Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jan 14-18, 2019
Uploaded by
klaire0219Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jan 14-18, 2019
Uploaded by
klaire0219Copyright:
Available Formats
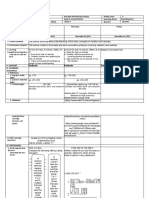
Grades 1-12 School DUQUIT HIGH SCHOOL Grade Level NINE
DAILY LESSON LOG Teacher ABIGAEL R. PINEDA Learning Area SCIENCE
Teaching Dates and Time January 14-18, 2019 Quarter FOURTH
Day 5
Day 1 Marangal 12:50 -1:40(Day
Day 2 Day 3 Day 4
Marangal 12:50 -1:40(Day 1) 4)
Matiyaga 2:50 – 3:40(Day 2) Marangal 12:00 -12:50(Day 2) Matiyaga 2:50 – 3:40(Day 3)
Matiyaga 2:50 – 3:40(Day 1) Matiyaga 2:50 – 3:40(Day
Mapagbigay 3:40 – 4:30(Day 2) Marangal 12:50 -1:40(Day 3) Mapagbigay3:40 – 4:30(Day 3)
Mapagbigay 3:40 – 4:30(Day 1) 4)
Mapagbigay 3:40 –
4:30(Day 4)
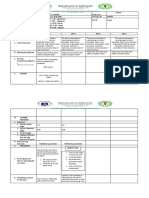
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards The learners demonstrate understanding of uniformly accelerated motion in two-dimensions using projectile motion as example, and conservation of linear momentum.
B. Performance Standards The learners should be able to propose ways to enhance sports related to projectile motion.
C. Learning The learners should be able to The learners should be able to
Competencies / Objectives describe the horizontal and describe the horizontal and
Write LC code for each vertical motions of a projectile. vertical motions of a projectile.
S9FE-Iva-34 S9FE-Iva-34
II. CONTENT FORCES and MOTION FORCES and MOTION FORCES and MOTION FORCES and MOTION FORCES and MOTION
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1.Teacher’s Guide pages
2. Learner’s Materials pages 233-234 233-234 238-241 238-241
3. Textbook pages
4. Additional Materials from
Learning Resource (LR) portal
B. Other Learning Resources
Note: Day 5 (or during vacant time)
*Checking of papers, Encoding of grades, IMs preparations
IV. PROCEDURES
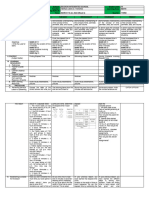
A. Reviewing previous What is the formula for UAM? What is the formula for
lesson or presenting the UAM?
new lesson
If a body maintains a constant If a body maintains a constant You learned in Grade 8 that the You learned in Grade 8 that
change in its velocity in a given change in its velocity in a given pull of gravity acts on all the pull of gravity acts on all
B. Establishing a purpose
for the lesson time interval along a straight time interval along a straight objects. So on Earth, when you objects. So on Earth, when
line, then the body is said to line, then the body is said to throw something up, it will go you throw something up, it
have a uniform acceleration. have a uniform acceleration. down. will go down.
Consider an airplane on a Consider an airplane on a Consider a stone dropped from Consider a stone dropped
runway preparing to takeoff. runway preparing to takeoff. a cliff. For equal time interval, from a cliff. For equal time
C. Presenting examples/
instances of new lesson Positions taken at equal time Positions taken at equal time the distance travelled increases interval, the distance
intervals. intervals. quadratically. travelled increases
quadratically.
The change in an airplane’s The change in an airplane’s Another example of free fall is a Another example of free fall
position for each time interval is position for each time interval is body thrown upward. As the is a body thrown upward.
D. Discussing new
increasing, it is moving faster increasing, it is moving faster ball goes up, it decelerates with As the ball goes up, it
concepts and practicing
new skills #1 and faster. This means that the and faster. This means that the a magnitude of 9.8m/s2 until it decelerates with a
plane is accelerating. plane is accelerating. stops momentarily and changes magnitude of 9.8m/s2 until
direction. it stops momentarily and
changes direction.
E. Discussing new N/A N/A N/A N/A
concepts and practicing
new skills #2
F. Developing mastery Try the next activity to further Try the next activity to further Do the next activities to further Do the next activities to
( Leads to Formative understand acceleration. understand acceleration. see the behavior of falling further see the behavior of
Assessment 3) objects. falling objects.
G. Finding practical
applications of concepts
Note: Day 5 (or during vacant time)
*Checking of papers, Encoding of grades, IMs preparations
and skills in daily living
From the activity you related From the activity you related Remember that the magnitudes Remember that the
distance and time. In computing distance and time. In computing of the two velocities are equal, magnitudes of the two
the slope, you divided distance the slope, you divided distance but they have opposite velocities are equal, but
H. Making generalizations
by the time which is actually the by the time which is actually the directions velocity is upward they have opposite
and Abstractions about
the lesson speed of the can. speed of the can. when it was thrown but directions velocity is
downward when it returns. upward when it was thrown
but downward when it
returns.
I. Evaluating learning
J. Additional activities for
application or remediation
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
evaluation.
B. No. of learners who
require additional activities
for remediation.
C. Did the remedial lessons
work? No. of learners who
have caught up with the
lesson.
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation.
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did these work?
F. What difficulties did I
Note: Day 5 (or during vacant time)
*Checking of papers, Encoding of grades, IMs preparations
encounter which my
principal or supervisor can
help me solve?
G. What innovation or
localized materials did I
use/discover which I wish to
share with other teachers?
Prepared by: Checked by: Noted:
ABIGAEL R. PINEDA SARAH G. DACUNG MARISSA Q. ROXAS
SST- III HT Designate Principal III
Note: Day 5 (or during vacant time)
*Checking of papers, Encoding of grades, IMs preparations
You might also like
- Advanced Math (PSE Module 9.1)Document3 pagesAdvanced Math (PSE Module 9.1)Jhune SobrepeñaNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Force Systems: This Module Aims That The Students Will Be Able ToDocument11 pagesEquivalent Force Systems: This Module Aims That The Students Will Be Able ToMONIQUE UNICO100% (1)
- Ansys Polymat Users GuideDocument238 pagesAnsys Polymat Users GuideVicky PolychronidouNo ratings yet
- ZZ - Introduction To Lorentz Geometry Curves and Surfaces by Alexandre Lymberopoulos and Ivo Terek CoutoDocument351 pagesZZ - Introduction To Lorentz Geometry Curves and Surfaces by Alexandre Lymberopoulos and Ivo Terek Coutorajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- DLL Research 7Document5 pagesDLL Research 7Mary Dignos100% (1)
- Grade 9 Quarter 4 DLL Science 9Document53 pagesGrade 9 Quarter 4 DLL Science 9Willy TimbalNo ratings yet
- Free Fall LabDocument6 pagesFree Fall LabSunday Glo M. Cabuyao100% (1)
- Latest Earth&Lifesci Remelyndaily Lesson Log (DO No42 s2016)Document33 pagesLatest Earth&Lifesci Remelyndaily Lesson Log (DO No42 s2016)Remelyn OcatNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodic Exams Science Gr.7 With KeyDocument6 pages3rd Periodic Exams Science Gr.7 With Keyklaire0219100% (2)
- Boiler CalculationsDocument6 pagesBoiler CalculationsJesther Marlou C. OrongNo ratings yet
- ParallelogramsDocument6 pagesParallelogramsJày CaneteNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 10 6th WK Q1Document5 pagesDLL Science 10 6th WK Q1redNo ratings yet
- DLL Q3-MATH 9 WEEK 5-ProportionDocument4 pagesDLL Q3-MATH 9 WEEK 5-ProportionAngela Camille Paynante67% (3)
- INDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLAN - Abigael PinedaDocument2 pagesINDIVIDUAL DEVELOPMENT PLAN - Abigael Pinedaklaire021950% (2)
- Grade 9 3rd QTR DLL-4th-week 18-22Document6 pagesGrade 9 3rd QTR DLL-4th-week 18-22jonathan ian ubasNo ratings yet
- Latest Earthsci Remelyndaily Lesson Log (DO No42 s2016)Document22 pagesLatest Earthsci Remelyndaily Lesson Log (DO No42 s2016)Remelyn OcatNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 DLL Math q3 Week 25Document4 pagesGrade 1 DLL Math q3 Week 25GinNo ratings yet
- Nov 4-9Document4 pagesNov 4-9ABIGAEL R. PINEDANo ratings yet
- Feb11 15Document4 pagesFeb11 15klaire0219No ratings yet
- Nov 26-29Document4 pagesNov 26-29ABIGAEL R. PINEDANo ratings yet
- Jan 7-11, 2019Document4 pagesJan 7-11, 2019ABIGAEL R. PINEDANo ratings yet
- Dec 3-7Document4 pagesDec 3-7klaire0219No ratings yet
- Oct 22-26Document4 pagesOct 22-26klaire0219No ratings yet
- Oct 8-12Document4 pagesOct 8-12klaire0219No ratings yet
- Oct. 2-6, 2023Document7 pagesOct. 2-6, 2023Glen Grace GorgonioNo ratings yet
- DLL-3rd-week 13-17Document7 pagesDLL-3rd-week 13-17Jerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Quarter 2 DLL Science 5 1Document9 pagesWeek 11 Quarter 2 DLL Science 5 1MARILEN TORRANONo ratings yet
- Q3 DLL Exam Week March 25 29Document3 pagesQ3 DLL Exam Week March 25 29Mark SolivaNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q3W2 EspinosaDocument5 pagesSci9 Q3W2 Espinosamarinelle.eslabonNo ratings yet
- Q3 LESSON G7 DL W6 March 11 15Document13 pagesQ3 LESSON G7 DL W6 March 11 15Mark SolivaNo ratings yet
- Sci9 - Q3W1 - Espinosa DLLDocument4 pagesSci9 - Q3W1 - Espinosa DLLmarinelle.eslabonNo ratings yet
- September-4-8 2023-G8 ABEGAIL REYESDocument5 pagesSeptember-4-8 2023-G8 ABEGAIL REYESAbegail ReyesNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Quarter 2Document5 pagesWeek 8 Quarter 2Lydito Marvin PabilonaNo ratings yet
- DLL-PR1-Week-2 With Catch UP Friday IntegrationDocument7 pagesDLL-PR1-Week-2 With Catch UP Friday IntegrationVernald SabalzaNo ratings yet
- DLL 6 ResearchDocument4 pagesDLL 6 ResearchMary DignosNo ratings yet
- DLL4 Math 8 Week 2Document3 pagesDLL4 Math 8 Week 2Angela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- WLP - Math 4 - Q3 - W8Document10 pagesWLP - Math 4 - Q3 - W8Geraldine Ison ReyesNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan Mathematics Bruno q2 w1Document3 pagesWeekly Learning Plan Mathematics Bruno q2 w1Leonardo Bruno JrNo ratings yet
- Oct. 14 18 1Document5 pagesOct. 14 18 1Charlotte CalauadNo ratings yet
- Dll-Template-Grade 9 - Aug. 29 To Week 1 - AmaDocument4 pagesDll-Template-Grade 9 - Aug. 29 To Week 1 - AmaAileen AbandoNo ratings yet
- 8th Week DLLDocument6 pages8th Week DLLLuie Transfiguracion IINo ratings yet
- Apprentice Teaching: Lesson Plan Summary TemplateDocument6 pagesApprentice Teaching: Lesson Plan Summary Templateapi-538475699No ratings yet
- Loraine - q2 WLP Week-4Document17 pagesLoraine - q2 WLP Week-4allisonkeating04No ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1shyfly21No ratings yet
- DLL PE 8 Week 3 3rdDocument3 pagesDLL PE 8 Week 3 3rdKimberlyn ManonsonNo ratings yet
- DLL Diss 3Document3 pagesDLL Diss 3Matthew Evan EstevesNo ratings yet
- Kinder-New-DLL Week7 - Day5Document4 pagesKinder-New-DLL Week7 - Day5GRACEL MAE JUANNo ratings yet
- G5 DLL Q4 Week 1 MathDocument11 pagesG5 DLL Q4 Week 1 MathJener Portacio MontemayorNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 7 W4Document5 pagesDLL - Science 7 W4Joanne Diaz JacintoNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - Mathematics 3 - Q4 - W1Arriane Sumile JimenezNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: ScienceDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: Sciencemercy sacrizNo ratings yet
- DLL-2nd-week 7-12Document6 pagesDLL-2nd-week 7-12Jerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q4 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q4 - W4Lendel Mariz CepilloNo ratings yet
- Pre-K Q4 W9 Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesPre-K Q4 W9 Lesson PlanJessecca CarambiasNo ratings yet
- Math DLL Week 14Document12 pagesMath DLL Week 14Dian VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- DLL-4th-week 18-22Document7 pagesDLL-4th-week 18-22Jerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- 6th Week September 29, 2023 English DLL Grade 9Document8 pages6th Week September 29, 2023 English DLL Grade 9Aileen AbandoNo ratings yet
- Sept. 2 6Document5 pagesSept. 2 6Charlotte CalauadNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4Document8 pagesDaily Lesson Log: Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4leny santosNo ratings yet
- DLL-PR1-Week-5 With Catch Up Friday IntegrationDocument17 pagesDLL-PR1-Week-5 With Catch Up Friday IntegrationVernald SabalzaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 7 W3Document6 pagesDLL - Science 7 W3Joanne Diaz JacintoNo ratings yet
- Sept 3-7Document5 pagesSept 3-7klaire0219No ratings yet
- Math 4 Week 6Document10 pagesMath 4 Week 6Neriza JeanNo ratings yet
- DLL English-2 Q3W5Document15 pagesDLL English-2 Q3W5Edelle BaritNo ratings yet
- G9 Q3 Week-3Document6 pagesG9 Q3 Week-3Crisiel OcampoNo ratings yet
- INTRO Jan.23 27 2022Document2 pagesINTRO Jan.23 27 2022Editha RobillosNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5Document5 pagesDay 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5klaire0219No ratings yet
- Sept 3-7Document5 pagesSept 3-7klaire0219No ratings yet
- Oct 22-26Document4 pagesOct 22-26klaire0219No ratings yet
- July 16-20Document4 pagesJuly 16-20klaire0219No ratings yet
- Sept 10-14Document5 pagesSept 10-14klaire0219No ratings yet
- Oct 8-12Document4 pagesOct 8-12klaire0219No ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Abigael R. PinedaDocument1 pagePrepared By:: Abigael R. Pinedaklaire0219No ratings yet
- Individual Workweek Accomplishment ReportDocument2 pagesIndividual Workweek Accomplishment Reportklaire0219No ratings yet
- Individual Workweek Accomplishment ReportDocument2 pagesIndividual Workweek Accomplishment Reportklaire0219No ratings yet
- Individual Workweek Accomplishment ReportDocument2 pagesIndividual Workweek Accomplishment Reportklaire0219No ratings yet
- Aug 13-17Document6 pagesAug 13-17klaire0219No ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippinesklaire0219No ratings yet
- Aug 6-11Document4 pagesAug 6-11klaire0219No ratings yet
- IwarDocument8 pagesIwarklaire0219No ratings yet
- Intermediate English For Physics " Friction "Document7 pagesIntermediate English For Physics " Friction "Wenimanwati WaruwuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Assignment OnDocument5 pagesElectrical Assignment OnAreesha soomroNo ratings yet
- Tomic Tructure Otes: Quantum NumbersDocument2 pagesTomic Tructure Otes: Quantum NumbersYuNeng KhongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Second Order Linear Pdes: A (X, Y) UDocument19 pagesChapter 3. Second Order Linear Pdes: A (X, Y) UCherry CharanNo ratings yet
- Name: Joyce Ann R. Cañaveral Section: 12 STEM 2: Laboratory Work No. 2Document3 pagesName: Joyce Ann R. Cañaveral Section: 12 STEM 2: Laboratory Work No. 2Joyce CañaveralNo ratings yet
- Si Brochure Draft ch123 PDFDocument29 pagesSi Brochure Draft ch123 PDFJosuè Omar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Sfa Vessels Guide July22Document40 pagesSfa Vessels Guide July22Ilias ZilakosNo ratings yet
- Tsmart Butterfly ValvesDocument100 pagesTsmart Butterfly ValvesElif UsluNo ratings yet
- Pump DatasheetDocument15 pagesPump DatasheetHedi Ben MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cable Silicoando Tipo Vulcanizao-SihfDocument1 pageCable Silicoando Tipo Vulcanizao-SihfErick MüllerNo ratings yet
- En 1434-4Document47 pagesEn 1434-4onebluelineNo ratings yet
- Angles in Trigonometry: Quarter 2-Week 1 LessonDocument39 pagesAngles in Trigonometry: Quarter 2-Week 1 LessonEarl Lawrence IbanNo ratings yet
- Exploring Tensile Testing A Comprehensive GuideDocument8 pagesExploring Tensile Testing A Comprehensive Guideabdalla27bidoNo ratings yet
- Class VII Science Chapter Heat WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass VII Science Chapter Heat Worksheetchandramani.goswamiNo ratings yet
- CICA CraneSafetyBulletin287GroundPressureDocument1 pageCICA CraneSafetyBulletin287GroundPressureEphraim BarezNo ratings yet
- WoPhO 2013 Physics Cup - Problem 10Document1 pageWoPhO 2013 Physics Cup - Problem 10PhC2013100% (1)
- Solved A Hot Water Stream at 80°C Enters A Mixing Chamber With CheggDocument3 pagesSolved A Hot Water Stream at 80°C Enters A Mixing Chamber With Cheggsalim.22en1No ratings yet
- Assignment EwtDocument19 pagesAssignment Ewtjishnu mohananNo ratings yet
- NG3S238 CFD Assingment Cover Sheet 2020-21Document5 pagesNG3S238 CFD Assingment Cover Sheet 2020-21Ahmed Al SayedNo ratings yet
- Part 2 of 5Document8 pagesPart 2 of 5mick.pride81No ratings yet
- Part C-Procedure and Methods For Testing and Accepting Final Materials As Used in A Product Made From Compositions On The Positive ListDocument3 pagesPart C-Procedure and Methods For Testing and Accepting Final Materials As Used in A Product Made From Compositions On The Positive ListJiaxin TanNo ratings yet
- 1462 TATA NicorDocument2 pages1462 TATA NicorMiguelNo ratings yet
- Headspace 1st YearDocument390 pagesHeadspace 1st YearBarbara RichardsNo ratings yet
- Frames: Es 11: Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument17 pagesFrames: Es 11: Statics of Rigid BodiesMark OñaNo ratings yet