Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 12 - The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Angela Felix0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesThe endocrine system regulates many essential functions in the body through glands that secrete hormones. It controls water balance, growth and metabolism, reproduction, immune function, blood glucose levels, heart rate, and more. The major glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and ovaries/testes. Hormones act on target tissues to increase or decrease various processes. Imbalances can result in disorders like dwarfism, diabetes, infertility, or thyroid disease.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe endocrine system regulates many essential functions in the body through glands that secrete hormones. It controls water balance, growth and metabolism, reproduction, immune function, blood glucose levels, heart rate, and more. The major glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and ovaries/testes. Hormones act on target tissues to increase or decrease various processes. Imbalances can result in disorders like dwarfism, diabetes, infertility, or thyroid disease.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesModule 12 - The Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Angela FelixThe endocrine system regulates many essential functions in the body through glands that secrete hormones. It controls water balance, growth and metabolism, reproduction, immune function, blood glucose levels, heart rate, and more. The major glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and ovaries/testes. Hormones act on target tissues to increase or decrease various processes. Imbalances can result in disorders like dwarfism, diabetes, infertility, or thyroid disease.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Module 12: The Endocrine System
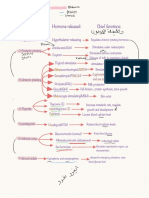
Function of the Endocrine System:
1. Water balance - it controls the solute concentration of the blood.
2. Uterine contraction and milk release - it regulates uterine contractions during delivery of the new born and stimulates milk release from
the breasts in lactating females.
3. Growth metabolism and tissue maturation - the endocrine system regulates the growth of many tissues, such as the bone and muscle,
and the rate of metabolism of many tissues, which helps maintain a normal body temperature and normal mental functions.
4. Ion regulation - it regulates sodium ions, potassium ions, and calcium ions concentration in the blood.
5. Heart rate and blood pressure regulation - it helps regulate the heart rate and blood pressure and helps the body for physical activity.
6. Blood glucose control - it regulates blood glucose levels and other nutrients in the blood.
7. Immune system regulation - it helps control the production and functions of immune cells.
8. Reproductive functions control - it controls the development and the function of the reproductive systems in males and females.
Disorder Associated
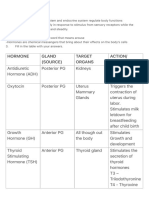
Gland Hormone Target Response with undersecretion Disorder Associated with
Tissues oversecretion
1. Anterior
Pituitary A. Growth Most tissues - Increases protein
hormone/Somatotropin synthesis
- breakdown of lipids dwarfism Giantism in childhood
- release of fatty acids
from cells Acromegaly in adulthood
-increase blood
glucose level
B. Thyroid stimulating
hormone/TSH Thyroid gland Increase thyroid hypothyroidism Goiter-enlarge thyroid gland
hormone - can also develop if there
secretion( thyroxine iodine deficiency in the diet
and triiodothyronine)
C. Adrenocorticotropic Adrenal cortex Increase scretion of of Increase skin pigmentation at
hormone/ACTH glucocorticoid -Anorexia highconcentration
hormones such as
cortisol - weakness
- low blood pressure
D. Melanocyte Melanocytes in Skin pigmentation Albinism Darker skin coloration
stimulating skin
hormone/MSH
E. Luteinizing - Ovary in - Promotes ovulation
hormone/LH or females and progesterone - infertility - infertility in men
interstitial cell - Testes in production in ovary
stimulating males - testosterone - stop ovulation in -polycystic ovary syndrome in
hormone/ICSH synthesis and support women women
for sperm cell
production in testis
F. Prolactin - Ovary and - Stimulates milk
mammary production and Less milk production Over production of milk
gland in prolongs progesterone
females secretion following
- Testis in ovulation and during
males pregnancy
- increases sensitivity
to LH in males
G. Follicle stimulating - Follicles in - Promote follicle
hormone/FSH ovary in maturation and Incomplete development o
females estrogen secretion in of puberty
- semineferous ovary
tubules in - sperm cell production
males in testis
2. Posterior A. Antidiuretic
pituitary hormone/ADH kidney Increases water Diabetes insipidus -
gland reabsorption(less
water is lost as urine)
B. Oxytocin - Uterus -increases uterine
Prolong labor - in men low sexual drive
-Mammary contraction
gland - increases milk “let - menstrual difficulty and
down” from mammary ovarian failure in women
gland
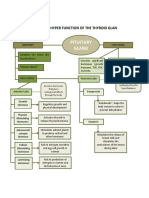
3. Thyroid A. Thyroid - Increases metabolic
gland hormones( thyroxine most cells of rates Infant-cretinism- a Grave’s disease
and triiodothyronine) the body - Essential for normal condition in which the - a type of hyperthyroidism
process of growth and person is mentally resulting from the production
maturation retarded and has a short of abnormal protein by the
stature with abnormally immune system that are
formed skeletal similar in structure and
structures function to TSH
Adult-myxedema - is the =accompanied by bulging of
accumulation of fluid and the eyes, a condition called
other molecules in the exophthalmia
subcutaneous tissue
B. Calcitonin - Decreases rate of
Primary bone bone breakdown
- prevent large
increase in blood
calcium ion levels
following a meal
4.Parathyro Parathyroid hormone Bone - Increase rate of bone
id gland kidneys breakdown by Hypoparathyroidism- it Hyperparathyroidism-it can
osteoclasts cab be the result of result to a tumor of a
- increase vitamin D injury or surgical parathyroid gland
synthesis removal of the thyoid - increase bone resorption and
- essential for gland elevate calcium ion level
maintennance of - can result to reduced
normal blood calcium rate of bone resorption
leveld and reduced vitan D
formation
4. Adrenal Epinephrine/Adrenalin - Heart Increases cardiac can result in physical can damage your blood
medulla and Norepinephrine - blood vessels output and mental symptoms, vessels, increase your blood
- liver Increases blood flow such as: anxiety. pressure, and elevate your risk
- also called the fight-or- - fat cells to skeletal muscles depression. changes in of heart attacks or stroke
flight hormone because and heart blood pressure.
of their role in preparing Increases release of
the body for vigorous glucose and fatty acids
physical activity
5. Adrenal A. Mineralcorticoids( Ald - kidneys Increase rate of - low blood pressure
cortex osterone) - to a lesser sodium transport into -Lose of potassium and retain
degree body - low sodium level and sodium
intestine and Increase rate of potassium level
sweat gland potassium excretion
B. Glucorticoid (cortisol) Most tissues - Increase fat and - fatigue
like liver fat, protein breakdown
skeletal - Increase glucose -low blood pressure - High blood pressure
muscle,immune synthesis from amino -Addison's disease can
tissue acids develop if your immune - osteoporosis
- Increase blood system attacks your
nutrient levels adrenal glands and - muscle weakness
severely damages your
adrenal cortex. When - excess production of cortisol
90% of the adrenal from a tumor in the adrenal
cortex is destroyed, your gland or elsewhere in the body
adrenal glands will not (ectopic Cushing's syndrome)
be able to produce or a tumor of the pituitary
enough of the gland ...
steroid hormones cortis
ol and aldosterone.
C. Adrenal androgens Most tissues Insignificant in males
Increase female - loss of sexual drive -hirsutism (excessive hair
sexual drive,pubic hair gowth
and axillary hair - loss of muscle mass
growth and strength
6. Pancreas A. Insulin Especially Increase uptake and
liver,skeletal use of glucose and Diabetes mellitus Hyperinsulinemia which is link
muscle,adipose amino acids to obesity and heart disease
tissue
B. Glucagon Primary liver Increase breakdown of your cells don't store sugar,
of glycogen and If they drop too low, the and instead, sugar stays in
release of glucose into individual may become your bloodstream.
the circulatory system disoriented, dizzy or Glucagonoma leads to
even pass out. diabetes-like symptoms and
other severe symptoms,
including: high blood sugar.
excessive thirst and hunger
due to high blood
7.Testes Testosterone Most tissues - Aids in sperm cell
production - Reduce sexual drive - excessive facial and body
- Maintenance of hair aggression
functional reproductive - erectile dysfunction
organs -infertility
- secondary sex
characteristics -
sexual behavior
8.Ovaries Estrogen and Most tissues - Aid in uterine and - Interfere with sexual
progesterone mammary function and - Lump of breast
development and development
function - also increase risk of - irregular menstrual period
- External genitalia obesity
structure
- secondary sex -osteoporosis and
characteristics cardiovascular disease
- sexual behavior
- menstraul cycle
9. Prostaglandin Most tissues - Mediate inflammatory High
Uterus,ovar responses -arthritis levels of prostaglandins are
ies , - Increase uterine produced in response to injury
inflamed contraction - mentrual cramping or infection and cause
tissues - ovulation inflammation, which is
associated with the symptoms
of redness, swelling, pain and
fever. This is an important part
of the body's normal healing
process.
10. Thymus thymosin Immune tissues Promotes immune Low resistance
system development
and function
11. Pineal melatonin hypothalamus Inhibit secretion of - restlesness -reset circadian rhythms
gland gonadotropin - sleepness
releasing - poor stress response -lower core body temperature
hormone,thereby - insomia
inhibiting reproduction
You might also like
- Complete The Table Below.: Hormone Gland (Source) Target ActionDocument2 pagesComplete The Table Below.: Hormone Gland (Source) Target ActionFrancess Thea PascuaNo ratings yet
- Assignment IN NutritionDocument5 pagesAssignment IN NutritionJasper SeeNo ratings yet
- Sigh EndsDocument3 pagesSigh Endsmacy kang (maceeeeh)No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDocument5 pagesAnterior Pituitary Hormone: Hormones Target Organ Effects Hormone Sign & SymptomsDevia OktaviandraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Control and Coordination FinalDocument5 pagesChemical Control and Coordination Finalakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument3 pagesHormonesAdhara SalfarlieNo ratings yet
- hORmones in Plants Class Note Class 10 ...Document4 pageshORmones in Plants Class Note Class 10 ...AceHunterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument4 pagesChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- BSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemDocument38 pagesBSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemAngelika ButaslacNo ratings yet
- On The Posterior Surface of Thyroid GlandDocument2 pagesOn The Posterior Surface of Thyroid GlandRica Marie G. UyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands WorksheetDocument3 pagesEndocrine Glands Worksheeteyra rosliNo ratings yet
- Endorine SystemDocument4 pagesEndorine SystemMichaela Shianne E. MatituNo ratings yet
- HSB The Endocrine System Csec NotesDocument4 pagesHSB The Endocrine System Csec NotesGiaaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System ReviewerDocument4 pagesEndocrine System ReviewerAngelie Man-onNo ratings yet
- 41) Sex Hormones (C. Patho)Document33 pages41) Sex Hormones (C. Patho)Haider AliNo ratings yet
- Glands SummaryDocument3 pagesGlands SummaryRokaia RagehNo ratings yet
- Science: Endocrine & Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesScience: Endocrine & Nervous SystemLUISE DANIELLA DELOS REYES DOLOTALLASNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDocument3 pagesEndocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sci q3 ReviewerDocument9 pagesSci q3 ReviewerElmar Arcian VicenteNo ratings yet
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDocument38 pagesHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument10 pagesMCN ReviewergreinabelNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PDFDocument5 pagesEndocrine PDFRegina SantosNo ratings yet
- Stress Hormone, Any Form of Stress It Is Elevated Pituitary Lactogenic HormoneDocument3 pagesStress Hormone, Any Form of Stress It Is Elevated Pituitary Lactogenic HormoneAthalia amaris SanchezNo ratings yet
- Chap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesDocument11 pagesChap9 Endocrine Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- Science 3rdDocument8 pagesScience 3rdDaniella lurionNo ratings yet
- HY EndocrineDocument61 pagesHY EndocrineKiranNo ratings yet
- HY EndocrineoeDocument62 pagesHY EndocrineoebrownsmilansNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- Big Picture F: MetalanguageDocument13 pagesBig Picture F: Metalanguagejohanna deguzmanNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesAnaPhy Lec - Endocrine SystemReigh DakotaNo ratings yet
- Notes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesNotes in Science LT 10 - Endocrine SystemAlven ReyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument12 pagesEndocrine GlandMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- Endocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationDocument4 pagesEndocrinesys TEM: Principles of Chemical CommunicationCatherine Joy delos SantosNo ratings yet
- GQA Science10 - Q3 - Wk1 2 - Endocrine and Reproductive System - GQA .LRQADocument17 pagesGQA Science10 - Q3 - Wk1 2 - Endocrine and Reproductive System - GQA .LRQALevi AckermanNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument6 pagesBio ReviewerMildred MarcosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: FunctionDocument24 pagesEndocrine System: FunctionCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Endocrine SystemDocument24 pages2018 - Endocrine SystemCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine System (Summary of Hormones)Document3 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine System (Summary of Hormones)Rishelle Mae Miñoza PilonesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesEndocrine SystemCHIQUI JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemZennith AngawaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System 1Document36 pagesFemale Reproductive System 1Rahil PatelNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyDocument8 pagesEndocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees Endocrinologyzonia kilashNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Biology ReviewerDocument10 pagesGrade 10 Biology ReviewerNadine Victoria DizonNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System NotesDocument11 pagesThe Endocrine System NotesArce JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv Human Anatomy and Physiology: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument12 pagesUnit - Iv Human Anatomy and Physiology: Very Short Answer QuestionsRK YeleswarapuNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyDocument8 pagesEndocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyMohammad AlHamdanyNo ratings yet
- Physiology Self WorkDocument17 pagesPhysiology Self WorkpaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - MCN ReviewerDocument12 pagesChapter 5 - MCN ReviewerPrincess Queenie OlarteNo ratings yet
- No Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesNo Gland Hormone Its Function Pituitary GlandKush KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT IIDocument10 pagesChapter 2 UNIT IIAyen LatosaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - q3 ReviewerDocument16 pagesScience 10 - q3 ReviewerNicole Lapu-osNo ratings yet
- Note 17 Dec 2021Document2 pagesNote 17 Dec 2021mNo ratings yet
- Concept Pituitary GlandDocument14 pagesConcept Pituitary GlandCHRISTINE JOY. MOLINANo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDocument3 pagesENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine CompiledDocument20 pagesEndocrine CompiledGeraldine MaeNo ratings yet
- Making Babies: The Definitive Guide to Improving Your Fertility and Reproductive HealthFrom EverandMaking Babies: The Definitive Guide to Improving Your Fertility and Reproductive HealthNo ratings yet
- Module 13 - The Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesModule 13 - The Digestive SystemAngela FelixNo ratings yet
- Module 1-10Document56 pagesModule 1-10Angela FelixNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesModule 10 - The Nervous SystemAngela FelixNo ratings yet
- Module 11 - Special SensesDocument6 pagesModule 11 - Special SensesAngela FelixNo ratings yet
- Histologi Organ Dan Sistem Sirkulasi PoltekkesDocument28 pagesHistologi Organ Dan Sistem Sirkulasi PoltekkesJeon WonwooNo ratings yet
- Motor Point IndexDocument4 pagesMotor Point IndexFerry Dimyati100% (1)
- Radiologi Fraktur Dan DislokasiDocument37 pagesRadiologi Fraktur Dan DislokasiMuthia KamillaNo ratings yet
- Nerve Adaptation in Response To Mechanical Loading - Marko BodorDocument32 pagesNerve Adaptation in Response To Mechanical Loading - Marko Bodorpuntocom111No ratings yet
- Shoulder Impingement SyndromeDocument21 pagesShoulder Impingement SyndromeivannaOctavianiNo ratings yet
- SIM in OphthalmologyDocument249 pagesSIM in OphthalmologyErica Christine Cortez100% (3)
- Student Guide To The Frog Dissection DissectionDocument3 pagesStudent Guide To The Frog Dissection Dissectionladyv939No ratings yet
- 2nd Year Key of SEQs 17-10-12Document7 pages2nd Year Key of SEQs 17-10-12Mudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Sternum PDFDocument1 pageSternum PDFKun HanifahNo ratings yet
- FipatDocument49 pagesFipataskherNo ratings yet
- Jezicki MozakDocument36 pagesJezicki MozakSinisa RisticNo ratings yet
- GIT MnemonicsDocument20 pagesGIT MnemonicsAhmed AbdelgelilNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident: Case PresentationDocument76 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: Case PresentationSi VeekeeNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Yoga Teachers TrainingDocument17 pagesCase Study: Yoga Teachers TrainingKaran PatelNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NotesDocument17 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes NotessaleemNo ratings yet
- CLasificación de Glosectomias 2019Document7 pagesCLasificación de Glosectomias 2019Karla Rojas NoeNo ratings yet
- Kriya For Polarity BalanceDocument2 pagesKriya For Polarity BalanceLut TenNo ratings yet
- Lower ExtremitiesDocument14 pagesLower ExtremitiesNicko PerezNo ratings yet
- 22 Gait DisordersDocument13 pages22 Gait DisordersAbhilekh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Facial Growth and Facial OrthopedicsDocument211 pagesFacial Growth and Facial OrthopedicsMCU Ortho100% (2)
- The Interceptive OrthodonticsDocument67 pagesThe Interceptive OrthodonticsArun Shyam0% (1)
- The IntegumentDocument15 pagesThe Integumentludiegues752No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Oral CavityDocument72 pagesAnatomy of Oral CavityWahaj MujahidNo ratings yet
- In The AfterglowDocument22 pagesIn The AfterglownnurnadillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Excretion in Humans - 2023-2024Document41 pagesChapter 13 Excretion in Humans - 2023-2024buhNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antityr DrugsDocument23 pagesThyroid and Antityr Drugsmsmobile shNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2402 Lab 5 Vital Signs Lab 2Document8 pagesBIOL 2402 Lab 5 Vital Signs Lab 2William DelphNo ratings yet
- Titles List of E N T Branch at StudentDocument1 pageTitles List of E N T Branch at Studentheba youssefNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument7 pagesHeart AnatomyArjon BalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quizbook PDFDocument92 pagesAnatomy Quizbook PDFLipid Berger67% (3)