Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Step Voltage Insulation Resistance Test
Step Voltage Insulation Resistance Test
Uploaded by
alvin me0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageThe document discusses different types of insulation testing. The dielectric discharge test can identify excess discharge currents from damaged or contaminated layers in multi-layer insulation, which other tests may not detect. The step voltage insulation resistance test subjects insulation to increasing voltages over time to reveal effects of moisture, dirt, aging or damage that may not be seen at lower voltages. Local weak spots have less influence at low voltage but their effect rapidly increases with higher test voltages, shown by a decreasing insulation resistance.
Original Description:
Original Title
Step voltage insulation resistance test
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different types of insulation testing. The dielectric discharge test can identify excess discharge currents from damaged or contaminated layers in multi-layer insulation, which other tests may not detect. The step voltage insulation resistance test subjects insulation to increasing voltages over time to reveal effects of moisture, dirt, aging or damage that may not be seen at lower voltages. Local weak spots have less influence at low voltage but their effect rapidly increases with higher test voltages, shown by a decreasing insulation resistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageStep Voltage Insulation Resistance Test
Step Voltage Insulation Resistance Test
Uploaded by
alvin meThe document discusses different types of insulation testing. The dielectric discharge test can identify excess discharge currents from damaged or contaminated layers in multi-layer insulation, which other tests may not detect. The step voltage insulation resistance test subjects insulation to increasing voltages over time to reveal effects of moisture, dirt, aging or damage that may not be seen at lower voltages. Local weak spots have less influence at low voltage but their effect rapidly increases with higher test voltages, shown by a decreasing insulation resistance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Guide to modern insulation testing Types of insulation testing
DD value Tested material status
>4 bad
2-4 critical
<2 good
Table 3: Values of dielectric discharge
The dielectric discharge test is very useful for testing a multi-layer insulation. This test
can identify excess discharge currents that occur when one layer of a multi-layer
insulation is damaged or contaminated. This condition will not be detected by both the
spot test and the polarization index test. Discharge current will be higher for known
voltage and capacitance if an internal layer is damaged. The time constant of this
individual layer will differ from other layers, causing a higher current than that of a sound
insulation.
3.5 Step voltage insulation resistance test
According to Figures 2 and 3 the insulation resistance Riso does not depend on voltage.
But in practice this happens quite often. Testing with a voltage far below the one
expected in service often reveals moisture and dirt in insulation, whereas effects of
ageing or mechanical damage of a fairly clean and dry insulation may not be revealed at
such low stress. The step voltage method is very useful when testing with an instrument
that has a lower test voltage than the rated test voltage of the tested item. In other
words, step voltage test gives us useful results even in case we are not able to stress
insulation with nominal electrical voltages.
The influence of local weak spots is small at low voltage, but rapidly increases by
increasing the test voltage. A rapidly decreasing insulation resistance indicates this
process.
The step voltage measurement is simple. The device under test is exposed to different
test voltages that are applied in steps. The voltage starts at the lowest value and
increases with defined steps up to the highest level. Figure 8 shows an example of a
step voltage test with five voltage steps and five equal time periods. The recommended
ratio for the test voltage steps is 1 to 5. At each step, test voltage should be applied for
the same length of time T which is usually 60 s. The application of increased voltage
creates electrical stresses on internal insulation cracks. Results can also be corrected to
working temperature. For more information see chapter 5.2. Influence of temperature.
15
You might also like
- ASTM D-877 Rigidez Dieléctrica Del Aceite (Electrodos de Discos Planos)Document6 pagesASTM D-877 Rigidez Dieléctrica Del Aceite (Electrodos de Discos Planos)Noé Rafael Colorado Sósol100% (1)
- Lab Report 1Document14 pagesLab Report 1api-355836337No ratings yet
- Astm D877Document6 pagesAstm D877Ricardo ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionFrom EverandIndustrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Highway Design Manual: Chapter 19: Reinforced Concrete Box Culverts and Similar StructuresDocument40 pagesHighway Design Manual: Chapter 19: Reinforced Concrete Box Culverts and Similar StructuresKashif Masud100% (2)
- Lee Smolin - A Real Ensemble Interpretation of Quantum MechanicsDocument14 pagesLee Smolin - A Real Ensemble Interpretation of Quantum MechanicsGeorge OvermeireNo ratings yet
- What Is Insulation TestingDocument5 pagesWhat Is Insulation Testingmohd_hasanudin4364No ratings yet
- What Is Insulation TestingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Insulation Testingsender2000No ratings yet
- The Basics of Insulation TestingDocument6 pagesThe Basics of Insulation TestingbhpNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Testing AnDocument9 pagesInsulation Resistance Testing AnShaban SattiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Insulation Testing Digest 5 and 10 KV PDFDocument2 pagesDiagnostic Insulation Testing Digest 5 and 10 KV PDFIsrael JosueNo ratings yet
- Spot Reading TestDocument1 pageSpot Reading Testalvin meNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Test PDFDocument2 pagesInsulation Resistance Test PDFusman haroonNo ratings yet
- Operation of Meters and TestingDocument21 pagesOperation of Meters and TestingDorwinNeroNo ratings yet
- Insulation ResistanceDocument2 pagesInsulation ResistanceDEADMAN0% (1)
- Testing of Transformers: T.R.Sathyanarayana RaoDocument24 pagesTesting of Transformers: T.R.Sathyanarayana RaoBasudev Patra100% (1)
- MMT Insul Testing - 01Document6 pagesMMT Insul Testing - 01Dean BartlettNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Insulation TestingDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Insulation TestingkarthikumarNo ratings yet
- Guide To Modern Insulation Testing Types of Insulation TestingDocument1 pageGuide To Modern Insulation Testing Types of Insulation Testingalvin meNo ratings yet
- Entendiendo Las Mediciones de Resistencia de AislamientoDocument5 pagesEntendiendo Las Mediciones de Resistencia de AislamientoMarco VelvelNo ratings yet
- Sistem Proteksi: Insulation ResistanceDocument23 pagesSistem Proteksi: Insulation ResistanceArif Febriansyah JuwitoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Testing GuideDocument9 pagesTransformer Testing GuideShravan RawalNo ratings yet
- The Dielectric Discharge Test: Figure 1. Insulation Test Currents During ChargingDocument4 pagesThe Dielectric Discharge Test: Figure 1. Insulation Test Currents During Chargingpatelsuhas21No ratings yet
- Dielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using VDE ElectrodesDocument5 pagesDielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using VDE ElectrodesAngie CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 - High Voltage Testing of EquipmentDocument16 pagesChap 6 - High Voltage Testing of Equipmenthadrien100% (1)
- Megger TestDocument1 pageMegger TestHamada ElsharawyNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting With Insulation Resistance Test InstrumentsDocument18 pagesTroubleshooting With Insulation Resistance Test Instrumentsebersworld_2011No ratings yet
- High Voltage EngineeringDocument17 pagesHigh Voltage Engineeringelectricalengineer841411No ratings yet
- 1guide To DC Testing of InsulationDocument10 pages1guide To DC Testing of InsulationNeeraj pathakNo ratings yet
- AgostoDocument4 pagesAgostoBoy TulaNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using VDE ElectrodesDocument9 pagesDielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using VDE ElectrodesMarious EesNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using Disk ElectrodesDocument6 pagesDielectric Breakdown Voltage of Insulating Liquids Using Disk ElectrodesViviana Vanessa VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Presentation On InsulationDocument23 pagesPresentation On InsulationMuhammad asifNo ratings yet
- Site Work Part 3Document13 pagesSite Work Part 3Chea VirakNo ratings yet
- Testing of InsulationDocument27 pagesTesting of Insulationகவி பாரதி முத்துசாமிNo ratings yet
- D1816 12.unlockedDocument5 pagesD1816 12.unlockedIsmael SuarezNo ratings yet
- Breaker Technical InspectionDocument3 pagesBreaker Technical InspectionLee Anthony SigaNo ratings yet
- Gen Write UpDocument11 pagesGen Write Upsarirag100% (2)
- D00vec36 PDFDocument28 pagesD00vec36 PDFIrshad AliNo ratings yet
- HV Lab 2019 Isulation Tester: Types of Insulation Resistance Tests 1Document5 pagesHV Lab 2019 Isulation Tester: Types of Insulation Resistance Tests 1حسن علي جاسمNo ratings yet
- HV Lab 2019 Isulation Tester: Types of Insulation Resistance Tests 1Document5 pagesHV Lab 2019 Isulation Tester: Types of Insulation Resistance Tests 1حسن علي جاسمNo ratings yet
- HV Lab 2019 Isulation Tester: Types of Insulation Resistance Tests 1Document5 pagesHV Lab 2019 Isulation Tester: Types of Insulation Resistance Tests 1حسن علي جاسمNo ratings yet
- Basic Insulation TestingDocument2 pagesBasic Insulation TestingGabriel Zenarosa LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusDocument29 pagesHigh Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusNRCM EEENo ratings yet
- High Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusDocument29 pagesHigh Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusNRCM EEENo ratings yet
- Tests Using Multi-Voltage Megger Insulati On TestersDocument12 pagesTests Using Multi-Voltage Megger Insulati On TestersChea VirakNo ratings yet
- El. Stability TesterDocument23 pagesEl. Stability Testergplese0No ratings yet
- Electrical Notes 1Document36 pagesElectrical Notes 1SWAROOPAN1No ratings yet
- Afects On Winding MeasurementDocument7 pagesAfects On Winding MeasurementJuju shakyaNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J Epes 20180705 12 PDFDocument6 pages10 11648 J Epes 20180705 12 PDFbelayneh ayichewNo ratings yet
- D 877 - 00 - Rdg3ny0wmgDocument6 pagesD 877 - 00 - Rdg3ny0wmgPrakash MakadiaNo ratings yet
- Little Known Facts About Dissipation Factor TestingDocument3 pagesLittle Known Facts About Dissipation Factor TestingedgardNo ratings yet
- Partial DischargeDocument5 pagesPartial DischargeAbdul AhadNo ratings yet
- Unit5 HveDocument29 pagesUnit5 Hveview eeehodNo ratings yet
- 1502957487lectrure 7 KUETDocument13 pages1502957487lectrure 7 KUETAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- D 1816 - 03 - Rde4mtytmdmDocument5 pagesD 1816 - 03 - Rde4mtytmdmPrakash MakadiaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestsDocument2 pagesDiagnostic TestsDavid_Allen_007No ratings yet
- Davis Instruments Technical LibraryDocument12 pagesDavis Instruments Technical LibraryYutthapong TuppadungNo ratings yet
- Transformer Electrical TestsDocument2 pagesTransformer Electrical Testsganesamoorthy1987No ratings yet
- Dielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC 60243Document1 pageDielectric Strength ASTM D149, IEC 60243Pugel YeremiasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Insulation Resistance Testing: Maintenance, Repair & Operations Test & MeasurementDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Insulation Resistance Testing: Maintenance, Repair & Operations Test & Measurementmatthew kagurabadzaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1169 Metodo para Resistividad PDFDocument7 pagesAstm D 1169 Metodo para Resistividad PDFJose Maria Castillo HernandezNo ratings yet
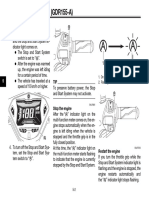
- Aerox Restarting The EngineDocument1 pageAerox Restarting The Enginealvin meNo ratings yet
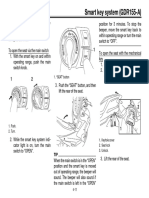
- Aerox Smart Key SystemDocument1 pageAerox Smart Key Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2Document1 pageSystems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2alvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Stop and Start SystemDocument1 pageAerox Stop and Start Systemalvin meNo ratings yet
- Systems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageSystems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application PapersDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application Papersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Aerox Seat Opening and ClosingDocument1 pageAerox Seat Opening and Closingalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- 2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 page2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocument1 pageFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNo ratings yet
- High Fault ResistanceDocument1 pageHigh Fault Resistancealvin meNo ratings yet
- Maximum AC Current AbsorptionDocument1 pageMaximum AC Current Absorptionalvin meNo ratings yet
- Behavior With PV PlantDocument1 pageBehavior With PV Plantalvin meNo ratings yet
- Waveform of The AC CurrentDocument1 pageWaveform of The AC Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Document1 pageCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNo ratings yet
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocument1 pageLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNo ratings yet
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocument1 pageTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNo ratings yet
- DC Ground Fault AnalysisDocument1 pageDC Ground Fault Analysisalvin meNo ratings yet
- Hazard of Direct CurrentDocument1 pageHazard of Direct Currentalvin meNo ratings yet
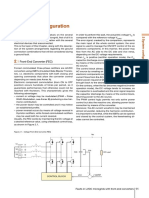
- 2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)Document1 page2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)alvin meNo ratings yet
- Elimination of SynchronizationDocument1 pageElimination of Synchronizationalvin meNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution SystemsDocument1 pageAdvantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution Systemsalvin meNo ratings yet
- Sensitive Electronic LoadsDocument1 pageSensitive Electronic Loadsalvin meNo ratings yet
- Electrical Distribution NetworksDocument1 pageElectrical Distribution Networksalvin meNo ratings yet
- Ambient Temperature Around The Miniature Circuit BreakerDocument1 pageAmbient Temperature Around The Miniature Circuit Breakeralvin meNo ratings yet
- Gender of Nouns in SpanishDocument12 pagesGender of Nouns in SpanishWilson OleaNo ratings yet
- Errors in Chemical Analysis - Lecture 3Document20 pagesErrors in Chemical Analysis - Lecture 3Acidri AbdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Long Span Network Arch Bridges in TimberDocument250 pagesLong Span Network Arch Bridges in TimberAlin SalageanNo ratings yet
- All Models W ExplanationDocument63 pagesAll Models W Explanationpayal1407No ratings yet
- Chapter 30 Even AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter 30 Even AnswersCarlos GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- E6000 Complete Operating ManualDocument154 pagesE6000 Complete Operating ManualsudeshbhagganNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Math 1060 Project Buried Treasure 1Document3 pagesKami Export - Math 1060 Project Buried Treasure 1api-442829868No ratings yet
- Finding The Determinant by Cofactor ExpansionDocument2 pagesFinding The Determinant by Cofactor ExpansionobulakhNo ratings yet
- Surge Current Protection Using SuperconductorDocument21 pagesSurge Current Protection Using SuperconductorpraneethNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Salesmens, Customers, OrdersDocument12 pagesAssignment On Salesmens, Customers, OrderssancokeNo ratings yet
- Transfix Dga 500: GE Grid SolutionsDocument2 pagesTransfix Dga 500: GE Grid Solutionslxd.hepNo ratings yet
- Parental Warmth, Rejection, and Creativity: The Mediating Roles of Openness and Dark Personality TraitsDocument8 pagesParental Warmth, Rejection, and Creativity: The Mediating Roles of Openness and Dark Personality TraitsShiningShadow HunterNo ratings yet
- Syllable Structure Algorithm (SSA) - SimplifiedDocument3 pagesSyllable Structure Algorithm (SSA) - SimplifiedGrzesiek BaranowskiNo ratings yet
- Mri Artifacts FinalDocument44 pagesMri Artifacts FinalSunny SbaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 - Concrete Mix Design DishanDocument20 pagesTest 1 - Concrete Mix Design DishanYasndra AbeygunewardhaneNo ratings yet
- Material Balance ExamplesDocument15 pagesMaterial Balance ExamplesD KaurNo ratings yet
- 18 Mat 21Document3 pages18 Mat 21Dhruti GowdaNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document58 pagesCH 03Girmole WorkuNo ratings yet
- Web Server Administration: Advance JavaDocument31 pagesWeb Server Administration: Advance Javaaaaaaaa2010No ratings yet
- A Study of Pile FatigueDocument92 pagesA Study of Pile Fatiguesitti.a100% (1)
- AS - NZ Standards ListDocument6 pagesAS - NZ Standards Listmarkigldmm918No ratings yet
- Topology of Random Simplicial Complexes: A Survey: Matthew KahleDocument21 pagesTopology of Random Simplicial Complexes: A Survey: Matthew KahleProfilo SofiaNo ratings yet
- TR 670408Document34 pagesTR 670408gerenciaNo ratings yet
- Designand Analysisof Injection Moldingof MineralDocument11 pagesDesignand Analysisof Injection Moldingof MineralSadam AlmaqtariNo ratings yet
- Impedance MatchingDocument53 pagesImpedance MatchingEnricoLiaNo ratings yet
- GUEVARRA Syllabus Math 2teaching Math in The Intermediate GradesDocument7 pagesGUEVARRA Syllabus Math 2teaching Math in The Intermediate GradesVanessa L. VinluanNo ratings yet
- Data Management Concepts: 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing As Prentice Hall, AIS, 11/e, by Bodnar/HopwoodDocument57 pagesData Management Concepts: 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing As Prentice Hall, AIS, 11/e, by Bodnar/HopwoodDiva SabillahNo ratings yet