Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solubility - The Amount of Solute That Will
Solubility - The Amount of Solute That Will
Uploaded by
Shayne Cordero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document discusses key concepts in science including the scientific method, elements, compounds, mixtures, solutions, and the occurrence of elements. It outlines the scientific method as a process involving observation, questioning, hypothesis, experimentation, analysis, and conclusion. It defines elements as types of atoms, compounds as mixtures of two or more elements, and mixtures as having variable compositions and being either homogeneous or heterogeneous in appearance and composition. It also provides definitions and explanations regarding solutes, solvents, saturated and unsaturated solutions, and factors that influence solubility.
Original Description:
review
Original Title
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key concepts in science including the scientific method, elements, compounds, mixtures, solutions, and the occurrence of elements. It outlines the scientific method as a process involving observation, questioning, hypothesis, experimentation, analysis, and conclusion. It defines elements as types of atoms, compounds as mixtures of two or more elements, and mixtures as having variable compositions and being either homogeneous or heterogeneous in appearance and composition. It also provides definitions and explanations regarding solutes, solvents, saturated and unsaturated solutions, and factors that influence solubility.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageSolubility - The Amount of Solute That Will
Solubility - The Amount of Solute That Will
Uploaded by
Shayne CorderoThis document discusses key concepts in science including the scientific method, elements, compounds, mixtures, solutions, and the occurrence of elements. It outlines the scientific method as a process involving observation, questioning, hypothesis, experimentation, analysis, and conclusion. It defines elements as types of atoms, compounds as mixtures of two or more elements, and mixtures as having variable compositions and being either homogeneous or heterogeneous in appearance and composition. It also provides definitions and explanations regarding solutes, solvents, saturated and unsaturated solutions, and factors that influence solubility.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Scientific Method ■ Element: one type of
● Process atom (gold)
● Body of techniques ■ Compounds: mixture
● Acquiring knowledge of 2 or more elements
(H2O, CO2)
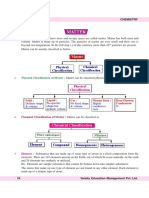
Epistemology ● Mixtures
➔ Truth, knowledge ○ Variable compositions
■ Homogenous:
Simulation Hypothesis uniformed
appearance and
Cogito Ergo Sum composition
■ Heterogeneous: non-
Uniformitarianism uniform appearance
and composition
Empiricism
➔ Use of sense - object ● Solute - substance that is dissolved
● Solvent -
1. Observation
2. Asking question - Why? Aquaeus Solution (aq) - H2O
3. Making Hypothesis (Educated
Guess) Saturated Solution - no more solute
4. Testing Hypothesis dissolves
(Experimentation) Unsaturated Solution - more solute
5. Recording (Analysis) dissolves
6. Conclusion (Generalization)
Solubility - the amount of solute that will
December 12, 2017 dissolve in a specified volume or mass of
solvent
3500, Egyptians, Mesopotamians ➔ Heat increases solubility
➔ Solubility of gases increases with
1774 - Antoine Lavoisier pressure
➔ Solubility of gases decreases with
Physical Chemistry increasing temperature
Analytical Chemistry
Organic Chemistry Occurrence of Elements
Inorganic Chemistry
Biochemistry Human body
Elements - 88 naturally occurring elements
Matter
● Pure substances
○ Fixed compositions
You might also like
- Robinson, R. A. - Stokes, R. H. - Electrolyte Solutions-Dover Publications (1959) PDFDocument507 pagesRobinson, R. A. - Stokes, R. H. - Electrolyte Solutions-Dover Publications (1959) PDFBrayan De Sousa0% (2)
- NSHE GRADE 7 NotesDocument78 pagesNSHE GRADE 7 NotesJB Mangundu71% (7)
- 6 - Cluster 2 - Properties of and Changes in Substances - Manitoba - Grade 5 ScienceDocument51 pages6 - Cluster 2 - Properties of and Changes in Substances - Manitoba - Grade 5 ScienceZabrinaNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade - Week 2 Mixing SubstancesDocument12 pages5th Grade - Week 2 Mixing Substancesapi-254428474100% (1)
- Notes - Unit 1of Matter and Measurment - Answer Key PacketDocument25 pagesNotes - Unit 1of Matter and Measurment - Answer Key PacketLizeth PautaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mixture SubstancesDocument27 pagesGrade 7 Mixture SubstancesRoSs Adrales Areleg100% (1)
- DLL Science 7 First QuarterDocument5 pagesDLL Science 7 First QuarterShaynie Mhe Amar Antonio100% (9)
- Experiment 3 Pulsed Column Liquid-Liquid Extraction ColumnDocument13 pagesExperiment 3 Pulsed Column Liquid-Liquid Extraction ColumnFikri IlyasNo ratings yet
- Engine Oil CoolersDocument26 pagesEngine Oil Coolersbetoven8437100% (2)
- As and A Level Chemistry Core Practical 7 Inorganic and Organic Unkowns Student Teacher Technician Worksheets PDFDocument8 pagesAs and A Level Chemistry Core Practical 7 Inorganic and Organic Unkowns Student Teacher Technician Worksheets PDFjosecostaz8724100% (1)
- Laboratory Methods of Organic ChemistryDocument449 pagesLaboratory Methods of Organic Chemistryapi-3723687100% (12)
- ME Sci 6 Q1 0103 SGDocument9 pagesME Sci 6 Q1 0103 SGRuthaliya IbrahimNo ratings yet
- N16 - Classification of MaterialDocument3 pagesN16 - Classification of MaterialEliana SaragihNo ratings yet
- Science 6 DLL q1wk1d4Document9 pagesScience 6 DLL q1wk1d4Yram Ecarg OudiserNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Introduction To MatterDocument33 pagesUnit 2 - Introduction To MatterAna MorenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 As GM 2024std Notes CanvasDocument64 pagesChapter1 As GM 2024std Notes CanvasnhlakeswmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Intro To Biology Test Study Sheet Brady 23 - 24Document2 pagesUnit 1 Intro To Biology Test Study Sheet Brady 23 - 24Jack SchumacherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SolutionDocument84 pagesChapter 2 Solutionhulk alanNo ratings yet
- Integumentary Physical Therapy: Donning of Sterile GlovesDocument12 pagesIntegumentary Physical Therapy: Donning of Sterile GlovesVenice Marie CordetaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7-Properties of Solutions CopyDocument37 pagesTopic 7-Properties of Solutions CopyKenneth DalionNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NoteDocument20 pagesChemistry NoteCarlNo ratings yet
- OLevel - IP Pure Chemistry CactusnotesDocument95 pagesOLevel - IP Pure Chemistry CactusnotestokkianmingNo ratings yet
- Chemistrylecturewps OfficeDocument12 pagesChemistrylecturewps Officeniconiconii BANGTANXARMYNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Module 3Document32 pagesScience 7 Module 3Lilah Blair100% (3)
- Matter ClassifiedDocument20 pagesMatter ClassifiedShefa CapurasNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Solutions Part 1Document37 pagesMixtures and Solutions Part 1Jessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- 01 Classifying Matter. English TextDocument39 pages01 Classifying Matter. English TextAngel Naranjo TortosaNo ratings yet
- Concept LearningDocument42 pagesConcept LearningssignnNo ratings yet
- Corepure2 Chapter 7::: Methods in Differential EquationsDocument35 pagesCorepure2 Chapter 7::: Methods in Differential EquationsdnaielNo ratings yet
- CHE 422 Fall 2021 L4Document12 pagesCHE 422 Fall 2021 L4Zain GillaniNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument70 pagesSolutionsSantanu DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument5 pagesIntroduction To ChemistryKeliana Marie CastinoNo ratings yet
- Plasticity II 2022Document40 pagesPlasticity II 2022Juan PabloNo ratings yet
- Pure and Impure Substances CSEC STUDENTDocument16 pagesPure and Impure Substances CSEC STUDENTNikolas PalmerNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric Relationships: Ms. PeaceDocument80 pagesStoichiometric Relationships: Ms. PeaceRita LimNo ratings yet
- 210 Lecture 1 Melting Points Spring 2023-24Document19 pages210 Lecture 1 Melting Points Spring 2023-24Leya ChahineNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science - Secondary 1Document7 pagesIntegrated Science - Secondary 1siubb0112No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRYGeorgia LanuzoNo ratings yet
- COGPSYCH-MT ReviewerDocument8 pagesCOGPSYCH-MT ReviewerTrixia LoveNo ratings yet
- Part 1 G7 STE - REVIEWERDocument7 pagesPart 1 G7 STE - REVIEWERVannie Mondero100% (1)
- Chapter 16 SolutionsDocument28 pagesChapter 16 SolutionsDeepak SainiNo ratings yet
- Example of Non Unique Solution of PDE Example 2 General Solution To Homogeneous 1 Order PDEDocument1 pageExample of Non Unique Solution of PDE Example 2 General Solution To Homogeneous 1 Order PDEShreshth SinghNo ratings yet
- Example of Non Unique Solution of PDE Example 2 General Solution To Homogeneous 1 Order PDEDocument1 pageExample of Non Unique Solution of PDE Example 2 General Solution To Homogeneous 1 Order PDEShreshth SinghNo ratings yet
- Solo Ladder BeowulfDocument1 pageSolo Ladder Beowulfapi-256004886No ratings yet
- Classificationofmatter 140910134732 Phpapp01Document4 pagesClassificationofmatter 140910134732 Phpapp01janneeshaaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ThermodynamicsDocument73 pagesLecture 1 - ThermodynamicsNgọc ĐàoNo ratings yet
- UTS UTS: Understanding Thy Self (University of San Carlos) Understanding Thy Self (University of San Carlos)Document7 pagesUTS UTS: Understanding Thy Self (University of San Carlos) Understanding Thy Self (University of San Carlos)s2whmvvjqvNo ratings yet
- G12 - Classification of MatterDocument32 pagesG12 - Classification of MatterChristian CatacutanNo ratings yet
- November Monthly PlanDocument1 pageNovember Monthly PlanPhoebe AstudilloNo ratings yet
- CHM1 11 - 12 Q1 0201 FDDocument18 pagesCHM1 11 - 12 Q1 0201 FDTacooNo ratings yet
- ES 102-Act-Domains-of-Learning-Odi, John Harold T.-BEED 2ADocument2 pagesES 102-Act-Domains-of-Learning-Odi, John Harold T.-BEED 2AJoseph StalinNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document8 pagesGen Chem 2royalNo ratings yet
- Resources FPDDocument7 pagesResources FPDapi-484169182No ratings yet
- ECHE101 ReviewerDocument3 pagesECHE101 ReviewerCherry LimNo ratings yet
- Modes of Discourse Descriptive Narrative Expository Argumentative Persuasive Examples of UseDocument2 pagesModes of Discourse Descriptive Narrative Expository Argumentative Persuasive Examples of UsevedasewahNo ratings yet
- Cogsci 1 Lecture NotesDocument14 pagesCogsci 1 Lecture Notesamanda oNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem II Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesGen Chem II Finals ReviewerjkierstencvergaraNo ratings yet
- Stage 1: Desired Results: Learning Outcome(s)Document4 pagesStage 1: Desired Results: Learning Outcome(s)api-487917897No ratings yet
- Julián Alejandro Daza RamírezDocument15 pagesJulián Alejandro Daza RamírezJulian Alejandro Daza RamirezNo ratings yet
- C4 Chemistry SRP MaterialDocument11 pagesC4 Chemistry SRP MaterialDhaksheysh.NNo ratings yet
- Organizing MatterDocument13 pagesOrganizing Matterapi-449002661No ratings yet
- Simulated Annealing: Petru ElesDocument58 pagesSimulated Annealing: Petru ElesGooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiinNo ratings yet
- BQ2, Franco Arenas IsamarDocument15 pagesBQ2, Franco Arenas IsamarIsamar FrancoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Quantities in Chemical Reactions: Chapter Five: Chemist's CounterDocument4 pagesUnit 3: Quantities in Chemical Reactions: Chapter Five: Chemist's CounterSathya NamaliNo ratings yet
- 24a. Chemistry Quiz 1 - OutlineDocument2 pages24a. Chemistry Quiz 1 - OutlineAdam El HajjNo ratings yet
- Jeroh Erbert Denzel N Atoz - MODULE-1-NARRA - 2021-03-02 - W1noeDocument4 pagesJeroh Erbert Denzel N Atoz - MODULE-1-NARRA - 2021-03-02 - W1noeJeroh AtozNo ratings yet
- Rural Dairy Technology PDFDocument123 pagesRural Dairy Technology PDFSajjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Recrystallization and Manufacture of Aspirin: The Practicum of Organic ChemistryDocument21 pagesRecrystallization and Manufacture of Aspirin: The Practicum of Organic ChemistryEra MelaniaNo ratings yet
- Mystery of Solubility - Retrograde (Temperature Inverse) Solubility - Why Does It Happen - Nikhilesh Mukherjee - Pulse - LinkedInDocument6 pagesMystery of Solubility - Retrograde (Temperature Inverse) Solubility - Why Does It Happen - Nikhilesh Mukherjee - Pulse - LinkedInmtaha85No ratings yet
- Human Chemistry I PDFDocument426 pagesHuman Chemistry I PDFzerocool86No ratings yet
- Salt Effect in Distillation - A Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesSalt Effect in Distillation - A Literature Reviewcombo162No ratings yet
- TEST-1 Liquid Solution 06.04.2020Document4 pagesTEST-1 Liquid Solution 06.04.2020tarunNo ratings yet
- Stability Dr. Myasar Alkotaji 26Document14 pagesStability Dr. Myasar Alkotaji 26اسامه عمر عثمانNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit - 2 - Topic 1Document49 pagesEdexcel IAS Chemistry Classified Unit - 2 - Topic 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Lec5.Recovery and Purification of Fermentation ProductsDocument26 pagesLec5.Recovery and Purification of Fermentation Productsannaduraipillai50% (2)
- Solubility of Stearic Acid in Various Organic Solvents PDFDocument4 pagesSolubility of Stearic Acid in Various Organic Solvents PDFNestor Armando Marin SolanoNo ratings yet
- 1.4 - Sorting Materials Into GroupsDocument5 pages1.4 - Sorting Materials Into GroupsSNo ratings yet
- B.SC - Semester Chemistry - Syllabus ToDocument23 pagesB.SC - Semester Chemistry - Syllabus ToMan Deep SinghNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry MCQDocument4 pagesInorganic Chemistry MCQOmSilence2651No ratings yet
- TM 2000-19 PDFDocument22 pagesTM 2000-19 PDFmilecsaNo ratings yet
- United States Pharmacopoeia Food Chemicals CodexDocument3 pagesUnited States Pharmacopoeia Food Chemicals CodexДима ВараваNo ratings yet
- Performance Chemicals GuideDocument45 pagesPerformance Chemicals Guidetopguitar100% (1)
- Year 7 SLGDocument38 pagesYear 7 SLGMeetaDeviNo ratings yet
- Colloid: Solutions and Other MixturesDocument19 pagesColloid: Solutions and Other MixturesnivehthaaNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept Solution Practice Set ObjectiveDocument3 pagesMole Concept Solution Practice Set ObjectiveGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Properties and HandlingDocument25 pagesAmmonia Properties and HandlingJohn Harken100% (2)
- Journal 8 Solubility of Organic CompoundsDocument8 pagesJournal 8 Solubility of Organic CompoundsRochelle Joyce Olmilla BersaminNo ratings yet
- Solutions and Their Properties: CHM 112 M. PrushanDocument36 pagesSolutions and Their Properties: CHM 112 M. PrushanLouie Jay LidoNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil DewaxingDocument9 pagesCrude Oil DewaxingEleonoraNo ratings yet