Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bulla Notes: Micro Lab
Uploaded by
Von HippoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bulla Notes: Micro Lab
Uploaded by
Von HippoCopyright:
Available Formats
Bulla Notes 2016
MICRO LAB
Outline
I. Development of the Endocrine System
II. Histology of the Endocrine System
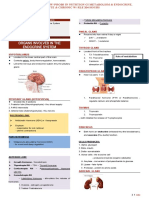
I. DEVELOPMENT OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
A. Summary of Anlage and Fate
ANLAGE FATE
1. Rathke’s Pouch Anterior Pituitary Gland or
Adenohypophysis
2. Anterior Wall of Rathke’s Pouch Pars Distalis, Pars Tuberalis
3. Posterior Wall of Rathke’s Pouch Pars Intermedia
4. Infundibulum Infundibular Stalk, Infundibular
Process
5. Infundibulum Posterior Pituitary Gland or
Neurohypophysis
6. Primordial Thyroid Gland Thyroid Diverticulum
7. Ultimobronchial Bodies Parafollicular Cells
8. Foregut Dorsal Pancreatic Bud
9. Hepatic Diverticulum Gallbladder, Ventral Pancreatic
Bud
10. Dorsal Pancreatic Bud Body, tail and isthmus of the
pancreas, ducts of Santorini
and Wirsung
11. Ventral Pancreatic Bud Head, uncinate process of the
pancreas and duct of Wirsung
12. Intermediate Mesoderm Urogenital Ridge
13. Urogenital Ridge Gonadal Ridge, Bipotential
Gonad
14. Gonadal Ridge Primary and secondary sex
cords
15. Primary sex cords Seminiferous tubules
16. Secondary Sex cords Primordial ovary or testes
17. Gonadal Primordium Primordial cells and Somatic
progenitor cells
18. Somatic Progenitor cells Sertoli cells and Leydig Cells
19. Bipotential Gonad Supporting Cell precursors
20. Supporting Cell Precursors Follicular cells, steroidogenic
Precursors
21. Steroidogenic Precursors Theca Interna, cells of Leydig
Bulla Notes Page 1
Bulla Notes 2016
B. Germ Layers of Origin
ECTODERM MESODERM ENDODERM
1. Pituitary Gland 1. Adrenal Cortex of Adrenal 1. Thyroid Gland
2. Pineal Gland Medulla 2. Parathyroid Glands
3. Adrenal Medulla of Adrenal 2. Leydig Cells (intermediate 3. Pancreas (Islets of
Glands mesoderm) Langerhans)
3. Theca Interna Cells
II. HISTOLOGY OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
A. Summary of Endocrine Cells/Glands and their Secretions
ENDOCRINE CELL/GLAND HORMONE/SECRETION
I. Anterior Pituitary Gland
1. Pars Distalis
a. Acidophils
a.1. Somatotrophs Somatotropin
Growth Hormone
a.2. Mammotrophs Prolactin
b. Basophils
b.1. Thyrotrophs Thyroid Stimulating
Hormone
b.2. Gonadotrophs Follicle Stimulating
Hormone
Luteinizing Hormone
b.3. Corticotrophs Adrenocorticotrophic
Hormone
2. Pars Intermedia Melanocyte Stimulating
Hormone
Pro-opio melanocortin
3. Pars Tuberalis none
II. Posterior Pituitary Gland Antidiuretic Hormone
(not responsible for the
production of the hormones; they
only act as storage for the
hormones)
Oxytocin
III. Thyroid Gland
1. Follicular Cells T3 and T4
2. Parafollicular Cells Calcitonin
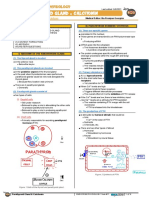
IV. Parathyroid Glands
1. Chief cells Parathyroid hormone
Bulla Notes Page 2
Bulla Notes 2016
ENDOCRINE CELL/GLAND SECRETION
V. Adrenal Glands
1. Adrenal Cortex
a. Zona Glomerulosa Aldosterone
b. Zona Fasciculata Glucocorticoids (Cortisol
and Cortisone)
c. Zona Reticularis Androgen, sex hormones
2. Adrenal Medulla
a. Chromaffin Cells Catecholamines
(Epinephrine and
Norepinephrine)
VI. Testes
a. Leydig Cells Testosterone
b. Sertoli Cells Inhibin
ENDOCRINE CELL/GLAND HORMONE/SECRETION
VII. Ovary
a. Theca Interna Cells Estrogen
b. Granulosa Lutein Cells Progesterone
(from Corpus Luteum)
c. Theca Lutein Cells Estrogen
d. Interna Cells Steroid precursors
VIII. Pineal Gland
a. Pinealocytes Serotonin (day hormone)
Melatonin (night hormone)
IX. Pancreas
1. Islets of Langerhans
a. Alpha Cells Glucagon
b. Beta Cells Insulin
c. Delta Cells Somatostatin (growth
hormone inhibitor)
d. G Cells Gastrin
e. F Cells Pancreatic Polypeptide
2. Pancreatic Acinar Cells Pancreatic Acini
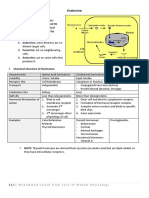
B. Additional Notes
Neurophypophysis does not synthesize hormones. Their secretions come from the
thalamus. They only serve as storage for the hormones produced by the thalamus.
The Herring Bodies are where the hormones are stored.
Aldosterone secretion is influenced by Renin-Angiotensin System.
Pancreatic acini surrounds the Islets of Langerhans.
The Alpha cells of the pancreas are located in the periphery or at the side.
The Beta cells of the pancreas are located at the center.
The Delta and F cells are scattered.
Bulla Notes Page 3
Bulla Notes 2016
Insulin helps glucose to enter the cell.
Glucagon acts when blood glucose levels are low.
Granulosa cells are responsible for converting the Androgen produced by theca interna
cells to Estrogen through the enzyme Aromatase.
Leydig Cells are located outside the seminiferous tubules.
Sertoli Cells are supporting cells.
Calcitonin lowers blood Calcium levels while Parathyroid hormone elevates blood
Calcium levels.
The Syncitiotrophoblast cells of the placenta secrete the HCG or Human Chorionic
Gonadotropin Hormone.
Progesterone secreted by the Corpus Luteum and Granulosa Lutein Cells will maintain
the pregnancy during its early stages.
Oxytocin is the milk let down hormone.
Prolactin stimulates milk production.
TSH or Thyroid stimulating hormone influences synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Luteinizing Hormone is the primary hormone for ovulation.
The secondary hormone for ovulation is FSH or Follicle Stimulating Hormone.
The Zona Glomerulosa cells are arranged in clumps or cords.
Zona Fasciculata cells are arranged vertically.
Zona Reticularis cells form anastomosing cords surrounded by capillaries.
Pancreas is both exocrine and endocrine in function.
Thyroid gland, Pineal gland, pituitary gland, adrenal gland and parathyroid gland are
purely endocrine in function.
Hypoactive thyroid will have squamous follicular cells.
Hyperactive thyroid will have columnar follicular cells.
Normoactive thyroid will have cuboidal follicular cells.
Prolactin hormone is inhibited by Dopamine.
Growth Hormone is inhibited by Somatostatin.
Inhibin inhibits additional production of FSH.
Pineal glands contain brain sands/Corpora Arenacea/Psammoma Bodies which serve as
landmarks during radiographic examination of the brain.
Parenchyma of pineal glands are pinealocytes.
Chromaffin cells are found in the adrenal medulla.
Chromophil cells are the characteristic cells of Pars Distalis.
Bulla Notes Page 4
You might also like
- Serotonin: The Mediator that Spans EvolutionFrom EverandSerotonin: The Mediator that Spans EvolutionPaul M. PilowskyNo ratings yet
- Cham PowerpointDocument19 pagesCham PowerpointElizabeth GenotivaNo ratings yet
- CAPE Bio Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesCAPE Bio Mark Schemeron97150% (2)
- (Springer Series in Wood Science) W. E. Hillis (auth.), John W. Rowe (eds.)-Natural Products of Woody Plants_ Chemicals Extraneous to the Lignocellulosic Cell Wall-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1.pdfDocument1,274 pages(Springer Series in Wood Science) W. E. Hillis (auth.), John W. Rowe (eds.)-Natural Products of Woody Plants_ Chemicals Extraneous to the Lignocellulosic Cell Wall-Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (1.pdfArmandoNo ratings yet
- M18 Mari2036 07 Ig C18 PDFDocument5 pagesM18 Mari2036 07 Ig C18 PDFJelian GraceNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System XVDocument10 pagesEndocrine System XVaraineNo ratings yet
- 1.13 - The Endocrine SystemDocument6 pages1.13 - The Endocrine SystemUwen NalpNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesEndocrine SystemnandaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument13 pagesEndocrine SystemSherChereNo ratings yet
- Physio 1Document6 pagesPhysio 1amjadNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Short Review Original PDFDocument13 pagesEndocrine System Short Review Original PDFBijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document8 pagesChapter 9Bea SeloterioNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument13 pagesEndocrineElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Lecture EndocrineDocument16 pagesNursing Lecture EndocrineAedge010100% (3)
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pages10 Endocrine SystemMardy Martin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Study GuideDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Study GuideCarla Andrea AbayaNo ratings yet
- Embryology IntermediateDocument9 pagesEmbryology IntermediateMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Endocrine OctoberDocument70 pagesEndocrine OctoberMohamed FarahatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemRoeisa SalinasNo ratings yet
- Name of The GlandDocument3 pagesName of The GlandSajeevNo ratings yet
- Moraj 3 ADocument12 pagesMoraj 3 AMohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Topic3.2 Physiology Hypothalamus and Pituitary HormonesDocument4 pagesTopic3.2 Physiology Hypothalamus and Pituitary HormonesRen AlvNo ratings yet
- 10 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pages10 Endocrine SystemGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesThe Endocrine SystemRODGIELYN MAE GEJONNo ratings yet
- Physio 2Document5 pagesPhysio 2amjadNo ratings yet
- Hormones List - NavyaDocument4 pagesHormones List - NavyaNavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- 047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland CalcitoninDocument4 pages047 Endocrinology Physiology Parathyroid Gland Calcitoninیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands - 1st - ChapterDocument12 pagesEndocrine Glands - 1st - Chaptervarun kumarNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Endocrine System HandoutsDocument6 pagesPRINTED Endocrine System HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 1016MSC T1 2023 Module 5 Tutorial WorksheetsDocument21 pages1016MSC T1 2023 Module 5 Tutorial WorksheetsTina HussainiNo ratings yet
- E N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryDocument3 pagesE N D O C R I N E System: Hormonal Control of A. PituitaryMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Midterm - AnaphyDocument6 pagesMidterm - AnaphyJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Endocrine DisordersDocument15 pagesPediatric Endocrine Disorderscandiaangeltherese1318238No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Quarter 3 - EndocrineDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Quarter 3 - Endocrinerafaelesguerra028No ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System NotesShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Topic3.1 Physiology Introduction To EndocrinologyDocument7 pagesTopic3.1 Physiology Introduction To EndocrinologyRen AlvNo ratings yet
- 6-TheR 608# Hormones & Reprod-IIDocument15 pages6-TheR 608# Hormones & Reprod-IIHamza HassanNo ratings yet
- Asda Packet I G Part 1Document45 pagesAsda Packet I G Part 1anamika_roy_5No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine System13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Ncert Page Wise Q Chem Control Set2Document10 pagesNcert Page Wise Q Chem Control Set2Vogolus machatteNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ilmu Biomedik Dasar: Nama: Jamilah Kelas: 1B KeperawatanDocument32 pagesTugas Ilmu Biomedik Dasar: Nama: Jamilah Kelas: 1B KeperawatanJamilah p3No ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine System: Properties: Mechanisms of Hormone ActionaudreyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 085347 PDFDocument30 pagesEndocrine System 085347 PDFClyde ReyesNo ratings yet
- Histology EndocrineDocument5 pagesHistology EndocrineIsaac DoringoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Histology LecDocument4 pagesEndocrine Histology LecrustincrealinaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System ReviewerDocument23 pagesEndocrine System ReviewerKimberly Joy GregorioNo ratings yet
- Endo ReviewerDocument5 pagesEndo ReviewerZIAN LABADIANo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Study NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System - Study Notesruchikaydv007No ratings yet
- Lecture: Male Reproductive PhysiologyDocument8 pagesLecture: Male Reproductive Physiologyvalerie obehiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemynaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument7 pagesEndocrine PhysiologyLomongo ChristianNo ratings yet
- 13 HisDocument98 pages13 HisRIMI SALOUMNo ratings yet
- Metabolism ConceptDocument76 pagesMetabolism ConceptrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Communication PG 64-65 QsDocument1 pageEndocrine Communication PG 64-65 Qsf6v9pqg2zzNo ratings yet
- Test QuestionsDocument25 pagesTest QuestionsssNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-Worksheet MTIDocument4 pagesEndocrine System-Worksheet MTIKolynNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissueDocument14 pagesCell and TissueMr. Sujan LamsalNo ratings yet
- 22 Chemical Co-OrdinationDocument47 pages22 Chemical Co-OrdinationRachna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Embryology and Phylogeny in Annelids and Arthropods: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology ZoologyFrom EverandEmbryology and Phylogeny in Annelids and Arthropods: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology ZoologyNo ratings yet
- Joint and Connective Tissue Disorders: QuestionsDocument11 pagesJoint and Connective Tissue Disorders: QuestionsVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Adnexal Mass in Pregnancy UpToDate PDFDocument21 pagesAdnexal Mass in Pregnancy UpToDate PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Gyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesDocument8 pagesGyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis Policy StatementsDocument6 pagesLeptospirosis Policy StatementsKay RuzNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Performance of International Ovarian Tumor Analysis IotaDocument7 pagesDiagnostic Performance of International Ovarian Tumor Analysis IotaVon HippoNo ratings yet
- KissPrep-Anatomy Physiology PDFDocument1 pageKissPrep-Anatomy Physiology PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection (Book) : NephrologyDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract Infection (Book) : NephrologyVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric EmergencyDocument3 pagesPsychiatric EmergencyVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric 3: Suicide (DR Rosales) June 8, 2011Document4 pagesPsychiatric 3: Suicide (DR Rosales) June 8, 2011Von HippoNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology-Mood StabilizerDocument5 pagesPsychopharmacology-Mood StabilizerVon Hippo100% (1)
- Psychiatric 3: Suicide (DR Rosales) June 8, 2011Document4 pagesPsychiatric 3: Suicide (DR Rosales) June 8, 2011Von HippoNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric 3: Substance Abuse (DR Rosales) : Substance Use Related DisordersDocument11 pagesPsychiatric 3: Substance Abuse (DR Rosales) : Substance Use Related DisordersVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Suicide, Psychiatric Emergency, Substance Abuse PDFDocument14 pagesSuicide, Psychiatric Emergency, Substance Abuse PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Child PsychiatryDocument6 pagesChild PsychiatryVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Adult Emergency PDFDocument2 pagesAdult Emergency PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Alipio, Camille Flores, Faith: Transcribed byDocument7 pagesAlipio, Camille Flores, Faith: Transcribed byVon HippoNo ratings yet
- CLINPATH Finals ReviewerDocument28 pagesCLINPATH Finals ReviewerVon HippoNo ratings yet
- 1) Any Medical Student or GraduateDocument27 pages1) Any Medical Student or GraduateVon HippoNo ratings yet
- PEDIA2 2.01b Fluids Electrolytes Summary TablesDocument4 pagesPEDIA2 2.01b Fluids Electrolytes Summary TablesVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Motor System: Three Types of Movement Generated by Motor SystemDocument10 pagesMotor System: Three Types of Movement Generated by Motor SystemVon Hippo100% (1)
- Recalls: 2nd Shifting ExamDocument13 pagesRecalls: 2nd Shifting ExamVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal: Al HerniaDocument3 pagesAbdominal: Al HerniaVon Hippo100% (1)
- Brainstem Lesions Trans 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesBrainstem Lesions Trans 2019 PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Vitamins B ComplexDocument4 pagesVitamins B ComplexVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Patho B Prelims RBCDocument12 pagesPatho B Prelims RBCVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Ob Gyne PDFDocument27 pagesOb Gyne PDFVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Scenario: CPT Case 9 Neonatal SepsisDocument15 pagesClinical Scenario: CPT Case 9 Neonatal SepsisVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes YMDocument8 pagesFluid and Electrolytes YMVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Gold 2019 Pocket Guide Final WmsDocument49 pagesGold 2019 Pocket Guide Final WmsFrensi Ayu PrimantariNo ratings yet
- Book: - RecordingDocument8 pagesBook: - RecordingVon HippoNo ratings yet
- UltraSonic Processors - CatalogDocument2 pagesUltraSonic Processors - Catalogdéborah_rosalesNo ratings yet
- Kleinman Culture and DepressionDocument3 pagesKleinman Culture and DepressionАлександра Курленкова100% (1)
- Final Project Report Kiran MazumdarDocument31 pagesFinal Project Report Kiran MazumdarPrajot Morajkar100% (3)
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- CV Christopher Lean Jan 2024 Without ReferencesDocument5 pagesCV Christopher Lean Jan 2024 Without Referencesapi-399765628No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Nikoleta RudnikNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Aspects of Sitting and StandingDocument2 pagesFundamental Aspects of Sitting and StandingMeenakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Staar Eoc 2016test Bio F 7Document39 pagesStaar Eoc 2016test Bio F 7api-293216402No ratings yet
- Taxonomy of Haematococcus PluvialisDocument2 pagesTaxonomy of Haematococcus PluvialisKomathi BalasupramaniamNo ratings yet
- "Material Ecocriticism and The Creativity of Storied Matter" by Serpil OppermannDocument16 pages"Material Ecocriticism and The Creativity of Storied Matter" by Serpil OppermannoppermanNo ratings yet
- A Substitution Mutation in The Myosin Binding Protein C Gene in Ragdoll Hypertrophic CardiomyopathyDocument4 pagesA Substitution Mutation in The Myosin Binding Protein C Gene in Ragdoll Hypertrophic CardiomyopathyRoy SzeNo ratings yet
- Pulse Flour From Wheat MillerDocument23 pagesPulse Flour From Wheat MillerCao Trọng HiếuNo ratings yet
- TGD FrameworkDocument10 pagesTGD FrameworkMatthew KleeNo ratings yet
- Determination of Formaldehyde in Tofu From Ciputat Traditional Market With Colorimetry MethodDocument6 pagesDetermination of Formaldehyde in Tofu From Ciputat Traditional Market With Colorimetry Methodhali taekookNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Your Results 5/5Document5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Your Results 5/5Pearl PascuaNo ratings yet
- Cat ExamDocument25 pagesCat Examlahsivlahsiv684No ratings yet
- Angiogenesis and Direct Myocardial RevascularizationDocument364 pagesAngiogenesis and Direct Myocardial RevascularizationPerdana SidaurukNo ratings yet
- Sociology Handout 5Document13 pagesSociology Handout 5Carzo Aggy MugyNo ratings yet
- ZIZKA Bromeliaceae ChileDocument22 pagesZIZKA Bromeliaceae ChileJoaquín Eduardo Sepúlveda AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Recognition, Signaling, and Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks Produced by Ionizing Radiation in Mammalian Cells - The Molecular ChoreographyDocument89 pagesRecognition, Signaling, and Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks Produced by Ionizing Radiation in Mammalian Cells - The Molecular ChoreographyMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- Pathomorophology. (Medicine, 3 Course)Document10 pagesPathomorophology. (Medicine, 3 Course)Joy JoyNo ratings yet
- Noncanonical Transnitrosylation Network Contributes To Synapse Loss in Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument18 pagesNoncanonical Transnitrosylation Network Contributes To Synapse Loss in Alzheimer's DiseasedmitworNo ratings yet
- Muscle Biopsy A Diagnostic Tool in Muscle DiseasesDocument9 pagesMuscle Biopsy A Diagnostic Tool in Muscle DiseasesRosa AquinoNo ratings yet
- XLD Agar - Manufcture by TM MediaDocument3 pagesXLD Agar - Manufcture by TM MediaKunal VermaNo ratings yet
- Kaid Seloua-PdbDocument9 pagesKaid Seloua-Pdbseloua kaidNo ratings yet
- Recent DevelopmentsDocument295 pagesRecent DevelopmentsGabriel PinheiroNo ratings yet
- USAID BD Handbook Oct 2015 508Document280 pagesUSAID BD Handbook Oct 2015 508vasconcelos1322No ratings yet