Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mettalic Crystal Structure
Uploaded by
Nur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mettalic Crystal Structure
Uploaded by
Nur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolCopyright:
Available Formats
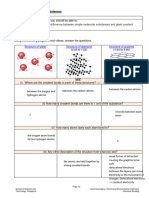
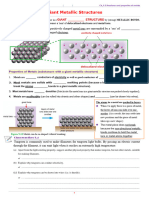
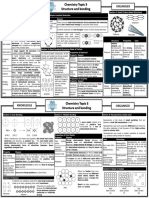
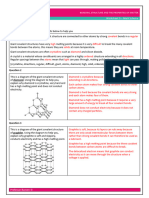
METTALIC CRYSTAL STRUCTURE IONIC LATTICE GIANT MOLECULE
Simplest crystal structure because High melting point: Consist of particles held together by
every lattice point in a crystal is 1) Strong electrostatic force covalent bonds.
occupied by an atom of the same between ions of opposite
metal. charges
2) Requires more energy to
-Tends to be densely packed overcome the attraction
Good conductor of heat: Hard but brittle: DIAMOND
1) Bonding2 electron are 1) Strong electrostatic force
delocalized over the entire make it hard but if a Does not conduct electricity:
crystal strong force is applied, 1) Each C atom covalently bonded
2) The mobility makes the the ions layer shift slightly to 4 other C in tetrahedral
metal good conductor of 2) Ions of the same charge arrangement by strong covalent
heat are brought side-by-side bonding
and so the crystal repels 2) So no free moving electrons
itself and repulsion crack
the crystal Very strong covalent bond:
1) Have high melting point 3550°C
2) Very hard
-used in cutting tools and grinding
Metal Strength: Does not conduct electricity in GRAPHITE
Great cohesive force resulting from solid but does so in molten or
delocalization is responsible for aqueous solution: Electric conductor:
metal strength 1) Ions are not free to move 1) Each C is connected with 3
because are held strongly other C by covalent bond
Have wide range of melting points by electrostatic force in forming 6-member rings that
and hardness depend on packing fixed position form flat layer which are held
efficiency of the crystal structure 2) When the solid melt, ions loosely by weak VDW forces.
and the number of valence electron are free to move thus 2) C use only 3 of its 4 valence
available for bonding. conducting electricity electron so it has one unused
electron
3) The electron are able to move
freely does conduct electricity
High melting point similar to that of
diamond:
1) In order to melt graphite, it isn’t
enough to loosen one sheet
from another
2) Have to break the covalent
bonding thoughout the whole
structure
Softness of graphite:
1) 6-member rings form flat layer
which are held loosely by weak
Van Der Walls forces
2) The layers are able to slide
past each other resulting in
softness of graphite.
-Used as lead in pencil and lubricant
You might also like
- Anaesthesia and Intensive Care A-Z E-BookDocument657 pagesAnaesthesia and Intensive Care A-Z E-BookDiana Hriscu83% (6)
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding ReportDocument7 pagesCovalent Bonding ReportGun TnNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryyashwanthgovindarajNo ratings yet
- (Chemical Bonding) H2 Chem NotesDocument11 pages(Chemical Bonding) H2 Chem Notesblah blehNo ratings yet
- b6 Condensed Matter PhysicsDocument70 pagesb6 Condensed Matter PhysicsAndrew OrrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5s1062579No ratings yet
- Types of CrystalsDocument12 pagesTypes of CrystalsSpace MonkeyNo ratings yet
- Srinadh18560-ES312 Assignment 1Document10 pagesSrinadh18560-ES312 Assignment 1Jammigumpula PriyankaNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Giant Covalent StructuresDocument2 pages9.3 Giant Covalent StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 4 StudyDocument5 pagesChemistry Unit 4 StudycurtisNo ratings yet
- SCINOTESDocument2 pagesSCINOTESMark Beduya CuffeeNo ratings yet
- 6.1 SolidDocument30 pages6.1 SolidAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- 28.9.2022 4.5 Metallic BondingDocument17 pages28.9.2022 4.5 Metallic BondingJungun HwangNo ratings yet
- CH4 Atoms CombiningDocument4 pagesCH4 Atoms CombiningHazim AlJabrNo ratings yet
- Past Year CHM 678 (Chapt 2)Document16 pagesPast Year CHM 678 (Chapt 2)Nurul Aiman HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Compounds Properties & Metals and IonsDocument42 pagesIonic and Covalent Compounds Properties & Metals and IonsHillary DalitNo ratings yet
- 3 2 4-MacromoleculesDocument10 pages3 2 4-Macromoleculesareeb9187No ratings yet
- 9.5 Giant Metallic StructuresDocument2 pages9.5 Giant Metallic StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2: Olid TateDocument48 pagesChapter - 2: Olid TateAkshit KumarNo ratings yet
- MECH 3830 1: Chapter 1-TextbookDocument8 pagesMECH 3830 1: Chapter 1-TextbookharnoorNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument2 pagesIonic Bondingdigjhon6No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- c3 Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesc3 Structure and BondingNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Part - 2Document34 pagesChapter 7 - Part - 2Najam Ul QadirNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument12 pagesChemical BondingNelsonNo ratings yet
- A2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20837Document6 pagesA2AS CHEM REVISED Support 20837Tianming KingsleyNo ratings yet
- New Note Chapter 9 Structures and Properties of Substances - 2020 - Student VersionDocument46 pagesNew Note Chapter 9 Structures and Properties of Substances - 2020 - Student VersionkarinhyhoNo ratings yet
- Diffusion in Solids: Issues To Address..Document26 pagesDiffusion in Solids: Issues To Address..Tuna ÇelikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solid State: Dr. Amiya PriyamDocument82 pagesIntroduction To Solid State: Dr. Amiya PriyamVishal VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Chemistry: Structure & Properties of Matter Class 7Document43 pagesGrade 12 Chemistry: Structure & Properties of Matter Class 7Ashley UmNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Document3 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes On StructuresDocument7 pagesChem Notes On StructuresHey thereNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids SummaryDocument2 pagesBonding in Solids SummaryarachnidkatNo ratings yet
- Types of CrystalsDocument2 pagesTypes of CrystalsMeahgan Renee FeudoNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic Bondingonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- 11.5.2020 - Solid States NEET DHOOM Series #1Document88 pages11.5.2020 - Solid States NEET DHOOM Series #1AlokNo ratings yet
- Lesson5 - Structure of Crystalline and Amorphous LiquidsDocument19 pagesLesson5 - Structure of Crystalline and Amorphous LiquidsLemonadeNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering: L3Document36 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering: L3SbonganjaloNo ratings yet
- Revisions About Chapter 3Document21 pagesRevisions About Chapter 3杨国涓faithNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 G11 Test 2 HL MSDocument3 pages2022-2023 G11 Test 2 HL MSZHOU TIN YUI RICHARD G11G-34No ratings yet
- Bonding (Diamond, Graphite, Fullerene and Silicon-Dioxide)Document1 pageBonding (Diamond, Graphite, Fullerene and Silicon-Dioxide)Safe GuardNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Crystal StructuresDocument6 pagesBasic Concepts of Crystal StructuresjoyandreaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SummaryDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding SummaryKiara LimNo ratings yet
- 9.2: The Solid State of Matter: Skills To DevelopDocument7 pages9.2: The Solid State of Matter: Skills To DevelopGraviton Manzano OlarteNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent MoleculesDocument34 pagesGiant Covalent MoleculesaqutiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Structure..Document6 pagesChemical Bonding Structure..rachelNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Lesson 3 Types of SolidsDocument11 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Lesson 3 Types of SolidsYeji SeoNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Short NotesDocument8 pagesChemistry Short NotesZainab HassanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document83 pagesUnit 5mtayyab zahidNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageIonic and Covalent Bonding Cheat Sheet: by ViaAnnaglory NkayalaNo ratings yet
- MS Worksheet 9Document2 pagesMS Worksheet 9alvaressaschaNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemical BondsDocument19 pages9 Chemical BondsAdiba TasnimNo ratings yet
- ElectronicDocument34 pagesElectronicChin Yit YeeNo ratings yet
- W3W4 BTD1123 Chapter 2 Mat Structure N BondingDocument62 pagesW3W4 BTD1123 Chapter 2 Mat Structure N BondingHakim ShahmiNo ratings yet
- Bond Energy PDFDocument21 pagesBond Energy PDFYolandra Herman100% (1)
- Ttrans Therm EnergyDocument1 pageTtrans Therm EnergyZafirah SuffianNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-XII-Ch-1 - Solid State-MinhadDocument6 pagesHsslive-XII-Ch-1 - Solid State-MinhadZonicNo ratings yet
- Fancy Finesse Events Business PlanDocument35 pagesFancy Finesse Events Business PlanNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Key Formulas: Confidential Appendix 1 (1) CS/STA408Document2 pagesKey Formulas: Confidential Appendix 1 (1) CS/STA408Nur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-1 INTRO-mac 2019Document24 pagesCHAPTER-1 INTRO-mac 2019Nur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 SoundDocument39 pagesChapter4 SoundNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Deforestation: Destruction of Natural Forests For DevelopmentsDocument21 pagesDeforestation: Destruction of Natural Forests For DevelopmentsNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- INNOVATIONDocument1 pageINNOVATIONNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-TEXTDocument50 pagesChapter 2-TEXTNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- TanninsDocument2 pagesTanninsNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- INNOVATIONDocument1 pageINNOVATIONNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- INNOVATIONDocument1 pageINNOVATIONNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Time Management & Organizational SkillsDocument13 pagesTime Management & Organizational SkillsNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital Theory - Tutorial 1 - BLDocument1 pageMolecular Orbital Theory - Tutorial 1 - BLNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Job Task Analysis: Click Here, To Explore Additional Templates and Resources For Free inDocument1 pageJob Task Analysis: Click Here, To Explore Additional Templates and Resources For Free inNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Cell Reproduction 1: Mitosis in Root TipsDocument7 pagesCell Reproduction 1: Mitosis in Root TipsNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5Document5 pagesTutorial Chapter 5Nur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Procedure CHM Exp 2Document38 pagesProcedure CHM Exp 2Nur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Cawangan Perak: CHM 258 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Laboratory ReportDocument4 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Cawangan Perak: CHM 258 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Laboratory ReportNur Aqilah Ainaa Binti Sahrol100% (1)
- Copper & PPRDocument6 pagesCopper & PPRAbdul RaoofNo ratings yet
- BIONANOTECHNOLOGYDocument34 pagesBIONANOTECHNOLOGYJerome AndonissamyNo ratings yet
- Concrete Formwork Checklist at SiteDocument6 pagesConcrete Formwork Checklist at Sitedineshkmr373100% (1)
- Arc Flash and Other Electrical Safety HazardsDocument24 pagesArc Flash and Other Electrical Safety HazardsJulios Charl Panuncialman TagupaNo ratings yet
- Agricultural PollutionDocument3 pagesAgricultural PollutionOlukunle AlabetutuNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International GCSE Biology Chapter 16 Learning PlanDocument2 pagesEdexcel International GCSE Biology Chapter 16 Learning Planandrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Drilling V2Document66 pagesIntroduction To Drilling V2mikibala100% (2)
- 101 - Electron TheoryDocument2 pages101 - Electron TheorySeagullian DaveNo ratings yet
- Solvents Used in PharmacyDocument19 pagesSolvents Used in PharmacyMuhammad Mustafa IjazNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Activation of Triacetone Triperoxide - FulltextDocument47 pagesUltrasonic Activation of Triacetone Triperoxide - FulltextMario SchutzNo ratings yet
- Science Magazine 5828 2007-05-25Document119 pagesScience Magazine 5828 2007-05-25sumersoft1100% (1)
- Bs7531 Grade y MasterDocument1 pageBs7531 Grade y Masterheena jainNo ratings yet
- 2074 1 2015 AMD2 Reff2020Document16 pages2074 1 2015 AMD2 Reff2020ocsspectroNo ratings yet
- Haemin Crystal Practical PreparationDocument4 pagesHaemin Crystal Practical PreparationSHAKTINo ratings yet
- Todays Wastes, Tomorrow's Energy: Phoenix' BiotechnologyDocument22 pagesTodays Wastes, Tomorrow's Energy: Phoenix' BiotechnologyMahesh AithalNo ratings yet
- IR OrganometallicDocument21 pagesIR OrganometallicYanti Yana HalidNo ratings yet
- Uvod-HEMIND Vol69 No3 p219-330 May-Jun 2015Document119 pagesUvod-HEMIND Vol69 No3 p219-330 May-Jun 2015MomirNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Lecture NotesDocument28 pagesElectrochemistry Lecture NotesRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Asphalt - MC 800 (Superior) - Superior Refining Company, LLC (Husky Energy)Document11 pagesAsphalt - MC 800 (Superior) - Superior Refining Company, LLC (Husky Energy)Lindsey BondNo ratings yet
- Last But Not Least: Drilling MethodsDocument38 pagesLast But Not Least: Drilling MethodsNeilNo ratings yet
- Cell GebeticsDocument7 pagesCell GebeticsRavindraNo ratings yet
- Industrial Pollution and ControlDocument3 pagesIndustrial Pollution and ControlChanduNo ratings yet
- Structural SpecificationsDocument23 pagesStructural SpecificationsAlvin AbanganNo ratings yet
- APES TestDocument34 pagesAPES Testdanna94No ratings yet
- FormalineDocument2 pagesFormalineJawharaNo ratings yet
- Minoclair: Hematology DevicesDocument2 pagesMinoclair: Hematology DevicesAlina AlexandruNo ratings yet
- List Preventive Maintenance DRG450-60S5MDocument16 pagesList Preventive Maintenance DRG450-60S5MJppi PtkNo ratings yet
- Runaway ReactionsDocument5 pagesRunaway ReactionsDaniel SantosNo ratings yet
- Polyacrylamide A Review of The Use Effectiveness ADocument6 pagesPolyacrylamide A Review of The Use Effectiveness AJeffrey LavariasNo ratings yet