Professional Documents
Culture Documents
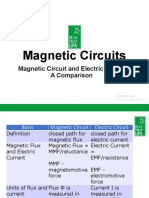
Magnetic equivalent Symbol Units Electric equivalent Symbol: φ I R G = 1/R
Uploaded by
Michał Majchrzak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageMagnetic circuits can be modeled analogously to electrical circuits. Some key similarities include:
1) Magnetomotive force (MMF) in magnetic circuits is analogous to electromotive force (EMF) in electrical circuits.
2) Magnetic reluctance is analogous to electrical resistance, while magnetic permeance is analogous to electrical conductance.
3) Several circuit laws have analogous relationships between magnetic and electric concepts, such as Ohm's law, Gauss's law, and relationships involving magnetic flux, field, and density.
Original Description:
Original Title
mag data
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMagnetic circuits can be modeled analogously to electrical circuits. Some key similarities include:
1) Magnetomotive force (MMF) in magnetic circuits is analogous to electromotive force (EMF) in electrical circuits.
2) Magnetic reluctance is analogous to electrical resistance, while magnetic permeance is analogous to electrical conductance.
3) Several circuit laws have analogous relationships between magnetic and electric concepts, such as Ohm's law, Gauss's law, and relationships involving magnetic flux, field, and density.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageMagnetic equivalent Symbol Units Electric equivalent Symbol: φ I R G = 1/R
Uploaded by
Michał MajchrzakMagnetic circuits can be modeled analogously to electrical circuits. Some key similarities include:
1) Magnetomotive force (MMF) in magnetic circuits is analogous to electromotive force (EMF) in electrical circuits.
2) Magnetic reluctance is analogous to electrical resistance, while magnetic permeance is analogous to electrical conductance.
3) Several circuit laws have analogous relationships between magnetic and electric concepts, such as Ohm's law, Gauss's law, and relationships involving magnetic flux, field, and density.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Analogy between 'magnetic circuits' and electrical circuits Magnetic equivalent Symbol Units Electric equivalent Symbol Magnetomotive
force (MMF) E ampere-turn Definition of EMF Magnetic Field H ampere/meter Electric field E Magnetic Flux weber Electric Current I Hopkinson's Law or Rowland's Law Ohm's Law Reluctance 1/Henry Electrical resistance R Permeance Henry Electric conductance G = 1/R relation between B and H Microscopic Ohm's Law Magnetic Flux Density B B tesla Current density J permeability Henry/meter Electrical conductivity
Magnetomotive force (MMF)
F= H * dl ; force around close loop ; length of looped wire F= n* I ; turns current
Magnetic flux
= B * dS ; induction area ; weber = volts* secends
Circuit Laws Gauss's law
= 1 + 2 + ;
Magnetic capacitivity
Cm = u0 * ur * S / l [H] ; u = ur * u0 ; area length
Magnetic inductance
XL = L =2f
Inductance is the ability of an inductor to store energy in a magnetic field
-E = L * dI / dt E = L * I^2 /2
Magnetic field magnetic B field and a magnetic H field
B=u*H ; u = ur * u0 ; permeability
Force on moving charges static B
F = q * v x B ; charge velocity magnetic field
Force on moving current static B
F=B*I*l
Faraday's Law: Electric force due to a changing B-field
U = - d / dt
You might also like
- Electromagnetics ConceptsDocument3 pagesElectromagnetics ConceptsvasilzhmendakNo ratings yet
- 1.magnetic Circuits PDFDocument3 pages1.magnetic Circuits PDFTanishq MudaliarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic CircuitsDocument15 pagesMagnetic CircuitsPrianshu JyosyulaNo ratings yet
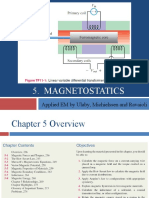
- Magnetostatics: Applied EM by Ulaby, Michielssen and RavaioliDocument38 pagesMagnetostatics: Applied EM by Ulaby, Michielssen and RavaioliFaizzwan FazilNo ratings yet
- Mimay, Noeh M. Bsee - 2B Electromagnetics Tutorial Problem 62Document6 pagesMimay, Noeh M. Bsee - 2B Electromagnetics Tutorial Problem 62Glorilie PazNo ratings yet
- Magnetostatics: Applied EM by Ulaby, Michielssen and RavaioliDocument37 pagesMagnetostatics: Applied EM by Ulaby, Michielssen and RavaioliAshraf YusofNo ratings yet
- ch1 Magnetic CircuitsDocument66 pagesch1 Magnetic CircuitsRaymundo III ApaleNo ratings yet
- 7 e Applied EMCh 5Document38 pages7 e Applied EMCh 5Azmienz HierzanzNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic PrinciplesDocument56 pagesElectromagnetic PrinciplesBacha NegeriNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuit: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesMagnetic Circuit: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamkbayanNo ratings yet
- MagnetostaticsDocument37 pagesMagnetostaticskumbie nyashonjekaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic CircuitsDocument17 pagesMagnetic CircuitsVijay Nand100% (1)
- Be Emtl MaterialDocument57 pagesBe Emtl Materialsravan_451No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Electro Statics Part IIDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Electro Statics Part IINagai KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument53 pagesUnit 1 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismOdellien SajaNo ratings yet
- Pdf24 MergedDocument100 pagesPdf24 MergedOana DrăganNo ratings yet
- 6.question Bank With Answers (2 Marks) - 1Document10 pages6.question Bank With Answers (2 Marks) - 1Durgesh DhoreNo ratings yet
- Pre TaskDocument5 pagesPre Taskkevin narvaez henriquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1a - Magnetic CircuitDocument9 pagesChapter 1a - Magnetic CircuitahamdNo ratings yet
- Formulas For The Skin EffectDocument13 pagesFormulas For The Skin EffectzerferuzNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits and IntroductionDocument32 pagesMagnetic Circuits and Introductionsandesh sagar TripathiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument170 pagesUnit 2 PDFSaurabh RajNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits and Other Basics Unit-I: Prepared by Dr. A.Venkadesan, Ap/Eee, NitpyDocument28 pagesMagnetic Circuits and Other Basics Unit-I: Prepared by Dr. A.Venkadesan, Ap/Eee, NitpyAbhimanyu PerumalNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits: Satyam Kumar: 21SCSE1010304 Tushar Talan: 21SCSE1010405 Ankit Kumar: 21SCSE1011261Document13 pagesMagnetic Circuits: Satyam Kumar: 21SCSE1010304 Tushar Talan: 21SCSE1010405 Ankit Kumar: 21SCSE1011261SATYAM KUMAR 21SCSE1010304No ratings yet
- Em PDFDocument88 pagesEm PDFFranck Duprey MvogoNo ratings yet
- Microwave Technology PresentationDocument11 pagesMicrowave Technology PresentationVani ChitkaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Magnetic CircuitsDocument16 pagesChapter 12: Magnetic CircuitsMukul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Propagation Model PDFDocument21 pagesPropagation Model PDFis23cNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Waveguide Characterization Using HfssDocument5 pagesRectangular Waveguide Characterization Using HfssidalmirNo ratings yet
- Magnetic CircuitDocument29 pagesMagnetic Circuitsujalshirke1904No ratings yet
- D.C. Machin BaidaDocument53 pagesD.C. Machin BaidaLeonard ValdezNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Basic Terminology: Magnetic FluxDocument8 pagesUnit-I Basic Terminology: Magnetic FluxhariNo ratings yet
- Ep&c2 El1Document19 pagesEp&c2 El1Jeffrey Wong QYNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Fields, Hall Effect and Electromagnetic InductionDocument12 pagesMagnetic Fields, Hall Effect and Electromagnetic Inductionwina ariffNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Electromagnetic CircuitsDocument27 pagesLesson 1 Electromagnetic CircuitsjohnpaulshobayanNo ratings yet
- EE 533 EE 533 Microwave Integrated Circuits Microwave Integrated CircuitsDocument11 pagesEE 533 EE 533 Microwave Integrated Circuits Microwave Integrated CircuitsDiDo Mohammed AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering: BY R. Sivaprasad, Lecturer in Eee, Govt. Polytechnic, SatyaveduDocument69 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering: BY R. Sivaprasad, Lecturer in Eee, Govt. Polytechnic, Satyavedurathina4careerNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Fundamentals of Electromagnatism & Transformers: Magnetic CircuitDocument10 pagesUnit-III Fundamentals of Electromagnatism & Transformers: Magnetic CircuitPathan NagulMeeraNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits: Magnetic Circuit and Electric Circuit: A ComparisonDocument13 pagesMagnetic Circuits: Magnetic Circuit and Electric Circuit: A ComparisonTrisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theoryee231Document14 pagesElectromagnetic Theoryee231Pradhunya KambleNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument6 pagesElectromagnetismspidyan100% (1)
- EMT Two MarksDocument23 pagesEMT Two MarksRamesh KamathNo ratings yet
- Power and Machine Lecture 2 and 3: Contact DetailsDocument29 pagesPower and Machine Lecture 2 and 3: Contact DetailsMahy MagdyNo ratings yet
- Det1013 - Electrical Technology: Magnetic Circuit, Electromagnetism & Electromagnetic InductionDocument41 pagesDet1013 - Electrical Technology: Magnetic Circuit, Electromagnetism & Electromagnetic InductionfaizNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Energy: Physics 54Document6 pagesElectromagnetic Energy: Physics 54Y.y. KuoNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Ckts PDFDocument22 pagesMagnetic Ckts PDFRIYA KNo ratings yet
- EE201 em TheoryDocument9 pagesEE201 em TheoryElakkiya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- MECH2406 2020 Sec3 Magnetic 0309Document14 pagesMECH2406 2020 Sec3 Magnetic 0309Leo Wong100% (1)
- L2 2 Maxwell EquationsDocument37 pagesL2 2 Maxwell Equationskwaleed717No ratings yet
- Electro-Motion Devices: Lecture 4-Magnetic CircuitsDocument76 pagesElectro-Motion Devices: Lecture 4-Magnetic Circuitshazem ab2009No ratings yet
- Magnetic CircuitDocument7 pagesMagnetic CircuitjosgauNo ratings yet
- EMF 2m 6m 10m-FlowerDocument21 pagesEMF 2m 6m 10m-FlowerFLOWERNo ratings yet
- Magnetotelluric Method by DDDocument10 pagesMagnetotelluric Method by DDpriyanshudwivediNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 3Document18 pagesLect 2 3Prof AliNo ratings yet
- Ac/Dc Machinery Chapter Compilation: John Alfred A. Ceniza BSME-5Document42 pagesAc/Dc Machinery Chapter Compilation: John Alfred A. Ceniza BSME-5John A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- All Units QB NewwDocument12 pagesAll Units QB NewwSanjana MenonNo ratings yet
- Inductors and TransformersDocument19 pagesInductors and Transformersnikolovb298No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)