Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 13 19 TD PG 1
9 13 19 TD PG 1
Uploaded by
api-493355126Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 13 19 TD PG 1
9 13 19 TD PG 1
Uploaded by
api-493355126Copyright:
Available Formats
Critical Care: Hemodynamics and drips
Definitions:3
Stroke Volume : the amount of blood the heart pumps with EACH BEAT
Cardiac output_ ___ : expressed in L/min, is the amount of blood the heart pumps in ONE MINUTE (SV x HR)
Cardiac index : the cardiac output expressed as a flow (L/min) per body surface area (m2), since CO for a
250 lb person is expected larger than a 100 lb person
Heart rate : the number of contractions (or beats) in one minute
Contractility : the “strength” of contraction at a given preload and afterload
Preload : is the degree of myocardial distension prior to shortening and largely depends on the
amount of ventricular filling (venous return)
Afterload : is the force against which the ventricles must act in order to eject blood, and is largely
dependent on the arterial blood pressure and vascular tone. Also, can be Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) .
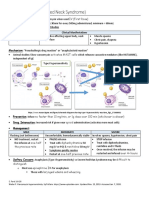
Target organ and receptor “refresher”
TAKE AWAY:
When thinking about the
HEART and BETA AGONISM,
the effect will be:
Increased heart rate and/or
contractility .
TAKE AWAY:
When thinking ARTERIES and ALPHA
AGONISM, the effect will be:
Constriction .
Nitric Oxide , will vasodilate
The other constricting receptor when
activated: V1 and 2 .
Matching Critical Care Drips Main Receptor: Circle: Vasopressor, inotrope, or vasodilator
1. Norepinephrine (Levophed) Selective α1-receptor Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
2. Phenylephrine (Neo-synephrine) V1 receptor agonist Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
3. Dobutamine (Dobutrex) α1-receptor Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
4. Epinephrine (Adrenaline) Nitric oxide (vein and Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
artery)
5. Nitroglycerin (“Nitro”) β1-receptor initially Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
6. Milrinone (Primacor) cGMP and Nitric oxide Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
7. Vasopressin (Vasostrict) α1-receptor and β1- Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
receptor
8. Sodium Nitroprusside (Nipride) Β agonist, Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
9. Dopamine Vasopressor inotrope vasodilator
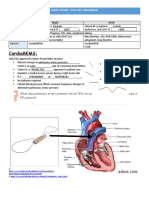
HANDS-ON: The SWAN line
*White line: “VIP,” able to infuse multiple COMPATIBLE
drips into this line
*Blue line: CVP, central venous pressure, helps
determine fluid balance. Can infuse into CVP and draw
blood but will not have a reading during this time
*Yellow line: PAP, pulmonary arterial pressure, helps
see pulmonary hypertension and fluid balance
*SVo2: measures the end result of O2 consumption and
delivery
*CO and CI are included on monitor, as well as Temp
FYI: Nurses “calibrate” the line every morning using a
carefully drawn sample from the PAP and running a “mixed
venous” gas on the “rapid point” machine
Brain storming:
Increased heart rate will initially INCREASE cardiac
output
Increased SVR will INCREASE blood pressure
Decreased SVR will INCREASE cardiac output
initially
https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Swan-Ganz+catheter
1. Lexi-Comp Online. Lexi-Comp, Inc. Hudson, OH. Available at: http://online.lexi.com/crlonline. Acce AMA Citation
2. Maclaren R, Dasta JF. Chapter 13. Use of Vasopressors and Inotropes in the Pharmacotherapy of Shock. In: DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG,
Posey L. eds. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 9e New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2014.
http://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com.maproxy.palni.edu/content.aspx?bookid=689§ionid=45310473. Accessed September 11, 2019.
3. Vincent J. L. (2008). Understanding cardiac output. Critical care (London, England), 12(4), 174. doi:10.1186/cc6975. Accessed October, 2018.
You might also like
- Icu 4Document7 pagesIcu 4GemilleDaphneAndradaNo ratings yet
- Anaphylactic Shock Due To Contrast Dye Allergy HF Due To Left Ventricle Damage and MIDocument3 pagesAnaphylactic Shock Due To Contrast Dye Allergy HF Due To Left Ventricle Damage and MIpsyNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation Hypertension AtfDocument4 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation Hypertension AtfMariaNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation-2Document40 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation-2Juliza FelicianoNo ratings yet
- 5e69b4ff83ed0-Fluid Responsiveness, Dynamic and Static Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument28 pages5e69b4ff83ed0-Fluid Responsiveness, Dynamic and Static Hemodynamic Monitoringyulya100% (1)
- Mekanisme Dari Blood Pressure Regulation 1. Hemodynamic Factors (CO, TPR, Etc)Document9 pagesMekanisme Dari Blood Pressure Regulation 1. Hemodynamic Factors (CO, TPR, Etc)Caroline AgathaNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument27 pagesBlood PressureSreedeep TejaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NotesDocument82 pagesPharmacology Noteslira shresthaNo ratings yet
- MS4 Exam 2Document27 pagesMS4 Exam 2JessNo ratings yet
- 036.12 - Cardiovascular Pharmacology) VasopressorsDocument14 pages036.12 - Cardiovascular Pharmacology) VasopressorsOliver JacobeNo ratings yet
- 27 Cardio SpoDocument114 pages27 Cardio SpovinanoermayaniNo ratings yet
- Central Venous Pressure 55Document2 pagesCentral Venous Pressure 55Pamipam100% (1)
- Blood Pressure Regulation MechanismsDocument68 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation MechanismsPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Cvs Regulation Part 2Document57 pagesCvs Regulation Part 2NyamsNo ratings yet
- Almoete NR23 - NCP RHD (Module 9 Cardiac)Document3 pagesAlmoete NR23 - NCP RHD (Module 9 Cardiac)Gail NamangdanNo ratings yet
- NCP For Liver CirrhosisDocument25 pagesNCP For Liver CirrhosisWendy Escalante100% (1)
- Drug Treatment of HypertensionDocument36 pagesDrug Treatment of HypertensionAngetile KasangaNo ratings yet
- Cp201012 Learning Light-395Document2 pagesCp201012 Learning Light-395jyothiNo ratings yet
- Jantung - Acute Heart FailureDocument32 pagesJantung - Acute Heart FailurefaradibaNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic DrugsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic DrugsbezaleeljonelNo ratings yet
- Hemodinamik MonitoringDocument18 pagesHemodinamik MonitoringSonia P SNo ratings yet
- Leanna R. Miller: LRM ConsultingDocument20 pagesLeanna R. Miller: LRM ConsultingreneecolemanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis&Manajemen ShockDocument8 pagesDiagnosis&Manajemen ShockHJKIMNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP HypertensionJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Vaso Pressors and InotropesDocument18 pagesVaso Pressors and InotropesBabu RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- How To Deal Acute Pulmonary OedemDocument23 pagesHow To Deal Acute Pulmonary Oedemdhika2496No ratings yet
- Fundamentals UpdatedDocument12 pagesFundamentals UpdatedJulie AnnNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Heart DiseaseDocument6 pagesHypertensive Heart DiseaseAndrea GuidoteNo ratings yet
- LOW Cardiac Output: Use of Inotropes in Critical CareDocument5 pagesLOW Cardiac Output: Use of Inotropes in Critical CareRiimsha AaymNo ratings yet
- Bio Crisis - 2nd DayDocument4 pagesBio Crisis - 2nd DayaryanjimeraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyLizeth Querubin93% (15)
- ICU One Pager Vasopressors.1.2Document1 pageICU One Pager Vasopressors.1.2Nguyễn Ngọc Quỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyCassie ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Monitoring HemodinamikDocument20 pagesMonitoring HemodinamikAmriansyah PranowoNo ratings yet
- Presiune de Sânge MeasurementDocument3 pagesPresiune de Sânge MeasurementAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- MODULE VI: Cardiac MedicationsDocument2 pagesMODULE VI: Cardiac MedicationsVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemFisco DessereiNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Measurement: Matthew Ward MBCHB Frca Jeremy A Langton MD Frca IltmDocument5 pagesBlood Pressure Measurement: Matthew Ward MBCHB Frca Jeremy A Langton MD Frca IltmAyesha FirdousNo ratings yet
- Tams NCP and DrugDocument5 pagesTams NCP and DrugNicholas Xavier VenturaNo ratings yet
- 1 VascularDocument75 pages1 Vasculareman el saeedNo ratings yet
- Bu SuryaniDocument68 pagesBu SuryaniMaulana SaputraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrythmiasDocument37 pagesCardiac ArrythmiasRubina100% (1)
- Drugs For ShockDocument3 pagesDrugs For Shockrenz bartolomeNo ratings yet
- Control of ABP: BY: Makkawi .A.A. Osman B.SC, M.SC Department of Physiology Session NoDocument31 pagesControl of ABP: BY: Makkawi .A.A. Osman B.SC, M.SC Department of Physiology Session NoHomed OpriNo ratings yet
- Describe in General Terms Each of The Autonomic Nervous System?Document9 pagesDescribe in General Terms Each of The Autonomic Nervous System?vitas4scNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument4 pagesHemodynamic MonitoringHazelGraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 LaDocument5 pagesChapter 3 LaDindin Lou MendozaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics: Ncmb418 - Critical Care Nursing Rle Midterm LectureDocument7 pagesHemodynamics: Ncmb418 - Critical Care Nursing Rle Midterm LectureKyle Saberon100% (1)
- Circulație CoroarăDocument2 pagesCirculație CoroarăAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY ICU and ACSDocument22 pagesDRUG STUDY ICU and ACSSheila Mae ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP SGH DianaDocument2 pagesNCP SGH Dianadaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology 3: BIOE 3340Document31 pagesCardiovascular Physiology 3: BIOE 3340sam manNo ratings yet
- Cheat ECGDocument3 pagesCheat ECGNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Intra Aortic Balloon CounterpulsationDocument68 pagesIntra Aortic Balloon CounterpulsationpriyathasanNo ratings yet
- Indirectly Acting Sympathomimetics: 1) AmphetamineDocument7 pagesIndirectly Acting Sympathomimetics: 1) AmphetamineTamim Al-TamimiNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure-For StudentsDocument79 pagesBlood Pressure-For StudentsAshok Kumar P100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- Bernadas NCPDocument3 pagesBernadas NCPBernadas, Jhon Kristopher C.No ratings yet
- 4 30 20 Clinial Pearl ReflectionDocument1 page4 30 20 Clinial Pearl Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 1 24 20 Vancomycin Mue ReflectionDocument1 page1 24 20 Vancomycin Mue Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 10 28 19 Mock Code Lab ReflectionDocument1 page10 28 19 Mock Code Lab Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Lutheran Health Network Remote Rotation OrientationDocument18 pagesLutheran Health Network Remote Rotation Orientationapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 5 11 20 Preceptor Pre ReflectionDocument1 page5 11 20 Preceptor Pre Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 10 30 20 Residency Panel ReflectionDocument1 page10 30 20 Residency Panel Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Final 2019 Mue Report Vancomycin CTR With GraphsDocument6 pagesFinal 2019 Mue Report Vancomycin CTR With Graphsapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Vancomycin Auc With Answers 1Document64 pagesVancomycin Auc With Answers 1api-493355126No ratings yet
- 3 7 20 Doctors Day Poison Prevention ReflectionDocument1 page3 7 20 Doctors Day Poison Prevention Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 9-11-19 Vitals Student Lab ReflectionDocument1 page9-11-19 Vitals Student Lab Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Ashp Residency Information PPDocument13 pagesAshp Residency Information PPapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 11 5 19 Journal Club Pre and Post Reflection Infant Meningitis and UtiDocument1 page11 5 19 Journal Club Pre and Post Reflection Infant Meningitis and Utiapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 10 10 19 Cardiomem-Lvad Topic Discussion ReflectionsDocument1 page10 10 19 Cardiomem-Lvad Topic Discussion Reflectionsapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 1 22 20 Ashp Meeting Residency PresentationDocument1 page1 22 20 Ashp Meeting Residency Presentationapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 2-17-20 Pharmacist Auc Guided Dosing Educational Slide ShowDocument1 page2-17-20 Pharmacist Auc Guided Dosing Educational Slide Showapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 3 10 20 Kidney Camp Lecture ReflectionDocument1 page3 10 20 Kidney Camp Lecture Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 12 6 19 Auryxia Ferric Citrate For P and T MeetingDocument1 page12 6 19 Auryxia Ferric Citrate For P and T Meetingapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Summative Eval IdDocument2 pagesSummative Eval Idapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 1-16-20 Senior Circle CBD ReflectionDocument1 page1-16-20 Senior Circle CBD Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Pearls Merged 4Document18 pagesPearls Merged 4api-493355126No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Christina FordDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae Christina Fordapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 10 10 19 Heart Failure-Lvad Cardiomems Topic DiscussionDocument4 pages10 10 19 Heart Failure-Lvad Cardiomems Topic Discussionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Drug ReviewDocument3 pagesDrug Reviewapi-493355126No ratings yet
- 2 26 20 Drug Induced Pancreatitis Lecture ReflectionDocument1 page2 26 20 Drug Induced Pancreatitis Lecture Reflectionapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Kolcaba's Theory of Comfort in The Emergency DepartmentDocument6 pagesKolcaba's Theory of Comfort in The Emergency DepartmentNoka OlympiaNo ratings yet
- Morpho KrokDocument106 pagesMorpho KrokPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Point-of-Care Ultrasound: State of The Art in Medical School EducationDocument12 pagesCardiac Point-of-Care Ultrasound: State of The Art in Medical School Educationmariano villavicencioNo ratings yet
- Haad 1 Questions HeartDocument17 pagesHaad 1 Questions HeartPatpat De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument2 pagesQuestion BankSARMITHA S SNo ratings yet
- Esencias Florales California Detallado (Inglés)Document54 pagesEsencias Florales California Detallado (Inglés)Rosa Martin HuelvesNo ratings yet
- Oxford Desk Reference Acute MedicineDocument851 pagesOxford Desk Reference Acute Medicinejones dondo100% (3)
- Diagnosis and Treatment in Internal Medicine Oxford University Press 1St Edition Patrick Davey Full ChapterDocument67 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment in Internal Medicine Oxford University Press 1St Edition Patrick Davey Full Chapterbenito.burnett216100% (19)
- Fifa Pcma FormDocument15 pagesFifa Pcma Formyousra AhmedNo ratings yet
- Through The Decades (Beta) - Blocker Use and Outcomes in Acute Coronary Syndromes.Document8 pagesThrough The Decades (Beta) - Blocker Use and Outcomes in Acute Coronary Syndromes.Tony Miguel Saba SabaNo ratings yet
- HPN and DM LectureDocument23 pagesHPN and DM Lectureivy rose duhilagNo ratings yet
- JHLT Abstract 2019-1Document1 pageJHLT Abstract 2019-1G WNo ratings yet
- HP II P5 Cardiovascular System, HeartDocument72 pagesHP II P5 Cardiovascular System, HeartNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- An MRIDocument41 pagesAn MRIAsim AliNo ratings yet
- AAP Common Cardiac Issues in Pediatrics 2018 PDFDocument786 pagesAAP Common Cardiac Issues in Pediatrics 2018 PDFiahmad9No ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle: DR Rida Ajmal KhanDocument29 pagesCardiac Cycle: DR Rida Ajmal KhanMooma fatimaNo ratings yet
- Ana Print 3Document12 pagesAna Print 3Ade AlcarazNo ratings yet
- CALIBRE™ MEGARAD™ 2081-15: Polycarbonate ResinDocument3 pagesCALIBRE™ MEGARAD™ 2081-15: Polycarbonate ResinmikeybhabaNo ratings yet
- Transposition of The Great ArteriesDocument29 pagesTransposition of The Great ArteriesbookwormMD100% (1)
- Pathophysiology and Investigation of Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument4 pagesPathophysiology and Investigation of Coronary Artery DiseasekartikaparamitaNo ratings yet
- ANN Online CourseDocument7 pagesANN Online CourseJovan Varona NealaNo ratings yet
- Iii. Hasil Dan PembahasanDocument10 pagesIii. Hasil Dan PembahasanHarditya FirdhausNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmia in Children PDFDocument50 pagesCardiac Arrhythmia in Children PDFNorhafizah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CTDocument7 pagesCardiac CTdaniel7pintiliiNo ratings yet
- Infective EndocarditiDocument31 pagesInfective EndocarditiMansi DabolaNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis and Exercise Lab 2016Document8 pagesHomeostasis and Exercise Lab 2016kNo ratings yet
- Practice Test (2014)Document16 pagesPractice Test (2014)Ali GhahremanNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Test BankDocument21 pagesCH 14 Test BankKrestine Molle100% (1)
- Grailstones - A Complete Guide To Crystal HealingDocument20 pagesGrailstones - A Complete Guide To Crystal HealingChaoticOrchestra100% (3)
- Step 2 CK - Nbme Form 4Document87 pagesStep 2 CK - Nbme Form 4geraldchi100% (8)