Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beams May Sulat
Uploaded by
RonnieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beams May Sulat
Uploaded by
RonnieCopyright:
Available Formats
19.
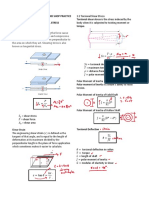
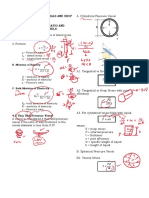
Beams
Beam. A structural member which is
subjected to loads acting transversely to
its longitudinal axis.
Types of Beams:
1. Simple beam
2. Cantilever beam
3. Overhanging beam
4. Fixed beam
5. Continuous beam
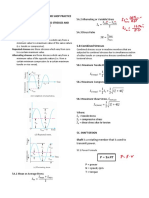
Reaction/Shear:
𝑅=𝑉=𝑃
Maximum Moment (At Fixed End)
𝑀 = 𝑃𝐿
Maximum Deflection (At Free End)
𝑃𝐿3
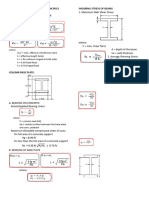
1. Simple Beam. A beam supported at 𝛿=
3𝐸𝐼
both outer ends.
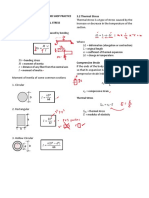
3. Fixed Beams
Reaction/Shear:
𝑃
𝑅=𝑉=
2
Reaction/Shear:
Maximum Moment (At Center and Ends)
𝑃
𝑅=𝑉= 𝑃𝐿
2 𝑀=
8
Maximum Moment (At point of Load)
Maximum Deflection (At center)
𝑃𝐿
𝑀= 𝑃𝐿3
4 𝛿=
192𝐸𝐼
Maximum Deflection (At point of Load)
Solving for Reactions:
3
𝑃𝐿 A. Summation of Forces vertical is zero.
𝛿=
48𝐸𝐼 Σ𝐹𝑉 = 0
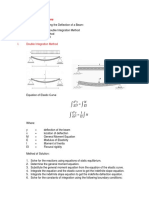
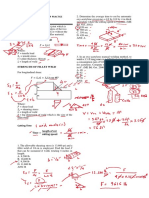
2. Cantilever Beam. A beam which is B. Summation of moments at a point
anywhere in the beam is zero.
completely supported at one end by being
framed into a solid wall.
Σ𝑀𝐴 = 0 Σ𝑀𝐵 = 0
Shear and Moment:
1. SHEAR at any point on the beam is
equal to the summation of all the forces
on the left side of the point. Refer to the
load Diagram.
2. MOMENT at any point on the beam is
equal to the summation of all the
moments on the left side of the point on
the beam. Refer to the Shear Diagram.
Example:
1. A simple supported beam of length 8m
carries point loads of 4 kN and 6 kN at a
distance of 2m and 4m from the left end.
Calculate the maximum moment.
A. 20 kNm
B. 16 kNm
C. 12 kNm
D. 24 kNm
ANS: B
2. A cantilever beam of length 2m carries
a distributed load of 3 kN/m over a
length of 1m from the fixed end.
Calculate the maximum moment.
A. 1.5 kNm
B. 3 kNm
C. 6 kNm
D. 4.5 kNm
ANS: A
3. A fixed beam AB, 6m long is carrying a
point load of 50 kN at its center. The
amount of inertia of the beam is 78 x 106
mm4 and the value of E for the beam
material is 2.1 x 105 N/mm2.
Find the maximum deflection.
A. 2.18 mm
B. 4.57 mm
C. 6.75 mm
D. 3.43 mm
ANS: D
You might also like
- TOS 3 Unit 1 Fixed Beams & Continuous Beams and TorsionDocument19 pagesTOS 3 Unit 1 Fixed Beams & Continuous Beams and TorsionKrushna100% (1)
- Unit 3: Longitudinal Direct Bending Stresses in Beams: Eng. Strength of Materials Iii (Mst31A)Document31 pagesUnit 3: Longitudinal Direct Bending Stresses in Beams: Eng. Strength of Materials Iii (Mst31A)Tony NgoneloNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Basics and Formulae - Vijay SirDocument26 pagesMachine Design Basics and Formulae - Vijay SirAnirudhgandhi RavipalliNo ratings yet
- Tos 3Document126 pagesTos 3RIYA AhujaNo ratings yet
- Tos 3: Unit 1: Fixed & Continuous Beams and Effects of TorsionDocument19 pagesTos 3: Unit 1: Fixed & Continuous Beams and Effects of TorsionAftab HawaldarNo ratings yet
- PME9 Engineering-MechanicsDocument13 pagesPME9 Engineering-MechanicsKAL ELNo ratings yet
- Sec Module 02Document15 pagesSec Module 02kenji belanizo0% (1)
- Strength of Materials: Machine Design 1Document28 pagesStrength of Materials: Machine Design 1John ReyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 C1 ArchDocument28 pagesLesson 5 C1 Archazerai2000No ratings yet
- Bending Deformation, Strain and Stress in BeamsDocument21 pagesBending Deformation, Strain and Stress in BeamsWolelaw FikaduNo ratings yet
- Beam Horizontal Structral MemberDocument47 pagesBeam Horizontal Structral MemberTemoor AbbasNo ratings yet
- Tos Notes 1,2,3Document13 pagesTos Notes 1,2,3Star Youtuber Prashant100% (1)
- Unit 3a Spanning Members - Beams - Bending StressesDocument10 pagesUnit 3a Spanning Members - Beams - Bending StressesTanvi KhochareNo ratings yet
- Section 3,4: Bending Deformation, Strain and Stress in BeamsDocument20 pagesSection 3,4: Bending Deformation, Strain and Stress in BeamsRasool AkhterianNo ratings yet
- Physics InterferenceDocument23 pagesPhysics InterferencechutiyaaaNo ratings yet
- TOS 22402 Winter 19th I SCHEME Paper Model Answer PaperDocument25 pagesTOS 22402 Winter 19th I SCHEME Paper Model Answer Paperirshadmirza753No ratings yet
- Section 3,4: Bending Deformation, Strain and Stress in BeamsDocument20 pagesSection 3,4: Bending Deformation, Strain and Stress in BeamsRasool AkhterianNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2: Shear and Bending in BeamsDocument37 pagesUnit - 2: Shear and Bending in BeamsRobert DownieNo ratings yet
- Radiation Pattern: Antenna and Wave PropagationDocument8 pagesRadiation Pattern: Antenna and Wave Propagationabdulla qaisNo ratings yet
- Strength 4 May 2021Document3 pagesStrength 4 May 2021Jon SnowNo ratings yet
- MOS-2 MarksDocument18 pagesMOS-2 MarksGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials FormulasDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials FormulasDeo WarrenNo ratings yet
- Conjugate Beam MethodDocument3 pagesConjugate Beam MethodBlessy Marie SottoNo ratings yet
- BEEE NotesDocument367 pagesBEEE NotesCyril Robinson Azariah JCNo ratings yet
- Tos1 MidtermDocument2 pagesTos1 MidtermMa.Zyra M. DascoNo ratings yet
- Stresses in BeamsDocument1 pageStresses in BeamsJulie Ann MontalbanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Shear and Moment in Determinate BeamsDocument13 pagesModule 2 Shear and Moment in Determinate Beamsatingelaay YNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Shear and Moment in Determinate BeamsDocument13 pagesModule 2 Shear and Moment in Determinate BeamsshnslaveNo ratings yet
- 2018-Me-184 MMDocument28 pages2018-Me-184 MMKhizer Nauman RanaNo ratings yet
- Bending Test - 060103Document8 pagesBending Test - 060103CE 19 Kaushlendra KumarNo ratings yet
- IB Phys GNTP C.4 Standing Waves and ResonanceDocument9 pagesIB Phys GNTP C.4 Standing Waves and Resonancea20142174No ratings yet
- Scheme of Valuation JUNE-2019 PHYSICS (33) Q.NO. Value Points Part-ADocument11 pagesScheme of Valuation JUNE-2019 PHYSICS (33) Q.NO. Value Points Part-ANaruto tvNo ratings yet
- Shear and Torsional Stress 2022 May Sulat2xDocument2 pagesShear and Torsional Stress 2022 May Sulat2xRonnieNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Les #11 Influence Line - ApplicationDocument4 pagesModule 1 - Les #11 Influence Line - Applicationcutie4everrNo ratings yet
- Timber Design Values 1Document14 pagesTimber Design Values 1Sharlette SaulNo ratings yet
- 00 Unit I Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Vibrations StudentDocument21 pages00 Unit I Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Vibrations StudentKanishk MehtaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structures - II 2 Mark by Nambi RajanDocument10 pagesAircraft Structures - II 2 Mark by Nambi RajanNambi RajanNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Stresses & Strains PDFDocument48 pages1.introduction To Stresses & Strains PDFErNo ratings yet
- Lesson4 BeamDeflectionsDocument6 pagesLesson4 BeamDeflectionsMikeNo ratings yet
- 3.shear Force and Bending Moment - For LectureDocument109 pages3.shear Force and Bending Moment - For LectureArpit GondaliyaNo ratings yet
- Force Area 2Document10 pagesForce Area 2RajeswariSathishNo ratings yet
- SCIA1401Document140 pagesSCIA1401Wadi SharanNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures Part I HandoutDocument6 pagesTheory of Structures Part I HandoutRaymund PertudoNo ratings yet
- Stress (Normal)Document2 pagesStress (Normal)kmscoachNo ratings yet
- Designs of Beams: Laterally Supported BeamDocument4 pagesDesigns of Beams: Laterally Supported BeamAppoch Kaye RolloqueNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Material PropertiesDocument28 pagesLecture 3 - Material PropertiesJay VeeNo ratings yet
- Exp # 04Document8 pagesExp # 04Savaiz HannanNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Part 2Document22 pagesElectricity - Part 2Anonymous CommentatorNo ratings yet
- ES 13 - 3rd Long Exam CoverageDocument7 pagesES 13 - 3rd Long Exam CoverageMaj DelfinNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument3 pagesStrength of MaterialspaoloNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument15 pagesNOTESMar Jhon Paulo MojicaNo ratings yet
- Steel Design Formulas and Principles - CompressDocument6 pagesSteel Design Formulas and Principles - CompressClint SusarnoNo ratings yet
- Review of Deflections of Structures: Ceng 141Document34 pagesReview of Deflections of Structures: Ceng 141Marcelo AbreraNo ratings yet
- To Determine Central Deflection of Simply Supported Beam by A Concentrated Load at The MidDocument4 pagesTo Determine Central Deflection of Simply Supported Beam by A Concentrated Load at The MidzainNo ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 6Document55 pages02 Chapter 6Abdul Rafay Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Stress and Deformation AnalysisDocument64 pagesStress and Deformation AnalysisSara Ben AmaraNo ratings yet
- Laser Diffraction and InterferenceDocument7 pagesLaser Diffraction and Interferencesamantha rathNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Flywheels May SulatDocument3 pagesFlywheels May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Welded Joints and Shop Practice May SulatDocument1 pageWelded Joints and Shop Practice May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Clutches 2022 May SulatDocument3 pagesClutches 2022 May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Columns 2022 May SulatDocument2 pagesColumns 2022 May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Brakes May SulatDocument2 pagesBrakes May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Wire Ropes May SulatDocument3 pagesWire Ropes May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Helical GearsDocument2 pagesHelical GearsRonnieNo ratings yet
- Helical Gears May SulatDocument2 pagesHelical Gears May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Worm Gears May SulatDocument3 pagesWorm Gears May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Worm GearsDocument3 pagesWorm GearsRonnieNo ratings yet
- Bevel GearsDocument2 pagesBevel GearsRonnieNo ratings yet
- THERMO 2 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY 2022 W - SolutionsDocument6 pagesTHERMO 2 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY 2022 W - SolutionsRonnieNo ratings yet
- Bevel Gears May SulatDocument2 pagesBevel Gears May SulatRonnieNo ratings yet
- Wire RopesDocument3 pagesWire RopesRonnieNo ratings yet
- THERMO 4 PROCESSES OF IDEAL GAS 2022 NewDocument12 pagesTHERMO 4 PROCESSES OF IDEAL GAS 2022 NewRonnieNo ratings yet
- REFRIGERATIONDocument5 pagesREFRIGERATIONRonnieNo ratings yet
- Thermo 1 Basic Concepts 2022 W SolutionsDocument9 pagesThermo 1 Basic Concepts 2022 W SolutionsRonnieNo ratings yet
- Gas Cycle 1 Carnot CycleDocument3 pagesGas Cycle 1 Carnot CycleRonnieNo ratings yet
- Gas Cycle 2 Otto CycleDocument3 pagesGas Cycle 2 Otto CycleRonnieNo ratings yet
- Gas Cycle 3 Diesel CycleDocument3 pagesGas Cycle 3 Diesel CycleRonnieNo ratings yet
- THERMO 4 PROCESSES OF IDEAL GAS 2022 NewDocument12 pagesTHERMO 4 PROCESSES OF IDEAL GAS 2022 NewRonnieNo ratings yet
- Thermo 3 Ideal Gas 2022 OnlineDocument4 pagesThermo 3 Ideal Gas 2022 OnlineRonnieNo ratings yet
- Engineering EconomyDocument6 pagesEngineering EconomyRonnieNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument12 pagesHeat TransferRonnieNo ratings yet
- Keys Splines and Couplings May Sulat2xDocument3 pagesKeys Splines and Couplings May Sulat2xRonnieNo ratings yet
- Variable Combined Stresses and Shaft Design 2022 May Sula2xDocument4 pagesVariable Combined Stresses and Shaft Design 2022 May Sula2xRonnieNo ratings yet
- Poissons Ratio Pressure Vessels 2022 May Sulat2xDocument3 pagesPoissons Ratio Pressure Vessels 2022 May Sulat2xRonnieNo ratings yet
- Shear and Torsional Stress 2022 May Sulat2xDocument2 pagesShear and Torsional Stress 2022 May Sulat2xRonnieNo ratings yet
- Bending and Thermal Stress 2022 May Sulat2xDocument2 pagesBending and Thermal Stress 2022 May Sulat2xRonnieNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-1Document166 pagesMechanics of Materials-1Eemesh NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document49 pagesChapter 5ISRAEL HAILUNo ratings yet
- GCV401 - Structural Analysis - Chapter IV - Internal Loadings Developed in Structural MembersDocument11 pagesGCV401 - Structural Analysis - Chapter IV - Internal Loadings Developed in Structural MembersOec EngNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem No. 5 Sample Problem No. 6Document2 pagesSample Problem No. 5 Sample Problem No. 6MelvinGutierrezSingayanNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology-NagpurDocument6 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology-NagpurNikhil MulikNo ratings yet
- Eng. 6002 Ship Structures 1 Hull Girder Response Analysis: Lecture 7: Review of Beam TheoryDocument21 pagesEng. 6002 Ship Structures 1 Hull Girder Response Analysis: Lecture 7: Review of Beam TheorybalsamNo ratings yet
- Engr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDocument30 pagesEngr. Yoshiaki C. Mikami, Bsce Msce-Ste RMP: Prepared byDenzel NgNo ratings yet
- Shear and Moment Diagrams For Frames Shear and Moment Diagrams For FramesDocument5 pagesShear and Moment Diagrams For Frames Shear and Moment Diagrams For FramesYurene HornaNo ratings yet
- ENS 161 - Statics of Rigid Bodies: Lesson 8: Internal ForcesDocument38 pagesENS 161 - Statics of Rigid Bodies: Lesson 8: Internal ForcesHamghad LambasNo ratings yet
- TOS 1-Internal Loadings Developed in Structural MembersDocument3 pagesTOS 1-Internal Loadings Developed in Structural MembersAndrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Problems On SFD and BMD On Beams With Point LoadsDocument33 pagesLecture 8 Problems On SFD and BMD On Beams With Point Loadsshaheer asifNo ratings yet
- 1.0 The Use of Midas Software in Teaching Ce CoursesDocument34 pages1.0 The Use of Midas Software in Teaching Ce CoursesJake CortezNo ratings yet
- AWC Beam FormulasDocument26 pagesAWC Beam FormulasR ASTUSNo ratings yet
- Shear and Moment Diagrams On FramesDocument22 pagesShear and Moment Diagrams On FramesRonald Llemit TominesNo ratings yet
- CE 151 Chapter 5 Lecture NotesDocument37 pagesCE 151 Chapter 5 Lecture NotesNAJEB PENDIAMANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document78 pagesChapter 04Bikash Chandra DasNo ratings yet
- CE70-Structural Theory: Analysis of Statically Determinate StructuresDocument12 pagesCE70-Structural Theory: Analysis of Statically Determinate StructuresJaymark S. GicaleNo ratings yet
- Solution To Problem 406 - Shear and Moment Diagrams - Strength of Materials ReviewDocument2 pagesSolution To Problem 406 - Shear and Moment Diagrams - Strength of Materials ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Shear and Moment in Beams by Method of Area - ARCH31S6Document39 pagesModule 6 - Shear and Moment in Beams by Method of Area - ARCH31S6Rose Anne ApiladoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures IDocument74 pagesTheory of Structures ISumaya AL-SiyabiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials: Analysis and Design of Beams For BendingDocument37 pagesMechanics of Materials: Analysis and Design of Beams For BendingZeeshan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Structural 3 Q PDocument14 pagesStructural 3 Q PKusum KalitaNo ratings yet
- Building StructuresDocument26 pagesBuilding StructuresYuan MingNo ratings yet
- Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument4 pagesShear Force and Bending MomentTariq HasanNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument9 pagesStrength of MaterialsAhmad WafiuddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Beam DeflectionDocument17 pagesLecture 5 - Beam DeflectionHollowq RixkNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Theory Ii: (Statically Indeterminate Structure)Document16 pagesStructural Analysis Theory Ii: (Statically Indeterminate Structure)Adonis C. BibatNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Lecture 1 - CE 2011 Structural Analysis IDocument10 pagesWeek 7 - Lecture 1 - CE 2011 Structural Analysis IGuhananth GuhaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures: By: Engr. Ma. Angelica C. Avillanosa, MsceDocument42 pagesTheory of Structures: By: Engr. Ma. Angelica C. Avillanosa, MsceIvy Jill JuradaNo ratings yet