Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts of Human Skin
Uploaded by
Divine SantotomeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of Human Skin
Uploaded by
Divine SantotomeCopyright:
Available Formats
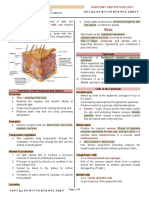
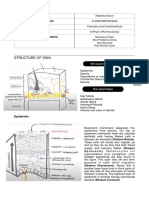
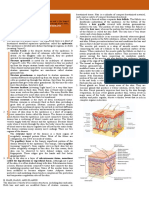
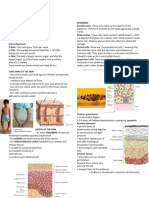
PARTS OF THE HUMAN SKIN
AND ITS FUNCTIONS
SWEAT PORE HAIR SHAFT
DERMAL PAPILLAE
It is the outer layer of skin that has
no blood vessels supply, and the
EPIDERMIS
cells in the squamous epithelium
receive blood via diffusion.
The epidermis is also responsible for
[ SEBACEOUS
the synthesis of Vitamin D under GLAND
the exposure of UV rays from the
AR MU
sunlight.
RE SC
Dermis or corium, which is the inner
DERMIS
CT LE
OR
layer of skin, is comparatively
PI
thicker than the epidermis.
LI
The blood vessels present in the
dermis provide nourishment and
(HYPODERMIS)
waste removal from its cells as well
SUBCUTIS
as from the base of the epidermis.
The hypodermis is the innermost
PACINIAN
and thickest layer of the skin
HAIR FOLLICLE CORPUSCLE
instead is the deeper subcutaneous
MEISSNER'S
tissue made of fat and connective SWEAT GLAND CORPUSCLE
tissue.
Hypodermis contains a large
amount of fat which function as HAIR FOLLICLE, ARCTOR PILI MUSCLE, SEBACEOUS GLAND, HAIR
energy storage. SHAFT
The thick layer protects the This part of the skin is strongly associated with the
external agents and also acts as an skin’s temperature regulation function.
insulator, protecting against cold. Hair Follicle- sac from which the hair grows
Arrector Pili- band of muscle tissue which connects
MAJOR LAYERS
OF the hair follicle to the dermis; when stimulated (by
THE SKIN cold or fight/ flight response), the muscle will
contract and cause the hair to become more
SWEAT PORE
SWEAT GLAND AND perpendicular to the surface.
The sweat system is strongly associated with Sebaceous Gland- empties an oily secretion called
regulating body temperature and secreting urea. sebum into the hair follicle near the surface of the
Sweat/ Apocrine gland- small tubular structures skin.
situated within and under the skin that discharge Hair shaft- is the part of your hair that can be seen
sweat through tiny openings called Sweat Pores. above your scalp. The primary purpose for this is to
Sweat- a transparent, colorless, acidic fluid with a trap a layer of air to add insulation.
peculiar odor; contains some fatty acids and mineral
matter.
NERVE FIBER, PACINIAN CORPUSCLE, MEISSRE'S CORPUSCLE
LAYERS OF THE EPIDERMES
These parts are associated with the sense of touch.
Stratum Corneum- outermost layer; composed of
Nerve fiber- the axon and/ or dendrites of a neuron.
migrated dead skin cells; filled with keratin
Meissner’s corpuscle- the ending of the neuron
Stratum lucidum- is responsible for the capability of
where a touch is detected.
the skin to stretch. -It also contains a protein that is
Pacinian corpuscle- detect gross pressure changes
responsible for the degeneration of skin cells.
and vibrations in the skin.
Stratum granulosum- help to form a waterproof
barrier that functions to prevent fluid loss from the
body
Stratum spinosum- keratinization begins here
Stratum Germinativum/ Basale- deepest and
thinnest layer of the epidermis; considered
epidermal “stem cells”
You might also like
- 5 - IntegDocument8 pages5 - IntegGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Drill String Design 4.11Document23 pagesDrill String Design 4.11Ryan Tan Ping Yi100% (1)
- A-P Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDocument19 pagesA-P Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemMONIQUE VELASCO100% (1)
- FRM Part 2 - Practice Book - Volume 2 - 2021Document146 pagesFRM Part 2 - Practice Book - Volume 2 - 2021Mridul Saraf100% (1)
- Orange BookDocument43 pagesOrange BookbiosiriNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture (Reviewer)Document4 pagesZoology Lecture (Reviewer)Maria GrasyaNo ratings yet
- African Cookbook 2nd EditionDocument144 pagesAfrican Cookbook 2nd EditionTuğçe Dinçer100% (1)
- Volume PDFDocument10 pagesVolume PDFBelon Kaler Biyru IINo ratings yet
- Virtual Certified Supplier Quality ProfessionalDocument1 pageVirtual Certified Supplier Quality ProfessionalPapaiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntegumentary System ReviewerLly Isidoro100% (2)
- Skin PDFDocument57 pagesSkin PDFravindra sharma100% (1)
- A. I. Ii. Iii.: Protection. Serving As The Covering of The Body, ItDocument9 pagesA. I. Ii. Iii.: Protection. Serving As The Covering of The Body, ItFrancis100% (1)
- The Greater Heaven Meditation - Meridian Qigong - Energy Gates QigongDocument9 pagesThe Greater Heaven Meditation - Meridian Qigong - Energy Gates Qigongspiraldao100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Stratum GerminativumChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- The Stages of Development and Developmental TasksDocument11 pagesThe Stages of Development and Developmental TasksDivine SantotomeNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Certificate en 10204Document1 pageSample Test Certificate en 10204api-3703379100% (3)
- MS Road Marking & Furniture - DRAFTDocument16 pagesMS Road Marking & Furniture - DRAFTfadhilahNo ratings yet
- PX 95 Service ManualDocument167 pagesPX 95 Service Manualidigiti100% (1)
- Anaphy MidtermsDocument28 pagesAnaphy MidtermsxeanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-NotesDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-NotesAkirah Jewelle JaenNo ratings yet
- Structure of Skin, Skin Problems, Hair Structure and Hair Growth CycleDocument8 pagesStructure of Skin, Skin Problems, Hair Structure and Hair Growth CycleRakshita GroverNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument8 pagesAnaphy ReviewerMark GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Histom 8 9 10Document5 pagesHistom 8 9 10Jehira OcampoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesIntegumentary System - Anatomy and PhysiologyHan CallejaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 1Document12 pagesIntegumentary System 1Akemi LeeNo ratings yet
- Burns SemDocument29 pagesBurns SemEsther Marie SazonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Epidermis Dermis: Stratum Corneum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Granulosum Papillary LayerDocument4 pagesIntegumentary System Epidermis Dermis: Stratum Corneum Stratum Lucidum Stratum Granulosum Papillary LayerNu Ri LeeNo ratings yet
- WEEK 5 TRANS AnaphyDocument2 pagesWEEK 5 TRANS AnaphygazzyngsalvadorNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemAliyah ZalzosNo ratings yet
- Integumentary & Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary & Skeletal SystemMaisonette MichNo ratings yet
- 176 Anatomy Integumentary SystemDocument29 pages176 Anatomy Integumentary SystemJoana Mae PortezaNo ratings yet
- Workbook Activity #13: Integumentary System (Skin) General ObjectiveDocument5 pagesWorkbook Activity #13: Integumentary System (Skin) General ObjectiveAmbaw PutiiNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Ana PhysioDocument11 pagesMODULE 4 Ana Physiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 IntegumentaryDocument2 pagesChapter 5 IntegumentaryElle UgaddanNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 & 6Document18 pagesTopic 5 & 6PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System - ANAPHYDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System - ANAPHYmariaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System of VertebratesDocument16 pagesIntegumentary System of VertebratesJamie LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Integ NotesDocument10 pagesInteg Notesannj.ras.swuNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerDocument27 pagesAnaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerFAITH EFONDONo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: (Anatomy of The Skin, Hair, and Nails)Document3 pagesThe Integumentary System: (Anatomy of The Skin, Hair, and Nails)Venus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System NotesDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System NotesDale Gil JuliaNo ratings yet
- The Skin (Anaphy)Document2 pagesThe Skin (Anaphy)ALEXANDRA COLLEEN ALEGRENo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Integumentary SystemChristine Joy MadronioNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Reviewer PDF Skin Nail (Anatomy) 2Document1 pageIntegumentary System Reviewer PDF Skin Nail (Anatomy) 2Shiem TrabocNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - The Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesLesson 3 - The Integumentary SystemJoseayn EspenidoNo ratings yet
- Cells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDocument5 pagesCells Are Scattered Around: Pigment That Affords The Skin Some Protection Against Ultraviolet RadiationDimple Lexiry GloriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary SystemJade Karen Lingo-lingoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument10 pagesIntegumentary SystemBago CPSNo ratings yet
- Integument System ActivityDocument5 pagesIntegument System ActivityeywatsarawatNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System TransesDocument5 pagesIntegumentary System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- 5 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pages5 Integumentary SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesIntegumentary SystemCelyn DeañoNo ratings yet
- Integ PPT BasedDocument12 pagesInteg PPT BasedKathleen BalauagNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument49 pagesIntegumentary SystemCUEVA Cristine JaneNo ratings yet
- Body MembranesDocument10 pagesBody MembranesCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesIntegumentary SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Fapc 111Document12 pagesIntegumentary System Fapc 111Marquisha Fiona De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Diseases of The Skin: M. Angelica Selim, M.D. Dermatopathology Unit Pathology DepartmentDocument53 pagesInflammatory Diseases of The Skin: M. Angelica Selim, M.D. Dermatopathology Unit Pathology DepartmentIsaac MaderoNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Diseases of The Skin: M. Angelica Selim, M.D. Dermatopathology Unit Pathology DepartmentDocument53 pagesInflammatory Diseases of The Skin: M. Angelica Selim, M.D. Dermatopathology Unit Pathology DepartmentDr Jyotiprakash ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyFaithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary SystemCriscia Lene OlatNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Integumentary System 1Document5 pagesAnaphy Integumentary System 1xz598vbhjnNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary Report FinalDocument28 pagesThe Integumentary Report FinalTrizza VelosoNo ratings yet
- Integumantory System NoteDocument24 pagesIntegumantory System Notezekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Document4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology With Pathophysiology Lecture (Midterms)Millen ArenasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document30 pagesLecture 1Dr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 - Integumentary System (Review Material)Document13 pagesGROUP 1 - Integumentary System (Review Material)SALGIE SERNALNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System IncludesDocument29 pagesIntegumentary System IncludesRhena TogoresNo ratings yet
- Angee 11Document4 pagesAngee 11lunadawsonesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MusicDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MusicDivine SantotomeNo ratings yet
- Noble ProfessionDocument5 pagesNoble ProfessionDivine SantotomeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDivine SantotomeNo ratings yet
- How Will You Make Your Own QR Code?: Here's All You Need To Do!Document1 pageHow Will You Make Your Own QR Code?: Here's All You Need To Do!Divine SantotomeNo ratings yet
- Concept of Individual DifferencesDocument1 pageConcept of Individual DifferencesDivine SantotomeNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Human SkinDocument1 pageParts and Functions of Human SkinDivine SantotomeNo ratings yet
- Surigao Del Sur Tourist SpotDocument12 pagesSurigao Del Sur Tourist SpotDivine SantotomeNo ratings yet
- Trial 2017 MRSM p3 Answer Scheme BioDocument9 pagesTrial 2017 MRSM p3 Answer Scheme Biolittle princessNo ratings yet
- Stuffed PeppersDocument2 pagesStuffed PeppersDewayne AginNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Clinical Prep SheetDocument3 pagesPostpartum Clinical Prep SheetKurata432No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Test Bank PDFDocument20 pagesDwnload Full Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Test Bank PDFamess.trias.xpuax100% (13)
- Nestle Project AssignmentDocument21 pagesNestle Project AssignmentAwais AfzalNo ratings yet
- The Status Quo of Children On The Global SceneDocument8 pagesThe Status Quo of Children On The Global SceneAruuka SerikbayNo ratings yet
- Insanity Workout Deluxe Calendar SimpleDocument1 pageInsanity Workout Deluxe Calendar SimpleCristian Manuel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Suicide by Firearm Toolkit For ChangeDocument28 pagesSuicide by Firearm Toolkit For ChangeSara WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Polish Recipe PDFDocument3 pagesPolish Recipe PDFfoodprinteuNo ratings yet
- The Following Provisional Lis of Students Are Eligible For Under TakingDocument2 pagesThe Following Provisional Lis of Students Are Eligible For Under TakingRäHùl KãshèttíNo ratings yet
- DDC SVC Bro 0002Document35 pagesDDC SVC Bro 0002SonthiMNo ratings yet
- Convergent Plate BoundariesDocument45 pagesConvergent Plate Boundariesjherwinperez2007No ratings yet
- Tycab Cable Ties CatalogueDocument2 pagesTycab Cable Ties CataloguesaravanakumarNo ratings yet
- NTE121 Germanium PNP Transistor Audio Frequency Power AmplifierDocument2 pagesNTE121 Germanium PNP Transistor Audio Frequency Power AmplifierDabro FabioNo ratings yet
- Suzuki 2017 Genuine Rigging Parts and AccessoriesDocument29 pagesSuzuki 2017 Genuine Rigging Parts and AccessoriesJose Luis HuilaNo ratings yet
- Your Booking at The Westin Chennai Velachery Is Confirmed!Document3 pagesYour Booking at The Westin Chennai Velachery Is Confirmed!Siddharth SwainNo ratings yet
- Crustaceans: Distinguishing Characteristics of CrustaceaDocument11 pagesCrustaceans: Distinguishing Characteristics of CrustaceamushfiqurNo ratings yet
- Sogang KLEC - Confirmation For Self-Quarantine Location - ENGDocument1 pageSogang KLEC - Confirmation For Self-Quarantine Location - ENGAlive StillNo ratings yet
- P.E.S. Pu CollegeDocument6 pagesP.E.S. Pu CollegeSamrudh BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet - Fresh Water Pump PDFDocument8 pagesDatasheet - Fresh Water Pump PDFalliancemarine2011No ratings yet