Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Typhoon Is A Mature Tropical Cyclone That Develops Between 180
Uploaded by
Angelmicah Cordenete0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views3 pagesA typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere, in the region referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, which is the most active tropical cyclone basin. The northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions for forecasting purposes: eastern, central, and western. While the RSMC in Japan names each typhoon, 18 countries in the affected region coordinate the main name lists. A typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, while hurricanes occur in the Atlantic or northeastern Pacific and tropical cyclones occur in the South Pacific or Indian Ocean.
Original Description:
Original Title
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere, in the region referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, which is the most active tropical cyclone basin. The northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions for forecasting purposes: eastern, central, and western. While the RSMC in Japan names each typhoon, 18 countries in the affected region coordinate the main name lists. A typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, while hurricanes occur in the Atlantic or northeastern Pacific and tropical cyclones occur in the South Pacific or Indian Ocean.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views3 pagesA Typhoon Is A Mature Tropical Cyclone That Develops Between 180
Uploaded by
Angelmicah CordeneteA typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere, in the region referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, which is the most active tropical cyclone basin. The northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions for forecasting purposes: eastern, central, and western. While the RSMC in Japan names each typhoon, 18 countries in the affected region coordinate the main name lists. A typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, while hurricanes occur in the Atlantic or northeastern Pacific and tropical cyclones occur in the South Pacific or Indian Ocean.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
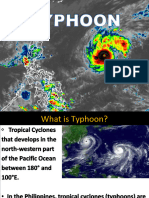
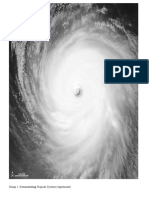
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and
100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the
Northwestern Pacific Basin,[1] and is the most active tropical cyclone
basin on Earth, accounting for almost one-third of the world's annual
tropical cyclones. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific
Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to
140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E). The
Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclone
forecasts is in Japan, with other tropical cyclone warning centers for the
northwest Pacific in Hawaii (the Joint Typhoon Warning Center), the
Philippines and Hong Kong. While the RSMC names each system, the
main name list itself is coordinated among 18 countries that have
territories threatened by typhoons each year.[2] A hurricane is a storm
that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or the northeastern Pacific Ocean, a
typhoon occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, and a tropical
cyclone occurs in the South Pacific or the Indian Ocean.[2
Agency monitor typhoon
Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical Astronomical
Services Administration (PAGASA) PAGASA is an agency under the
Department of Science and Technology (DOST). It provides real-time
updates about the weather and typhoon alerts.
What is the Philippines prone to typhoons
Why is the Philippines prone to typhoons? It is because the Philippines
is geographically located along the Pacific region near the Equator
which is prone to tropical cyclones and storms.
What condition favour the formation of
tyhoons
Like any tropical cyclone, there are a few main requirements for
typhoon formation and development: (1) sufficiently warm sea surface
temperatures, (2) atmospheric instability, (3) high humidity in the lower
to middle levels of the troposphere, (4) enough Coriolis effect to
develop a low pressure center, (5) a pre- ...
The conditions favor for a typhoon to form is it needs the f.f. warm
water winds colliding and air pressure
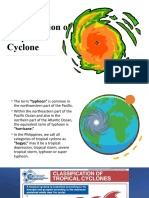
What are the diffenrent tropical cyclone categories
1 Tropical Cyclone. Less than 125 km/h. Gales. Minimal house
damage. ...
2 Tropical Cyclone. 125 - 164 km/h. Destructive winds. ...
3 Severe Tropical Cyclone. 165 - 224 km/h. Very destructive winds. ...
4 Severe Tropical Cyclone. 225 - 279 km/h. Very destructive winds. ...
5 Severe Tropical Cyclone. More than 280 km/h. Extremely
destructive winds.
What is PAR
Philippine Area of Responsibility. The Philippine Area of Responsibility
(PAR) is an area in the Northwestern Pacific where PAGASA, the
Philippines' national meteorological agency monitors weather
occurrences.
You might also like
- Typhoon WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesTyphoon WPS OfficeNoo NameeNo ratings yet
- Where Do Hurricanes, Typhoons & Cyclones Come From? | 2nd Grade Science Edition Vol 3From EverandWhere Do Hurricanes, Typhoons & Cyclones Come From? | 2nd Grade Science Edition Vol 3No ratings yet
- A TyprDocument1 pageA Typrdan teNo ratings yet
- What Is TyphoonDocument3 pagesWhat Is TyphoonLay100% (1)
- Gahhahahaha Typhoon YummyDocument17 pagesGahhahahaha Typhoon Yummyアブドゥルカリム エミールNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document15 pagesUnit 4Imran Ul haq (Ammar choudhary)No ratings yet
- Typhoon Grade 8Document27 pagesTyphoon Grade 8Paul Senen Didulo74% (43)
- Science TyphoonDocument3 pagesScience TyphoonNelson Budol100% (1)
- Understanding TyphoonsDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Typhoonssherme.ordenezaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Tropical Revolving Systems (TRS)Document91 pagesUnit 2 - Tropical Revolving Systems (TRS)Noli ChristianNo ratings yet
- Weather Disturbances and Other PhenomenaDocument3 pagesWeather Disturbances and Other PhenomenaVoxDeiVoxNo ratings yet
- Typhoon: Typhoon (Disambiguation) Tropical Cyclone Basins TyphooDocument10 pagesTyphoon: Typhoon (Disambiguation) Tropical Cyclone Basins TyphooVanellope VonschweettzNo ratings yet
- A A A Typhoon FormationDocument5 pagesA A A Typhoon FormationEva Mae ForcadillaNo ratings yet
- 1 TyphoonDocument33 pages1 TyphoonCamlon KhajarNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - Understanding Typhoon PDFDocument33 pagesGrade 8 - Understanding Typhoon PDFSam Agustine Rosil0% (1)
- Get To Know The Typhoon: With Francis Gil BautistaDocument18 pagesGet To Know The Typhoon: With Francis Gil BautistaRaul Carl CapinpuyanNo ratings yet
- Typhoon: Typhoon (Disambiguation) Tropical Cyclone BasinsDocument2 pagesTyphoon: Typhoon (Disambiguation) Tropical Cyclone BasinsJoy ABNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tropical Cyclones - Evans PDFDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Tropical Cyclones - Evans PDFgjw1684100% (2)
- Typhoon 2022 2023Document46 pagesTyphoon 2022 2023vhdemaala.tshsNo ratings yet
- Classification of Tropical CycloneDocument11 pagesClassification of Tropical CycloneAPPLE JEAN YECYECNo ratings yet
- Typhoon FormationDocument25 pagesTyphoon FormationRhyzaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Hydro, Tropical Cyclone, and MonsoonDocument28 pagesIntro To Hydro, Tropical Cyclone, and MonsoonJairah AngueNo ratings yet
- Science 5 Week4 Day3 4Document30 pagesScience 5 Week4 Day3 4Shiela Marie MiñozaNo ratings yet
- TyphoonDocument1 pageTyphoonemanNo ratings yet
- Understandingtyphoons 141127052908 Conversion Gate02Document21 pagesUnderstandingtyphoons 141127052908 Conversion Gate02RosielNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 2 LESSON 4 Understanding TyphoonsDocument18 pagesQUARTER 2 LESSON 4 Understanding TyphoonsJose BundalianNo ratings yet
- 262 631 1 SMDocument33 pages262 631 1 SMJunnoKaiserNo ratings yet
- Met o 2Document9 pagesMet o 2Benigno MartinNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument3 pagesNomenclatureMiyangNo ratings yet
- TyphoonDocument1 pageTyphoonJean Rose IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For TyphoonDocument1 pageReviewer For TyphoonGianbantigueNo ratings yet
- Group 5 BPED 21Document3 pagesGroup 5 BPED 21Angelo Joseph ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- CiclonesDocument4 pagesCiclonesAnthony RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 TyphoonDocument2 pagesGrade 8 TyphoonGhen HipolitoNo ratings yet
- John Alvin and The - Pokey GroupsDocument21 pagesJohn Alvin and The - Pokey GroupsPrecious SanianoNo ratings yet
- Weather-Disturbances W3-SCIENCE TABOTABODocument61 pagesWeather-Disturbances W3-SCIENCE TABOTABOKimjustKIM:3No ratings yet
- Extreme Weather ConditionsDocument30 pagesExtreme Weather ConditionsAbdurrauf UsmanNo ratings yet
- Good Morning Grade 8 Students. Have You Wondered What Happens in TheDocument117 pagesGood Morning Grade 8 Students. Have You Wondered What Happens in TheChristine GaculaNo ratings yet
- Science8 q2 Mod4 Understanding TyphoonsDocument6 pagesScience8 q2 Mod4 Understanding TyphoonsArgyll PaguibitanNo ratings yet
- TyphoonDocument18 pagesTyphoonJovelle HarinaNo ratings yet
- Precautionary and Safety Measures For Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument5 pagesPrecautionary and Safety Measures For Hydrometeorological HazardsStephanie mari MercedNo ratings yet
- Pacific Ocean: How Does Pacific Ocean Helps in Forming Typhoon?Document2 pagesPacific Ocean: How Does Pacific Ocean Helps in Forming Typhoon?Robbie William G. SañoNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document35 pagesModule 2GracielaNo ratings yet
- Tsholo Tropical CycloneDocument9 pagesTsholo Tropical CycloneMoabīí ÏdkNo ratings yet
- Tropical Cyclones, Hurricanes and TyphoonsDocument90 pagesTropical Cyclones, Hurricanes and TyphoonsPhilip Jayson L. LestojasNo ratings yet
- Philippines Natural Disaster: Typhoon Resilient ArchitectureDocument10 pagesPhilippines Natural Disaster: Typhoon Resilient ArchitectureRita BorgesNo ratings yet
- Understanding The TyphoonsDocument25 pagesUnderstanding The TyphoonsDICES MNK Wesley L. ArconNo ratings yet
- What Are The Potential Hydrometeorological HazardsDocument15 pagesWhat Are The Potential Hydrometeorological HazardsANTON GABRIEL PRECIOSONo ratings yet
- Group Demonstration: Science 8Document28 pagesGroup Demonstration: Science 8Ed TapuroNo ratings yet
- Hydrometrological HazardsDocument23 pagesHydrometrological HazardsIril IanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 4 - Lecture - Understanding TyphoonDocument25 pagesModule 2 4 - Lecture - Understanding Typhoonredox francisco100% (1)
- Typhoon HandoutsDocument1 pageTyphoon HandoutsMabellee CabreraNo ratings yet
- Module 2Q SCI 8 2Document20 pagesModule 2Q SCI 8 2PeterClomaJr.No ratings yet
- Typhoons in The Philippines PDFDocument65 pagesTyphoons in The Philippines PDFThirdy EstolanoNo ratings yet
- Typhoon LPDocument13 pagesTyphoon LPMaykhaila GallegoNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document11 pagesGroup 1Neb Louies Vallescas LaguaNo ratings yet
- How Typhoons DevelopDocument15 pagesHow Typhoons DevelopJohnny RebieeeNo ratings yet
- Hurricane Vs TornadoesDocument11 pagesHurricane Vs TornadoesMelanie Valladares RNo ratings yet
- Sci8 Q2 Mod3 UnderstandingTyphoon v5Document12 pagesSci8 Q2 Mod3 UnderstandingTyphoon v5Angelique Benlota MolanidaNo ratings yet
- Solution:: Chart TitleDocument3 pagesSolution:: Chart TitleDani LubosNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Essential Elements of Information - 2021-02-07-02-25-31-pm - 2022-09-01-09-50-31-AmDocument2 pagesAssignment 3 Essential Elements of Information - 2021-02-07-02-25-31-pm - 2022-09-01-09-50-31-AmMelissa Jeane Masayon CoyocaNo ratings yet
- It's + There's+: іменник (sun, wind)Document26 pagesIt's + There's+: іменник (sun, wind)Юля СтепанюкNo ratings yet
- Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan 10-Day Weather Forecast - The Weather ChannelDocument4 pagesLahore, Punjab, Pakistan 10-Day Weather Forecast - The Weather ChannelPervez IqbalNo ratings yet
- FLT #1 LS5 Safety Practices in Time of DisasterDocument10 pagesFLT #1 LS5 Safety Practices in Time of DisasterAshley RañesesNo ratings yet
- OPIC - Advanced 4Document4 pagesOPIC - Advanced 4Kristine Syra CastilloNo ratings yet
- Office of Civil Defense Ro2: October 29, 2018 Usec Ricardo B JaladDocument2 pagesOffice of Civil Defense Ro2: October 29, 2018 Usec Ricardo B JaladFrancis Joseph Maano ReyesNo ratings yet
- Tropical Cyclone Notes Excluding EssayDocument6 pagesTropical Cyclone Notes Excluding Essaysimplykim0101_109216No ratings yet
- Pressure BeltsDocument3 pagesPressure BeltsmabilashNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2.2 TyphoonDocument2 pagesQuiz 2.2 TyphoonRuth Camus Dela Pena100% (1)
- Geography Project: Natural Disasters and Their ManagementDocument10 pagesGeography Project: Natural Disasters and Their ManagementNimbusNo ratings yet
- Mangolayon, Omar - Eye Witness FinalDocument9 pagesMangolayon, Omar - Eye Witness FinalOmar Palma Gil MangolayonNo ratings yet
- Hurricanes, Cyclones and Typhoons Are All Types of Tropical Storms. But What's The Difference Between Them?Document5 pagesHurricanes, Cyclones and Typhoons Are All Types of Tropical Storms. But What's The Difference Between Them?JanelleNo ratings yet
- What The 'Bleep' Did She Say?Document9 pagesWhat The 'Bleep' Did She Say?Tony StaufferNo ratings yet
- Disaster Around Me: Typhoon: YolandaDocument2 pagesDisaster Around Me: Typhoon: YolandaCateleen BacaniNo ratings yet
- Keys Es Weather Patterns and Severe Storms CHP 20 Teacher NotesDocument24 pagesKeys Es Weather Patterns and Severe Storms CHP 20 Teacher Notesapi-235000986No ratings yet
- MET O 2 7th WK ModuleDocument18 pagesMET O 2 7th WK ModuleJonalyn CordovaNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: ReferencesDocument7 pagesAcknowledgement: Referencesdwayne420No ratings yet
- 593aa PDFDocument246 pages593aa PDFMohdFaridNo ratings yet
- Thunderstorms, Tornadoes and HurricanesDocument38 pagesThunderstorms, Tornadoes and Hurricanesjuthayavannan2012No ratings yet
- Tornado Aldi Maulana Muhammad XI MIPADocument10 pagesTornado Aldi Maulana Muhammad XI MIPAAldi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- 262 631 1 SMDocument33 pages262 631 1 SMJunnoKaiserNo ratings yet
- Advisory: Department of The Interior and Local GovernmentDocument2 pagesAdvisory: Department of The Interior and Local GovernmentDina Jane PeñaresNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - Science - Q2 - Wk6 - GLAKDocument20 pagesGrade 8 - Science - Q2 - Wk6 - GLAKANGEL MANGLICMOTNo ratings yet
- DLP Science 8 Wk3D2 2nd QTRDocument2 pagesDLP Science 8 Wk3D2 2nd QTRLianne Marie CabanginNo ratings yet
- White Paper FinalDocument10 pagesWhite Paper Finalapi-620125845No ratings yet
- Chapt9 12Document5 pagesChapt9 12RHEANNE OSEANo ratings yet
- Katrina HurricaneDocument2 pagesKatrina HurricaneAnnu DdNo ratings yet
- History of Hurricanes and Floods in JamaicaDocument13 pagesHistory of Hurricanes and Floods in JamaicaPHILLIP RODNEYNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- The Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (598)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationFrom EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (37)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (111)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (139)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)