Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Elements
Uploaded by
Ranjith Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views19 pages1. Precast concrete elements are cast and cured in a manufacturing plant using durable steel forms that allow for reuse, reducing costs compared to site-cast concrete.
2. Elements such as slabs, beams, columns, and wall panels are commonly used and provide increased structural efficiency through prestressing with steel strands.
3. On site, precast elements are lifted into place using cranes and assembled similarly to structural steel, allowing for faster erection less affected by weather.
Original Description:
Original Title
3.ELEMENTS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Precast concrete elements are cast and cured in a manufacturing plant using durable steel forms that allow for reuse, reducing costs compared to site-cast concrete.
2. Elements such as slabs, beams, columns, and wall panels are commonly used and provide increased structural efficiency through prestressing with steel strands.
3. On site, precast elements are lifted into place using cranes and assembled similarly to structural steel, allowing for faster erection less affected by weather.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views19 pages3 Elements
Uploaded by
Ranjith Kumar1. Precast concrete elements are cast and cured in a manufacturing plant using durable steel forms that allow for reuse, reducing costs compared to site-cast concrete.
2. Elements such as slabs, beams, columns, and wall panels are commonly used and provide increased structural efficiency through prestressing with steel strands.
3. On site, precast elements are lifted into place using cranes and assembled similarly to structural steel, allowing for faster erection less affected by weather.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
1.
PLANT-CASTING OF PRECAST ELEMENTS
Concrete elements, cast and cured in a manufacturing plant, then
transported to the construction site.
Plant casting allows increased efficiency and higher quality control.
Durable, permanent steel forms are reused many times, reducing
formwork costs compared to site cast concrete.
Use of Type III, high early strength cement and steam curing allow
concrete members to be cast and cured in as little as 24 hours.
Controlled casting conditions and high quality forms allow for greater
control of surface finishes.
Structural elements
are commonly
reinforced with tightly
stretched
pretensioned steel
strands, which
provide increased
structural efficiency.
Conventional steel
reinforcing isadded
for resistance to
thermal and other
secondary stresses.
• On the construction site,
precast concrete
elements are lifted into
place and assembled into
structural assemblies in a
process similar to that used
for structural steel.
• Compared to site cast
concrete, precast
concrete erection is
faster and less affected by
adverse weather
conditions.
A VACUUM LIFTING DEVICE IS USED TO LIFT
AND PLACE PRECAST
CONCRETE PRANKS.
PRECAST, PRESTRESSED
CONCRETE
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS
1.PRECAST CONCRETE SLABS
• Used for floor and roof decks.
• Deeper elements (toward the right
below) span further than those that
are shallower (toward the left).
• Right: Hollow core slabs stacked at
the precast plant.
2.PRECAST CONCRETE BEAMS AND GIRDERS
• Provide support forslabs.
• The projecting reinforcing bars will bond with concrete cast
on site.
• Right: Inverted tee beams supported by precast
columns.
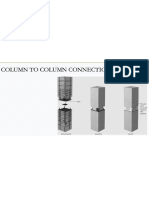
3.PRECAST CONCRETE COLUMNS
Providesupport for beam
and slab elements.
Sincetheseelements carry
mainly axial loads with little
bending force, they may
be conventionally
reinforced without
prestressing.
Or, long, slender multistory
elements may be
prestressed to provide
resistance to bending
forces during handling and
erection (columnsat right).
4.PRECAST CONCRETE WALL
PANELS
• Precast concrete wall
panels may be solid (right),
hollow, or sandwiched
(with an insulating core).
• Wall panels can be ribbed,
to increase their vertical
span capacity while
minimizing weight, or
formed into other special
shapes (below).
5.OTHER PRECAST CONCRETE
ELEMENTS
• Precast concrete stairs
(below)
• Uniquely shaped structural
elements for a sports stadium
(right)
ASSEMBLY CONCEPTS FOR
PRECAST CONCRETE BUILDINGS
• Vertical support can be
provided by precast
columns and beams
(above), wall panels
(below), or a
combination of all three.
• The choice of roof and
floor slab elements
depends mainly onspan
requirements.
• Precast slab elements
are frequently also used
with other vertical
loadbearing systems
such as site cast
concrete, reinforced
masonry, or steel.
• Above: Precast
concrete structure
consistingofsolidwall
panels and hollow core
slabs.
• Below: A single storey
warehouse consisting of
double tees supported
by insulated sandwich
wall panels.
Assembly Concepts
for Precast Concrete
Buildings
• A parking garage
structure consisting
of precast double
tees supported by
inverted tee
beams on
columns.
MANUFACTURING OF PRECAST
CONCRETE STRUCTURES ELEMENTS
1.Casting Hollow Core Planks
• Precast elements are
manufactured in
casting beds, 800 ft or
more in length.
• High-strength steel
strands are strung the
length of the bed
and tensioned.
• Conventional
reinforcing, weld
plates, blockouts,
lifting loops, and
other embedded
items are addedas Untensioned prestressing strands can be seen in the left-
needed. most casting bed. In the bed second from the right, low-
slump concrete for hollow core slabs is being formed over
• Concrete is placed. tensioned strands using an extrusion process. A completed
hollow core casting is visible at the far right.
2.Prestressing and Reinforcing Steel
• Many precast
elements contain
both prestressing
strands and
conventional
reinforcing.
• Right: The prestressing
strands for an AASHTO
girder are depressed
into a shallow v- shape
to most efficiently
resist tensile forces in
the beam. Shear stirrups
are formed from
conventional steel
reinforcing.
Casting Hollow Core Planks
• Once the concrete
has cured to
sufficient strength,
the castings are cut
into sections of
desired length
(above).
• In some cases,
transverse bulkheads
are inserted to divide
the casting bed into
sections before
concrete is placed. In
this case, only the
prestressing strands
need to be cut to
separate the sections
(below).
Casting Hollow Core Planks
• Individual sections are
lifted from the casting
bed (right) and
stockpiled to await
shipping to the
construction site.
Casting Hollow Core Planks
• Precast concrete
elements are
shipped to the
construction siteby
truck and erected
on site bycrane.
Casting Hollow Core Planks
• Samplehollow
core slab
sections of
varying depths.
• At bottom left,
note the
insulated
sandwich floor
pan
You might also like
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyFrom EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyNo ratings yet
- 0013 Bt5-Precast ConstructionDocument27 pages0013 Bt5-Precast ConstructionUzumakwin BatagaNo ratings yet
- How to Build a Global Model Earthship Operation II: Concrete WorkFrom EverandHow to Build a Global Model Earthship Operation II: Concrete WorkNo ratings yet
- Precastconstruction 150403143707 Conversion Gate01Document26 pagesPrecastconstruction 150403143707 Conversion Gate01ruksarNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cast Contruction: Aayush Lakhawat Abhishek Gupta Ayushi Bansal Deeksha ManchandaDocument26 pagesPre-Cast Contruction: Aayush Lakhawat Abhishek Gupta Ayushi Bansal Deeksha ManchandaBhavin PeshawariaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cast and Pre-Stressed ConcreteDocument26 pagesPre-Cast and Pre-Stressed ConcreteAshuNo ratings yet
- Merged Assignments CM 6th SemDocument83 pagesMerged Assignments CM 6th SemAshuNo ratings yet
- Precast FactoryDocument25 pagesPrecast Factoryamirsh78No ratings yet
- Prestress ConcreteDocument135 pagesPrestress ConcreteNishant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Pre-Stressing: Pre-Stressed Concrete Member Is ADocument47 pagesPre-Stressing: Pre-Stressed Concrete Member Is AAbu ZaforNo ratings yet
- Pre Stressed Concrete StructuresDocument39 pagesPre Stressed Concrete StructuresmUSI100% (1)
- Struktur Beton PrategangDocument56 pagesStruktur Beton PrategangDewanto MarstarNo ratings yet
- Precast ConcreteDocument69 pagesPrecast Concretejaffna100% (2)
- Types of Construction Slabs: Presented ToDocument12 pagesTypes of Construction Slabs: Presented TomikeskiedooNo ratings yet
- Pre - Stress Concrete: Submitted byDocument16 pagesPre - Stress Concrete: Submitted byTinzar LattNo ratings yet
- Composite BeamsDocument37 pagesComposite BeamsAbdallahNo ratings yet
- Precast Concrete Frame With Moment ConnectionDocument32 pagesPrecast Concrete Frame With Moment ConnectionmaizansofiaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Reinforced ConcreteDocument58 pagesTopic 2 Reinforced ConcreteVARSHNEE A/P ARUL RAJAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Floor and Roof SystemsDocument46 pagesGroup 1 - Floor and Roof Systemsalangadi.jm70No ratings yet
- BT5 Module-3Document48 pagesBT5 Module-3Jessa Mae S. SilvelaNo ratings yet
- Pre - Stress ConcreteDocument16 pagesPre - Stress ConcreteKashyap ChintuNo ratings yet
- Module 7 (Part 2)Document21 pagesModule 7 (Part 2)Roel Dylan A. MesiasNo ratings yet
- Floor System2Document63 pagesFloor System2DHEESHNA DILEEP 200545No ratings yet
- Post Tensioned SlabDocument38 pagesPost Tensioned Slabmadz heussafNo ratings yet
- Ce Technical Elective 2 Lesson 1Document23 pagesCe Technical Elective 2 Lesson 1Christian Jerome A. GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete 2Document30 pagesPrestressed Concrete 2Mehdi AliNo ratings yet
- Types of Construction Slabs: By: Ar. Parul JainDocument8 pagesTypes of Construction Slabs: By: Ar. Parul Jainparul jainNo ratings yet
- PrecastDocument35 pagesPrecastalyssa0% (1)
- Report On Post Tensioning & Pre TensioningDocument11 pagesReport On Post Tensioning & Pre TensioningSharandeep Sandhu100% (2)
- Types of SlabsDocument8 pagesTypes of SlabsTannum Negi90% (29)
- ADVANCED MULTI-STOREY CONSTRUCTION Notes-1Document38 pagesADVANCED MULTI-STOREY CONSTRUCTION Notes-1kgatoNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete - Dis 2020Document48 pagesPrestressed Concrete - Dis 2020Nur Aieshah NasirNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Prestressed ConcreteDocument20 pagesChap 2 Prestressed ConcreteKookie BTSNo ratings yet
- Pre Stressed ConcreteDocument47 pagesPre Stressed ConcreteBurakku Rōzu100% (2)
- Method of Speedy ConstructionDocument35 pagesMethod of Speedy ConstructionKaramjeet Singh100% (2)
- Pre-Stressed Concrete Pre - Tensioning Difference Between Pre - Post TensioningDocument24 pagesPre-Stressed Concrete Pre - Tensioning Difference Between Pre - Post TensioningMohhamad YasinNo ratings yet
- By: Ar. Vikas Kumar NirmalDocument8 pagesBy: Ar. Vikas Kumar NirmalMaria Fe GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Types of Slabsppt PDF FreeDocument8 pagesTypes of Slabsppt PDF FreeMaria Fe GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Pranay Kumar Tode Pktode@yahoo - Co.i NDocument44 pagesPranay Kumar Tode Pktode@yahoo - Co.i NToyeeb ArowonaNo ratings yet
- Steel Trusses PDFDocument73 pagesSteel Trusses PDFmayuresh barbarwar100% (1)
- Beams and ColumnsDocument19 pagesBeams and ColumnsTinzar LattNo ratings yet
- Post Tension IngDocument40 pagesPost Tension IngMmuthu KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- PSC - IntroductionDocument48 pagesPSC - IntroductionJames SantosNo ratings yet
- 8 - Chapter 11-1Document33 pages8 - Chapter 11-1JCNo ratings yet
- Concrete Frame BuildingsDocument100 pagesConcrete Frame BuildingsNuwantha UduwageNo ratings yet
- Complex Structures and BehaviourDocument225 pagesComplex Structures and BehaviourmohamedNo ratings yet
- Pretensioned Precast Slab UnitsDocument7 pagesPretensioned Precast Slab UnitsDhruv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Precast ConcreteDocument69 pagesPrecast Concretecapriciouskash70% (10)
- Jacketing: Er. Shaikh Arshad Vjti Mtech CMDocument21 pagesJacketing: Er. Shaikh Arshad Vjti Mtech CMnazeer_mohdNo ratings yet
- Framed Structures 1Document4 pagesFramed Structures 1Festus NgumbiNo ratings yet
- Concrete SlapDocument3 pagesConcrete SlapareprasertNo ratings yet
- Mall of Asia Construction MethodsDocument10 pagesMall of Asia Construction MethodsCarla Madlangbayan MalenabNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Cement Concrete Slab: Columns BeamsDocument9 pagesReinforced Cement Concrete Slab: Columns BeamsPeter SmithNo ratings yet
- Pre-Stressed Post Tension ConcreteDocument9 pagesPre-Stressed Post Tension ConcreteManal KhatibNo ratings yet
- Composite ConstructionDocument30 pagesComposite ConstructionJiggy MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Design, Loading & Structural SystemDocument75 pagesDesign, Loading & Structural SystemLuqman_Haqeem_3054100% (2)
- Presentation - Frame Construction in Concrete SteelDocument23 pagesPresentation - Frame Construction in Concrete SteelOlay KwongNo ratings yet
- Isolated Col or Pad FoundationDocument8 pagesIsolated Col or Pad FoundationLeroy LifestyleNo ratings yet
- CE 363 08 Building-SuperstructureDocument76 pagesCE 363 08 Building-SuperstructurePromita ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Multi Speciality Hospital Synopsis UpdatedDocument8 pagesMulti Speciality Hospital Synopsis UpdatedRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3Document1 pageSheet 3Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- AD PLANN-Model8Document1 pageAD PLANN-Model8Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4Document1 pageSheet 4Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Retreat Final SheetDocument1 pageRetreat Final SheetRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Net Case StudyDocument1 pageNet Case StudyRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- FF1Document1 pageFF1Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- AD PLANN-Model7Document1 pageAD PLANN-Model7Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- AD PLANN-Model4Document1 pageAD PLANN-Model4Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- AD PLANN-Model1Document1 pageAD PLANN-Model1Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- AD PLANN-Model6Document1 pageAD PLANN-Model6Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Net Case Study 1Document1 pageNet Case Study 1Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- AD PLANN-Model5Document1 pageAD PLANN-Model5Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- AD PLANN-ModelDocument1 pageAD PLANN-ModelRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Net Case StudyDocument1 pageNet Case StudyRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Advertisement: Log inDocument4 pagesAdvertisement: Log inRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroDocument57 pages1 IntroRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- 2types of ConstructionDocument12 pages2types of ConstructionRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Nbo - National Buildings OrganisationDocument11 pagesNbo - National Buildings OrganisationRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- 4 DetailsDocument6 pages4 DetailsRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Building Technology 1 - Building Materials: Midterm ProjectDocument68 pagesBuilding Technology 1 - Building Materials: Midterm ProjectAngeLyn CaguimbalNo ratings yet
- SVKM'S Nmims Mukesh Patel School Technology Management and Engineering Strength of Materials LabDocument5 pagesSVKM'S Nmims Mukesh Patel School Technology Management and Engineering Strength of Materials LabBender GamingNo ratings yet
- Astm C990-03Document4 pagesAstm C990-03Joanne WaiNo ratings yet
- Evergreen LogisticsDocument1 pageEvergreen LogisticsAlex RelagioNo ratings yet
- Compositesforalternativerailwaysleepers StampedDocument9 pagesCompositesforalternativerailwaysleepers Stampedflower 86No ratings yet
- Pendampingan Pengelolaan Sampah Mandiri Menggunakan Konsep Thermal Insinerasi Di Desa Kebakalan Kecamatan Karanggayam Kebumen Jawa TengahDocument8 pagesPendampingan Pengelolaan Sampah Mandiri Menggunakan Konsep Thermal Insinerasi Di Desa Kebakalan Kecamatan Karanggayam Kebumen Jawa TengahDedi FatchurohmanNo ratings yet
- 50 CRV 4Document2 pages50 CRV 4saptotoNo ratings yet
- Columbus 2021 Steel Catalogue v2 WebDocument31 pagesColumbus 2021 Steel Catalogue v2 WebOnesrohdnolb OnesrohdnolbNo ratings yet
- Item No. Description of Works QTY Unit Unit Cost Amount (P)Document29 pagesItem No. Description of Works QTY Unit Unit Cost Amount (P)AYSON N. DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Steel Grades Equivalence Table1 PDFDocument13 pagesSteel Grades Equivalence Table1 PDFVictor ParvanNo ratings yet
- Tds-Ws-801-En (1) VS 01Document3 pagesTds-Ws-801-En (1) VS 01paola choquehuancaNo ratings yet
- Conductor CodesDocument2 pagesConductor CodesFirs LasNo ratings yet
- Deleterious Substances in AggregatesDocument34 pagesDeleterious Substances in AggregatesheminNo ratings yet
- Bronze BushingDocument6 pagesBronze BushingVijet BhandiwadNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis: SML Films LTDDocument16 pagesCompetitive Analysis: SML Films LTDRajan DodejaNo ratings yet
- Specification ASTM D3350 PDFDocument110 pagesSpecification ASTM D3350 PDFraja reyhanNo ratings yet
- An Improved Method For Estimation of Ramberg-Osgood Curves Ofsteels From Monotonic Tensile PropertiesDocument15 pagesAn Improved Method For Estimation of Ramberg-Osgood Curves Ofsteels From Monotonic Tensile PropertiesAsad MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Casting Defects & CausesDocument15 pagesCasting Defects & CausesAbhinav Pratap MauryaNo ratings yet
- Tensile Stress Strain Examples - PDFDocument23 pagesTensile Stress Strain Examples - PDFMeghrajNo ratings yet
- Recommendations For Design and Construction of Ultra High Strength Concrete Structures, - DraftDocument4 pagesRecommendations For Design and Construction of Ultra High Strength Concrete Structures, - DraftMashfiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Concrete Beam Design (CSA A23.1-94)Document2 pagesConcrete Beam Design (CSA A23.1-94)marijean catuiraNo ratings yet
- Mix DesignDocument74 pagesMix DesignKarthikeyan m.karthiNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Textile IndustryDocument7 pagesPolymers in Textile IndustryOmar HernandezNo ratings yet
- Science PPT q3Document66 pagesScience PPT q3Jezer Dzi ArimaNo ratings yet
- 11 Practical Recycling Applications of Crushed Waste Glass in Construction Materials A Review 2017Document25 pages11 Practical Recycling Applications of Crushed Waste Glass in Construction Materials A Review 2017juan diazNo ratings yet
- NYRYDocument5 pagesNYRYAhmad Arif SaktiNo ratings yet
- Enb 04 0553 PDFDocument4 pagesEnb 04 0553 PDFDanielLaraNo ratings yet
- Shield: S Galum - 55% Al-Zn Alloy Coated Steel SheetDocument66 pagesShield: S Galum - 55% Al-Zn Alloy Coated Steel SheetAjay RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Clay Packet GuideDocument4 pagesClay Packet Guideapi-290985916100% (1)
- Incoterms 2020 Transport Obligations Cost RisksDocument1 pageIncoterms 2020 Transport Obligations Cost Riskskuuku asmahNo ratings yet