Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hormones and Glands Chart
Uploaded by
Mechelle Chen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesA chart on the different hormones in the human body
Original Title
Hormone Chart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA chart on the different hormones in the human body
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesHormones and Glands Chart
Uploaded by
Mechelle ChenA chart on the different hormones in the human body
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
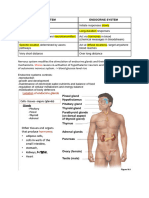
Gland/Structure Hormones Made Function Leads to/Act on
Hypothalamus Growth-hormone releasing Stimulates release of (GH) Anterior pituitary
-integrates endocrine & Corticotropin-releasing Stimulates release of (ACTH) Anterior pituitary
nervous systems Thyrotropin-releasing Stimulates release of (TSH) Anterior pituitary
-receives inputs and initiates Gonadotropin-releasing Stimulates release of FSH and LH Anterior pituitary
endocrine responses
Anterior Pituitary Growth (GH) Stimulates growth factors Liver, bone, muscles
-Located at base of brain & Adrenocorticotropic Stimulates release of glucocorticoids Adrenal glands
attached to hypothalamus (ACTH)
-produced by anterior & Thyroid-stimulating (TSH) Stimulates release of thyroid Thyroid gland
released in response to hormones
hypothalamus FSH & LH Stimulates production of gametes and Reproductive systems
sex hormones
Prolactin Stimulates milk Mammary gland
Posterior Pituitary Antidiuretic Reabsorption of H2O by kidneys Stored in posterior
Acts on kidneys
-produced by hypothalamus Oxytocin Induces uterine contractions & milk Stored in posterior
& stored in posterior release Acts on female reproductive
Thyroid Gland Thyroxine & Increase basal metabolic rate, affect
-butterfly-shaped gland Triiodothyronine metabolic processes, regulate long
-regulated by hypothalamus- bone growth
pituitary axis
Adrenal Cortex Mineralocorticoids Increases reabsorption of Na by
kidneys
-two glands on each kidney Glucocorticoids Long-term stress response Increase blood glucose level
-outer layer by stimulating synthesis of
glucose and gluconeogenesis
Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine & Short-term stress response Increase heart, breathing
-inner layer norepinephrine rates, blood pressure,
glucose, accelerate
breakdown of glucose and
fats
Pancreas Insulin Decrease glucose levels by promoting Converts glucose to glycogen
uptake of glucose by liver
-located b/w stomach & Glucagon Increases blood glucose levels by
small intestine promoting breakdown of glycogen
Ovaries Estradiol Regulates development &
maintenance of cycles
Progesterone Prepares uterus for pregnancy
Hormones Function Acts on Additional Information
Auxin Cell elongation, apical dominance, Phototropism -Master growth regulator
directs flowering, fruit ripening, Gravitropism
inhibition of abscission, relay for Apical Dominance
blue and red-light responses Abscission
Cytokinin Promotes cytokinesis, delay Senescence -Cell division
senescence (aging), promotes Apical Dominance -most abundant in growing
differential in meristem tissues
-effects are in combination
with other hormones
Gibberellins Shoot elongation, seed Synthesized in root and stem apical -stem, fruit & seed growth
germination, fruit & flower meristems -abscisic acid is a strong GA
maturation, delay aging and break Senescence antagonist
dormancy Dormancy
Abscisic Acid Cause abscission, inhibits stem Accumulates as response to -Dormancy
elongation, induces dormancy, stressful environmental conditions -counteracts GA and auxin
closes stomata Dormancy
Short-term drought response
Ethylene Fruit ripening, flower wilting, leaf Produced in aging tissues and -volatile gas (C2H4)
fall nodes of stems -aging
Systemin Plant responses to wounds, initiates Distributed systemically in the plant -anti-herbivory
production of jasmonic acid, body
prevent digestion from herbivores Herbivory
Methyl Salicylate (MeSa) Responses to infection by parasites Causes hypersensitive response -Immune response
or pathogen (HR) & systemic acquired response
(SAR)
Pathogens & Parasites
You might also like
- Winning against Prostatitis in the Elderly. Insider’s View of a Medical Worker.From EverandWinning against Prostatitis in the Elderly. Insider’s View of a Medical Worker.No ratings yet
- 2ND Gen Bio Prelim NotesDocument8 pages2ND Gen Bio Prelim NotesRalph RadazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- Assignment IN NutritionDocument5 pagesAssignment IN NutritionJasper SeeNo ratings yet
- HSB The Endocrine System Csec NotesDocument4 pagesHSB The Endocrine System Csec NotesGiaaNo ratings yet
- Hormone Table with Glands and ActionsDocument2 pagesHormone Table with Glands and ActionsFrancess Thea PascuaNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument3 pagesHormonesAdhara SalfarlieNo ratings yet
- Estrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesDocument57 pagesEstrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Article and Table - Peptide HormonesDocument3 pagesArticle and Table - Peptide HormonesZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Endocrine System NotiieeDocument34 pagesPharmacology of The Endocrine System Notiieekyla marie bardillon tarayaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument14 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- endorine systemDocument27 pagesendorine systemBenjamin YickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Control and CoordinationDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Control and Coordinationpranithg17No ratings yet
- Control and Coordination in Plants and Hormones in AnimalsDocument4 pagesControl and Coordination in Plants and Hormones in AnimalsAceHunterNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands WorksheetDocument3 pagesEndocrine Glands Worksheeteyra rosliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- X ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFDocument9 pagesX ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- Science Inquiry (Chapter 1)Document50 pagesScience Inquiry (Chapter 1)Nancy HastingNo ratings yet
- (Bio) 4THDocument21 pages(Bio) 4THZoe CataquizNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledDdsNo ratings yet
- Hormone Functions and Gland SourcesDocument3 pagesHormone Functions and Gland SourcesLaisa RarugalNo ratings yet
- BIOS5130 Week 9 Slides W - o AnswersDocument47 pagesBIOS5130 Week 9 Slides W - o AnswersOkikiola JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine and Metabolism SystemDocument8 pagesDiscussion 2.1 Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine and Metabolism SystemAnjar AniNo ratings yet
- Some Endocrine Glands and Their HormonesDocument3 pagesSome Endocrine Glands and Their HormonesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Science PortfolioDocument81 pagesScience PortfolioVismaya ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine SystemKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDocument10 pagesEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine System (Summary of Hormones)Document3 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine System (Summary of Hormones)Rishelle Mae Miñoza PilonesNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting on the UterusDocument45 pagesDrugs Acting on the UterusMohd ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Family and Drug MOA Physiologic Effect Indications Side EffectsDocument11 pagesFamily and Drug MOA Physiologic Effect Indications Side EffectsraquelNo ratings yet
- GoogleDocument2 pagesGoogletzNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 085347 PDFDocument30 pagesEndocrine System 085347 PDFClyde ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseDocument2 pagesPituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseHiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- Threatened Abortion DrugsDocument1 pageThreatened Abortion DrugsDivine Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and LactationDocument16 pagesPregnancy and LactationsukantaryNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology Lecture 1Document10 pagesHuman Physiology Lecture 1Lorenz L. Llamas IIINo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormones, Their Inhibitors and Fertility and Antifertility AgentsDocument29 pagesGonadal Hormones, Their Inhibitors and Fertility and Antifertility AgentsGopal Prasad DahalNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Document3 pages11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNo ratings yet
- Assignment MetabolismDocument10 pagesAssignment MetabolismCherrylyn RaytosNo ratings yet
- Control metabolism and balance with endocrine systemDocument24 pagesControl metabolism and balance with endocrine systemCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: FunctionDocument24 pagesEndocrine System: FunctionCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- Hormone Abbreviation Function Target Cell Related Diseases: Gland Which Secretes The HormoneDocument4 pagesHormone Abbreviation Function Target Cell Related Diseases: Gland Which Secretes The HormoneMarianne Jubille CataquisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Endocrine System NoteDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NoteFumzy AdelakunNo ratings yet
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: PancreasDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Pancreaselvie21No ratings yet
- The Role of Hormones in the Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesThe Role of Hormones in the Endocrine SystemAshly Santhosh KNo ratings yet
- GlandDocument2 pagesGlandsmith joeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PDFDocument5 pagesEndocrine PDFRegina SantosNo ratings yet
- Ph119.1 Final NotesDocument13 pagesPh119.1 Final NotesANDREA GAIL ANONUEVONo ratings yet
- Chemical Control and Coordination FinalDocument5 pagesChemical Control and Coordination Finalakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- Pituitary: Posterior PosteriorDocument4 pagesPituitary: Posterior PosteriorMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cell Communication-Rumen MetabolismDocument11 pagesCell-Cell Communication-Rumen MetabolismChala Tekalign HareruNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture 5 Hormone ChartDocument2 pagesBiology Lecture 5 Hormone Chartmark_pedersen_6No ratings yet
- Module 12 - The Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesModule 12 - The Endocrine SystemAngela FelixNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Organ Hormone EffectDocument6 pagesEndocrine System: Organ Hormone EffectEmma KowalNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Winter ReverieDocument5 pagesWinter ReverieMechelle ChenNo ratings yet
- Standing Waves: Monday, March 20Document21 pagesStanding Waves: Monday, March 20Mechelle ChenNo ratings yet
- HydroDocument2 pagesHydroMechelle ChenNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaDocument3 pagesHemophiliaMechelle ChenNo ratings yet
- NewspaperDocument5 pagesNewspaperMechelle ChenNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument1 pageLetterMechelle ChenNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaDocument4 pagesHemophiliaMechelle ChenNo ratings yet
- HemophiliaDocument4 pagesHemophiliaMechelle ChenNo ratings yet
- Revisiting The Fascist Subtext of Attack On Titan - Some Notes On A Modern Reactionary AnimeDocument10 pagesRevisiting The Fascist Subtext of Attack On Titan - Some Notes On A Modern Reactionary AnimeSouthern FuturistNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 1Document10 pagesLiterature Review 1FahimAnwar100% (1)
- CDC Project Proposal TemplateDocument11 pagesCDC Project Proposal TemplateMirza ArfanNo ratings yet
- Footloose The Musical ScriptDocument89 pagesFootloose The Musical Scriptjasmyn.spinks1307100% (1)
- 2013 SAMPLE BAR EXAM QUESTIONSDocument11 pages2013 SAMPLE BAR EXAM QUESTIONShellojdeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter9E2010 PDFDocument29 pagesChapter9E2010 PDFmariahx91No ratings yet
- Extraction of Rare Earth Oxides From Discarded Compact - 2019 - Minerals EngineDocument10 pagesExtraction of Rare Earth Oxides From Discarded Compact - 2019 - Minerals EnginepHNo ratings yet
- CLASIFICACION RESUMEN Caton - Et - Al-2018-Journal - of - Clinical - PeriodontologyDocument12 pagesCLASIFICACION RESUMEN Caton - Et - Al-2018-Journal - of - Clinical - PeriodontologyDaniela RojasNo ratings yet
- JAC - 2023 - ModelQuestion - 9 - Math 1Document4 pagesJAC - 2023 - ModelQuestion - 9 - Math 1Chandan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Review Center Association of The Philippines vs. Ermita 583 SCRA 428, April 02, 2009, G.R. No. 180046Document2 pagesReview Center Association of The Philippines vs. Ermita 583 SCRA 428, April 02, 2009, G.R. No. 180046Almer Tinapay100% (1)
- 1 Fill in The Right Article: X / The. 21pDocument3 pages1 Fill in The Right Article: X / The. 21pNo YesNo ratings yet
- Afsm 2011Document4 pagesAfsm 2011Rakshit SehgalNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Self-Care ReflectionDocument2 pagesMental Health and Self-Care Reflectionapi-472652222No ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Meaning and Scope of Public FinanceDocument21 pagesChapter 2-Meaning and Scope of Public FinanceyebegashetNo ratings yet
- Letter of Undertaking for Cargo ReleaseDocument1 pageLetter of Undertaking for Cargo ReleaseSitiJamilahAlimanNo ratings yet
- Gramatica Limbii Engleze Cls 1-4 - Cristina JohnsonDocument8 pagesGramatica Limbii Engleze Cls 1-4 - Cristina JohnsonGeorgiana CosminaNo ratings yet
- DLP Format - FilipinoDocument4 pagesDLP Format - FilipinoLissa Mae MacapobreNo ratings yet
- Budak Historia Salonitana and Historia Salonitana Maior Compatibility ModeDocument17 pagesBudak Historia Salonitana and Historia Salonitana Maior Compatibility Modeprofa92No ratings yet
- Access NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpDocument5 pagesAccess NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Chapter 14 - UpKamjith PadinjareveeduNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Warfare - Part 2.mind GamesDocument16 pagesSpiritual Warfare - Part 2.mind GamesAnonymous D83RFJj34No ratings yet
- Direction: Read Each Question Carefully. Choose The Letter of The CorrectDocument4 pagesDirection: Read Each Question Carefully. Choose The Letter of The CorrectHanna Grace HonradeNo ratings yet
- Production Planning and Control System SynopsisDocument6 pagesProduction Planning and Control System Synopsisgvani3333No ratings yet
- Flexible Budgets and Variance AnalysisDocument50 pagesFlexible Budgets and Variance AnalysisRanjini SettyNo ratings yet
- PMI ACP HandbookDocument57 pagesPMI ACP HandbookvluxNo ratings yet
- Scanners Accurrcy PDFDocument73 pagesScanners Accurrcy PDFdanielcorrea999No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Practices andDocument12 pagesHuman Resource Management Practices andMoathNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Module Week 4 Converted From PDF To WordDocument10 pagesOral Com Module Week 4 Converted From PDF To WordRowena Francisco Go VillorenteNo ratings yet
- Summary Covers Exam MaterialDocument30 pagesSummary Covers Exam MaterialWriting ServiceNo ratings yet
- Hospital Sector Data Analysis: Price, Market Cap, Sales & Valuation RatiosDocument3 pagesHospital Sector Data Analysis: Price, Market Cap, Sales & Valuation RatiosYash SinghalNo ratings yet
- DSC MatDocument41 pagesDSC MatRamuCivilNo ratings yet