y jan boshe.
Prkufizimi 1. (NNBASHKSIA). Bashksia A sht nnbashksi e
bashksis B, nse do element i bashksis A njkohsisht i
takon edhe bashksis B. Simbolikisht shnojm A B.
Pra, A B x A x B.
Nse A nuk sht
shnojm A B.
nnbashksi
bashksis
simbolikisht
P.sh. nse A = {1, 2,3}, B = {1, 2,3, 4,5}, C = {2,3, 4,5}, ather A B, A C.
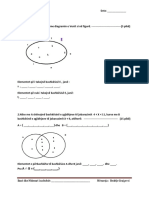
N figurn vijuese, me an t diagramit t Venit jan paraqitur
bashksit A, B ku A B.
ALGJEBRA
B
x
A
sht e qart se pr do bashksi A vlejn: A A dhe A.
Le t sqarojm pohimin:
A pr do bashksi A ,
q nse e shprehim me fjal do t thot:
do element i bashksis i takon bashksis A .
sht e qart se nj bashksi, le t themi X nuk sht nnbashksi e nj
bashksie tjetr Y , nse n bashksin X gjendet nj element q nuk
gjendet n bashksin Y . Pr shembull, bashksia {1,3,5,7} nuk sht
nnbashksi e bashksis {1, 2,3, 4,5,6} , sepse 7 sht n bashksin e
par por nuk sht n bashksin e dyt.
Kshtu pohimi A do t ishte i pasakt nse e gjejm nj element n
bashksin i cili nuk sht n bashksin A. Por, nj element t till
nuk mund ta gjejm sepse bashksia nuk ka asnj element.
Konkludojm se vlen A , pr do bashksi A.
Prkufizimi 2. (BARAZIA E BASHKSIVE). Nse A B dhe B A,
ather themi se bashksit jan t barabarta.
Simbolikisht shnojm A = B. Pra, bashksit A, B prmbajn t njjtat
elemente.
Prkufizimi 3. (NNBASHKSIA E MIRFILLT). Nse A B dhe
A B ather themi se A sht nnbashksi e mirfillt e
bashksis B. Simbolikisht shnojm A B.
Shembulli 4. Jan dhn bashksit
A = {x | x Z , x > 1},
BASHKSIT
B = { y | y N , y plotpjestohet me 2} ,
C = {z | z sht numr ift m i madh se 10}.
Cila prej tyre sht nnbashksi e bashksis W = {2, 4, 6,...}?
A sht ndonjra nnbashksi e mirfillt e bashksis W ?
Zgjidhja.
Vrejm se:
A = {2,3, 4,5,...}, B = {2, 4,6,8,...}, C = {12,14,16,18,...}.
Tani sht e qart se bashksit B, C jan nnbashksi t bashksis W .
Bashksia C sht nnbashksi e mirfillt e bashksis W . Mund t
shkruajm B W , C W .
2. VEPRIMET ME BASHKSI
Prkufizimi 1. (PRERJA- ) Prerja e bashksive A, B sht bashksia e
elementeve t prbashkta t tyre. Pra,
A B = {x | x A dhe x B}.
N figurn vijuese sht paraqitur diagrami i Venit pr prerjen e
bashksive.
B
A B
Kshtu nse A = {4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11}, B = {2, 4,6,8,10,12,14}, ather
A B = {4,6,8,10}.
N prgjithsi, prerja e ndonj familje t bashksive, sht bashksia e
elementeve q i takojn secils prej bashksive t asaj familje.
Pra
A = {x | x A ,
iI
pr do i I }.
ALGJEBRA
Shnimi 1. I paraqet bashksi indeksash.
Shembulli 5. Nse:
A1 = {1, 2,3, 4,5}, A2 = {2,3, 4,5,6}, A3 = {3, 4,5,6,7}, A4 = {4,5,6,7,8},
A5 = {5,6,7,8,9} ather
5
A = A A A A A = {5}.
i
i =1
A = {1, 2,...,8}.
i =1
Bashksit A, B quhen disjunkte nse A B = .
P.sh. nse A = {x N | x numr ift}, B = {x N | x numr tek}, ather
A B = .
N rastin e prgjithshm, bashksit Ai , i I jan disjunkte nse
A =.
i
Bashksit n nj familje bashksish themi se jan n dyshe disjunkte
(ose reciprokisht disjunkte) nse do dyshe e bashksive n at familje
sht disjunkte.
Shembulli 6. Le t jen dhn bashksit
A1 = {1, 2,3, 4,...}
A2 = {2,3, 4,5,...}
A3 = {3, 4,5,6,...}
...
An = {n, n + 1, n + 2, n + 3,...}
...
Ather qart se:
A =
i
A =
i
BASHKSIT
Nga ky shembull kuptojm se edhe pse bashksit Ai , i
jan
disjunkte, ato nuk jan disjunkte n dyshe.
P.sh. A1 A2 = {2,3, 4,5,...} .
Prmes shembullit vijues do t shohim se nse bashksit jan n dyshe
disjunkte ather ato jan disjunkte
Shembulli 7. Le t jen:
A1 = {x N | x = 4k , k N }
A2 = {x N | x = 4k + 1, k N }
A3 = {x N | x = 4k + 2, k N }
A4 = {x N | x = 4k + 3, k N }.
Bashksit A1 , A2 , A3 , A4 jan n dyshe disjunkte sepse Ai Aj = , pr
i j , i, j {1, 2,3, 4}.
4
Po ashtu edhe
A =. Pra, bashksit
i
A1 , A2 , A3 , A4 jan disjunkte.
i =1
Prkufizimi 2. (UNIONI- ) Unioni i bashksive A, B sht bashksia e
elementeve q i takojn s paku njrs prej bashksive t dhna.
Pra,
A B = {x | x A ose x B}.
N figurn vijuese sht paraqitur diagrami i Venit pr unionin e
bashksive.
A
B
A B
Kshtu nse A = {4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11}, B = {2, 4,6,8,10,12,14}, ather
A B = {2, 4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,14}.
N prgjithsi, unioni i ndonj familje t bashksive, sht bashksia e
elementeve q i takojn s paku njrs prej bashksive t asaj familje.
ALGJEBRA
Pra
A = { x | x A , pr ndonj i I }
i
iI
ose
A = { x | ekziston i I , x A }.
iI
Zbrthim (coptim, ndarje, particion) i bashksis S sht familja F e
nnbashksive joboshe pr t cilat:
1) do dy elemente (bashksi) nga F jan disjunkte, pra
(Fi , Fj F, i j , Fi Fj = ) .
2) Unioni i elementeve (bashksive) nga F sht bashksia S , pra
= S , Fi F.
Le t kuptojm zbrthimin prmes ilustrimeve vijuese:
F1
F5
F3
F4
F2
F1
F3
F2
Figura 1
F1
F2
F3
Figura 2
Figura 3
Qart se n figurn 1, familja
F = {F1 , F2 , F3 , F4 , F5}
paraqet zbrthim t bashksis S sepse do dy bashksi Fi , Fj S ,
i, j = 1, 2,3, 4,5 kan prerje boshe si dhe
F = S.
i
i =1
N figurat 2 dhe 3 nuk kemi zbrthim t bashksis S . Arsyetoni.
Shembulli 8.
i) do bashksi njlementshe {x} ka saktsisht nj zbrthim, dhe at
{{x}}.
ii) Pr do bashksi S , bashksia P = { X } sht zbrthim i bashksis S .
BASHKSIT
iii) Nse A sht nnbashksi e mirfillt joboshe e bashksis S , athere
familja { A, A} paraqet zbrthim t bashksis S .
iv) Bashksia {1, 2,3} ka kto zbrthime:
{{1},{2},{3}}
{{1, 2},{3}}
{{1,3},{2}}
{{1},{2,3}}
{{1, 2,3}}
Vrejm se familja e bashksive {{1, 2},{2,3}} nuk sht zbrthim pr
asnj bashksi sepse elementi 2 i takon dy elementeve (bashksive) t
familjes.
Po ashtu, vrejm se {{1},{2}} nuk sht zbrthim i bashksis {1, 2,3}
sepse {1} {2} {1, 2,3}. Megjithat familja {{1},{2}} sht zbrthim i
{1, 2}.
Prkufizimi 3. (NDRYSHIMI, DIFERENCA- \ ) Ndryshimi i bashksive
A, B sht bashksia q prmban elementet q i takojn
bashksis A por jo bashksis B. Pra,
A \ B = {x | x A dhe x B}.
N figurn vijuese sht paraqitur diagrami i Venit pr ndryshimin e
bashksive A \ B.
A
B
A\ B
Kshtu nse A = {4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11}, B = {2, 4,6,8,10,12,14}, ather
A \ B = {5,7,9,11}.
Prkufizimi 4. (NDRYSHIMI SIMETRIK- ) Ndryshimi simetrik i
bashksive A, B sht bashksia e prkufizuar si vijon
ALGJEBRA
AB = ( A \ B ) ( B \ A).
N figurn vijuese sht paraqitur diagrami i Venit pr ndryshimin
simetrik t bashksive A, B .
AB
Kshtu nse A = {4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11}, B = {2, 4,6,8,10,12,14}, ather
AB = ( A \ B ) ( B \ A) = {5,7,9,11} {2,12,14} = {2,5,7,9,11,12,14}.
Prkufizimi 5. (KOMPLEMENTI) Nse A sht nnbashksi e bashksis I ,
ather komplementi i bashksis A n lidhje me I sht
bashksia e elementeve q i takojn bashksis I por jo
bashksis A. Pra
AI = {x | x I dhe x A}.
D.m.th. AI = I \ A. 1
AI
P.sh. Nse I = {1, 2,3,...,10}, A = {2, 4,6,8,10} athere AI = {1,3,5,7,9}.
Shembulli 9. sht dhn bashksia S = {0,1, 2,...,10}.
a) T caktohen bashksit
Komplementi i bashksis A ndonjher shnohet me A ' ose
AC .
BASHKSIT
10
x x
A = x | x S S , B = y | y S y S .
3
2 4
b) T caktohen: A B, A B, A \ B, B \ A, AB, AS .
Zgjidhja.
a)
Duhet t caktojm t gjith numrat x nga bashksia S pr t cilt
x x x
x x
S . Meq
=
mjafton t caktojm numrat x S q
2 4 4
2 4
plotpjestohen me 4, pra A = {0, 4,8}. Ngjashm veprojm me
bashksin B. Merret B = {0,3,6,9}.
b)
A B = {0,3, 4,6,8,9}, A B = {0}, A \ B = {4,8}, B \ A = {3,6,9}
AB = ( A \ B ) ( B \ A) = {3, 4,6,8,9}, AS = S \ A = {1, 2,3,5,6,7,9,10}.
Shembulli 10. Le t jet Z bashksia e numrave t plot. Le t
shnojm me Z C , ZT bashksit e numrave t plot ift dhe
tek, prkatsisht.
T caktohet:
Z C Z T , Z C Z T , Z C \ Z T , Z T \ Z C , Z C Z T , ( Z T ) Z , ( Z C ) Z .
Zgjidhja.
Lexuesi le t vrej se:
Z C Z T = Z , Z C Z T = , Z C \ Z T = Z C , Z T \ Z C = Z T ,
Z C ZT = ( Z C \ ZT ) ( ZT \ Z C ) = Z , ( ZT ) Z = Z ZT = Z C , ( Z C ) Z = Z \ Z C = ZT .
Shembulli 11. T vrtetohet se A \ B = A B.
Zgjidhja.
Duhet t tregojm se
x A \ B ather dhe vetm
x A B. Vrtet
x A \ B x A x B x A x B x A B.
ather nse
Prkufizimi 6. (BASHKSIA PARTITIVE) Bashksia e t gjitha
nnbashksive t bashksis A quhet bashksi partitive dhe
shnohet me P( A). Pra, P ( A) = { X | X A}.
Meq A dhe A A ather P ( A), A P ( A).
ALGJEBRA
11
Shembulli 12. Le t jen dhn bashksit
A = {1, 2}, B = {1, 2,3}, C = {1, 2,3,...,64}.
T caktohet P( A), P( B), P(C ).
Zgjidhja.
Qart se
P( A) = {,{1},{2}, A} ,
P ( B ) = {,{1},{2},{3},{1, 2},{1,3},{2,3}, B}.
Nse provojm t caktojm P (C ) do t vrejm se nj gj e till sht e
pamundur.
Ndoshta, dikush mund t sugjeroj iden q n kt rast t shfrytzojm
kompjuterin.
Vrejm s pari se kur bashksia A kishte 2 elemente ather P( A)
kishte 4 = 22 elemente.
N rastin e bashksis B me 3 elemente, P( B ) kishte 23 elemente.
N prgjithsi n rastin kur bashksia X ka n elemente, ather P( X )
ka 2n elemente.
Kshtu n rastin e bashksis C me 64 elemente, P (C ) ka 264 elemente.
Le t themi se e kemi br programin dhe q e posedojm nj kompjuter
q paraqet 106 bashksi n sekond. Por edhe me kt kompjuter nj
llogaritje e till do t ishte e pamundur.
Faktin se bashksia A ka k elemente e shnojm n( A) = k .
Shembulli 13. Le t jen A, B bashksi t fundme disjunkte. Tregoni se
A B sht e fundme dhe vlen n( A B ) = n( A) + n( B ).
Zgjidhja.
Le t jen A = {a1 , a2 ,..., an }, B = {b1 , b2 ,..., bm } | A B = .
Ather A B = {a1 , a2 ,..., an , b1 , b2 ,..., bm }. Pra n( A B) = n + m = n( A) + n( B).
BASHKSIT
12
3. LIGJET E ALGJEBRS S BASHKSIVE
Ligjet e algjebrs s bashksive do ti paraqesim n tabeln vijuese:
1
2
emrtimi
Ligjet komutative
Ligjet asociative
Ligjet distributive
Ligjet e De Morganit
A B = A B, A B = A B
Ligjet e komplementit
A A = , A A = U
Ligji i komplementit t
dyfisht
7 Ligjet idempotente
8 Ligjet e absorbimit
9 Ligjet e dominimit
10 Ligjet e identitetit
6
rregulla
A B = B A, A B = B A
A ( B C ) = ( A B) C ,
A ( B C ) = ( A B) C
A ( B C ) = ( A B) ( A C )
A ( B C ) = ( A B) ( A C )
A= A
A A = A, A A = A,
A ( A B) = A, A ( A B) = A
A = , A U = U
A = A, A U = A.
Shembulli 13. Duke zbatuar ligjet e algjebrs s bashksive t vrtetohen
identitetet:
a) (U A) ( B A) = A;
b) ( A) ( B A) = A;
c) ( B C ) A = ( B A) (C A);
d) ( A B ) ( A B) = A;
e) ( A B) ( A B) = A;
f) ( B U ) ( A ) = A B;
g) ( B ) ( A U ) = A B.
Zgjidhja.
Le t vrtetojm p.sh. pohimin e.
( A B ) ( A B) = (( A B ) A) (( A B ) B )
= ( A ( A B )) ( B ( A B))
= (( A A) ( A B )) (( B A) ( B B))
ALGJEBRA
13
= ( A ( A B )) (( A B) )
= A ( A B) = A .
Ngjashm vrtetohen rastet e tjera.
Shembulli 14. Le t jet E sht bashksi e fardoshme, kurse { Ai }iI
familje e bashksive. T vrtetohet se vlejn pohimet:
a) E Ai = ( E Ai );
iI
iI
b) E Ai = ( E Ai ).
iI
iI
Zgjidhja.
a) x E Ai x E x Ai
iI
iI
x E x Ai , pr ndonj i I
x E Ai , pr ndonj i I
x ( E Ai ).
iI
b) Ngjashm.
Shembulli 15. T vrtetohet se vlejn pohimet:
a) E \ Ai = ( E \ Ai )
iI
iI
b) E \ Ai = ( E \ Ai )
iI
iI
ku E sht bashksi e fardoshme, kurse { Ai }iI familje e
bashksive.
Zgjidhja.
a) x E \ Ai x E x Ai
iI
iI
x E x Ai , pr do i I
x E \ Ai , pr do i I
x ( E \ Ai ).
iI
Pra E \ Ai = ( E \ Ai ) .
iI
b) Ngjashm.
iI
BASHKSIT
14
4. PRODHIMI KARTEZIAN
Prkufizimi 1. Prodhimi kartezian A B i bashksive A dhe B sht
bashksia e t gjitha dysheve t renditura ( a, b) ashtu q
elementi i par i takon bashksis A kurse elementi i dyt i
takon bashksis s B.
Pra A B = {(a, b) | a A, b B}.
N prgjithsi prodhimi kartezian i bashksive A1 , A2 ,..., An sht
bashksia e n sheve t renditura, ashtu q elementi i i t i takon
bashksis Ai . Pra
n
A
i =1
= A1 A2 ... An = {(a1 , a2 ,..., an ) | i, ai Ai } .
Nse A1 = A2 = ... = An ather kemi A A ... A = An .
n
Shembulli 16. Jan dhn bashksit A = {1, 2,3}, B = {b, c}.
a) T njehsohet A B, B A, A A, B B.
b) A mund t prfundojm se A B = B A ?
c) A mund t prfundojm se n( A B ) = n( B A)?
Zgjidhja.
a) A A = {(1, b),(1, c),(2, b),(2, c),(3, b),(3, c)}
B A = {(b,1),(b, 2),(b,3),(c,1),(c, 2),(c,3)}
A A = {(1,1),(1, 2),(1,3),(2,1),(2, 2),(2,3),(3,1),(3, 2),(3,3)}
B B = {(b, b), (b, c), (c, b), (c, c)}.
b) Tregoni pse A B B A.
c) Tregoni pse n( A B ) = n( B A).
Shembulli 17. Jan dhn bashksit A = {a, b, c}, B = { , , }, C = {1, 2}.
a) T njehsohet ( A B ) C , A ( B C ).
b) T njehsohet A3 , C 2 .
c) A vlen ( A B ) C = A ( B C )?
ALGJEBRA
15
Zgjidhja.
I lihet lexuesit.
Shembulli 18. T vrtetohet se pr bashksit e fardoshme A, B, C vlen
( A B) ( A C ) = A ( B C ).
Zgjidhja.
( A B ) ( A C ) = {( x, y ) | ( x, y ) A B ( x, y ) A C}
= {( x, y ) | x A, y B x A, y C}
= {( x, y ) | x A, y B y C}
= {( x, y ) | x A y ( B C )}
= A ( B C ).
5. PARAQITJA E BASHKSIVE SI STRINGJE T
BITVE
Prkufizimi 1. Le t jet = {x1 , x2 ,..., xn } bashksi universale dhe A .
Bashksin A mund ta paraqesim me an t vargut t bitve
(0,1) t gjatsis n n t cilin biti i i t sht 1 nse xi A dhe
0 n t kundrtn. Ky string (varg) quhet karakteristika e
vektorit A .
Shembulli 19. Le t jet = {x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 , x5 , x6 , x7 } dhe A = {x1 , x2 , x5 }.
Ather vargu i bitve t bashksis A (karakteristika e
vektorit A ) do t jet 1100100.
Shembulli 20. Le t jet = {1, 2,3,...,13}.
a) T
caktohet
vargu
A = {2,3,5,7,11,13}.
bitve
bashksis
b) T caktohet bashksia e cila prfaqsohet me vargun e
bitve 1011001.
Zgjidhja.
a) 0110101000101 ;
b) {1,3, 4,7}.
BASHKSIT
16
Ngjashm, si patm veprimet me bashksi, t njjtat veprime mund ti
kryejm n rastin kur bashksit paraqiten me an t vargjeve t bitve.
N rastin kur duhet t caktojm vargun e bitve pr A B, vargjet e
bitve t bashksive A, B i konsiderojm si numra binar dhe i mbledhim
bit pr bit , kurse n rastin e A B i shumzojm bit pr bit.
Le t shohim kt prmes shembullit vijues.
Shembulli 21. Le t jet
= {x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 , x5 }, A = {x1 , x2 , x4 } , B = {x1 , x3 , x4 , x5 }.
a) T caktohet vargu i bitve pr bashksit A, B.
b) T caktohet vargu i bitve pr bashksit A B, A B.
Zgjidhja.
a) Vargjet e bitve pr bashksit A, B jan 11010, 10111, prkatsisht.
b) Sipr prshkrimit t msiprm kemi:
1 1 0 1 0
1 0 1 1 1
A B
1 0 0 1 0
A B
1 1 1 1 1
Komplementi i bashksis A caktohet duke ndryshuar bitin 0 n 1 dhe
anasjelltas.
P.sh. nse A -s i shoqrohet vargu i bitve
A = 11010001.
00101110
ather
Vrejm se edhe po t caktonim A B, A B n formn e zakonshme
dhe pastaj rezultatin ta shndrronim n form t vargut t bitve do t
merrej i njjti rezultat.
Detyr pune me komjuter:
T punohet programi i cili pr bashksin e dhn A paraqet P ( A).
ALGJEBRA
17
DETYRA PR USHTRIME T PAVARURA
1. T paraqiten elementet e bashksive:
a) A = {x | x N , 2 x < 7.2}.
b) B = {x | x N , x tek , x 11}.
2. a) Tregoni se {{a, b},{a, c}} {a, b, c}.
b) Pse {}?
3. Jan dhn bashksit A = {x |1 x 7}, B = {x | x (2,5)}, C = {1,5,6}.
Tregoni se ( AB )C = A( BC ).
4. Le t jen A = {x,1, 2,3, 4}, B = {a, b, 2, y}, C = {1, b}. Tregoni se vlejn
pohimet:
a) A \ ( B C ) = ( A \ B ) ( A \ C ),
b) A \ ( B C ) = ( A \ B) ( A \ C ).
5. Tregoni se nse A B B C ather A C.
6. A ekzistojn bashksit A, B, C t tilla q t vlejn barazimet?
A B
.
AC =
( A B) \ C =
7. sht dhn bashksia S = {0,1, 2,...,12}.
a) T caktohen bashksit
x+2
A = x | x S
S ,
3
y y
B = y | y S + S ,
2
5
z2
C = z | z S 25 S .
4
b) T caktohen: A ( B C ), B \ ( A C ),( A \ B ) \ C , AS ( B S \ C S )
8. sht dhn bashksia S = {0, 2, 4,6,8,10,12}.
a) T caktohen bashksit
BASHKSIT
18
2x x
A = x | x S S ,
3 2
y2
B = y | yS
+ 1 N
y+4
z2
C = z | z S > z .
4
b) T caktohen:
( A B) C ,( A \ C ) ( B \ C ), A ( B C ), A \ ( B \ ( A C ))
9. Le t jet R bashksia e numrave real. Le t jen Q, I bashksit e
numrave racional dhe iracional prkatsisht.
T caktohet: R I , Q I , R Q, Q R , I R , Q I .
10. Provoni nse vlejn pohimet vijuese:
a) ( A B ) C = ( A C ) ( B C )
b) ( A B ) C = ( A C ) ( B C )
c) A ( B \ C ) = ( A B) \ ( A C ).
11. Le t jen A, B bashksi t fundme. Bashksit A B, A B jan t
fundme dhe vlen n( A B ) = n( A) + n( B ) n( A B ).
12. Le t jet L drejtz e rrafshit. Pr do x L, le t jet C x rrethi me
rreze 1 dhe qendr n pikn x. far paraqesin bashksit
C
xL
C
xL
dhe
13. Le t jet { Ai : i I }, I familje e fardoshme e bashksive. Nse
P = Ai , S = Ai , ather tregoni se pr do k I vlen P Ak S .
iI
iI
k 1
14. Le t jet Ak = x | x N ,
x < k , k N . T caktohen bashksit
k
B = Ak , C = Ak .
k N
k N
15. sht dhn vargu i bashksive ( En ) nN , ku En = {n, n + 1, n + 2,...} .
Tregoni se
nN
= .
ALGJEBRA
19
16. Le t jet = {0,1, 2,...,15}
a) T caktohet vargu i bitve q i shoqrohet bashksis
{2,5,7,13,14,15}.
b)
T caktohet bashksia t cils i korrespondon vargu 1011101101.
c)
Nse A, B kan vargjet e bitve 00111100 1110 1001,
0101 00111010 0011 t caktohen vargjet e bitve pr bashksit
A B, A B, A, B.
You might also like
- BashkesiteDocument20 pagesBashkesiteqazed444100% (8)
- Teoria e NumraveDocument20 pagesTeoria e NumraveErblina Zeqiri100% (3)
- Relacionet Dhe FunksionetDocument13 pagesRelacionet Dhe FunksionetArgjendNo ratings yet
- Mate Ma TikaDocument377 pagesMate Ma TikalindOS50% (2)
- Matematika 6 AlbDocument224 pagesMatematika 6 Albcoupletea100% (1)
- Analiza Reale Qamil HaxhibeqiriDocument126 pagesAnaliza Reale Qamil HaxhibeqiriunazaNo ratings yet
- Analiza Funksionale 1 Ramadan ZejnullahuDocument178 pagesAnaliza Funksionale 1 Ramadan ZejnullahuunazaNo ratings yet
- Numrat Kompleks 22-32 PDFDocument11 pagesNumrat Kompleks 22-32 PDFElvin KutrolliNo ratings yet
- Logjika MatematikeDocument7 pagesLogjika MatematikeProgrammerNo ratings yet
- Zbulimet MatematikoreDocument7 pagesZbulimet MatematikoreAurela Elezaj43% (7)
- Ushtrime Nga Analiza Reale Islam ShehuDocument180 pagesUshtrime Nga Analiza Reale Islam Shehuunaza100% (4)
- Matematika 8 AlbDocument218 pagesMatematika 8 Albcoupletea100% (1)
- Induksioni MatematikeDocument16 pagesInduksioni Matematikeowls100% (1)
- Matematika 9Document128 pagesMatematika 9Paola100% (5)
- Matematika 3A Web 1Document161 pagesMatematika 3A Web 1Labinot AjaziNo ratings yet
- FSHMN Teste PDFDocument62 pagesFSHMN Teste PDFFatlum RreciNo ratings yet
- Matric atDocument18 pagesMatric atvalmir nuredini100% (2)
- Provimi Pranues Matematike 2016 PDFDocument3 pagesProvimi Pranues Matematike 2016 PDFBashkim Zeneli100% (1)
- MatematikaDocument461 pagesMatematikalorens shelliraNo ratings yet
- VIII INTEGRALI I CAKTUAR-detyra PDFDocument21 pagesVIII INTEGRALI I CAKTUAR-detyra PDFArgjendNo ratings yet
- BashkesiteDocument1 pageBashkesiteegzonaNo ratings yet
- Algjebra Lineare (2023)Document244 pagesAlgjebra Lineare (2023)AylaNo ratings yet
- Matematika 9 - Test Vleresues 1Document3 pagesMatematika 9 - Test Vleresues 1ReminaNo ratings yet
- Qarqet DigjitaleDocument13 pagesQarqet DigjitaleFortesaMujajNo ratings yet
- Vargjet Vargu Aritmetik Dhe GjeometrikDocument3 pagesVargjet Vargu Aritmetik Dhe Gjeometrikapi-2557697530% (2)
- Olimpiada Mat 2015Document7 pagesOlimpiada Mat 2015Olsi Hysa0% (1)
- TEST 2 ME 60 PYETJE MATEMATIKE Pa Pergjigje 2020Document6 pagesTEST 2 ME 60 PYETJE MATEMATIKE Pa Pergjigje 2020Teuta Domi Bimi100% (1)
- 01 Leksioni 5 SipefaqetDocument38 pages01 Leksioni 5 SipefaqetelisNo ratings yet
- Provim INF 101,102,103 INI 101,102Document3 pagesProvim INF 101,102,103 INI 101,102Roen KarabojaNo ratings yet
- Udhezues Matematika 9 PDFDocument153 pagesUdhezues Matematika 9 PDFAnomis❤No ratings yet
- I Incidenca - Bazat e Gjeometrise I. AxioDocument10 pagesI Incidenca - Bazat e Gjeometrise I. Axioana100% (1)
- Vargu NumerikDocument7 pagesVargu NumerikValdrin EjupiNo ratings yet
- Projekt Limiti I VargutDocument12 pagesProjekt Limiti I VargutValentina Shaqiri0% (1)
- ForcaDocument21 pagesForcaLeti Hanaj100% (1)
- Matematika ZbaviteseDocument13 pagesMatematika ZbaviteseAurela Elezaj75% (4)
- Kombinatorika - Pjesa 2 - LDocument7 pagesKombinatorika - Pjesa 2 - Larmend fanboiNo ratings yet
- Kalimi Nga Nje Grafik Te TjetriDocument33 pagesKalimi Nga Nje Grafik Te TjetriSonila Cela100% (5)
- Test Tremujori I Matematika 12Document5 pagesTest Tremujori I Matematika 12sindiNo ratings yet
- Analiza Reale Dhe Funksionale Kaliaj ZejnullahuDocument424 pagesAnaliza Reale Dhe Funksionale Kaliaj ZejnullahuunazaNo ratings yet
- Probabilitet Dhe Statistike Skripte FNA K H IIDocument82 pagesProbabilitet Dhe Statistike Skripte FNA K H IIIv Hysenbelli100% (2)
- 1.1 - Bashk.e Num Komp PDFDocument16 pages1.1 - Bashk.e Num Komp PDFDardan HusiNo ratings yet
- Ekuacionet LineareDocument15 pagesEkuacionet LineareDardan Husi100% (1)
- Teoria Probabilitetit 9.2Document25 pagesTeoria Probabilitetit 9.2shhNo ratings yet
- Test Matematike I VeshtireDocument4 pagesTest Matematike I Veshtireanon_461226584100% (1)
- Ligjerata 10 - Permutacionet Kombinacionet VariacionetDocument24 pagesLigjerata 10 - Permutacionet Kombinacionet VariacionetcoupleteaNo ratings yet
- Matematike - f3 - KL 9Document5 pagesMatematike - f3 - KL 9Maringlen XhaferriNo ratings yet
- KombinatorikaDocument27 pagesKombinatorikaAldjon Dodaj83% (6)
- Kursi I Matematikes Elementare PDFDocument234 pagesKursi I Matematikes Elementare PDFIlirHaziri73% (11)
- Bashkesite PDFDocument1 pageBashkesite PDF5qwk7kcc65No ratings yet
- Bashkësitë Detyre ShtepieDocument5 pagesBashkësitë Detyre Shtepieemmaislami18No ratings yet
- MATEMATIKËDocument22 pagesMATEMATIKËGetuarZekaj0% (1)
- KL VIDocument33 pagesKL VILiridon SulejmaniNo ratings yet
- Kollokviumi 1Document3 pagesKollokviumi 1FataNo ratings yet
- Shkolla Fillore e Mesme e Ulet - MatematikaDocument7 pagesShkolla Fillore e Mesme e Ulet - MatematikaArditKNo ratings yet
- Ushtrime Nga BashkesiteDocument6 pagesUshtrime Nga BashkesiteanaNo ratings yet
- Ushtrimet SD1 PDFDocument26 pagesUshtrimet SD1 PDFAjnurB12No ratings yet
- 3 Relacionet PDFDocument8 pages3 Relacionet PDFArdit FetaNo ratings yet
- Leksioni1 FinalDocument36 pagesLeksioni1 FinalGregori NovakuNo ratings yet
- Teori GjuheshDocument13 pagesTeori GjuheshManiaLaboriousNo ratings yet
- Logjike Dhe Matematik.Document18 pagesLogjike Dhe Matematik.Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- 2020 Fil&SocDocument7 pages2020 Fil&SocEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Manuali I Plote (Mesues)Document43 pagesManuali I Plote (Mesues)Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- 2019.model. Fil&Soc SkemaDocument8 pages2019.model. Fil&Soc SkemaEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Raport Publik msh2021Document178 pagesRaport Publik msh2021Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- pLANI SHQK, SUDE 2021-2022Document4 pagespLANI SHQK, SUDE 2021-2022Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Shnderrime Te Njevlereshme Dhe ProgresioneDocument21 pagesShnderrime Te Njevlereshme Dhe ProgresioneEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Forum Gusht 2018Document3 pagesForum Gusht 2018Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Liber Mesuesi Matematika Xii PegiDocument3 pagesLiber Mesuesi Matematika Xii PegiEdmir Asllani100% (6)
- Orari ShkollesDocument3 pagesOrari ShkollesEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- 16.03.2018 Matura Program Orientues, Matematike, 2019Document20 pages16.03.2018 Matura Program Orientues, Matematike, 2019Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- 26.8.2013 Standartet e DrejtoritDocument15 pages26.8.2013 Standartet e DrejtoritEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Sulivsn 1lDocument1 pageSulivsn 1lEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- GersaDocument2 pagesGersaEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Matematika 2010 Qershor ShqipDocument20 pagesMatematika 2010 Qershor ShqipEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Leksioni XII194Document13 pagesLeksioni XII194Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Tik 10Document3 pagesTik 10Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Matematike Shoqerore 4Document4 pagesMatematike Shoqerore 4Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Teknika Dhe Strategji Mesimedhenie++Document18 pagesTeknika Dhe Strategji Mesimedhenie++Edmir Asllani0% (2)
- A e Keni Ditur SeDocument2 pagesA e Keni Ditur SeEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Kreu 5 Hiperbola Dhe ParabolaDocument3 pagesKreu 5 Hiperbola Dhe ParabolaEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- 3003 Matematika 2009 Alb Napredno Nivo JuniDocument24 pages3003 Matematika 2009 Alb Napredno Nivo JuniEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Kreu 5 Hiperbola Dhe ParabolaDocument3 pagesKreu 5 Hiperbola Dhe ParabolaEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Tema 21 - Standardet e Profesionit Të Mësuesit158+Document11 pagesTema 21 - Standardet e Profesionit Të Mësuesit158+Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Metoda ERR++Document3 pagesMetoda ERR++Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Udhezimi NR 5 25 .02.2013 Per Standardet e Pergjithshme Te MesuesitDocument18 pagesUdhezimi NR 5 25 .02.2013 Per Standardet e Pergjithshme Te MesuesitJeartaCaushi100% (3)
- Ligj NR 69 21 06 2012Document25 pagesLigj NR 69 21 06 2012Armela PanajotiNo ratings yet
- Ligji Per ArsiminDocument3 pagesLigji Per ArsiminEdmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (Kualifikim)Document2 pages2.1 (Kualifikim)Edmir AsllaniNo ratings yet
- Shema Per Funksioni LinearTEST 4Document2 pagesShema Per Funksioni LinearTEST 4Faton AliuNo ratings yet