Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 Litre Engine With EDC: Issue 1
Uploaded by
RuanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 Litre Engine With EDC: Issue 1
Uploaded by
RuanCopyright:
Available Formats
01:01-03
Issue 1 en
9 litre engine with EDC
Function and Work Description
© Scania CV AB 1998-12, Sweden
1 711 384
9 engine with EDC
Description and Operation
Modifications to the 9 litre engine with
EDC in comparison with the 9 litre engine
without EDC
The most important modification to the 9 litre engine with EDC is that the engine has a new injection
pump, which is of the same type as the one fitted to the 14 litre engine.
This description covers modifications in comparison with the 9 litre engine without EDC. As for the
rest, the Operation and Work Description for the 9 litre engine applies.
2 © Scania CV AB 1999, Sweden 0100f16b.mkr
9 engine with EDC
Cylinder head
Modifications
• The position of the injectors is more upright.
The spray angle of the injectors has also
been modified.
• The injectors are now mounted with a clamp
instead of a cap nut.
• The intake and exhaust ports are narrower.
• The intake and exhaust valves have a
smaller head diameter due to the new
position of the injectors.
• New plastic rocker covers have been
designed. There is also a heat protection for
the rocker covers.
0100f16b.mkr © Scania CV AB 1999, Sweden 3
9 engine with EDC
Cylinder block
Modifications
• The timing gear housing has been modified,
due to the curved design of the injection
pump.
• The flywheel housing has sockets for EDC
sensors.
EDC sensors
Crank mechanism
Modifications
• The flywheel has new holes that are
detected by the EDC engine speed sensor.
• The pistons have been modified. The
compression cavity has a new location due
to the changed spray angle of the injector.
Also, the compression rings have a new
location.
4 © Scania CV AB 1999, Sweden 0100f16b.mkr
9 engine with EDC
Modifications to the fuel system of 9 litre
engine with EDC in comparison with 9 litre
engine without EDC
The engine has been fitted with an EDC injection pump with variable injection timing.
The control system EDC MS5 is used for the EDC. Troubleshooting in the EDC system can be
carried out with Scania Diagnosis.
The injector of cylinder 1 has an integral needle movement sensor connected to the EDC control unit.
For more information on the fuel system and EDC MS5, see section 3 Fuel and Exhaust system.
0335f13b.mkr © Scania CV AB 1999, Sweden 5
Work Description
Work Description
Modifications to the 9 litre engine with
EDC in comparison with the 9 litre engine
without EDC
There is no new Work Description for the 9 litre engine with EDC. However, some technical data
have been modified (new tolerances and tightening torques etc.)
For complete Work Descriptions, see section 1 and 3: 9 engine, Work Description and EDC MS5 for
in-line injection pump, Work Description.
Turbocharger
Technical data
Wear limits
Shaft radial clearance max 0,264 mm
Shaft axial clearance (after running-in) max 0,091 mm
Tightening torques
Bolts, turbocharger - exhaust pipe 50 Nm ± 7,5
V-clamp turbo exhaust pipe 20 Nm
Cylinder head
Technical data
Tightening torques
Cap nut for rocker cover, rocker cover sealing ring should be 30 Nm
oiled when tightening
6 © Scania CV AB 1999, Sweden 0105w16b.mkr
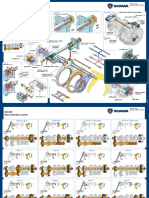
Work Description
New intake valve and maximally machined New exhaust valve and maximally machined
valve seat ring. valve seat ring. The surfaces at the arrows are in
line with each other.
Distance "B" between cylinder head level and valve disc
With new parts min 1,22 mm
With machined parts max 2,3 mm
Intake valve seat
Seat angle 20°
Width of the contact surface (A) 2,0 mm
Outside diameter of the valve seat ring 48,054 - 48,065 mm
Position of the valve seat ring (diameter) 48,000 - 48,016 mm
Setting dimensions for machining tool (C) 41,5 ± 0,5 mm
Exhaust valve seat
Seat angle 45°
Width of the contact surface (A) 2,6 mm
Outside diameter of the valve seat ring 46,054 - 46,065 mm
Position of the valve seat ring (diameter) 46,000 - 46,016 mm
Setting dimensions for machining tool (C) 37,3 ± 0,5 mm
0105w16b.mkr © Scania CV AB 1999, Sweden 7
You might also like
- Ec 290 BLCDocument361 pagesEc 290 BLCchanlin96% (52)
- F4RDocument42 pagesF4Rδαιβελ εςριησςα75% (4)
- Rover 100 TUD5 Overhaul ManualDocument59 pagesRover 100 TUD5 Overhaul ManualAndy Moe63% (8)
- ZF TransmisionDocument20 pagesZF Transmisionchikoo49950% (2)
- MAN B&W 6S50MC - Components DescriptionDocument182 pagesMAN B&W 6S50MC - Components DescriptionHải Nguyễn Văn67% (3)
- B CumminsDocument122 pagesB Cumminsmoises100% (5)
- Renault/ Proton SavvyDocument72 pagesRenault/ Proton Savvy胡瑞麟100% (5)
- Valves, Adjusting D7EDocument11 pagesValves, Adjusting D7Evitor santos50% (4)
- Engine Base & BlockDocument47 pagesEngine Base & Blockkr_abhijeet7235658750% (2)
- Scania HPI System EDCDocument29 pagesScania HPI System EDCnoran100% (1)
- NSU Repair ManualDocument48 pagesNSU Repair ManualGuille GimenoNo ratings yet
- Service Manual For Bf6m2012Document130 pagesService Manual For Bf6m2012Pedro Alfonso Perez100% (2)
- M551 M552Document96 pagesM551 M552Игорь100% (1)
- WB140-150 Final - 66747-2Document16 pagesWB140-150 Final - 66747-2email sharingNo ratings yet
- Ethanol Engine DSI9E: Issue 1Document5 pagesEthanol Engine DSI9E: Issue 1RuanNo ratings yet
- New Setting Solenoid Bearing in EDC Injection Pump and Various PartsDocument5 pagesNew Setting Solenoid Bearing in EDC Injection Pump and Various PartsjoaojitoNo ratings yet
- engine01LS3uz 1 PDFDocument34 pagesengine01LS3uz 1 PDFFeniars83% (6)
- 2004 KX250 Race TuningDocument5 pages2004 KX250 Race TuningKidKawieNo ratings yet
- Optiline: Product DescriptionDocument16 pagesOptiline: Product DescriptionrpmNo ratings yet
- 010602 Снятие Двигателя Dc16 На Авт. с Кабиной Типа t EnDocument8 pages010602 Снятие Двигателя Dc16 На Авт. с Кабиной Типа t EnFarah FakhirahNo ratings yet
- fC81047 Cursor9CamshaftTimingforCAMwithEXHAUSTBRAKEJuly2013rev1Document8 pagesfC81047 Cursor9CamshaftTimingforCAMwithEXHAUSTBRAKEJuly2013rev1Victor Pinedo100% (1)
- MDDocument2 pagesMDAbhijeet PramanikNo ratings yet
- Engine, Description: Service InformationDocument15 pagesEngine, Description: Service InformationDeepak D PillaiNo ratings yet
- Ace3 1122.03 GB PDFDocument16 pagesAce3 1122.03 GB PDFArpit VermaNo ratings yet
- TuningDocument16 pagesTuningKidKawie100% (1)
- Imo Pump Ace3 - 1122.03 - GBDocument16 pagesImo Pump Ace3 - 1122.03 - GBplatasturNo ratings yet
- E40G/EK40G E40J/EK40J: Service GuideDocument23 pagesE40G/EK40G E40J/EK40J: Service Guidemichael pachecoNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Deutz Dde 2012Document172 pagesService Manual Deutz Dde 2012Oscar Tello100% (2)
- New Engine Mercedes 260 Model 177Document17 pagesNew Engine Mercedes 260 Model 177along15102002No ratings yet
- S80 MCCDocument236 pagesS80 MCCAnonymous 8rb48tZS100% (1)
- Motor Derbi TerraDocument48 pagesMotor Derbi TerragovsNo ratings yet
- Service Training: Linde IC-Engined Fork Truck H 20/25/30 D-02 Type 351Document34 pagesService Training: Linde IC-Engined Fork Truck H 20/25/30 D-02 Type 351kashif AliNo ratings yet
- Cummins QSB59 EngineDocument34 pagesCummins QSB59 EnginesobirinNo ratings yet
- LR4 2010 5.0LDocument832 pagesLR4 2010 5.0LLuis Ramon Arguello RealNo ratings yet
- Range Rover 2010 5.0LDocument784 pagesRange Rover 2010 5.0LLuis Ramon Arguello RealNo ratings yet
- Gearbox Bull Gear High Vibration Due To Fluid InstabilityDocument26 pagesGearbox Bull Gear High Vibration Due To Fluid InstabilitySasi NimmakayalaNo ratings yet
- Cabeçote Motor c7Document8 pagesCabeçote Motor c7Alaina SousaNo ratings yet
- J-Serise Engine-USADocument29 pagesJ-Serise Engine-USACristian m VizcainoNo ratings yet
- SSP 254 - Audi A4 01 - Technical Features Pt2 (Eng)Document18 pagesSSP 254 - Audi A4 01 - Technical Features Pt2 (Eng)Concha SolerNo ratings yet
- Engine Torque Settings and Spec's 3.0L V6 SCDocument4 pagesEngine Torque Settings and Spec's 3.0L V6 SCMario MaravillaNo ratings yet
- 009-010-011-012 Service ManualDocument52 pages009-010-011-012 Service Manualhey_hop50% (4)
- M601-M601C Engineer S HandbookDocument70 pagesM601-M601C Engineer S HandbookAnton100% (2)
- STD Line: Product DescriptionDocument16 pagesSTD Line: Product DescriptionrpmNo ratings yet
- Imo ACGDocument16 pagesImo ACGMiguel Ponce100% (1)
- ENG - C7 and C9 ACERTDocument59 pagesENG - C7 and C9 ACERTBeniamin Kowoll100% (1)
- Service Experience MC EnginesDocument124 pagesService Experience MC EnginesStanislav RekyvchakNo ratings yet
- Heat Power Lab Exp Even Sem 2019Document86 pagesHeat Power Lab Exp Even Sem 2019MAYUR BHOSALENo ratings yet
- Sensor Tps BoschDocument3 pagesSensor Tps BoschHarold Rojas MorenoNo ratings yet
- Amalnath V J Prasidh M S Anees A Majeed Akshay Mohan Firoz KhanDocument19 pagesAmalnath V J Prasidh M S Anees A Majeed Akshay Mohan Firoz KhanPrasidh MayyanadNo ratings yet
- Specifi: CationsDocument3 pagesSpecifi: CationsRadek BabuszkiewiczNo ratings yet
- Medidas e Torques (C15 C18)Document50 pagesMedidas e Torques (C15 C18)caiocunhaconquista100% (1)
- Machine Design - LDocument2 pagesMachine Design - LNilesh Mistry (Nilesh Sharma)No ratings yet
- Working Model of I.C. Engine Without CamDocument24 pagesWorking Model of I.C. Engine Without CamNIravNo ratings yet
- Acert Technology c9Document71 pagesAcert Technology c9eng_ebrahim_200067% (3)
- Pps 604 Audi 30l v6 Tdi Biturbo Engine EngDocument23 pagesPps 604 Audi 30l v6 Tdi Biturbo Engine EngsinisaNo ratings yet
- Bridgestone TuningDocument34 pagesBridgestone TuningJuanNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological Universityrajushamla9927No ratings yet
- Plymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceFrom EverandPlymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceNo ratings yet
- How to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheFrom EverandHow to Run a Lathe - Volume I (Edition 43) The Care and Operation of a Screw-Cutting LatheRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Changes: Ti 04-05 06 14 en-GB Technical InformationDocument3 pagesChanges: Ti 04-05 06 14 en-GB Technical InformationRuanNo ratings yet
- Ti 01-06 01 11 en Technical Information: BackgroundDocument4 pagesTi 01-06 01 11 en Technical Information: BackgroundRuanNo ratings yet
- Background Service Solution: Ti 04-11 11 21 en-GB Technical InformationDocument13 pagesBackground Service Solution: Ti 04-11 11 21 en-GB Technical InformationRuanNo ratings yet
- Leakage From The Clutch Servo: BackgroundDocument3 pagesLeakage From The Clutch Servo: BackgroundRuanNo ratings yet
- Background: Ti 04-12 09 24 en-GB Technical InformationDocument2 pagesBackground: Ti 04-12 09 24 en-GB Technical InformationRuanNo ratings yet
- Changes: Ti 01-07 02 17 en-GB Technical InformationDocument3 pagesChanges: Ti 01-07 02 17 en-GB Technical InformationRuanNo ratings yet
- Background: Ti 01-08 09 26 en-GB Technical InformationDocument2 pagesBackground: Ti 01-08 09 26 en-GB Technical InformationRuanNo ratings yet
- Tid 0002599 01Document2 pagesTid 0002599 01RuanNo ratings yet
- Background Production Solution: Ti 01-07 03 19 en Technical InformationDocument2 pagesBackground Production Solution: Ti 01-07 03 19 en Technical InformationRuanNo ratings yet
- Tid 0001678 01Document3 pagesTid 0001678 01RuanNo ratings yet
- Background: Ti 01-15 08 27 en-GB Technical InformationDocument4 pagesBackground: Ti 01-15 08 27 en-GB Technical InformationRuanNo ratings yet
- Belt Transmission Bus: Issue 1Document20 pagesBelt Transmission Bus: Issue 1RuanNo ratings yet
- Leakage at The Oil Dipstick Flange Pipe On The Cylinder BlockDocument3 pagesLeakage at The Oil Dipstick Flange Pipe On The Cylinder BlockRuanNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilation: Issue 02Document22 pagesHeating and Ventilation: Issue 02RuanNo ratings yet
- 9 Litre Engine: Issue 2Document33 pages9 Litre Engine: Issue 2RuanNo ratings yet
- Automatic Engine Oil Filler: Issue 1Document4 pagesAutomatic Engine Oil Filler: Issue 1RuanNo ratings yet
- WSM 0000323 01Document34 pagesWSM 0000323 01RuanNo ratings yet
- 9 Litre Engine: Issue 2Document33 pages9 Litre Engine: Issue 2RuanNo ratings yet
- Gas Engines OSC9 G01 and OSC11 G03: en-GBDocument36 pagesGas Engines OSC9 G01 and OSC11 G03: en-GBRuanNo ratings yet
- The Removal and Fitting of Engines in Bus F94: Issue 1Document12 pagesThe Removal and Fitting of Engines in Bus F94: Issue 1RuanNo ratings yet
- Rear View Mirror Hino: Issue 1Document8 pagesRear View Mirror Hino: Issue 1RuanNo ratings yet
- Detail C Detail A Detail B: Power, See Page 2Document2 pagesDetail C Detail A Detail B: Power, See Page 2Ruan100% (1)
- Gas Engine OC9 G02 Function and Work Description: en-GBDocument104 pagesGas Engine OC9 G02 Function and Work Description: en-GBRuanNo ratings yet
- Volkswagen Workshop Manual (6-Speed Manual Gearbox 0A8)Document210 pagesVolkswagen Workshop Manual (6-Speed Manual Gearbox 0A8)jerryalfaNo ratings yet
- Boats and BoatingDocument12 pagesBoats and BoatingMurat KayaNo ratings yet
- Trane Model CRHR-400 Physical and Electrical SpecificationsNEWDocument1 pageTrane Model CRHR-400 Physical and Electrical SpecificationsNEWalfredjajNo ratings yet
- Autobend Pacemaker Headers PDFDocument88 pagesAutobend Pacemaker Headers PDFprivate 2No ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageDatasheet PDFMie IkanNo ratings yet
- Tiger DG700 Spare Parts ManualDocument758 pagesTiger DG700 Spare Parts ManualJame SmithNo ratings yet
- Smart Transportation: Jim MisenerDocument31 pagesSmart Transportation: Jim MisenerRajatNo ratings yet
- f29723 PDFDocument134 pagesf29723 PDFClemente Rafael Marval EscalonaNo ratings yet
- RAC Project New - MergedDocument16 pagesRAC Project New - MergedJAMES BONDNo ratings yet
- 300+ TOP Automobile Engineering Multiple Choice Questions AnswersDocument27 pages300+ TOP Automobile Engineering Multiple Choice Questions Answerser9824925568100% (1)
- Engine Spare 2020Document19 pagesEngine Spare 2020Ahmad Fauzan ZenNo ratings yet
- Fgtech BDM Mpc5xx User Manual CarDocument44 pagesFgtech BDM Mpc5xx User Manual Carmiki0% (1)
- Phan 01.2 - DTC ListDocument10 pagesPhan 01.2 - DTC ListLê HảiNo ratings yet
- Model 26-26D Manual-1008Document52 pagesModel 26-26D Manual-1008ArezkiNo ratings yet
- SB SeriesDocument9 pagesSB Seriesjrincon26No ratings yet
- Data Engineering SkyAir Gas R410 PDFDocument156 pagesData Engineering SkyAir Gas R410 PDFThái Vũ LươngNo ratings yet
- Detroit Diesel Series 60 Technical Construction FileDocument127 pagesDetroit Diesel Series 60 Technical Construction FileWise SoNo ratings yet
- m90 Manual PDFDocument30 pagesm90 Manual PDFRigoberto RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Arc 2021-23 PDFDocument83 pagesArc 2021-23 PDFhamirNo ratings yet
- The Driver's Edge: Safety Inspection FormDocument1 pageThe Driver's Edge: Safety Inspection FormJHelfNo ratings yet
- Engine Lubrication System: SectionDocument17 pagesEngine Lubrication System: Section801400No ratings yet
- Camless EnginesDocument23 pagesCamless EnginesNiketh RaiNo ratings yet
- Thunderbird X 500 Spare PartsDocument16 pagesThunderbird X 500 Spare PartsArihant BothraNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - SteeringDocument276 pagesGroup 7 - SteeringEnoc Arenas100% (1)
- Maint. Instr. MF Piston 50 100 and 200 DA Pnuem ActDocument24 pagesMaint. Instr. MF Piston 50 100 and 200 DA Pnuem ActJosé Daniel ArenasNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Accident Detection and Alert SystemDocument16 pagesVehicle Accident Detection and Alert SystemvachanaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Penjualan220720Document17 pagesLaporan Penjualan220720Kemang WorkNo ratings yet
- Gas Engine Technology Course OutlineDocument2 pagesGas Engine Technology Course OutlineFrankhil Serendipity RamosNo ratings yet