Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Quiz: The Frequency, (Ƒ)
Uploaded by
EdrianCliffDelPilar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Electrical
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesResearch Quiz: The Frequency, (Ƒ)
Uploaded by
EdrianCliffDelPilarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Del Pilar, Edrian Cliff BSME- the waveform for sine waves, or
Mech 2 the Pulse Width for square
waves.
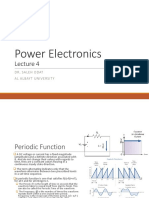
Research The Frequency, (ƒ) is the
number of times the
waveform repeats itself within
Quiz a one second time period.
Frequency is the reciprocal of
the time period, ( ƒ = 1/T )
with the unit of frequency
Sinusoids
being the Hertz, (Hz).
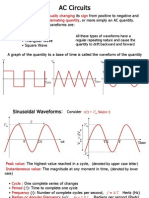
-Alternating Current, generally The Amplitude (A) is the
refers to a time-varying magnitude or intensity of the
waveform with the most signal waveform measured in
volts or amps.
common of all being called
a Sinusoid better known as
a Sinusoidal Waveform. Sine waves are in the form of:
-Also called as Sine waves. V(t)-Vmsin(wt)
-The shape obtained by plotting
the instantaneous ordinate
values of either voltage or
current against time is called
an AC Waveform.
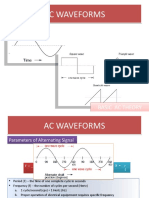
The type and shape of an AC
waveform depends upon the
generator or device producing
them, but all AC waveforms
consist of a zero voltage line
that divides the waveform into
two symmetrical halves. The
main characteristics of an AC
Waveform are defined as:
Complex Numbers
The Period, (T) is the length of
time in seconds that the -A Complex Number is a
waveform takes to repeat itself combination of a Real Number
from start to finish. This can also and an Imaginary Number.
be called the Periodic Time of
-Real numbers are any numbers Phasors
that you can think of.
It represents the angular
-Imaginary numbers are number
difference of the two sinusoidal
when squared gives a negative
result. waveforms. Also the terms
“lead” and “lag” as well as “in-
-It is a number that can be phase” and “out-of-phase” are
expressed in the form a + bi,
commonly used to indicate the
where a and b are real numbers,
and i is a solution of the relationship of one waveform to
equation x2 = −1. Because no the other with the generalized
real number satisfies this sinusoidal expression given as:
equation, i is called an A(t) = Am sin(ωt ± Φ)
imaginary number. For the representing the sinusoid in the
complex number a + bi, a is
time-domain form.
called the real part, and b is
called the imaginary part. -Basically a rotating vector,
simply called a “Phasor” is a
scaled line whose length
represents an AC quantity that
has both magnitude (“peak
amplitude”) and direction
(“phase”) which is “frozen” at
some point in time.
- It is a vector that has an arrow
head at one end which signifies
partly the maximum value of the
A complex number can be vector quantity ( V or I ) and
visually represented as a pair of partly the end of the vector that
numbers (a, b) forming a vector rotates.
on a diagram called an Argand
diagram, representing the Phasor Diagram of a
complex plane. "Re" is the real Sinusoidal Waveform
axis, "Im" is the imaginary axis,
and i satisfies i2 = −1.
Frequency Domain analyzed according to it's
response for different
-refers to the analysis of
frequencies.
mathematical functions or
signals with respect to
frequency, rather than time.
-a time-domain graph shows
how a signal changes over time,
whereas a frequency-domain
graph shows how much of the
signal lies within each given
frequency band over a range of
frequencies.
-A frequency-domain
representation can also include
information on the phase shift
that must be applied to each
sinusoid in order to be able to
recombine the frequency
components to recover the
original time signal.
-A time domain your
model/system is evaluated
according to the progression of
it's state with time. In Frequency
domain your model/system is
You might also like
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Electrical EnggDocument79 pagesModule 3 Electrical EnggAnand ANo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument30 pagesAC FundamentalsSouhardya RoyNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 AC Circuits NotesDocument35 pagesUNIT-2 AC Circuits NotesLatha Barla67% (3)
- Phasor Solution of CircuitsDocument6 pagesPhasor Solution of CircuitsjonydepNo ratings yet
- BEE Unit-IIDocument29 pagesBEE Unit-IIharishcheeeNo ratings yet
- EEEN 201 Lecture Notes-09Document16 pagesEEEN 201 Lecture Notes-09daglarduman510No ratings yet
- Basic Elec AssignmentDocument13 pagesBasic Elec AssignmentSharyn VillarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument19 pagesChapter Oneمصطفى احمد محيسنNo ratings yet
- M3 PPT 1 1 Phase Ac CircuitDocument67 pagesM3 PPT 1 1 Phase Ac CircuitUDhayNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Chapter ThreeDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Engineering Chapter Threetemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuits: Sinusoidal Sources and The Concept of Phasor in Circuit AnalysisDocument20 pagesFundamentals of Electric Circuits: Sinusoidal Sources and The Concept of Phasor in Circuit AnalysisJames BejareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3elecDocument28 pagesChapter 3elecJibril JundiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document17 pagesLecture 4Mouath AlsebaieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument31 pagesChapter 13 - Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadSajjad Hossain ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Steady-State AnalysisDocument13 pagesSinusoidal Steady-State Analysissarkar salamNo ratings yet
- Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument29 pagesSingle Phase AC Circuitskali hembramNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits: Continually Changing Sign Alternating QuantityDocument10 pagesAC Circuits: Continually Changing Sign Alternating QuantityMathew ClewlowNo ratings yet
- Lesson.1. Types of WavesDocument14 pagesLesson.1. Types of WavesLeeNo ratings yet
- Audio Lab, Department of Electronics, University of York, UKDocument12 pagesAudio Lab, Department of Electronics, University of York, UKjezwellsNo ratings yet
- Sinusoids and Phasors Complete GuideDocument1 pageSinusoids and Phasors Complete GuideHammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document21 pagesChapter 3alemu assefaNo ratings yet
- CKTS LESSON-SinusoidDocument36 pagesCKTS LESSON-SinusoidNicoNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current CircuitsDocument39 pagesAlternating Current CircuitsJiann ManingatNo ratings yet
- Electrical AC SirDocument93 pagesElectrical AC SirVedant SheshkerNo ratings yet
- Eepc 106 Module 1Document13 pagesEepc 106 Module 1Oreo WhiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 AC AnalysisDocument10 pagesChapter 3 AC AnalysisbehailuNo ratings yet
- Power Line Ee SubjectsDocument2 pagesPower Line Ee SubjectsCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Spectra Waves Statistics 2021Document53 pagesSpectra Waves Statistics 2021lucas GUILLAUMENo ratings yet
- Chapter_02Document54 pagesChapter_02suvamsarma67No ratings yet
- EE301 - AC and Sinusoidal WaveformsDocument7 pagesEE301 - AC and Sinusoidal WaveformsSatish KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Smith ChartDocument11 pagesSmith ChartBill WhiteNo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument21 pagesAC FundamentalsSheikh RaselNo ratings yet
- Signal Representations: Time to Frequency Domain ConversionDocument13 pagesSignal Representations: Time to Frequency Domain ConversionDJ AmoraNo ratings yet
- Why AC Instead of DCDocument15 pagesWhy AC Instead of DCPatricia DatinguinooNo ratings yet
- 05Document13 pages05Susana RojasNo ratings yet
- Ac Waveforms1Document4 pagesAc Waveforms1srinivasNo ratings yet
- Lecture OneDocument26 pagesLecture OneMustfa YaseenNo ratings yet
- AC Fundamentals ExplainedDocument48 pagesAC Fundamentals ExplainedParikshit SinghNo ratings yet
- Periodic Waves and Phasor AnalysisDocument63 pagesPeriodic Waves and Phasor AnalysisChiranjivi KuthumiNo ratings yet
- Ac FundamentalsDocument8 pagesAc FundamentalsPiku MajhiNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering - U2Document28 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering - U2Gaurav Kawde GkNo ratings yet
- AC Waveform and AC Circuit Theory of SinusoidsDocument14 pagesAC Waveform and AC Circuit Theory of SinusoidsJackie JonesNo ratings yet
- Sinusoids and Phasors ExplainedDocument22 pagesSinusoids and Phasors Explained;(No ratings yet
- AC CIRCUITS PARAMETERS AND QUANTITIESDocument7 pagesAC CIRCUITS PARAMETERS AND QUANTITIESKyle Joshua BunhanNo ratings yet
- Waveform. Sinusoidal Waveforms Are More Generally Called by Their Short Description As Sine WavesDocument10 pagesWaveform. Sinusoidal Waveforms Are More Generally Called by Their Short Description As Sine WavesJohn Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- EIE2100 AC CircuitsDocument91 pagesEIE2100 AC CircuitsP ChiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of AC CircuitsDocument49 pagesAnalysis of AC CircuitsScrappy WellNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Sinusoidal Ac Voltage Characteristics and DefinitionsDocument23 pagesSinusoidal Alternating Waveforms: Sinusoidal Ac Voltage Characteristics and DefinitionsOmar Ahmed0% (1)
- Fourier Transform and Series ReviewDocument53 pagesFourier Transform and Series ReviewDivyansh UmareNo ratings yet
- Eec203-Week 1Document62 pagesEec203-Week 1NicoNo ratings yet
- Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskDocument4 pagesAnnex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskMelanny MenesesNo ratings yet
- 2.AC Fundamental PDFDocument6 pages2.AC Fundamental PDFTanishq MudaliarNo ratings yet
- AC Peak, RMS, and Phase Measurement: AimsDocument4 pagesAC Peak, RMS, and Phase Measurement: AimsKaan IbisNo ratings yet
- Sinosoids and The Frequency DomainDocument3 pagesSinosoids and The Frequency DomainyogimgurtNo ratings yet
- T1-1 - Sinusoids and PhasorDocument29 pagesT1-1 - Sinusoids and PhasorMerlyn Len AytonaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to electromagnetic waves and the wave equationDocument19 pagesIntroduction to electromagnetic waves and the wave equationDASARI MPNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit AnalysisDocument48 pagesAC Circuit AnalysisRanjan VPNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument4 pagesResearch PaperannieNo ratings yet
- Ac TheoryDocument21 pagesAc TheoryRuwan CookNo ratings yet
- Me331-Quiz No. 3 - Problems OnlyDocument1 pageMe331-Quiz No. 3 - Problems OnlyEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Vibration Engineering: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoDocument15 pagesVibration Engineering: By: Engr. Ray H. MalonjaoEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- ME331-QUIZ NO. 4 - Part 2 - PROBLEMSDocument2 pagesME331-QUIZ NO. 4 - Part 2 - PROBLEMSEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- OOP Concepts ExplainedDocument20 pagesOOP Concepts ExplainedEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- ME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.2-Fluid StaticsDocument2 pagesME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.2-Fluid StaticsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Iterative Control Structure: Do (Statement ) While (Loop Repetition Condition)Document10 pagesIterative Control Structure: Do (Statement ) While (Loop Repetition Condition)EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- How Interface Works?Document7 pagesHow Interface Works?EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- ME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.1-Fluid PropertiesDocument1 pageME331 - Fluid Mechanics: Assignment No.1-Fluid PropertiesEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Conditional control structuresDocument12 pagesConditional control structuresEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week2 - Robot TechnologyDocument12 pagesWeek2 - Robot TechnologyEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- OOP Features in 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesOOP Features in 40 CharactersEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Liquidation Report Game CMTDocument1 pageLiquidation Report Game CMTEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week1a VisualStudioSetUpDocument4 pagesWeek1a VisualStudioSetUpEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week5 InheritancePolymorphismAbstraction PDFDocument18 pagesWeek5 InheritancePolymorphismAbstraction PDFEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional Arrays in C# (34Document8 pagesOne Dimensional Arrays in C# (34EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Expt 7Document3 pagesExpt 7EdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Week2a BasicElementsinC#Document9 pagesWeek2a BasicElementsinC#EdrianCliffDelPilar100% (1)
- RRL YouthDocument3 pagesRRL YouthEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Del Pilar - SOCSCI032Document1 pageDel Pilar - SOCSCI032EdrianCliffDelPilar100% (1)
- RATIONALEDocument2 pagesRATIONALEEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Excel BasicsDocument37 pagesExcel BasicsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Uts ImptDocument1 pageResearch Paper Uts ImptEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Effects of Climate Change Ion Society NOTESDocument1 pageEffects of Climate Change Ion Society NOTESEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Historical Background-Map-ExperienceDocument3 pagesHistorical Background-Map-ExperienceEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- An Organizational Strategy Road Map For AnalyticsDocument12 pagesAn Organizational Strategy Road Map For AnalyticsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Programming QuestionsDocument12 pagesProgramming QuestionsEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Delta-Wye Resistance Network TransformationDocument13 pagesDelta-Wye Resistance Network Transformationvillegreen9100% (2)
- ArticlesDocument2 pagesArticlesEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Designing For DigitalDocument4 pagesDesigning For DigitalEdrianCliffDelPilarNo ratings yet
- Probability Random Processes and StatisticsDocument23 pagesProbability Random Processes and Statisticsn SivagiriNo ratings yet
- Shife AssDocument14 pagesShife Assshiferaw meleseNo ratings yet
- CONICSDocument18 pagesCONICSjaywarvenNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Allanach EvansDocument81 pagesVector Calculus Allanach EvansTheBayesianJedi100% (1)
- VJC H2 Math P1Document4 pagesVJC H2 Math P1jimmytanlimlongNo ratings yet
- Mata30 TT1 2012FDocument14 pagesMata30 TT1 2012FexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Solving Trusses Including InclinedDocument24 pagesSolving Trusses Including Inclinedjikijoker0% (2)
- Linear Equations in 2 Variables Worksheet 3Document1 pageLinear Equations in 2 Variables Worksheet 3PRATHIKSHANo ratings yet
- Characteristic functions identify distributionsDocument20 pagesCharacteristic functions identify distributionsJimmyNo ratings yet
- Math6338 hw2Document6 pagesMath6338 hw2Fabian MolinaNo ratings yet
- 9A13701 Robotics and AutomationDocument4 pages9A13701 Robotics and AutomationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 10CSECMathsMay2011Workout4C Apr26Document18 pages10CSECMathsMay2011Workout4C Apr26Anderson AlfredNo ratings yet
- Juntilla W. Problem SetDocument8 pagesJuntilla W. Problem SetRey Cabrido RoseteNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra - WikipediaDocument15 pagesLinear Algebra - Wikipediatsvmpm1765No ratings yet
- Derivation of Species Mass Conservation Equation: +DR V V +DV V V+DV J J +DJ WDocument2 pagesDerivation of Species Mass Conservation Equation: +DR V V +DV V V+DV J J +DJ WManjunath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Mesh Sensitivity & Independence AnalysisDocument56 pagesMesh Sensitivity & Independence AnalysistusharNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Kedah SPM 2008 Add Maths Trial p2Document17 pagesMarking Scheme Kedah SPM 2008 Add Maths Trial p2tan_wooichoongNo ratings yet
- Full Solution AbbottDocument171 pagesFull Solution AbbottwitnessNo ratings yet
- Group TheoryDocument82 pagesGroup TheorybartheNo ratings yet
- Tratado Integrais 2Document1,004 pagesTratado Integrais 2Patricia SousaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 Foundations: PHYC30016 ElectrodynamicsDocument2 pagesProblem Set 1 Foundations: PHYC30016 ElectrodynamicsBella CarrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 The Central Limit TheoremDocument17 pagesLesson 5 The Central Limit TheoremIngel Force0% (1)
- Homework Stat 511Document11 pagesHomework Stat 511Ashish MalikNo ratings yet
- Problem 15.256: 1. Determine Velocities in A Body Rotating About A Fix AxisDocument3 pagesProblem 15.256: 1. Determine Velocities in A Body Rotating About A Fix AxisabhiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 - Algebra of Quadratics - The Quadratic FormulaDocument18 pagesLesson 15 - Algebra of Quadratics - The Quadratic FormulasriramaniyerNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS CALCULUS - MATH2301 December 2015Document4 pagesBUSINESS CALCULUS - MATH2301 December 2015bgpexpertNo ratings yet
- Math TordilloDocument105 pagesMath TordillolucasNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Chemical Processes, SolnDocument320 pagesOptimization of Chemical Processes, SolnCristhian GómezNo ratings yet
- Polynomial ManipulationDocument9 pagesPolynomial ManipulationPushpalatha ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Composite v17Document33 pagesComposite v17slamoriniereNo ratings yet
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesFrom EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)From EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionFrom EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- ARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)From EverandARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)No ratings yet
- C++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingFrom EverandC++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026From EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Power Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesFrom EverandPower Quality in Power Systems and Electrical MachinesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Ramblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowFrom EverandRamblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowNo ratings yet
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Winning in 2025: Digital and Data Transformation: The Keys to SuccessFrom EverandWinning in 2025: Digital and Data Transformation: The Keys to SuccessNo ratings yet