Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PRR2 Module2
Uploaded by
Michael Angelo GodinezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PRR2 Module2
Uploaded by
Michael Angelo GodinezCopyright:
Available Formats
ASIAN INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER STUDIES-CEBU
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL MODULE
1ST SEMESTER SY 2022-2023
SUBJECT: PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
READING MODULE 2:
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
READING
● Research is about using established methods to investigate a problem or question in detail
with the aim of generating new knowledge about it.
● Knowing the types of research and what each of them focuses on will allow you to better plan
your project, utilises the most appropriate methodologies and techniques and better
communicate your findings to other researchers and supervisors.
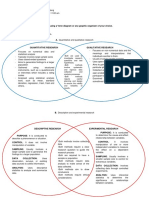
TYPES OF RESEARCH DESIGNS
1. QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH – Quantitative research methods are those research methods that use
numbers as its basis for making generalizations about a phenomenon. It emphasizes numerical
data analysis using computational techniques. The numbers used in statistical analysis originate
from objective scales of measurement of the units of analysis called variables. Four types of
measurement scale exist namely nominal, ordinal, ratio, and interval (see 4 Statistical Scales of
Measurement).
● Characteristics of quantitative research include descriptive and experimental
research design types.
● Best practices of quantitative research include both sample size accuracy and
data analysis performed precisely.
Quantitative research may also described as follows:
● It is “either descriptive, wherein subjects are measured once, or experimental, wherein
subjects are measured before and after” (Babbie, 2010)
● Data is “gathered using structured instruments. The results are based on large sample
sizes that are representative on the population and can be replicated” (Babbie, 2010)
● It has “clearly defined research questions to which objective answers are sought” (Babbie,
2010)
● It aims “to classify, features, count them, and construct statistical models in an attempt
to explain what is observed.” (Babbie, 2010)
A. CHARACTERISTICS
● Describe as objective research in contrast to qualitative research in contrast that
is subjective research.
Prepared by: Ms. Grace Tormis
ASIAN INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER STUDIES-CEBU
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL MODULE
1ST SEMESTER SY 2022-2023
SUBJECT: PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
● Characterized by objectiveness, in which is real or factual, not the emotional or
cognitive existence of the objective matters greatly to the artist, quantitative
research is analogous to scientific or experimental thinking.
● CONTAIN MEASURABLE VARIABLES - Data gathering instruments contain items
that solicit measurable characteristics of the population. These measurable
characteristics are referred to as the variables of the study such as age, the
number of children, educational status, and economic status.
● USE STANDARDIZED RESEARCH INSTRUMENTS - The data collection instruments
include questionnaires, polls, or surveys. Standardized, pre-tested instruments
guide data collection thus ensuring the accuracy, reliability and validity of data.
Pre-testing helps identify areas in the research instruments that need revisions.
It makes sure that respondents provide the expected answers or satisfies the
intent of the researcher to meet the research objectives.
● ASSUME A NORMAL POPULATION DISTRIBUTION - For more reliable data
analysis of quantitative data, a normal population distribution curve is preferred
over a non-normal distribution. This requires a large population, the numbers of
which depend on how the characteristics of the population vary. This requires
adherence to the principle of random sampling to avoid researcher’s bias in
interpreting the results that defeat the purpose of research.
● PRESENT DATA IN TABLES, GRAPHS, OR FIGURES - The data obtained using
quantitative methods are organized using tables, graphs, or figures that
consolidate large numbers of data to show trends, relationships, or differences
among variables. This fosters understanding to the readers or clients of the
research investigation.
● USE REPEATABLE METHOD - Researchers can repeat the quantitative method to
verify or confirm the findings in another setting. This reinforces the validity of
ground breaking discoveries or findings thus eliminating the possibility of
spurious or erroneous conclusions.
● CAN PREDICT OUTCOMES - Quantitative models or formula derived from data
analysis can predict outcomes. If-then scenarios can be constructed using
complex mathematical computations with the aid of computers.
● USE MEASURING DEVICES - Advanced digital or electronic instruments are used
to measure or gather quantitative data from the field. The instruments ensure an
objective and accurate collection of data provided that these are calibrated.
Calibration means that the instruments used by the researcher matches the
measurements of a reference instrument that is considered a standard.
B. DESCRIBING QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
1. MEASUREMENT – the most important factor in quantitative research,
which is why reliability and validity are embedded in its methodology.
Reliability speaks of consistency of a measure of a concept. According to
Bryman (2005), measurement is reliable if it contains the following
factors:
Prepared by: Ms. Grace Tormis
ASIAN INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER STUDIES-CEBU
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL MODULE
1ST SEMESTER SY 2022-2023
SUBJECT: PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
● STABILITY – There is a very little variation overtime in the results
obtained if it is administered to a group and read ministered
again.
● INTERNAL RELIABILITY – consistency of the scale or index
whether respondents scores on any one indicator tend to be
related to their scores on the other indicators
● INTER-OBSERVER CONSISTENCY- means being cautious of the
possibility of the inconsistency of observers when a great deal of
subjective judgement is involved, such as in recording of
observations or translating of data into categories and when
more than one observer is involved
● VALIDITY - refers to the issue of whether an indicator that is
developed to measure a concept really gauges that concept.
DIFFERENT KIND OF VALIDITY
● FACE-VALIDITY – reflects the content of the concept in
question. This may be undertaken by asking other people
whether the measure seems to be getting at the concept that
is focus on attention.
● CONCURRENT VALIDITY – employs a criterion on which cases
are known to differ and that is relevant to the concept in
question
● PREDICTIVE VALIDITY – uses a future criterion measure
rather than a contemporary one
● CONSTRUCT VALIDITY – deduces hypotheses from a theory
that is relevant to the concept
● CONVERGENT VALIDITY – the validity of a measure ought to
be gauged by comparing it to the measures of the same
concept developed through other measures.
2. CAUSALITY – strong on explaining why things happen in certain ways.
They are interested not only about phenomenon of things but the causes
of it.
3. GENERALIZATION – usually apprehensive about findings that cannot be
generalized. They pursue findings that can be generalized beyond the
margins of a certain context in which the research was undertaken.
4. REPLICATION – the ability to repeat an important component of an
activity.
C. WHY QUANTITATIVE MARKET RESEARCH IS USED?
● It helps collect quantitative data about the current market environment.
● The quantitative data can be used as a base for various marketing tools
like SWOT, strategy and designing the marketing mix
● It can result in out of the box innovation and improvements in products
and services
Prepared by: Ms. Grace Tormis
ASIAN INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER STUDIES-CEBU
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL MODULE
1ST SEMESTER SY 2022-2023
SUBJECT: PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
● It helps in understanding customers’ needs, wants and demands
● The company can get all the answers it wants to improve its product or
services from a specific set of questions
● It can be used when secondary market research has not proved fruitful
and additional, original data is needed to take a decision
D. ADVANTAGES OF THE QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
● Simple Data Collection: Quantitative research is carried out with a flock
of participants who represent the general population. Implementation of
a survey or any other method for the quantitative method will conduct
and analyze the results that are less time taking.
● Elimination of bias: Quantitative research offers no chance for biasing or
personal comments on the results. The outcomes are numerical and are
thus fair in maximum cases.
● Collection of accurate and reliable data: As most of the data is gathered,
examined and represented in numbers, the conclusions are very much
reliable and trustworthy. The number offers an honest outline of the
research without any discrepancies and with extreme accuracy.
● A huge scope of Data Analysis: Due to the implementation of statistical
methods, quantitative analysis offers a huge scope of data collection.
E. IMPORTANCE
● The importance of quantitative research lies greatly in the production of
results that should reflect precise measurement and an in-depth analysis
of data.
● It is also useful in obtaining an objective understanding of people, things,
places and events in this world; meaning, attaching accurate or exact
meanings to objects or subjects, rather than inflated meanings resulting
from the researcher’s bias or personal attachment to things related to
the research.
● This kind of research is likewise an effective method to obtain
information about specified personality traits of a group member or of
the group as a whole as regards the extent of the relationship of their
characteristics and the reason behind the instability of some people’s
characteristics (Mujis 2011; Gray 2012)
F. TYPES OF QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
5. EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH –a type of quantitative research that
authorizes researchers to “control the situation which allows them to
answer the question.
Prepared by: Ms. Grace Tormis
ASIAN INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER STUDIES-CEBU
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL MODULE
1ST SEMESTER SY 2022-2023
SUBJECT: PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
● It also supports the ability to limit alternative explanations and to
infer direct causal relationship in the study. (Anastas, 2000, as
cited in Salkind, 2010, pp 448-453)
● It is also applied as a gauge against which non-experimental
research is evaluated. It is also considered as a benchmark
because it stimulates significant confidence in the vigor and
reliability of causal findings. (Bryman, 2008)
TYPES OF EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH
● CORRELATIONAL RESEARCH – are based on pairs
of measures or scores for members of a single
sample and provide an indication of the
strengths of the relationship between two
variables that embody characteristics or
performance by that group. (Black, 1999, p.618)
o Also can be used in the process of
making predictions of values for one
variable based upon the values of the
other.
o Correlational studies are meant to
examine fields, to contemplate on the
likelihood of interrelations among a
number of pair variables, to see if future
research into possible causality is useful.
● CAUSAL-COMPARATIVE – it is considered as a
kind of descriptive research because it describes
existing conditions however it endeavours to
find out the causes of existing phenomena. (Gay,
1996 p. 321)
o It is about proving the cause-effect
relationships which descriptive and
correlational studies do not ascertain.
o In arriving at conclusions, establishing
causes must be done prudently, as other
variables, both known and unknown,
could still affect the outcome.
6. NON-EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH - Non-experimental research is
research that lacks the manipulation of an independent variable. Rather
than manipulating an independent variable, researchers conducting
non-experimental research simply measure variables as they naturally
occur (in the lab or real world).
TYPES OF NON-EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH
Prepared by: Ms. Grace Tormis
ASIAN INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER STUDIES-CEBU
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL MODULE
1ST SEMESTER SY 2022-2023
SUBJECT: PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
● DESCRIPTIVE RESEARCH - designed to give “answers to the
questions of who, what, where when and how which are linked
with a research problem.
o Descriptive research does not answer the question
“why” because it does not seek to explain why certain
things happen.
o It is applied only to describe what exists and to gather
information about the current status of a certain
phenomenon. (Anastas, 1999 as cited in Salkind and
Rasmussen, 2007, pp. 251-254)
o This type of research observes a subject or situation in a
“natural and unchanged” environment
● SURVEY RESEARCH – a survey is intended to acquire information
from people concerning the predominance, distribution, and
interrelations of variables within an identified group.
o Survey gathers evidence of people knowledge, opinions,
attitudes and values on various issues and concerns.
o Surveys are used to collect data that are mainly
quantitative.
G. NATURE OF VARIABLES
● Variables are changing qualities or characteristics of persons or things like
age, gender, intelligence, ideas, achievements, confidence, and so on that are
involved in your research study.
● Made up of the root word vary which means to undergo changes or to differ
from. (Suter 2013, p. 137)
TYPES OF VARIABLES
● Independent variable – variables that cause changes in the
subject
● Dependent variable – bears or manifests the effects caused by
the independent variable
● Extraneous variables - extra variables that crop up to create an
impact on the relationship between the independent and
dependent variable
● Participant variables- refers to the mood, emotions, or
intelligence of the subject
● Situational variables – pertain to the nature of the place: smelly,
chilly, cold, hot, spacious
Other types of variables (Suter2013; p.137; Thomas 2013; Schreiber
2012)
Prepared by: Ms. Grace Tormis
ASIAN INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER STUDIES-CEBU
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL MODULE
1ST SEMESTER SY 2022-2023
SUBJECT: PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
● Constant - do not undergo any changes during an experiment
● Attribute - characteristics of people;intelligence, creativity,
anxiety, learning styles,etc
● Covariate - included in the research study to create interactions
with independent and dependent variables.
● Continuous – quantitative in nature and is used in interval or ratio
scale of measurement
● Dichotomous – has only 2 result: zero or one
● Latent – cannot be directly observed like personality traits
● Manifest - can be directly observed to give proofs to latent
variables
● Exogenous – found outside an identified model
● Endogenous – found inside; as a part of identified model
VARIABLE RELATIONSHIPS
● The two variables are part and parcel of the research because the
first one is the cause and the second, the effect that you can
subject to any form of measurement.
H. EXAMPLES OF QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
● If any company likes to conduct a CSAT survey, quantitative data is gathered. It
can also collect the different metrics based on the goodwill of the enterprise or
the brand according to the customer. These metrics can be based on various
parameters like pricing, quality, and customer experience. It can be accomplished
using NPS or Net Promoter Score, and matrix table questions. These methods
offer data in the numeric forms that can be worked upon or studied later.
● An organization that is willing to organize an event can collect feedback from the
various attendees about the value of the company. By implementing a survey
template for an event, the enterprise can get a clear idea about the customer
satisfaction.
I. Resources
Baraceros E.L. (2016).Practical Research 2 (First Edition ed., pp.3-4) Cebu: Rex Bookstore.
Melegrito M.L. PHD and Mendoza D.J, Phd. (2016) Applied Research: An Introduction to
Quantitative Research Methods and Reporting Writing (pp. 1-3) Quezon City: Phoenix
Publishing House, Inc.
https://pediaa.com/what-is-the-difference-between-inquiry-and-
research/#:~:text=In%20brief%2C%20an%20inquiry%20is,facts%20and%20reach%20new%20conclusion
s.
Prepared by: Ms. Grace Tormis
ASIAN INSTITUTE OF COMPUTER STUDIES-CEBU
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL MODULE
1ST SEMESTER SY 2022-2023
SUBJECT: PRACTICAL RESEARCH 2
University of Southern California (2015). Quantitative methods. Retrieved on 3 January, 2015 from
http://goo.gl/GMiwt
Cite this article as: Regoniel, Patrick (January 3, 2015). Quantitative Research Methods: Meaning and
Characteristics [Blog Post]. In Research-based Articles. Retrieved
from https://simplyeducate.me/2015/01/03/quantitative-methods-meaning-and-characteristics/
https://www.marketing91.com/quantitative-market-research/
https://zipreporting.com/en/quantitative-research/what-is-quantitative-research.html
https://planningtank.com/market-research/quantitative-research
https://opentext.wsu.edu/carriecuttler/chapter/overview-of-non-experimental-
research/#:~:text=Non%2Dexperimental%20research%20is%20research,the%20lab%20or%20real%20w
orld).
Prepared by: Ms. Grace Tormis
You might also like
- Biology of KundaliniDocument190 pagesBiology of Kundalininityanandroy100% (1)
- Anderson Darling TestDocument45 pagesAnderson Darling Testpandyakavi100% (1)
- Handouts No. 01: Quantitative Research (Pr2)Document3 pagesHandouts No. 01: Quantitative Research (Pr2)Alvin Ray GarciaNo ratings yet
- Construction ProductivityDocument9 pagesConstruction ProductivityCristian ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument7 pagesResearch ReviewerEliza MaeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Quantitative ResearchDocument8 pagesLesson 1: The Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Quantitative ResearchAlma Cecilia Quiao100% (1)
- Practical Research 2 (Quantitative Research) : Mrs. Catherine Calixto-ValeraDocument17 pagesPractical Research 2 (Quantitative Research) : Mrs. Catherine Calixto-ValeraSt. Anthony of PaduaNo ratings yet
- Health Education Chapter 14 NotesDocument2 pagesHealth Education Chapter 14 Notes강하늘No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument50 pagesChapter 1 - Nature of Inquiry and ResearchJenie Espino100% (9)
- Principles of Biology 1592953983Document926 pagesPrinciples of Biology 1592953983Abdulfatai LanreNo ratings yet
- PR 2 - Handouts (WK 1-3)Document4 pagesPR 2 - Handouts (WK 1-3)Alrose HolgadoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Lesson 1Document3 pagesPractical Research 2 Lesson 1Pepito ManlolokoNo ratings yet
- Testing of HypothesisDocument90 pagesTesting of Hypothesiskumar030290No ratings yet
- Orca Manual 5 0 4Document1,330 pagesOrca Manual 5 0 4aminecasa129100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Solutions Solution Manual Introductory Econometrics For FinanceDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Solutions Solution Manual Introductory Econometrics For FinanceNazim Uddin MahmudNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - Lesson 1Document5 pagesPractical Research 2 - Lesson 1Chin KwonNo ratings yet
- Practical ResearchDocument8 pagesPractical Researchsrd9g6jj58No ratings yet
- RM-3 KueDocument41 pagesRM-3 KueElias SeidNo ratings yet
- Group 4 HandoutDocument5 pagesGroup 4 Handoutyhel laoNo ratings yet
- Lessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative ResearchDocument17 pagesLessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative Researchjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Quantitative Research 1. SystematicDocument12 pagesCharacteristics of Quantitative Research 1. SystematicisseylimboNo ratings yet
- Measurement ReviewerDocument6 pagesMeasurement ReviewerIan Daniel RosarioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quiz 1Document3 pagesLesson 3 Quiz 1VANESSA MOLUDNo ratings yet
- ResprojDocument11 pagesResprojlovelykat728No ratings yet
- 1ST QT Research ReviewerDocument12 pages1ST QT Research ReviewerAliah HernandezNo ratings yet
- pr2 NotesDocument8 pagespr2 Notesjclmaeramonal23No ratings yet
- PR 2 Reviewer (All Lessons)Document7 pagesPR 2 Reviewer (All Lessons)Jasmin MasaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Quantitative ResearchDocument6 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Quantitative Researchjuvylyn japosNo ratings yet
- Staffileno, Murphy, & Buchholz - Chapter 9Document39 pagesStaffileno, Murphy, & Buchholz - Chapter 9husseinkheiralhamidNo ratings yet
- RESEARCHDocument3 pagesRESEARCHKyla LacasandileNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research (PR 3)Document3 pagesQuantitative Research (PR 3)leibnagNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Research 2Document5 pagesHandouts in Research 2nona yamutNo ratings yet
- PracRes Notes PPT 2-4Document5 pagesPracRes Notes PPT 2-4030. Mozo, Athena Chelsea c.No ratings yet
- Hres13 - Chapter 2 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses and KindsDocument9 pagesHres13 - Chapter 2 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses and KindsJullien LagadiaNo ratings yet
- RVWR4RSRCHDocument4 pagesRVWR4RSRCHaarongabrielsales23No ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument12 pagesResearch MethodsAndrea Rose Morecho MahinayNo ratings yet
- Q1 PR2 Notes 2Document14 pagesQ1 PR2 Notes 2ericka khimNo ratings yet
- PR2 Final ReviewerDocument9 pagesPR2 Final ReviewerKristine Joy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 To 3Document12 pagesNotes 1 To 3leandro corditaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2: Senior High School Applied SubjectDocument45 pagesPractical Research 2: Senior High School Applied SubjectDebbie HidalgoNo ratings yet
- PracRes Notes PPT 2-11Document15 pagesPracRes Notes PPT 2-11030. Mozo, Athena Chelsea c.No ratings yet
- Criteria of Good Instruments: Validity & ReliabilityDocument11 pagesCriteria of Good Instruments: Validity & ReliabilityShintalrNo ratings yet
- PR02Document5 pagesPR02FITZ LIEZYLLE AGUIRRENo ratings yet
- PR ReviwerDocument5 pagesPR ReviwerMichelle CailaNo ratings yet
- Resesarch ReviewerDocument3 pagesResesarch ReviewerMa Jollie Mae BereNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Pr2 1st QuarterDocument5 pagesModule 2 Pr2 1st QuarterJelsie BastawangNo ratings yet
- Mims PR2 LC1 Quantitative ResearchDocument11 pagesMims PR2 LC1 Quantitative ResearchJester Guballa de LeonNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document4 pagesPractical Research 2Vinluan, Kaye Andrei P.No ratings yet
- Practical Research ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research ReviewerGenne kayeNo ratings yet
- Focuses On Gathering Numerical Data: QuantitativeDocument8 pagesFocuses On Gathering Numerical Data: QuantitativeCHIELOU MARIE T. POGOYNo ratings yet
- PR2 ExamreviewerDocument3 pagesPR2 ExamreviewerLeonah VelascoNo ratings yet
- Research NotesDocument8 pagesResearch Notestessamay0982No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Clarifying Quantitative Research DesignsDocument61 pagesChapter 8 - Clarifying Quantitative Research DesignsIconMaicoNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document3 pagesPractical Research 2Marjorie InguitoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - III (Final) PDFDocument8 pagesModule 1 - III (Final) PDFLyka Bactong DICES MNKNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Research DesignDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Research DesignSmarika SubediNo ratings yet
- PR ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR ReviewerVictoria Lourdes Mesias LoquinteNo ratings yet
- Al1 Final ReviewerDocument170 pagesAl1 Final ReviewerZay CaratihanNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument8 pagesResearch Reviewerela kikayNo ratings yet
- Research Final Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesResearch Final Exam ReviewerRhanessa Banacia NordanNo ratings yet
- Division Enhancement On Senior High School Inquiries Investigation and ImmersionDocument63 pagesDivision Enhancement On Senior High School Inquiries Investigation and ImmersionAshley Jade Hanna FloresNo ratings yet
- PR2 Lectures 1 and 2 Charaacteristics Strengths and WeaknessesDocument2 pagesPR2 Lectures 1 and 2 Charaacteristics Strengths and WeaknessesMiles MendozaNo ratings yet
- RES 1 Learning ContentDocument14 pagesRES 1 Learning ContentJaycob NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Pointers For Practical Research 2Document3 pagesPointers For Practical Research 2RyzaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument29 pagesNotesB12. Lacorte, Daniel Ross R.No ratings yet
- Eap - Module 4.1Document4 pagesEap - Module 4.1Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Peh111 - Module4 (Gas&ict)Document11 pagesPeh111 - Module4 (Gas&ict)Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Ucs121 Module4Document11 pagesUcs121 Module4Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- NTS112 Module 4.1Document3 pagesNTS112 Module 4.1Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Cp3net&cp3java - Module 3Document5 pagesCp3net&cp3java - Module 3Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Ucs121 - Module 3Document10 pagesUcs121 - Module 3Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- PHP121 - Module 3 (Ict and Humss)Document13 pagesPHP121 - Module 3 (Ict and Humss)Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Ict121 Module2Document5 pagesIct121 Module2Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- PRR2 Module3Document7 pagesPRR2 Module3Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- PHP121 - Module 2 (Ict and Humss)Document15 pagesPHP121 - Module 2 (Ict and Humss)Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- PRR2 Module1Document7 pagesPRR2 Module1Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Peh Iii - Module 1 (Gas & Ict)Document9 pagesPeh Iii - Module 1 (Gas & Ict)Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Ucs121 - Module 0Document4 pagesUcs121 - Module 0Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- PHP121 Module1Document7 pagesPHP121 Module1Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Ict121 Module1Document5 pagesIct121 Module1Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Ucs121 Module1Document7 pagesUcs121 Module1Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Cp3net&java Module1Document4 pagesCp3net&java Module1Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- PRR2 Module-4Document10 pagesPRR2 Module-4Michael Angelo GodinezNo ratings yet
- Quiz Chapter 2 (Pass - Quizchapter2)Document1 pageQuiz Chapter 2 (Pass - Quizchapter2)co caNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Service Quality Of: "Belleza Salon"Document50 pagesMeasuring The Service Quality Of: "Belleza Salon"ankitpatel611No ratings yet
- Ch13 Zikmund Measurement and ScaleDocument31 pagesCh13 Zikmund Measurement and Scalerohitoberoi1175% (4)
- Archivoguiaestudiante 2022112815815Document5 pagesArchivoguiaestudiante 2022112815815LADY MADELEY SOLIS CAMPOVERDENo ratings yet
- Statistic DataDocument2 pagesStatistic DataasbiniNo ratings yet
- Angela Verano MC MATH 15 Module 1Document12 pagesAngela Verano MC MATH 15 Module 1AN GE LANo ratings yet
- Study: Method For Information Management: Useful ResearchDocument11 pagesStudy: Method For Information Management: Useful ResearchMichellgutierrez7833No ratings yet
- Lec 5Document23 pagesLec 5Sama Atif Abdel-LatifNo ratings yet
- Analysing Moderated Mediation Effects: Marketing ApplicationsDocument42 pagesAnalysing Moderated Mediation Effects: Marketing ApplicationsVasan MohanNo ratings yet
- Ers5900 Week 67 Quantitative Research.1Document60 pagesErs5900 Week 67 Quantitative Research.1Hairil FaizNo ratings yet
- Method of Research (Activity 2) Noriza BocaboDocument3 pagesMethod of Research (Activity 2) Noriza BocaboTrisha Mae BocaboNo ratings yet
- Module 6. T-Test Two Sample TestDocument6 pagesModule 6. T-Test Two Sample TestBelle AmeNo ratings yet
- Lab Syllabus P248 01 L 4 Su18Document3 pagesLab Syllabus P248 01 L 4 Su18PohuyistNo ratings yet
- Forecasting Foreign Exchange Rate Using Robust Laguerre Neural NetworkDocument5 pagesForecasting Foreign Exchange Rate Using Robust Laguerre Neural NetworkRahul VyasNo ratings yet
- 1190-1592200966441-HND MSCP W12 Reliability and Validity of ResearchDocument12 pages1190-1592200966441-HND MSCP W12 Reliability and Validity of ResearchBarath TharmartnamNo ratings yet
- QM t4Document1 pageQM t4Vishal NarnauliaNo ratings yet
- Cross-Validation Strategies For Data With Temporal, Spatial, Hierarchical, or Phylogenetic StructureDocument17 pagesCross-Validation Strategies For Data With Temporal, Spatial, Hierarchical, or Phylogenetic StructurechoklitoNo ratings yet
- System Deign - LECTURE - 2Document97 pagesSystem Deign - LECTURE - 2amarnath grNo ratings yet
- PSM Estimation Confidence IntervalDocument55 pagesPSM Estimation Confidence IntervalNay LinNo ratings yet
- Carl, Bangalore e Schaeffer (2016) New Directions in Empirical Translation Process Research: Exploring The CRITT TPR-DBDocument323 pagesCarl, Bangalore e Schaeffer (2016) New Directions in Empirical Translation Process Research: Exploring The CRITT TPR-DBArthur Melo SaNo ratings yet
- MTH3901 Research Processes in Mathematics Individual AssignmentDocument3 pagesMTH3901 Research Processes in Mathematics Individual AssignmentRedzaNo ratings yet
- M1 Lesson 1Document6 pagesM1 Lesson 1Mary Grace Ferolino CañedaNo ratings yet
- Ways of Knowing and The Research ProcessDocument10 pagesWays of Knowing and The Research ProcessZinzi MaravillaNo ratings yet