Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Reproduction
Uploaded by
lucyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Reproduction
Uploaded by
lucyCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell reproduction: the main types
cell division | mitosis | meiosis | programmed cell death.
Cell division and mitosis are two different processes that occur naturally in many organisms. In
contrast to these two main processes, meiosis is a process of cell reproduction that usually only
occurs during sexual reproduction. The process of meiosis is important because it helps ensure that all
cells of an organism have unique genetic information and prevent the accumulation of mutations
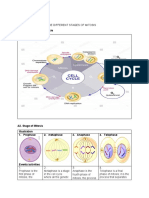
from generation to generation. The most common type of cell division is called mitosis, which occurs
in both plant and animal cells and involves dividing a single nucleus into four smaller nuclei destined
for each daughter cell. There are two main types of mitosis: interphase and anaphase. During
interphase, the chromosomes of all the cell's nuclei line up on a single plane and then are replicated.
Mitosis is then followed by anaphase and cytokinesis, where the nuclear material of one daughter
nucleus migrates to one side of the cell membrane, while the other daughter nucleus of the same
parent cell divides in an opposite fashion and creates two daughter cells. All cellular replication
requires DNA for each chromosome to be replicated. DNA is made up of nucleotides and each
nucleotide has a particular structure. These structures contain either a phosphate, a purine or a
pyrimidine. Purines and pyrimidines are paired bases. For example, adenosine contains an adenine
base with a pyrimidine base attached to it. When RNA is used as the template for replication, it works
in reverse and the RNA strand is copied into DNA.
The second main type of cell division is called meiosis, which only occurs in animals during
reproduction.
You might also like
- Cell Division LessonDocument9 pagesCell Division LessonGerry100% (1)
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- The Cell Cycle-TRFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Cycle-TRFmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & Meiosis NotesDocument6 pagesMitosis & Meiosis NotesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Document42 pagesChapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Nehjoy GerangueNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Structure and Cell DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- Compare The Processes of Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesCompare The Processes of Mitosis and MeiosisYolandaXieNo ratings yet
- TEXT READINGS Chapter - 16Document6 pagesTEXT READINGS Chapter - 16tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument17 pagesMitosisr2591220No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell DivisionLavanya Thevi100% (1)
- Heredity and Variation NotesDocument19 pagesHeredity and Variation NotesAmelia DavisNo ratings yet
- Science ResearchDocument3 pagesScience ResearchShaira Jea ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionZaineNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Note-Genetics Exam GuideDocument6 pagesLecture-Note-Genetics Exam GuideRoCkEnY FlOrEsNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - Cell DivisionDocument5 pages2.5 - Cell DivisionAlvin JovanNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument28 pagesMITOSIShariz mikhaelNo ratings yet
- Biologymeiosis 1 Group 2Document11 pagesBiologymeiosis 1 Group 2JonNelson GarciaNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument12 pagesMITOSISLarissa PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction, Process by Which Organisms Replicate Themselves.Document13 pagesReproduction, Process by Which Organisms Replicate Themselves.Vykin OngNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 2 Revision Notes GeneticsDocument3 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 2 Revision Notes GeneticsLakkiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Worksheet 4.2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Worksheet 4.2 Mitosis Vs MeiosisEvcha WangagNo ratings yet
- DEMODocument21 pagesDEMOChandrikka MandeNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Gcse BiologyDocument1 pageMitosis Gcse BiologycrainerNo ratings yet
- Bio 215 Notes Meiosis and MitosisDocument17 pagesBio 215 Notes Meiosis and MitosisPrecious ObhasedoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis and MeiosisShiela BelandresNo ratings yet
- Mitosis DefinitionDocument19 pagesMitosis DefinitionMar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 MitosisDocument10 pagesChapter 5 Mitosiswafa eliasNo ratings yet
- All in OneDocument18 pagesAll in OneSamay katariaNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Cell Reproduction and Genetics.Document3 pagesActivity 6 - Cell Reproduction and Genetics.Myrish Joy BangibangNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Cell Reproduction and GeneticsDocument3 pagesActivity 6 - Cell Reproduction and GeneticsMyrish Joy BangibangNo ratings yet
- Bio 202 2nd Exam TopicsDocument29 pagesBio 202 2nd Exam TopicsEdel John SivaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle LectureDocument3 pagesCell Cycle LectureR Jay LagdaminNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISION-MitosisDocument28 pagesCELL DIVISION-MitosisAVINASH VARMANo ratings yet
- Module 2 Meiosis and MitosisDocument88 pagesModule 2 Meiosis and MitosisSevdred CadelinaNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument5 pagesMITOSISdeepaNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument18 pagesMITOSISEdryan LambiquitNo ratings yet
- SZL B206 Principles of GeneticsDocument28 pagesSZL B206 Principles of Geneticsawuors249No ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document8 pagesLesson 4Marie Antonette BaligodNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesCell DivisionedukahonNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument7 pages4.2 Cell As A Unit of Lifehola adiosNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & Meiosis SheetDocument4 pagesMitosis & Meiosis SheetJoly Ann GesmanNo ratings yet
- Early March, Meiosis - Mitosis Study Guide (3.3)Document9 pagesEarly March, Meiosis - Mitosis Study Guide (3.3)ChanelleNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAngelo Gomez BadatoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle&MitosisDocument43 pagesCell Cycle&MitosisPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesCell DivisionLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 2Document9 pagesModule 2 Week 2Mycel Ann AcuzarNo ratings yet
- A1. Illustration of Cell CycleDocument5 pagesA1. Illustration of Cell CycleAllesa San JoseNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument49 pagesCell Cycle and Mitosishazharomar958No ratings yet
- Pre-Lab - Mitosis and MeiosisDocument12 pagesPre-Lab - Mitosis and MeiosisMaria Jose MartinezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Week 2Document10 pagesModule 2 Week 2Mycel Ann AcuzarNo ratings yet
- 5.cell DivisionDocument54 pages5.cell DivisionRaymond LundaNo ratings yet
- Processes in Nucleus Cell Biology: By: Furi Intan Wahyuni 4401408061Document10 pagesProcesses in Nucleus Cell Biology: By: Furi Intan Wahyuni 4401408061anon_811681548No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument31 pagesCell DivisionShin Thant Ko B10 June SectionNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyDocument52 pagesCell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyZuha HarithNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell DivisionNusrat ShoshiNo ratings yet
- Mystical Rose College of Science and Technology: Stage 1: InterphaseDocument4 pagesMystical Rose College of Science and Technology: Stage 1: InterphaseLaarni ToleteNo ratings yet
- What Happens When Food Reaches The StomachDocument9 pagesWhat Happens When Food Reaches The StomachAvegail MantesNo ratings yet
- F3 2021 Reproduction in PlantsDocument27 pagesF3 2021 Reproduction in PlantslastyngugiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes. " (Cbse)Document8 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes. " (Cbse)i uploadNo ratings yet
- Is Being Vegetarian The Way To Go For The WorldDocument1 pageIs Being Vegetarian The Way To Go For The WorldlucyNo ratings yet
- Life Lessons That Corona Virus Taught UsDocument1 pageLife Lessons That Corona Virus Taught UslucyNo ratings yet
- Happiness Is Not An Ideal of ReasonDocument1 pageHappiness Is Not An Ideal of ReasonlucyNo ratings yet
- What Is The Photosynthesis Process and How Does ItDocument1 pageWhat Is The Photosynthesis Process and How Does ItlucyNo ratings yet
- Depression and Work From HomeDocument1 pageDepression and Work From HomelucyNo ratings yet
- Is Humanity Enough To Handle Crisis and Serving PeDocument1 pageIs Humanity Enough To Handle Crisis and Serving PelucyNo ratings yet
- Blue Dot NetworkDocument1 pageBlue Dot NetworklucyNo ratings yet
- What Is Gene InheritingDocument1 pageWhat Is Gene InheritinglucyNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Will Give You PowerDocument1 pageKnowledge Will Give You PowerlucyNo ratings yet
- What If Dinosaurs Could Live in Our DaysDocument1 pageWhat If Dinosaurs Could Live in Our DayslucyNo ratings yet
- The DarwinDocument1 pageThe DarwinlucyNo ratings yet
- Describe The Natural Selection and Explain Its ImpDocument1 pageDescribe The Natural Selection and Explain Its ImplucyNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need EnzymesDocument1 pageWhy Do We Need EnzymeslucyNo ratings yet
- The Process of Cloning in A Modern WorldDocument1 pageThe Process of Cloning in A Modern WorldlucyNo ratings yet
- Describe Dinosaurs and Explain Why They CouldnDocument1 pageDescribe Dinosaurs and Explain Why They CouldnlucyNo ratings yet
- What Is The Main Structure of Human DNADocument1 pageWhat Is The Main Structure of Human DNAlucyNo ratings yet
- Comparing Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument1 pageComparing Eukaryotes and ProkaryoteslucyNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Use PCR TestsDocument1 pageWhy Do We Use PCR TestslucyNo ratings yet
- Explain The Process of Transporting Information byDocument1 pageExplain The Process of Transporting Information bylucyNo ratings yet
- A Theory of Gregor MendelDocument1 pageA Theory of Gregor MendellucyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentlucyNo ratings yet
- Describe Mitosis and Meiosis and Compare These ProDocument1 pageDescribe Mitosis and Meiosis and Compare These ProlucyNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis of Agricultural Machines BriefDocument3 pagesFunctional Analysis of Agricultural Machines BrieflucyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2lucyNo ratings yet
- Mechanization and Policy 2018-19Document18 pagesMechanization and Policy 2018-19lucyNo ratings yet
- Which Factors Regulate The Human PopulationDocument1 pageWhich Factors Regulate The Human PopulationlucyNo ratings yet
- Describe The Carbon Cycle MechanismDocument1 pageDescribe The Carbon Cycle MechanismlucyNo ratings yet
- FEB 599 CAT 2015-2016 First SemesterDocument2 pagesFEB 599 CAT 2015-2016 First SemesterlucyNo ratings yet
- 03 Data ModelingDocument60 pages03 Data ModelinglucyNo ratings yet