Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Map1
Uploaded by
Irvanda DvioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mind Map1
Uploaded by
Irvanda DvioCopyright:
Available Formats
Instruction must be concerned with the experiences and contexts that
make the student willing and able
to learn (readiness).
Instruction must be structured so that it can be easily grasped by the
Main Principles student (spiral organization).
Instruction should be designed to facilitate extrapolation and or fill in the
gaps (going beyond the
information given) by stimulating cognitive skills required for application.
Constructivism is ‘an approach to learning that holds that people actively Constructivism is the most supported approach to language learning
construct or make their own knowledge and that reality is determined by Constructivism? and its main contribution to educational psychology is the learner-
the experiences of the learner’ (E lliott et al., 2000, p. 256). centred approach, which emphasizes the autonomy of learners in the
process of their education as the realist philosophers such as Plato
claimed.
A major theme in the theoretical framework of Bruner is that learning is 1. The learner uses sensory input and does something with it, ultimately
an active process in which learners construct new ideas or concepts making meaning of it.
based upon their current and past knowledge.
2. Learning consists of both constructing meaning and constructing
The learner selects and transforms information, constructs hypotheses, systems of meaning. Learning is layered.
and makes decisions, relying on a cognitive structure to do so.
Top-down method Methods used
3. Learning occurs in the mind. Physical activity may be necessary, but
Cognitive structure (i.e., schema, mental models) provides meaning and is not sufficient alone.
organization to experiences and allows the individual to “go beyond the
information given”. 4. Learning involves language. Vygotsky believed that language and learning are
Constructivsm and Learning inextricably intermeshed.
5. Learning is a social activity
Learner Oriented Principles of Constructivism Learning
6. Learning is contextual. We do not isolate facts from the situations and
Conten Awareness environments in which they are relevant.
Individual Learning 7. Knowledge is necessary for learning. It is the basis of structure and
meaning-making. The more we know, the more we can learn.
Learning Awareness Principles of 8. Learning takes time; it is not spontaneous. Learners go over
Projects “Constructivism” information, ponder them, use them, practice, experiment.
Real and Complex Learning Principles of FLT in Foreign 9. Motivation is a necessary component, because it causes the
Language learner’s sensory apparatus to be activated. Relevance, curiosity, fun,
Collaborative Learning
Teaching accomplishment, achievement, external rewards and other motivators
Learner Autonomy facilitate ease of learning.
Language Awarness
Construtivism and Language Teaching
Creativity constructing knowledge, not receiving it
Intercultural Awareness thinking and analyzing, not accumulating memorizing
Foundation
Critical Thinking understanding and applying, not repeating back
Designing and Pursuing Project and Reasearch being active, not passive
Role Playing
Necessiate Multiple Learning Environments Activities
(1) Teacher serves as one of many resources for students, not
Situatuional and Contextual necessarily the primary source of information.
Theme and Content Based (2) The teacher engages students in experiences that challenge
previous conceptions of their existing knowledge.
Oral Presentation
(3) The teacher uses student responses in the planning of next lessons
and seeks elaboration of students’ initial responses.
Trivial (Cognitive) constructivism (4) The teacher encourages questions and discussion among students
by asking open-ended questions.
Radical constructivism.
(5) The teacher assists students to understand their own cognitive
Social constructivism. Schools of Constructivism processes (metacognition) by using cognitive terminology such as
Cultural constructivism. classify, analyze, create, organize, hierarchy, etc. when framing tasks.
Nine Characteristics of a Constructivist Teacher
Critical constructivism. (6) The teacher encourages and accepts student autonomy and initiative
by being willing to let go of classroom control.
(7) The teacher makes available raw data and primary resources, along
with manipulative and interactive physical materials.
(8) The teacher does not separate knowing from the process of finding
out nouns and verbs.
(9) The teacher facilitates clear communication from students in writing
and verbal responses, from the point of view that communication comes
from ones deep structural understanding of the concepts being
communicated. When they can communicate clearly and meaningfully,
they have truly integrated the new learning.
You might also like
- An Investigation of Teachers’ Questions and Tasks to Develop Reading Comprehension: The Application of the Cogaff Taxonomy in Developing Critical Thinking Skills in MalaysiaFrom EverandAn Investigation of Teachers’ Questions and Tasks to Develop Reading Comprehension: The Application of the Cogaff Taxonomy in Developing Critical Thinking Skills in MalaysiaNo ratings yet
- ESP Course Design - Group 1Document16 pagesESP Course Design - Group 1Rizqi Awallul BahriNo ratings yet
- For Unit 1Document27 pagesFor Unit 1Angielyn Montibon JesusNo ratings yet
- ALIPIO, Dwight S. Ii-Bee: Hilippine Ormal NIVERSITY North LuzonDocument2 pagesALIPIO, Dwight S. Ii-Bee: Hilippine Ormal NIVERSITY North LuzonDWIGHT ALIPIO100% (1)
- EVIDENCE 1 Loredo Jessa Mae D.Document10 pagesEVIDENCE 1 Loredo Jessa Mae D.April Grace Genobatin BinayNo ratings yet
- Final RequirementDocument4 pagesFinal RequirementCALVERO, MARICEL PAZ E.No ratings yet
- Lfhers: ConstructivismDocument17 pagesLfhers: ConstructivismDada Aguilar DelgacoNo ratings yet
- EDUC 8 FinalsDocument28 pagesEDUC 8 FinalsPrinz Pabz EspanolaNo ratings yet
- Principles Strats m1 TransDocument1 pagePrinciples Strats m1 TransKz MinaNo ratings yet
- TTL NotesDocument24 pagesTTL NotesKIMBERLY AVISONo ratings yet
- Annotation Template For Teacher I-III (Proficient Teacher)Document2 pagesAnnotation Template For Teacher I-III (Proficient Teacher)linelljoieNo ratings yet
- Global Trends MayaDocument10 pagesGlobal Trends MayaMay RamonesNo ratings yet
- PED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Document18 pagesPED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Mary Antonette JalosjosNo ratings yet
- Slide PPT - Cognitivsm and ConstructivismDocument17 pagesSlide PPT - Cognitivsm and ConstructivismSari AzhariyahNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered Teaching: Understanding LearningDocument34 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered Teaching: Understanding LearningStephen Leocadio DinagaNo ratings yet
- Tpeh Output 5Document5 pagesTpeh Output 5Shaira Colleen Merano VillamorNo ratings yet
- Pogoy Module 1Document5 pagesPogoy Module 1Nica PogoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11&12 - Edtech2Document20 pagesLesson 11&12 - Edtech2Kuya Tiong TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Reviewer SS2Document5 pagesReviewer SS2qzb2dtvx7pNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 1 GEC 3Document4 pagesModule 2 Lesson 1 GEC 3Rizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- Constructivism A Multidisciplinary Approach EDUENG04Document16 pagesConstructivism A Multidisciplinary Approach EDUENG04Jiro Hendrix AlbertNo ratings yet
- Task 3Document5 pagesTask 3Romeo Cabrera Jr.No ratings yet
- Act FaciDocument28 pagesAct Faciricapearl.zorillaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Constructivist TheoriesDocument15 pagesModule 6 Constructivist TheoriesChristian Emil ReyesNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF MULTIGRADE TEACHINGDocument3 pagesActivity 3 THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS OF MULTIGRADE TEACHINGAlexa Sofiyah Acorda100% (1)
- EDUC 3 LECTURE SEVEN PHILOSOPHIES of EDUCATIONDocument5 pagesEDUC 3 LECTURE SEVEN PHILOSOPHIES of EDUCATIONAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Week 3Document1 pageActivity 2 Week 3Keno ArakamaNo ratings yet
- Article 2 - Learning TheoriesDocument6 pagesArticle 2 - Learning TheoriesKavitha AlwisNo ratings yet
- Learning Sciences: Di RetrievalDocument1 pageLearning Sciences: Di RetrievalMosiah Araújo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FrameworkDocument8 pagesTheoretical FrameworkPaul Diga100% (1)
- Learning TheoriesDocument16 pagesLearning TheoriesMariele Rose MirandaNo ratings yet
- Isc 3701Document4 pagesIsc 3701Annemarie RossouwNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping Theories of Learning & Need AnalysisDocument2 pagesMind Mapping Theories of Learning & Need AnalysisAmyNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Lessons (Community Based)Document7 pagesCompilation of Lessons (Community Based)Maria GieNo ratings yet
- Integrative ReviewerDocument4 pagesIntegrative ReviewerKEMPIS, Jane Christine PearlNo ratings yet
- Learning With Action Research ReportDocument8 pagesLearning With Action Research ReportGelgel DecanoNo ratings yet
- IMD - Wk1 - Theories and Foundations of Instructional DesignDocument8 pagesIMD - Wk1 - Theories and Foundations of Instructional DesignRICHARD ALFEO ORIGINALNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories Comparison Table 1Document3 pagesLearning Theories Comparison Table 1api-296917124No ratings yet
- Module 3 - The Five Educational Learning TheoriesDocument2 pagesModule 3 - The Five Educational Learning TheoriesJames ReeydNo ratings yet
- Jake Angelo Biraquit - CONSTRUCTIVIST THEORYDocument32 pagesJake Angelo Biraquit - CONSTRUCTIVIST THEORYJake Angelo BiraquitNo ratings yet
- UMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: TH THDocument4 pagesUMF Unit-Wide Lesson Plan Template: TH THapi-607068017No ratings yet
- From Theory To Practice - A Cognitive Systems Biggs1993Document14 pagesFrom Theory To Practice - A Cognitive Systems Biggs1993Roger PazNo ratings yet
- Learning Theories FinalDocument5 pagesLearning Theories FinalJeo CapianNo ratings yet
- Lyva ActDocument6 pagesLyva Actletlyvalenzuela03No ratings yet
- ConstructivismDocument6 pagesConstructivismZarah HonradeNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies and Methodologies For Teaching and LearningDocument7 pagesTeaching Strategies and Methodologies For Teaching and Learningfrances ocampoNo ratings yet
- THEORYDocument2 pagesTHEORY12-A4 Tolentino, Wendell FNo ratings yet
- Teacher Development: Concept Concept ConceptDocument2 pagesTeacher Development: Concept Concept Conceptcristian ceballosNo ratings yet
- Planning A TaskDocument8 pagesPlanning A Taskjessik1326No ratings yet
- LESSON 4 and 5Document4 pagesLESSON 4 and 5Garcia Khristine Monique BadongNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument7 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentStephanie Joy Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning ProcessDocument5 pagesTeaching and Learning ProcessQurban NazariNo ratings yet
- En 119 PPT 4th LessonDocument15 pagesEn 119 PPT 4th LessonLa SierteNo ratings yet
- Santos Judy Ann A. Activity 1 Beed2a.....Document3 pagesSantos Judy Ann A. Activity 1 Beed2a.....Rosanna TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Science RWDocument1 pageScience RWjesicaorbaneja101696No ratings yet
- Tubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingDocument4 pagesTubigan - Modern Approaches Applicable To College TeachingihlaNo ratings yet
- Bba Sem 2 Ob 2022Document30 pagesBba Sem 2 Ob 2022Anmol GedaNo ratings yet
- Constructivist ReportDocument20 pagesConstructivist ReportFerdinand BacayNo ratings yet
- Activities For Lesson 7Document4 pagesActivities For Lesson 7Agung DewantaraNo ratings yet
- Amritsar Police StationDocument5 pagesAmritsar Police StationRashmi KbNo ratings yet
- Art of War Day TradingDocument17 pagesArt of War Day TradingChrispen MoyoNo ratings yet
- Changed Report 2015 PDFDocument298 pagesChanged Report 2015 PDFAnonymous FKjeRG6AFnNo ratings yet
- PetrifiedDocument13 pagesPetrifiedMarta GortNo ratings yet
- [18476228 - Organization, Technology and Management in Construction_ an International Journal] Adaptive Reuse_ an Innovative Approach for Generating Sustainable Values for Historic Buildings in Developing CountriesDocument15 pages[18476228 - Organization, Technology and Management in Construction_ an International Journal] Adaptive Reuse_ an Innovative Approach for Generating Sustainable Values for Historic Buildings in Developing Countrieslohithsarath bethalaNo ratings yet
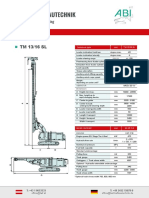
- ABI TM 13 16 SL - EngDocument1 pageABI TM 13 16 SL - EngJuan Carlos Benitez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and Implant DentistryDocument9 pagesGroup 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and Implant DentistryEsme ValenciaNo ratings yet
- The Time Machine Was First Published in 1984 As A Story Under The Name The Time Traveller in The National ObserverDocument1 pageThe Time Machine Was First Published in 1984 As A Story Under The Name The Time Traveller in The National ObservermarceNo ratings yet
- SecurityFund PPT 1.1Document13 pagesSecurityFund PPT 1.1Fmunoz MunozNo ratings yet
- Survivor's Guilt by Nancy ShermanDocument4 pagesSurvivor's Guilt by Nancy ShermanGinnie Faustino-GalganaNo ratings yet
- CRISTIAN COLCERIU - PERSONALITATI CLUJENE Prof - Dr.ing - POMPILIU MANEADocument21 pagesCRISTIAN COLCERIU - PERSONALITATI CLUJENE Prof - Dr.ing - POMPILIU MANEAcristian colceriu100% (2)
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument3 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousNatalia SalinasNo ratings yet
- Eapp Melc 12Document31 pagesEapp Melc 12Christian Joseph HerreraNo ratings yet
- Liquitex Soft Body BookletDocument12 pagesLiquitex Soft Body Booklethello belloNo ratings yet
- Pelayo PathopyhsiologyDocument13 pagesPelayo PathopyhsiologyE.J. PelayoNo ratings yet
- 1500 Series: Pull Force Range: 10-12 Lbs (44-53 N) Hold Force Range: 19-28 Lbs (85-125 N)Document2 pages1500 Series: Pull Force Range: 10-12 Lbs (44-53 N) Hold Force Range: 19-28 Lbs (85-125 N)Mario FloresNo ratings yet
- EP001 LifeCoachSchoolTranscriptDocument13 pagesEP001 LifeCoachSchoolTranscriptVan GuedesNo ratings yet
- 9881 enDocument345 pages9881 enSaid BenNo ratings yet
- March For Our LivesDocument22 pagesMarch For Our LivesLucy HanNo ratings yet
- 21 Tara Mantra-Wps OfficeDocument25 pages21 Tara Mantra-Wps OfficeAlteo FallaNo ratings yet
- De Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh Lop 12 So GD DT Thanh Hoa Nam Hoc 2015 2016Document11 pagesDe Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh Lop 12 So GD DT Thanh Hoa Nam Hoc 2015 2016Thuy LinggNo ratings yet
- Positive Psychology in The WorkplaceDocument12 pagesPositive Psychology in The Workplacemlenita264No ratings yet
- Ismb ItpDocument3 pagesIsmb ItpKumar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Marion Nicoll: Life & Work by Catharine MastinDocument147 pagesMarion Nicoll: Life & Work by Catharine MastinArt Canada InstituteNo ratings yet
- 300u Specs Diodo 300 Amps. 25 Dolares RadiosurtidoraDocument6 pages300u Specs Diodo 300 Amps. 25 Dolares RadiosurtidorarepelindNo ratings yet
- Sanskrit Subhashit CollectionDocument110 pagesSanskrit Subhashit Collectionavinash312590% (72)
- Report DR JuazerDocument16 pagesReport DR Juazersharonlly toumasNo ratings yet
- (Isaac Asimov) How Did We Find Out About AntarcticDocument24 pages(Isaac Asimov) How Did We Find Out About AntarcticDrBabu PSNo ratings yet
- Days Papers 2001Document341 pagesDays Papers 2001jorgefeitoza_hotmailNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument7 pages1 PBIndah Purnama TaraNo ratings yet































































![[18476228 - Organization, Technology and Management in Construction_ an International Journal] Adaptive Reuse_ an Innovative Approach for Generating Sustainable Values for Historic Buildings in Developing Countries](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/422064728/149x198/344a5742a7/1565947342?v=1)