Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NOTE CHAPTER 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation
Uploaded by
Nur AfiqahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NOTE CHAPTER 3 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation
Uploaded by
Nur AfiqahCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
CHAPTER 3:
THE MOLE CONCEPT, CHEMICAL FORMULA AND EQUATION
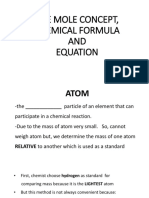
3.1 Relative Atomic Mass and Relative Molecules
Relative Atomic Mass Of an element Relative Atomic Mass Of an molecule
(RAM) (RMM)
Definition The average mass of an atom of the element The average mass of molecule compared to
compared to 1/12 of the mass of one 1/12 of the mass of one carbon-12 atom.
carbon-12 atom.
Fomulae
Average mass of an atom of the element Average mass of molecule
1/12 x mass of one carbon-12 atom. 1/12 x mass of one carbon-12 atom.
Example
Question
(OBJECTIVE)
RAM He is 4 means that: RMM H20 is 18 means that:
Average Mass of 1 atom of Helium is 4 times Mass of H20 is 18 times
the mass 1/12 carbon-12 atom the mass 1/12 carbon-12 atom
Why use Carbon -12 as standard??
1. Solid at room 2. Carbon-12 easily combines with 3. Found in most
temperature, so can other elements substanances
handled easily
Question
(OBJECTIVE)
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
No Element Symbol Relative No Element Symbol Relative
Atomic Mass Atomic Mass
1 Aluminium Al 27 21 Copper Cu 64
2 Silver Ag 108 22 Lithium Li 7
3 Argon Ar 40 23 Magnesium Mg 24
4 Barium Ba 137 24 Manganese Mn 24
5 Beryllium Be 9 25 Sodium Na 23
6 Boron B 11 26 Neon Ne 20
7 Bromine Br 80 27 Nickel Ni 59
8 Iron Fe 56 28 Nitrogen N 14
9 Fluorine F 19 29 Oxygen O 16
10 Phosphorus P 31 30 Lead Pb 207
11 Helium He 4 31 Rubidium Rb 85.5
12 Hydrogen H 1 32 Caesium Cs 133
13 Iodine I 127 33 Silicon Si 28
14 Potassium K 39 34 Scandium Sc 45
15 Calcium Ca 40 35 Tin Sn 119
16 Carbon C 12 36 Sulphur S 32
17 Chlorine Cl 35.5 37 Titanium Ti 48
18 Cobalt Co 59 38 Vanadium V 51
19 Crypton Kr 84 39 Xenon Xe 131
20 Chromium Cr 52 40 Zinc Zn 65
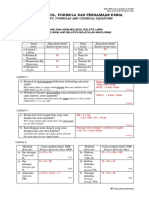
HOW TO CALCULATE RELATIVE MOLECULE MASS
Zn(OH)2 K4Fe (CN)6.3H20
Question
Answer: Answer: (OBJECTIVE)
=65 + 2(12 +1) =4 (39) + 56 + 6 (12+ 14) + 3(2(1) +16)
=91 =422
You can score CHEMISTRY. Understand
concept and Do Exercises
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
3.2 Moles Concepts
Formula to calculate
mole (n)
MV
Number of particles (N) ----------------------
---------------------- 1000
mass Volume
Avogadro Constant(NA) ---------------------- ----------------------
(6.02 X 1023) Molar Mass Molar Volume
Vm (rt)= 24 dm3mol-1
Vm (stp)= 22.4 dm3mol-1
Calculate number of Particles
Question
A gas jar is filled with 2 moles of oxygen gas, O2 (OBJECTIVE)
a) How many molecules of oxygen b) How many atoms of oxygen are there in the gas jar?
are there in the gas jar?
Solution: Solution:
N = n X NA N = n X NA
= 2 X 6.02X 1023 = 2 X 6.02X 1023 X 2 (Because 1 molecule O2 = 2 atoms Oxygen)
= 1.204 X 1023 = 2.408 X 1024
How many molecules are there in 672 cm2 of hydrogen gas, H2 at STP?
Step 1 : Find mole (n) = (672 /1000) dm3 ÷ 22.4 dm3
= 0.03 mol
Step 2: Find unknown ( Number of molecule) = n X NA
= 0.03 X (6.02 X 1023)
= 1.806 X 1022 molecules
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
3.3 Chemical Formula
Meaning: Chemical Formula is a representation of a chemical
substance using alphabets to represent the atoms of subscript
numbers to show the number of each the of atom found in the
elementary entities of the substances.
Cation Formula of cation Anion Formula of Anion
Sodium ion Na+ ion Chloride ion Cl- ion
Potassium ion K+ ion Bromide ion Br- ion
Silver ion Ag+ ion Iodide ion I- ion
Ammonium ion NH4+ ion Hydroxide ion OH- ion
Calcium ion Ca2+ ion Nitrate ion NO3- ion
Magnesium ion Mg2+ ion Manganate (VII) ion MnO4- ion
Zinc ion Zn2+ ion Oxide ion O2- Ion
Lead(II) ion Pb2+ ion Carbonate ion CO32- ion
Copper(II) ion Cu2+ ion Sulphate ion SO42- ion
Iron(II) ion Fe2+ ion Thiosulphate ion S2O3 2- ion
Iron (III) ion Fe3+ ion Dichromate (VI) ion Cr2O7 2- ion
Aluminium ion Al3+ ion Phosphate PO43- ion
How to create chemical formula
Aluminium carbonate???
Aluminium ion carbonate ion
Al3+ ion CO32- ion
Symbol Al CO3
Charge 3 2
Answer: Al2 (CO3)3
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
3.3 Chemical Formula
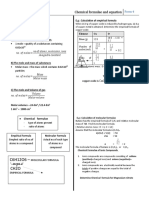
Empirical Formula Molecular Formula
Chemical Formula that shows the simplest Chemical Formula that shows the actual
ratio of the number of atoms of each number of the number of atoms of each Question
element in a compound element in a molecule of a compound
Propene = CH2 Propene = C3H6
How to calculate:
Hydrocarbons consists of carbon and hydrogen. 5.7 g of hydrocarbon contains 4.8g of carbon. If the
relative molecular mass of the hydrocarbon is 114, determine its molecular formula
Answer:
To calculate empirical Formula, use table
Element C H
Mass (g) 4.8 g 5.7-4.8= 0.9 g
Number of mole (mole) 4.8 0.9
----- = 0.4 mol ------ = 0.9 mol
12 1
Ratio 0.4 0.9
------ =1 ----- = 2.25
0.4 0.4
Simplest ratio 1x4=4 2.25 x 4 =9
Empirical Formula C4H9
Molecular Formula
(C4H9 ) n = 114
(4 (12) +9 (1) ) n =114
57 n =114
n =114 /57
Question
n= 2
Molecular Formula : (C4H9 ) n = ( C4H9 ) 2
Molecular Formula = C8H18
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
Experiment Empirical Formula
More reactive metal than Less reactive metal than Hydrogen (Cu, Pb)
Hydrogen (Al, Mg)
1. Weigh and record the mass of a 1. Weigh the mass of 12 cm glass tube using an electronic
crucible together with its lids balance and record its mass.
2. Rub 10 cm magnesium ribbon 2. Put some copper (II) oxide powder into the glass tube. Use
with a sand paper until shiny. Coil wooden splinter to move copper (II) oxide powder into the
the magnesium ribbon and put it in middle of the glass tube. Weigh the mass of the glass tube
the crucible. together with its contents and record the mass.
3. Weigh and record the mass of 3. Fill 2/3 of boiling tube with water.
the crucible together with its lied 4. Close boiling tube with a rubber stopper that has a 12 cm
and the coil of magnesium ribbon glass tube. Clamp the boiling tube onto the retort stand.
4. Heat the crucible without lid 5. Insert a few granules into another boiling tube. Add 1.0
5. When magnesium ribbon starts moldm-3 hydrochloric acid into the boiling tube until it is 1/3
to burn, close the crucible with its full.
lid. 6. Close the boiling tube with rubber stopper that has a 10 cm
6. Using a pair of tongs, lift the lid glass tube. Clamp the boiling tube onto the other retort stand.
slightly from time to time and 7. Connect the glass tube that contains copper (II) oxide
quickly place it back. powder as diagram.
7. When the burning of magnesium 8. Let the hydrogen flow for 10 seconds by allowing the air
ribbon is complete, take off the lid bubbles to be released in the water before starting the heating
and heat the crucible with high process.
temperature for 1 to 2 minute. 9. Heat the copper (II) oxide using spirit lamp with continuous
8. Put back the lid of the crucible flow of hydrogen has through the glass tube.
and allow it cool to room 10. Stop the heating when the black colour of Copper (II) oxide
temperature. turns brown completely.
9. Weigh the mass of crucible 11. Keep a continuous flow a hydrogen gas until the glass tube
together with its lids and its is cooled back to room temperature
contents again. 12. Remove the glass tube that contains brown powder.
10. Repeat the heating, cooling and Eliminate water drops at the end of the glass tube with a
weighing process until a constant cotton bad.
mass is obtained. 13. Weigh the mass of the glass tube together with its contents
11. Record the constant mass and record its mass.
14. Repeat the heating, cooling and weighing processes from
steps 9 to 13 until a constant mass reading is obtained.
15. Record the constant mass
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
More reactive metal than Hydrogen (Al, Mg) Less reactive metal than Hydrogen (Cu,Pb,Fe)
Data: Data:
Description Mass (g) Description Mass (g)
Crucible + lid Glass tube
Crucible + Lid + Mg ribbon Glass Tube + Copper (II) oxide
Crucible + Lid + Mg Oxide Class tube + Copper
Copper
Oxygen
Observation: Grey solid (Mg) turn to white (MgO) Observation: Black (CuO) turn to brown(Cu)
Chemical Equation: Chemical Equation:
2 Mg + O2 → 2MgO Zn+ 2HCl → ZnCl2 +H2
CuO +H2 → Cu +H2O
2H2 + O2 → H2O
Precautionary Step: Precautionary Step:
1) Rub 10 cm magnesium ribbon with a sand paper 1. Let the hydrogen flow for 10 seconds by
until shiny → to get rid the layer of magnesium allowing the air bubbles to be released in the
oxide. water before starting the heating process→ to
remove all air or oxygen gas in the glass tube.
2) When magnesium ribbon starts to burn, close This is because a mixture of hydrogen and air
the crucible with its lid. → to reduce magnesium can cause an explosion when ignited.
oxide from being released into surrounding in
the form of white smoke. 2. Keep a continuous flow a hydrogen gas until
the glass tube is cooled back to room
3) Using a pair of tongs, lift the lid slightly from temperature → to prevent oxidation of copper
time to time and quickly place it back. → to allow to form copper (II) oxide again.
oxygen from outside to enter so that the burning
process of magnesium occurs continously. 3. The glass tube needs to be dipped into the
water in the test tube → to prevent outside air
4) Repeat the heating, cooling and weighing from entering into the glass tube during the
process until a constant mass→ to ensure that the heating if the flow of hydrogen gas is stopped.
reaction is completed
4) Repeat the heating, cooling and weighing
process until a constant mass→ to ensure that
the reaction is completed .
Question
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
3.4 Chemical Equation
How to balance chemical equation??????
S
Can use method: Magic Box
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
How to solve calculation in Chemical
Equation???
Just try Do It
Burning of Aluminium in air is as follows:
4Al + 3O2 → 2Al203
What is the mass of aluminium oxide produced if 5.4g of aluminium is burnt completely in air?
[Relative atomic mass: O=16, Al=27]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
How to solve??
Unknown value Known Value
Chemical Formula Involved 2Al203 4Al
Mole (n) calculation y 5.4
-------- = 0.2 mol
27
Mole (n) equation 2 4
Relationship
y =0.2
---- -----
2 4
4 y= 0.2 x 2
4 y= 0.4
Y = 0.4 /4 =0.1 mol
Calculate value required Mass Al203 = n x RMM
= 0.1 x (2( 27)+ 3 (16))
=10.2 g
Question PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
CHAPTER 3 : The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation CHEMISTRY FORM 4 (KSSM)
RECAP
Terms Definition
1. Relative Atomic Mass Of an element The average mass of an atom of the element
(RAM)
compared to 1/12 of the mass of one carbon-12
atom.
2. Relative Atomic Mass Of an molecule The average mass of molecule compared to 1/12 of
(RMM)
the mass of one carbon-12 atom
3. Chemical Formula Chemical Formula is a representation of a chemical
substance using alphabets to represent the atoms of
subscript numbers to show the number of each the of
atom found in the elementary entities of the
substances.
4. Empirical Formula Chemical Formula that shows the simplest ratio
of the number of atoms of each element in a
compound
5. Molecular Formula Chemical Formula that shows the actual number
of the number of atoms of each element in a
molecule of a compound
You had Finished
this chapter
PREPARED BY: NUR AFIQAH BINTI YAHAYA
You might also like
- Calculate Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument22 pagesCalculate Chemical Formulae and EquationsfanatikaNo ratings yet
- Relative Atomic Masses ExplainedDocument7 pagesRelative Atomic Masses ExplainedDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Solution Asignment 1 Chem EngDocument6 pagesSolution Asignment 1 Chem EngVỹ KhangNo ratings yet
- 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument23 pages3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsHING LEE NA MoeNo ratings yet
- 3A Chemical Formulae and Equations-AnswerDocument10 pages3A Chemical Formulae and Equations-AnswerSiti NursahidahNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 f4 KSSM - Student 2021Document101 pagesChap 3 f4 KSSM - Student 2021Koo Rui CheeNo ratings yet
- Latihan Kimia Cuti Sekolah Part 1Document7 pagesLatihan Kimia Cuti Sekolah Part 1FATIN MAISARAH BINTI AHMAD MISWAN MoeNo ratings yet
- 3A Chemical Formulae and Equations-AnswerDocument11 pages3A Chemical Formulae and Equations-AnswerWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- Kimia JWP Bab 3Document23 pagesKimia JWP Bab 3CHA ZI YU MoeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form4 Chapter3 SPMDocument11 pagesChemistry Form4 Chapter3 SPMkaiqianNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Volume I - Xi Ready ReckonerDocument115 pagesChemistry Volume I - Xi Ready ReckonerSpedNo ratings yet
- Solution Asignment 1 Chem EngDocument14 pagesSolution Asignment 1 Chem EngDuy Do MinhNo ratings yet
- C6H12O6 - Ch2O: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument4 pagesC6H12O6 - Ch2O: Chemical Formulae and EquationOnez ManikNo ratings yet
- Medium AnsDocument5 pagesMedium AnsMR CAT MANNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocument36 pagesChemical Formulae and EquationsSiew Kiong WongNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and Equations ExplainedDocument37 pagesChemical Formulae and Equations ExplainedSiew Kiong WongNo ratings yet
- Question Score A Chapter 1Document14 pagesQuestion Score A Chapter 1Dee -AdilaNo ratings yet
- Quantities and EquationsDocument14 pagesQuantities and Equationsmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes For ch4Document24 pagesDetailed Notes For ch4Jemima KaishaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentalof ChemistryDocument66 pagesFundamentalof Chemistryrehanfazal9669No ratings yet
- The Mole Part 1Document8 pagesThe Mole Part 1Daniel BerryNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument33 pagesThe Structure of The AtomWilley TaluanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry ReviewDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry ReviewNaomi HeywardNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Test 1: 1 AS/SEP 2018/TEST 1/CHM131Document4 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Test 1: 1 AS/SEP 2018/TEST 1/CHM131EzzarenNo ratings yet
- TEST 1 LatihanDocument4 pagesTEST 1 LatihanNURUL AIDA OTHMANNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week7 Mole ConceptDocument48 pagesQ2 Week7 Mole ConceptLance SalotNo ratings yet
- Ch3 CompleteDocument48 pagesCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Bridging The Gap AnswerDocument11 pagesChemistry-Bridging The Gap AnswerMuhammad IzzuanNo ratings yet
- 12th Science HSC Chemistry NumericalsDocument23 pages12th Science HSC Chemistry NumericalsAliNo ratings yet
- Ch3 CompleteDocument48 pagesCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- c3 Chemical Formula (S)Document59 pagesc3 Chemical Formula (S)Wan nur Damia batrisyaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 CompleteDocument48 pagesCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - IB Prepared - ANSWERS - Bylikin, Murphy and Juniper - Oxford 2018Document106 pagesChemistry - IB Prepared - ANSWERS - Bylikin, Murphy and Juniper - Oxford 2018XamNo ratings yet
- CHM131 MAC 2019 exam: Density, isotopes, balancing equationsDocument4 pagesCHM131 MAC 2019 exam: Density, isotopes, balancing equationsijah rosmiNo ratings yet
- Treader NoteDocument55 pagesTreader NoteacazononlineNo ratings yet
- History and Subatomic Particle Review Take Two KEYDocument5 pagesHistory and Subatomic Particle Review Take Two KEYAlliya DaymonNo ratings yet
- PDF SPM Chemistry Form 4 Notes DLDocument10 pagesPDF SPM Chemistry Form 4 Notes DLJames SimNo ratings yet
- Ujian PBD Penggal 1 2022Document7 pagesUjian PBD Penggal 1 2022FARID ARIFIN BIN MD ARIFIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, Form 4 Malaysia EducationDocument7 pagesChemistry, Form 4 Malaysia EducationIkhwan AzimNo ratings yet
- Chem MoleDocument29 pagesChem Mole叶子临No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: Reactions of Substances Found in Living OrganismsDocument8 pagesFundamentals of Chemistry: Reactions of Substances Found in Living OrganismsRahi FurqanNo ratings yet
- 八大題型全攻略Document32 pages八大題型全攻略Jeff Suck100% (1)
- Mole ConceptDocument1 pageMole ConceptNaguib Zakaria67% (3)
- Basic Chemical Calculations-MergedDocument184 pagesBasic Chemical Calculations-MergedVishwajeet DhanwadeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Calculations ADocument8 pagesChemistry Calculations AKasunDilshanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula and EquationsDocument23 pagesChemical Formula and EquationsIza MohdSabriNo ratings yet
- Elements Symbols Formulas Activity Lab ManualDocument6 pagesElements Symbols Formulas Activity Lab ManualMaria Angela GeongoNo ratings yet
- Tea Bag + Sugar + Hot Water Tea TB + S + HW TDocument29 pagesTea Bag + Sugar + Hot Water Tea TB + S + HW TFidree AzizNo ratings yet
- W2 Lesson2 - GenChem - IsotopesDocument6 pagesW2 Lesson2 - GenChem - IsotopesLeanneMargaretC.RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 5 CalculationDocument35 pagesUnit 1 Part 5 CalculationI LOVE JAKENo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Worksheet PDFDocument10 pagesStoichiometry Worksheet PDFZIMBERNo ratings yet
- Chemistry tutorial questions on isotopes, compounds and equationsDocument6 pagesChemistry tutorial questions on isotopes, compounds and equationsAlesha QistinaNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry & Mole ConceptDocument18 pagesStoichiometry & Mole ConceptBenjamin JereyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Level 4C: (CHM415115) Mole Concept & Stoichiometry Theory Summary & Revision QuestionsDocument29 pagesChemistry Level 4C: (CHM415115) Mole Concept & Stoichiometry Theory Summary & Revision QuestionsS AdiaNo ratings yet
- Mole and Stoichiometry PIDocument38 pagesMole and Stoichiometry PIvinuns18No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Lactic Acid by Phosphonium Ionic Liquids: J An Mart Ak, Stefan SchlosserDocument12 pagesExtraction of Lactic Acid by Phosphonium Ionic Liquids: J An Mart Ak, Stefan SchlosserNiraj ThakreNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 QuestionsDocument5 pagesExercise 2 Questionsyuen lok hinNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Mole ConceptDocument18 pagesChapter3 Mole Conceptaayush_vijayvargia100% (1)
- Excel SheetDocument13 pagesExcel SheetDamien NaiduNo ratings yet
- IAS Chemistry SB1 Assessment T1Document4 pagesIAS Chemistry SB1 Assessment T1Loh Jun XianNo ratings yet
- Chem1AA3 Lecture 1 PDFDocument110 pagesChem1AA3 Lecture 1 PDFbhavanjeetNo ratings yet
- Slide Set of 195 Slides Based On The Chapter Authored by E.B. Podgorsak of The IAEA Publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6)Document195 pagesSlide Set of 195 Slides Based On The Chapter Authored by E.B. Podgorsak of The IAEA Publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6)SaRaNo ratings yet
- The Mole Concept: Learning CompetencyDocument14 pagesThe Mole Concept: Learning Competencylevi0417No ratings yet
- 01-Solution & Colligative Properties - Theory-FinalDocument10 pages01-Solution & Colligative Properties - Theory-FinalAnkit MishraNo ratings yet
- Determination of Concentration Acetic Acid in VinegarDocument11 pagesDetermination of Concentration Acetic Acid in VinegarKicauan KataNo ratings yet
- Part Test-1 (XI) JEE Main Only SolDocument11 pagesPart Test-1 (XI) JEE Main Only SolJ A YNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry U1 - Breakdown of SyllabusDocument24 pagesCAPE Chemistry U1 - Breakdown of SyllabusJevon SiddonNo ratings yet
- Accurately Calculate Nitrogen Requirement For Pressure PurgingDocument7 pagesAccurately Calculate Nitrogen Requirement For Pressure PurginglouayNo ratings yet
- First Term SS 2 Chemistry Scheme of WorkDocument74 pagesFirst Term SS 2 Chemistry Scheme of Workangus ogwucheNo ratings yet
- Problem As Cat Al Is Is 2018Document10 pagesProblem As Cat Al Is Is 2018Victor Daniel Martínez CarreteroNo ratings yet
- Chemy 101 1st 19-20 Test 1 Key CDocument8 pagesChemy 101 1st 19-20 Test 1 Key CmNo ratings yet
- Estimating air emissions from external floating roof storage tanksDocument4 pagesEstimating air emissions from external floating roof storage tanksn.hartonoNo ratings yet
- ASRJC 2020 J1 MYCT H2 Chem Paper 1 QPDocument7 pagesASRJC 2020 J1 MYCT H2 Chem Paper 1 QPJunityNo ratings yet
- Heat of Combustion ExperimentDocument8 pagesHeat of Combustion ExperimentAdrian MendozaNo ratings yet
- Test Ch#1 Class 9th Chem PDFDocument1 pageTest Ch#1 Class 9th Chem PDFShah Saqib100% (9)
- Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesManushi ShahNo ratings yet
- MedAngle Premed - Chemistry Review GuideDocument47 pagesMedAngle Premed - Chemistry Review Guideuswa anwerNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 StoichiometryDocument2 pagesActivity 5 StoichiometryBadit GamutNo ratings yet
- Practice StoichiometryDocument5 pagesPractice StoichiometryYohanes BAgus ChristiantNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry BookDocument121 pagesAs Level Chemistry Book11560100% (1)
- Kacmarek: Egan's Fundamentals of Respiratory Care, 10th Edition Chapter 6: Physical Principles of Respiratory Care Test BankDocument15 pagesKacmarek: Egan's Fundamentals of Respiratory Care, 10th Edition Chapter 6: Physical Principles of Respiratory Care Test BankYappie YappieNo ratings yet
- Plus One Chemistry Notes Chapter 1Document20 pagesPlus One Chemistry Notes Chapter 1psuresh_reddyNo ratings yet
- LKM 3 Kel-2 Stoikio MetriDocument16 pagesLKM 3 Kel-2 Stoikio MetriSalsabila AlmasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Guide to Ionic and Covalent BondsDocument17 pagesChemistry Guide to Ionic and Covalent BondsMary-Rose CasuyonNo ratings yet
- Che 201 Handout 2Document36 pagesChe 201 Handout 2Joy Prokash RoyNo ratings yet