Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ionic Bonding
Uploaded by
digjhon6Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ionic Bonding
Uploaded by
digjhon6Copyright:
Available Formats
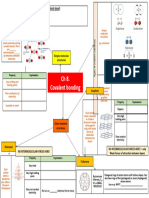
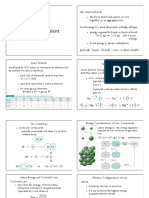
ionic bonding
·
the electrostatic force of attraction between cations and anion to form a
giant ionic Lattice
↳ elections transferred from metal to non-metal for full outer shell.
Covalent bonding + Dative covalent bonds
electrostatic force between shared of elections and the both
of attraction a
pair nuclei of atoms
·
.
Dative Lovalent Bonding
· Bond formed
W hen a lone pair of elections is donated/shared between two atoms
the electronsW ill be closer to the more electronegative element , as it pulls electrons.
↳ Reacts Just like covalent Bonds
Metallic Bonding
· the electrostatic force of attraction between the 've metallic ion and the delocalized electrons that
are free to move.
↳ greater the ion attractive force
charge on =
stronger
<Larger in Size Cions) weaker attraction (due to greater atomic radius
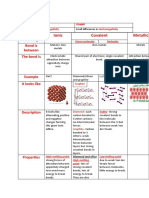
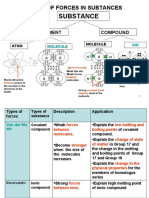
Bonding +
physical properties
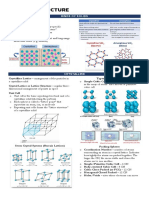
Crystal structures
lonic , metallic
Simple molecular + macromolecular
·
,
lonic
· ionic
Crystal Structures Have High melting +
boiling point
· often brittle, when
layers of ions shift, "Strong electrostatic forces
Holding ionic lattice
like charges the lattice (Requires overcome
repel , breaking apart lots of
energy to
into
fragments .
Metallic Crystal structures
.
·
Conductors -> delocalized electrons ,
free to move +
carry charge
smalleable , layers of the ions can slide over each other
(the deloculised elections prevent fragmentation
strong electrostatic force of attraction (high meeting point (
·
simple molecular
bonded
covalently molecules
·
sheld by van-der-walls forces which weak
weak are
very
<Little needed to overcome them
energy
Water has higher Bp Due to
Hydrogen bunds Bond polarity
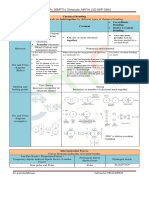
shapes of molecules Electronegativity
How is shape determined ? · the power of an atom to attract electrons towards
· no of lone
pairs and Bond pairs itself in a covalent bond
· which
naturally repel each other "To Reduce Repulsion Across The Molecule
>electronegativity increases
along the
period Catomic radius decreases nuclear
>(pLp>(pBp> BpBp
·
Decreases down a
group charge increases (
I
> Lone pairs have stronger repulsion due to HigherCharge density
. permanent Dipoly
-
the nuclei of
#
↳ attracted to one element
Only
*
towards itself
producing a S + S region
Induced dipole
influenced by another charged particle
Planar
You might also like
- ChemistryDocument20 pagesChemistryFatma SharifNo ratings yet
- MINDMAP - Covalent BondingDocument1 pageMINDMAP - Covalent BondingalanchenyinNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument131 pagesChemical BondingAnant VashishtNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding - FactRecallDocument1 pageIonic Bonding - FactRecallgabby fosterNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle DualityDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Implication of Wave Particle Dualityguiller139No ratings yet
- 2.2. How Bonding and Structure Are Related To The Properties of SubstancesDocument1 page2.2. How Bonding and Structure Are Related To The Properties of SubstancesatemisgoddesofhuntNo ratings yet
- 4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedDocument23 pages4 14 Chemical Bonding 1 Ionic Metallic Bonding JL EditedFN5052023 PRAMITA MAHENDRANNo ratings yet
- c3 Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesc3 Structure and BondingNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- St-ES: Wao.cDocument18 pagesSt-ES: Wao.cWilliam WangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Periodic Table - PeriodicityDocument5 pagesChapter 9 Periodic Table - Periodicitysitinur qahirahNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids SummaryDocument2 pagesBonding in Solids SummaryarachnidkatNo ratings yet
- Bonding A LevelDocument2 pagesBonding A LevelHamzah ArabicaNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanNo ratings yet
- L03 Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument20 pagesL03 Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingVivek vermaNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument4 pagesChemBrian Lim Fong Chee (Amkss)No ratings yet
- Bonding Knowledge OrganiserDocument1 pageBonding Knowledge Organisermya thet htar sweNo ratings yet
- O Level Pure Chem SummaryDocument75 pagesO Level Pure Chem SummaryEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument51 pagesChemical BondingAqualilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaDocument3 pages1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaPragna AnanthNo ratings yet
- 12th Grade Chemistry by Byju'sDocument54 pages12th Grade Chemistry by Byju'srohan rajNo ratings yet
- SCINOTESDocument2 pagesSCINOTESMark Beduya CuffeeNo ratings yet
- AQA Combined Science Structure and BondingDocument2 pagesAQA Combined Science Structure and Bondingali.a.226No ratings yet
- 02 BondingDocument24 pages02 Bondingiron_trNo ratings yet
- Bonds in Solid 4 SDocument5 pagesBonds in Solid 4 SS.M. Abdul Mannan MahdiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: N A R N A RDocument31 pagesChemical Bonding: N A R N A RGayathri Shrushti. V mm19b031No ratings yet
- Structure & Bonding Lec 02Document14 pagesStructure & Bonding Lec 02tishagirkar074No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5s1062579No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 2023Document16 pagesElectrochemistry 2023Arush GautamNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure-ReviewDocument1 pageBonding and Structure-Reviewcandyli3788No ratings yet
- CAN 1 Ionic Bonding Mat 2Document1 pageCAN 1 Ionic Bonding Mat 2Kev WattsNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesChemical BondingRaoulNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding: Lose e S Nonmetals With Favorable Electron Affinity Gain e 'SDocument11 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonding: Lose e S Nonmetals With Favorable Electron Affinity Gain e 'SGerlie VelascoNo ratings yet
- 2 Atomic StructureDocument43 pages2 Atomic StructureRafael ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Than Of: LinearDocument5 pagesThan Of: Linear임지우(공과대학 신소재공학)No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Structure..Document6 pagesChemical Bonding Structure..rachelNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Ionic Bonding: Pure Covalent Bonding Is Only Found in ElementsDocument3 pagesMetallic Bonding Ionic Bonding: Pure Covalent Bonding Is Only Found in ElementsFransisca ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Anonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument1 pageStructure and BondingeohomegrownappsNo ratings yet
- Type of Forces 1 Notes 2010Document26 pagesType of Forces 1 Notes 2010Mohd Iruan JanalNo ratings yet
- Static ElectricityDocument50 pagesStatic Electricityanas.asif2008No ratings yet
- Aqa Comb Sci MSDocument11 pagesAqa Comb Sci MSebridgesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bond: Valence ElectronDocument2 pagesAtomic Bond: Valence ElectronttitiNo ratings yet
- Band Theory, Semiconductors PDFDocument6 pagesBand Theory, Semiconductors PDFpervyguy738No ratings yet
- CHM031 Module 2 ReviewerDocument10 pagesCHM031 Module 2 Reviewerrain100% (1)
- MECH 3830 1: Chapter 1-TextbookDocument8 pagesMECH 3830 1: Chapter 1-TextbookharnoorNo ratings yet
- Atomic BondingDocument20 pagesAtomic BondingVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- Eicbornhabercycleposter 733782Document1 pageEicbornhabercycleposter 733782Joko SusiloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.4Document4 pagesLecture 1.4wemata7962No ratings yet
- 1 3-BondingDocument20 pages1 3-BondingBhPO2023No ratings yet
- Inter Atomic BondingDocument20 pagesInter Atomic BondingGUNJAN MUDGALNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondDocument8 pagesMetallic BonddigreeleeNo ratings yet
- 9 Chemical BondsDocument19 pages9 Chemical BondsAdiba TasnimNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals: Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesProperties of Metals: Metallic BondingNuan Ting NgNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding SummaryDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding SummaryKiara LimNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding O LevelDocument1 pageChemical Bonding O LevelChong56No ratings yet
- 06 CB Notes 2022Document6 pages06 CB Notes 2022Fitri armaya Jeffri (Greendaless)No ratings yet
- 2 2 2 Bonding and StructureDocument7 pages2 2 2 Bonding and StructureAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Promises From The BibleDocument16 pagesPromises From The BiblePaul Barksdale100% (1)
- Rapidjson Library ManualDocument79 pagesRapidjson Library ManualSai Kumar KvNo ratings yet
- Campos V BPI (Civil Procedure)Document2 pagesCampos V BPI (Civil Procedure)AngeliNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02Document4 pagesCambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02Azfar RashedNo ratings yet
- Team 12 Moot CourtDocument19 pagesTeam 12 Moot CourtShailesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2beloved Lizzo PDFDocument1 page2beloved Lizzo PDFAntwerpQueerChoir AQCNo ratings yet
- Life Without A Centre by Jeff FosterDocument160 pagesLife Without A Centre by Jeff Fosterdwhiteutopia100% (5)
- Burton 1998 Eco Neighbourhoods A Review of ProjectsDocument20 pagesBurton 1998 Eco Neighbourhoods A Review of ProjectsAthenaMorNo ratings yet
- Indian School Bousher Final Term End Exam (T2) : Academic Session - 2021-22 Grade: 7Document7 pagesIndian School Bousher Final Term End Exam (T2) : Academic Session - 2021-22 Grade: 7Shresthik VenkateshNo ratings yet
- How To Format Your Business ProposalDocument2 pagesHow To Format Your Business Proposalwilly sergeNo ratings yet
- Schopenhauer and KantDocument8 pagesSchopenhauer and KantshawnNo ratings yet
- Simple FTP UploadDocument10 pagesSimple FTP Uploadagamem1No ratings yet
- Wa0009.Document14 pagesWa0009.Pradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Official Memo: From: To: CCDocument4 pagesOfficial Memo: From: To: CCrobiNo ratings yet
- Stdy RCD PDFDocument204 pagesStdy RCD PDFBol McSafeNo ratings yet
- Wa0006.Document8 pagesWa0006.Poonm ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- FINN 400-Applied Corporate Finance-Atif Saeed Chaudhry-Fazal Jawad SeyyedDocument7 pagesFINN 400-Applied Corporate Finance-Atif Saeed Chaudhry-Fazal Jawad SeyyedYou VeeNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Tools in Studying Environmental ScienceDocument63 pagesKami Export - Tools in Studying Environmental ScienceBenBhadzAidaniOmboyNo ratings yet
- PMP Chapter-12 P. Procurement ManagementDocument30 pagesPMP Chapter-12 P. Procurement Managementashkar299No ratings yet
- Checklist of Requirements of Special Land Use PermitDocument1 pageChecklist of Requirements of Special Land Use PermitAnghelita ManaloNo ratings yet
- DentinogenesisDocument32 pagesDentinogenesisNajeeb UllahNo ratings yet
- BIM 360-Training Manual - MEP ConsultantDocument23 pagesBIM 360-Training Manual - MEP ConsultantAakaara 3DNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study For A Sustainability Based Clothing Start-UpDocument49 pagesFeasibility Study For A Sustainability Based Clothing Start-UpUtso DasNo ratings yet
- Independence of Costa RicaDocument2 pagesIndependence of Costa Ricaangelica ruizNo ratings yet
- FCI - GST - Manual On Returns and PaymentsDocument30 pagesFCI - GST - Manual On Returns and PaymentsAmber ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- AP Online Quiz KEY Chapter 8: Estimating With ConfidenceDocument6 pagesAP Online Quiz KEY Chapter 8: Estimating With ConfidenceSaleha IftikharNo ratings yet
- Deutz Common RailDocument20 pagesDeutz Common RailAminadav100% (3)
- 2.1BSA-CY2 - REVERAL, ANGELA R. - EXERCISE#1 - Management ScienceDocument3 pages2.1BSA-CY2 - REVERAL, ANGELA R. - EXERCISE#1 - Management ScienceAngela Ricaplaza ReveralNo ratings yet
- Court Documents From Toronto Police Project Brazen - Investigation of Alexander "Sandro" Lisi and Toronto Mayor Rob FordDocument474 pagesCourt Documents From Toronto Police Project Brazen - Investigation of Alexander "Sandro" Lisi and Toronto Mayor Rob Fordanna_mehler_papernyNo ratings yet
- Section 9 - Brickwork and BlockworkDocument6 pagesSection 9 - Brickwork and BlockworkShing Faat WongNo ratings yet