Professional Documents
Culture Documents
「 Sci Reviewer 」: Kinetic Molecular Theory › › Charles's Law
「 Sci Reviewer 」: Kinetic Molecular Theory › › Charles's Law
Uploaded by
Zhaina Carmelle RodelasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
「 Sci Reviewer 」: Kinetic Molecular Theory › › Charles's Law
「 Sci Reviewer 」: Kinetic Molecular Theory › › Charles's Law
Uploaded by
Zhaina Carmelle RodelasCopyright:
Available Formats
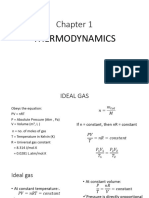
「 SCI REVIEWER 」 𝑉1 is initial volume
KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY 𝑃2 is final pressure
› Gasses are in constant random motion and 𝑉2 is final volume
frequently collide with one another
› The average kinetic energy of gas molecules is Charles’s Law
directly related to its temperature » Volume is directly proportional to the
temperature
PROPERTIES OF GASSES » As volume increases or decreases, temperature
Pressure (P) also increases or decreases
» Conversion: 𝑉 𝑉
» Formula: 𝑇1 = 𝑇2
1atm = 101,325 pascal (Pa) 1 2
14.7 pound per square (psi) » Where: 𝑉1 is initial volume
76 centimeters of mercury (cmHg)
760 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) 𝑇1 is initial temperature
76 torr
𝑉2 is final volume
101,325 kilo pascals (kPa)
𝑇2 is final temperature
Temperature (T) »
Conversion: Gay Lussac’s Law
9 » Pressure is directly proportional to the
℃ + 32 = ℉ temperature
5
5 » As pressure increases or decreases,
(℉ − 32) = ℃ temperature also increases or decreases
9
℃ + 273.15 = 𝐾 𝑃
» Formula: 𝑇1 =
𝑃2
1 𝑇2
Volume (V)
» Where: 𝑃1 is initial pressure
» Common units of Volume: (mL, L, 𝑚3 , 𝑐𝑚3 )
» Conversion: 𝑇1 is initial temperature
1L = 1000mL
1mL = 1𝑐𝑚3 𝑃2 is final pressure
Quantity (n) 𝑇2 is final temperature
» Measured in moles (mol) Combined Gas Law
» Conversion: » 2 properties should be constant and
1 mole = 6.022 x 1023 units of substance proportional
꒰ LAW OF GASSES ꒱ » Combination of 3 Law of Gasses
𝑃1 𝑉1 𝑃2 𝑉2
Boyle’s Law » Formula: =
𝑇1 𝑇2
» Pressure is inversely proportional to the
volume at constant temperature » Where: 𝑃1 𝑃2 is initial and final pressure
» As pressure increases, volume decreases and 𝑉1 𝑉2 is initial and final volume
vice versa
𝑇1 𝑇2 is initial and final temperature
» Formula: 𝑃1 𝑉1 = 𝑃2 𝑉2
٩꒰。•◡•。꒱۶
» Where: 𝑃1 is initial pressure
You might also like
- ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesThermodynamicsCherry ObiasNo ratings yet
- Physics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument20 pagesPhysics: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceMignus CarlsenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - Gas Laws and KMTDocument22 pagesChapter 05 - Gas Laws and KMTmijaggiNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Boyles LawDocument26 pagesBoyles LawIking De LaraNo ratings yet
- Power Cycle in f-100 EngineDocument21 pagesPower Cycle in f-100 Engineapi-583415219No ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical ChemistryDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Physical ChemistryRheanne SantosNo ratings yet
- Applications of Differential Equations in Civil EngineeringDocument10 pagesApplications of Differential Equations in Civil EngineeringAkmal KhanNo ratings yet
- ELET 2101 Lab Manual 5Document16 pagesELET 2101 Lab Manual 5hal jordanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document12 pagesLecture 9Md Al AminNo ratings yet
- Physics G10 S2 Laws Summary: 1. FluidsDocument4 pagesPhysics G10 S2 Laws Summary: 1. FluidsAdam Saeed FNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Q2 Wk1 2 Final VersionDocument50 pagesGas Laws Q2 Wk1 2 Final VersionclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 of Chapter 1 - Ideal Gas EquationDocument6 pagesPart 1 of Chapter 1 - Ideal Gas Equationloyovaf500No ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument66 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesDr. Sushil Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - State of Matter - Students Version CHM092 (2017)Document179 pagesCHAPTER 4 - State of Matter - Students Version CHM092 (2017)MUHAMMAD LUQMAN HAKIMI MOHD ZAMRINo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocument48 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-19824406No ratings yet
- 12 Unit 8-Gases-2020Document72 pages12 Unit 8-Gases-2020German CanizalesNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws PDFDocument12 pagesGas Laws PDFMara Erna TagupaNo ratings yet
- Gases: 5/75 Questions in Multiple Choice Almost Every Year in Free Response SectionDocument53 pagesGases: 5/75 Questions in Multiple Choice Almost Every Year in Free Response SectionZenobia Joy VillarbaNo ratings yet
- 6 Gaseous State 2023Document11 pages6 Gaseous State 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Gas Metering: by SNGPL-Metering DepartmentDocument15 pagesPresentation On Gas Metering: by SNGPL-Metering DepartmentbrianNo ratings yet
- Gas Law: Ref: Basic Chemistry, TimberlakeDocument22 pagesGas Law: Ref: Basic Chemistry, TimberlakeSofeaNo ratings yet
- GenChem Reviewer Quiz 4Document2 pagesGenChem Reviewer Quiz 4Raian PaderesuNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Physics2Document13 pagesLecture1 Physics2Kathryn IcuspitNo ratings yet
- CH5 States of MatterDocument26 pagesCH5 States of Mattersi qi wangNo ratings yet
- CHM 103 Lect 2Document39 pagesCHM 103 Lect 2SAMUELNo ratings yet
- 7 ThermalDocument69 pages7 ThermalKingsonNo ratings yet
- Boyles Law & Charles LawDocument24 pagesBoyles Law & Charles LawDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- Chem 110, Chapter 5 PDFDocument61 pagesChem 110, Chapter 5 PDFنواف السلميNo ratings yet
- C4-State of MatterDocument171 pagesC4-State of MatterLan FazlanNo ratings yet
- VapourDocument20 pagesVapourDon SebastianNo ratings yet
- Thermal 6 Gas LawsDocument19 pagesThermal 6 Gas LawsBrian TotmanNo ratings yet
- The Behavior of GasesDocument30 pagesThe Behavior of GasesPaolo BrequilloNo ratings yet
- G10 The Gas LawsDocument41 pagesG10 The Gas LawsjiahnasenetacamralNo ratings yet
- 1.gas LawsDocument30 pages1.gas LawsElaNo ratings yet
- Phys Chem II Gas Laws Lecture Notes - 230727 - 114428Document71 pagesPhys Chem II Gas Laws Lecture Notes - 230727 - 114428Tshiamo MotaungNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument19 pagesIdeal GasesTheLeaderDimitriosNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument16 pagesThermodynamicsSibisi SinethembaNo ratings yet
- 2 GasesDocument38 pages2 Gasesbaran.sarsinNo ratings yet
- 10 B Gas 3 4 5Document3 pages10 B Gas 3 4 5Ron Neil MicosaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Anna Marie Roja Rembrant Oniot James Peres Stephen Panadero Annie Oberio Iv-EmeraldDocument52 pagesGroup 5 Anna Marie Roja Rembrant Oniot James Peres Stephen Panadero Annie Oberio Iv-EmeraldDexter EnthusiastsNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4Document27 pagesIGCSE Science (Physics) : Unit P4SimonNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 Physical ChemistryDocument65 pagesTOPIC 1 Physical ChemistrySurendra Louis DupuisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter5 Class 11Document43 pagesChemistry Chapter5 Class 11Ravinder singhNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: General ChemistryDocument82 pagesIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: General ChemistryMinh Khoi Tran NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 28 - Charles - Law 2Document7 pagesLesson 28 - Charles - Law 2Jenny YoonNo ratings yet
- SHS Gr.12 Chap 9Document23 pagesSHS Gr.12 Chap 9Cj NacarioNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Heat - Chapter 17Document27 pagesTemperature and Heat - Chapter 17a71446508No ratings yet
- The Gas LawDocument30 pagesThe Gas LawDevs FusatoNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument85 pagesVolumetric Properties of Pure SubstancesKIM ASHLEY CARRILLONo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PPTDocument42 pagesChapter 5 PPTSaikumar PNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 The Properties of Gases SP23Document56 pagesChap 1 The Properties of Gases SP23iB13eNo ratings yet
- CHM1102 - Lecture 18-19Document10 pagesCHM1102 - Lecture 18-19EwartNo ratings yet
- NEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Thermodynamics S7 209Document79 pagesNEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Thermodynamics S7 209anantveersinghbrarNo ratings yet
- 03 Ib Chemistry (SL+HL) - S1.5 Ideal GasesDocument33 pages03 Ib Chemistry (SL+HL) - S1.5 Ideal GasesricardochavezrNo ratings yet
- CHME 222 - Lecture 4Document44 pagesCHME 222 - Lecture 4islam.lukmanov2003No ratings yet
- Gases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783Document34 pagesGases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document17 pagesUnit 1sumirNo ratings yet
- Gases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783Document34 pagesGases and The Atmosphere: Robert Boyle 1627-1691. Jacques Charles 1746-1823. J. Charles 1783ade dosmariaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry g11Document2 pagesChemistry g11Madelleine PaduaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 1Document26 pagesThermodynamics Module 1Piolo Lim AvenidoNo ratings yet
- STD 9 - Chemistry - Study of Gas LawsDocument5 pagesSTD 9 - Chemistry - Study of Gas LawsRamchandra MurthyNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1 - Lesson 3 - Part 2 - GAS LAWDocument46 pagesCHEM 1 - Lesson 3 - Part 2 - GAS LAWRoss TornNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry 2Document30 pagesPhysical Chemistry 2Michelle MenciasNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument37 pagesUntitledZhaina Carmelle RodelasNo ratings yet
- Creative WritingDocument20 pagesCreative WritingZhaina Carmelle RodelasNo ratings yet
- Dialogu EDocument16 pagesDialogu EZhaina Carmelle RodelasNo ratings yet
- 「 Cw Reviewer 」: Diction - Literary ElementsDocument2 pages「 Cw Reviewer 」: Diction - Literary ElementsZhaina Carmelle RodelasNo ratings yet
- 5 - MatLab TutorialDocument3 pages5 - MatLab TutorialSimay OğuzkurtNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Xi Physics 2023-24Document3 pagesPractice Paper Xi Physics 2023-24Siddhi PatilNo ratings yet
- Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM) : Working PrincipleDocument4 pagesVibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM) : Working PrincipleDina Assefa100% (1)
- Losito MeasurementDocument2 pagesLosito Measurementgrace paglicawanNo ratings yet
- Review MT 2 MCQDocument8 pagesReview MT 2 MCQRobby MulyadiNo ratings yet
- LC08 L2SP 118066 20130813 20200913 02 T1 MTLDocument7 pagesLC08 L2SP 118066 20130813 20200913 02 T1 MTLrehan pambudiNo ratings yet
- Lab4 Proposal Group G3 - Impact of A JetDocument7 pagesLab4 Proposal Group G3 - Impact of A JetMohd Haikal ShukorNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Active & Reactive Power: Comparison ChartDocument3 pagesDifference Between Active & Reactive Power: Comparison ChartMateen AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1st Semester WorksheetsDocument42 pages1st Semester WorksheetsMang friesNo ratings yet
- Faraday LawDocument19 pagesFaraday Lawalif fudenNo ratings yet
- OPTISONIC 3400 C - 4 InchDocument3 pagesOPTISONIC 3400 C - 4 InchMuhammad RizkyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Micro-Project: Topic: Study of Pressure Measuring DevicesDocument18 pagesHydraulics Micro-Project: Topic: Study of Pressure Measuring DevicesGvanNo ratings yet
- Lec14-Cross Product, Torque, and Angular MomentumDocument13 pagesLec14-Cross Product, Torque, and Angular MomentumpvriiscNo ratings yet
- ExamView - Circles Quiz 1 ReviewDocument9 pagesExamView - Circles Quiz 1 ReviewSlowed and ReverbedNo ratings yet
- Boiler CalculationDocument3 pagesBoiler CalculationVivekanandanNo ratings yet
- Buck-Boost Converter As Power Factor Correction Controller For Plug-In Electric Vehicles and Battery Charging ApplicationDocument6 pagesBuck-Boost Converter As Power Factor Correction Controller For Plug-In Electric Vehicles and Battery Charging Applicationprakhar agrawalNo ratings yet
- Relés de Controle Plug-InDocument2 pagesRelés de Controle Plug-InMilson Ramos Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- ACCE 1 M - L01 IntroductionDocument31 pagesACCE 1 M - L01 IntroductionMike SantosNo ratings yet
- NOV PHY SC P1 Grade 10 and MemoDocument26 pagesNOV PHY SC P1 Grade 10 and Memotusokwakhe langaNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document3 pagesWa0002.PrajwalNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics PYQs 1990 To 2022 110530 1670823515775 PDFDocument214 pagesThermodynamics PYQs 1990 To 2022 110530 1670823515775 PDFSandeep AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Kaiterra Sensedge Brochure - April 2023Document16 pagesKaiterra Sensedge Brochure - April 2023FELIX DOSSNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Capacitive ReactanceDocument4 pagesLab 2 - Capacitive Reactanceali basitNo ratings yet
- Motion in Straight LineDocument12 pagesMotion in Straight LineamitctoNo ratings yet
- Exam 03: Chapters 20-22: /38 05: Chapter 21 /38 /38 06: Chapter 21 /38 /38 07: Chapter 22 /38 /38 08: Chapter 22 /38Document9 pagesExam 03: Chapters 20-22: /38 05: Chapter 21 /38 /38 06: Chapter 21 /38 /38 07: Chapter 22 /38 /38 08: Chapter 22 /38Feliks SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction - DPP 02 - Lakshya JEE 2024Document3 pagesElectromagnetic Induction - DPP 02 - Lakshya JEE 2024abhishekff25No ratings yet