Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 25 Jul 2022
Uploaded by
Sunny KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 25 Jul 2022
Uploaded by
Sunny KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
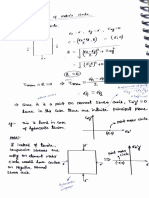
WATER REQUIREMENTS OF CROPSs 33
where D mean depth of water stored in the r0ot
Zone
1.7 1. 1.4m
2
1 8 computed as below
Deviation from the mean at upper end (absolute value)
1.7 1.4 -0.3
Deviation from the mean at lower end 1 . 1 -1.4 = 0.3.
d Average of the absolute values of devia-
0.3 +0.3
tions from mean 30.
2
U'sing Eq. (2.3), we have, n -1 0.30 0.786 or 78.6% Ans.
1.4
8. Consumptive Use or Evapotranspiration ( )
Consumptive use for a particular crop may be defined as the total amount of
water used by the plants in transpiration (building of plant tissues, etc.) and
evaporation from adjacent soils, in any specified time. The values of consumptive
use (C) may be different for different crops, and may be different for the same
crop at different times and places.
In
fact, the consumptive use for a given crop at a given place
throughout the day, throughout the month and throughout the crop period. Values
may vary
ofdaily consumptive use or monthly consumptive use, are generally determined
for a given crop and at a given place. Values of monthly consumptive use over the
entire cropP period, are then used to determine the irrigation requirement of the
crop.
2.8.1. Transpiration. The Consumptive use* or Evapotranspiration (Cu), as
stated above, infact, is the combined measure
of transpiration loss (transpiration)
and the
evaporation lost from the soil body* surrounding the plant.
The transpiration is defined as the
process by which the water leaves a living
plant during photosynthis, through its leaves, to enter
the atmosphere as water vapour.
Transpiration, infact, occurs, when the plant manufactures carbohydrates for its
growth, by the process of photosynthesis. What actually happens is, that the water
extracted by the plant-root system from the soil, is transferred to the plant leaves; and
the surface of each
on
plant leaf, photosynthesis occurs, where the air enters the stomata
openings in the leaf surface, and the chloroplasts within the leaf utilise carbon dioxide
trom the air along with a very very small portion of the available moisture, to manutac-
ture
carbohydrates.As air enters the leaf, the water escapes through the stomata, and
8
evaporated lost) the atmosphere. It should be understood that transpiration oceurs
to
during photosynthesis, which usually occurs during the sun-light; and hence, most of
te transpiration will oxcur during the day light hours. So much so that about 95% of
the total
transpiration occurs during the day time alone.
On
the otler hand, tihe evapuration continues throughout the day aand night,
although its rate may be ditferent. Moreover, the transpirati0n loss, not only
depends upon the avalable sun ight, but also upon tie available moisture, since
Strictly speakng, the consunptive use may be defined as the amount of water used in the
evapotranspiratinn from an area under vegetaton, plus the water used by the plants in their
etabolic process for building of plant issues. Since the quantity of water used in metabolie
process is insignificant compared to evapotranspiration, the terms 'consumptive use (C and
ebapotranspiration (E) are consulered as one andl the same thing.
This also includes the water body, when plants grow within a water body.
You might also like
- Crop Water Requirements 2n3Document48 pagesCrop Water Requirements 2n3IrfanButtNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Crop Water Requirements: 3.1 Evapotranspiration ProcessDocument27 pagesChapter-3: Crop Water Requirements: 3.1 Evapotranspiration ProcessKuba100% (1)
- MGV Drainage DesignDocument19 pagesMGV Drainage Designewanz89No ratings yet
- Soil and Water Conservation: Free E-BookDocument12 pagesSoil and Water Conservation: Free E-BookPrasun KumarNo ratings yet
- EvapDocument10 pagesEvapPaucar M. ELioNo ratings yet
- MeteorologicalTechnologyInternational Sept2011Document122 pagesMeteorologicalTechnologyInternational Sept2011Sophie PeyridieuNo ratings yet
- Hydrology Conventional Problems PyqDocument25 pagesHydrology Conventional Problems PyqSunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three 3. Crop Water RequirementsDocument32 pagesChapter Three 3. Crop Water RequirementsbulchaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 CWR (Updated)Document35 pagesChapter - 3 CWR (Updated)Aboody AbdulselamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Evaporation, Transpiration & Infiltration: BFC 32002 HydrologyDocument51 pagesChapter 3. Evaporation, Transpiration & Infiltration: BFC 32002 HydrologyAsyiqindiniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (CWR)Document35 pagesChapter 3 (CWR)Reffisa JiruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (CWR)Document37 pagesChapter 3 (CWR)Mūssā Mūhābā ZēĒthiopiāNo ratings yet
- LEC# 3 (Chapter 2, Text) : Crop Water Requirements (CWR)Document44 pagesLEC# 3 (Chapter 2, Text) : Crop Water Requirements (CWR)naeem ullahNo ratings yet
- Lec#3-Crop Water RequirementDocument44 pagesLec#3-Crop Water RequirementZain50% (2)
- What Is Irrigation?Document41 pagesWhat Is Irrigation?AMOS KAYODENo ratings yet
- Week8 IE LDocument19 pagesWeek8 IE LFaris AhmadNo ratings yet
- Consumptive Use of Water: Chapter - 7Document13 pagesConsumptive Use of Water: Chapter - 7Arnab MondalNo ratings yet
- EECF - 3142 - IWR-Crop Water Requirement - UpdatedDocument24 pagesEECF - 3142 - IWR-Crop Water Requirement - UpdatedCaroline MuthoniNo ratings yet
- Determination of Reference Evapotranspiration - EtoDocument25 pagesDetermination of Reference Evapotranspiration - Etodisasa abebeNo ratings yet
- Ssss Hydro Geo Chapter TwoDocument9 pagesSsss Hydro Geo Chapter Twobatamo doleboNo ratings yet
- Measure and Apply Irrigation Water ClassDocument20 pagesMeasure and Apply Irrigation Water Classmerga abdetaNo ratings yet
- Wmo Chapter10 EvaporationDocument10 pagesWmo Chapter10 EvaporationZulkifli Yasin HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 Sprinkler EkitDocument17 pagesLab 7 Sprinkler EkitRuby Ekit100% (1)
- Transpiration & Evapotranspiration: Presented By: Loren, Shahaina TuaineDocument28 pagesTranspiration & Evapotranspiration: Presented By: Loren, Shahaina TuaineHarvey JamesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document17 pagesChapter 4kidus sileshNo ratings yet
- Toic 5 HYDROLOGY - LLANODocument9 pagesToic 5 HYDROLOGY - LLANOMang KanorNo ratings yet
- EvaporationDocument41 pagesEvaporationGoodluck NyagybNo ratings yet
- ETassinmDocument16 pagesETassinmHundesaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3ananiya dawitNo ratings yet
- Consumptive Use and Estimation of Irrigation Water RequirementDocument8 pagesConsumptive Use and Estimation of Irrigation Water RequirementQushik Ahmed ApuNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Cropwater RequirmentDocument66 pagesChapter - 3: Cropwater Requirmentbini1221No ratings yet
- WMO8 Ed2008 PartI Ch10 Up2010 enDocument10 pagesWMO8 Ed2008 PartI Ch10 Up2010 enAlex GomezNo ratings yet
- Hafta.Document26 pagesHafta.raiden timberlandNo ratings yet
- HWRE Unit 2 EvapotranspirationDocument14 pagesHWRE Unit 2 EvapotranspirationYerukala MadhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CWRDocument38 pagesChapter 3 CWRTekalegn DemsisNo ratings yet
- EH Lec - 7Document8 pagesEH Lec - 7Arsalan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3Gauravtripathi858No ratings yet
- Chapter 3, Soil-Plant - Water RelationshipDocument27 pagesChapter 3, Soil-Plant - Water RelationshipMelesse ShewaferaNo ratings yet
- EAB2301 Note 2-Crops Water Requirement Soil MoistureDocument25 pagesEAB2301 Note 2-Crops Water Requirement Soil MoistureKarolina DermawanNo ratings yet
- V. Chanka PotometerDocument4 pagesV. Chanka PotometervasuNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Crop Water RequirementDocument6 pages1.3 Crop Water RequirementgaspardalvinoNo ratings yet
- Hydrology 2Document31 pagesHydrology 2Kaye TrishaNo ratings yet
- Crop Water RequirementsDocument60 pagesCrop Water RequirementsNaeem Ul HussnainNo ratings yet
- Crop Water Requirements 2n3Document44 pagesCrop Water Requirements 2n3Muhammad Usman100% (2)
- CH 1 Irrigation 2017 2018Document28 pagesCH 1 Irrigation 2017 2018Ahmed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Evapotranspiration: Objectives: To Define The Term Evapotranspiration' To Know How To Measure EvapotranspirationDocument1 pageEvapotranspiration: Objectives: To Define The Term Evapotranspiration' To Know How To Measure EvapotranspirationEkala XuhalxNo ratings yet
- Hydrology and Irrigation Engineering - 15CV73: VII SemesterDocument21 pagesHydrology and Irrigation Engineering - 15CV73: VII SemesterShriNo ratings yet
- Hydrology and Irrigation Engineering - 15CV73: VII SemesterDocument21 pagesHydrology and Irrigation Engineering - 15CV73: VII SemesterShriNo ratings yet
- Keller KarmeliDocument7 pagesKeller KarmeliGustavo Haddad Souza VieiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five LatestDocument14 pagesChapter Five LatestHussen MohammedNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGY AND WATER QUALITY CONTROL FirstDocument7 pagesHYDROLOGY AND WATER QUALITY CONTROL FirstAljon LanguingNo ratings yet
- Evapotranspiration: University of Southeastern Philippines Bo. Obrero, Davao CityDocument13 pagesEvapotranspiration: University of Southeastern Philippines Bo. Obrero, Davao CityJC AsisNo ratings yet
- Water Requirement of CropsDocument5 pagesWater Requirement of CropsShahid RøckzzNo ratings yet
- 1.5.4 Abiotic FactorsDocument59 pages1.5.4 Abiotic FactorsKai Ling PhonNo ratings yet
- Manual Nuevo de Puertas AutomaticasDocument69 pagesManual Nuevo de Puertas AutomaticasANDRESDILORENZINo ratings yet
- Garnier and Berger1986. Effect of Water Stress On Stem Diameter Changes of PeachDocument18 pagesGarnier and Berger1986. Effect of Water Stress On Stem Diameter Changes of PeachElla MoNo ratings yet
- HYDROLOGYDocument4 pagesHYDROLOGYferrerjohnford213No ratings yet
- Ijmqe 151020Document8 pagesIjmqe 151020Boutheina DouhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Crop Water RequirementsDocument21 pagesChapter 3 Crop Water RequirementsabdulazizNo ratings yet
- Eva Po TranspirationDocument16 pagesEva Po TranspirationJanineRianneBagsicNo ratings yet
- Covenant University: Surface & Groundwater HydrologyDocument25 pagesCovenant University: Surface & Groundwater HydrologyOlawuyi OluwatamiloreNo ratings yet
- Crop Water Requirment (CWR) : Chapter ThreeDocument60 pagesCrop Water Requirment (CWR) : Chapter ThreeAbra SemenehNo ratings yet
- Irrigation EfficienciesDocument21 pagesIrrigation EfficienciesHeleana Faye BundocNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Jul 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 25 Jul 2022Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Aug 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Aug 2022Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 09 Sep 2021Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 09 Sep 2021Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Mar 2022Document19 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Mar 2022Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 03 Jun 2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 03 Jun 2022Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Mar 2022Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Mar 2022Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Water Supply 1-10Document10 pagesWater Supply 1-10Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 01 Mar 2022Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 01 Mar 2022Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Highway 1 13Document13 pagesHighway 1 13Sunny KumarNo ratings yet
- CPM PertDocument7 pagesCPM PertSunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Water Resources of Karnataka - PPT 2Document215 pagesWater Resources of Karnataka - PPT 2lokhande_rajuNo ratings yet
- Australianhandbook of Stream Roughness CoefficientsDocument28 pagesAustralianhandbook of Stream Roughness CoefficientsAnonymous 1n5HpBjNo ratings yet
- Watershed Management Case StudyDocument43 pagesWatershed Management Case StudyJabeenunisa INo ratings yet
- Reading - GK 1 - 10Document13 pagesReading - GK 1 - 10Ngô Hiểu NhiênNo ratings yet
- R10 Climate ChangeDocument7 pagesR10 Climate ChangeAngelica AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Indian Geography Questions With Answers: en Savoir Plus OKDocument6 pagesTop 100 Indian Geography Questions With Answers: en Savoir Plus OKAkash KotaNo ratings yet
- North America PhysicalDocument13 pagesNorth America PhysicalegalNo ratings yet
- DPPM Unit V Ques & AnsDocument6 pagesDPPM Unit V Ques & AnsVamshi TangelapallyNo ratings yet
- Ielts Academic Reading Practice Test 1 4076721935Document3 pagesIelts Academic Reading Practice Test 1 4076721935Lol LolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Hanna JbrNo ratings yet
- Humidity Measurements PDFDocument45 pagesHumidity Measurements PDFThesisNo ratings yet
- Methods of Design Flood ComputationDocument13 pagesMethods of Design Flood ComputationAaron Ongsitco Escosio100% (1)
- Ifeolwapo: MoladeDocument6 pagesIfeolwapo: MoladeIfe KoladeNo ratings yet
- Science of The Total Environment: Farhad Misaghi, Fatemeh Delgosha, Mostafa Razzaghmanesh, Baden MyersDocument10 pagesScience of The Total Environment: Farhad Misaghi, Fatemeh Delgosha, Mostafa Razzaghmanesh, Baden Myersmahdi najafzadehNo ratings yet
- The Hydrological CycleDocument6 pagesThe Hydrological CycleF A L L E NNo ratings yet
- Climate QUESTION AND ANSWERSDocument5 pagesClimate QUESTION AND ANSWERSAlex KavalakattNo ratings yet
- How Does El Ni ̃no Southern Oscillation Affect Rice-ProducingDocument14 pagesHow Does El Ni ̃no Southern Oscillation Affect Rice-Producingdaniela cristanchoNo ratings yet
- NO. Judul Shop Drawing STATUS Diajukan Tanggal Aproval Nomor Shop DrawingDocument34 pagesNO. Judul Shop Drawing STATUS Diajukan Tanggal Aproval Nomor Shop DrawingAhmadNo ratings yet
- Guwahati Geographuy PDFDocument13 pagesGuwahati Geographuy PDFMridul BarmanNo ratings yet
- Hydrographic Surveys: 130390106054 - Darshan Shah 130390106053 - Bhavik Shah 130390106050 - Nakul RavalDocument52 pagesHydrographic Surveys: 130390106054 - Darshan Shah 130390106053 - Bhavik Shah 130390106050 - Nakul Ravalbehzad parsiNo ratings yet
- Monsoons and ITCZ: The Philippine Weather SystemDocument16 pagesMonsoons and ITCZ: The Philippine Weather SystemDog GodNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 2Document3 pagesAssignment # 2faizanNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Geography Africa PDFDocument7 pagesKnowledge Geography Africa PDFOliver SansumNo ratings yet
- Cloud Formation PDFDocument7 pagesCloud Formation PDFAdonisNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade 5 ScienceDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Grade 5 ScienceJennifer Jorge AquinoNo ratings yet
- Integrated Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System Based RUSLE Modelling For Estimation of Soil Loss in Western Himalaya - IndiaDocument11 pagesIntegrated Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System Based RUSLE Modelling For Estimation of Soil Loss in Western Himalaya - IndiajoseapbNo ratings yet
- Soil Components and Soil ProfileDocument4 pagesSoil Components and Soil ProfilemramagroNo ratings yet