Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map For Print
Uploaded by
babitha sOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map For Print
Uploaded by
babitha sCopyright:
Available Formats
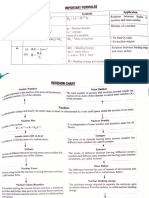
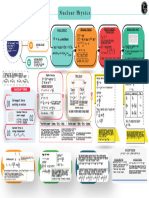
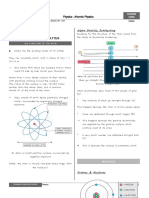
R RoAL
Nuclear radius
Ro-1.2x 101 m
A-mass no.
of protons and neutrons
Consist
zx, A Z+N= mass number
V- 4/3nR Size of nucleus
V 4/3nRA
Nuclear volume Composition aocnumber
N no. oT
neuuo
Density mass of nucleus /volurme
Nucdear density The to
of nucieus
minimum energy required separate
nucleons into its constituent protons and
Nuclear binding energy neutrons.
AM=Zm,+(AZImal-M E AMc
mmass of proton Mass defect
mamass of neutron
Rate
M=mass of nucleus of decay of a radioactive
Law of
proportional to the amount of
NUCLEI radioactive substance present
Heavy doubly lonised He lon decay dN/dt N
Disintegration of heavy N- N, e
Decay of 1 alpha particle cause a-particle elements into
decrease In atomic no. (Z) by 2 and
mass no. (A) by 4 Radioactivity comparitively klighter
elements by emission of
Time taken by radioactive substance to
reduce to haif of t s initial
a p.Y Haff life
In 5+ and decay mass number remains Properties of a B. y concentration
T2-0.633/A
uncnanged, wnereas n e atomic numper goes
up Dy ih p* and atomic no. goes down by 1 in P-partice
B+
Discovered by By Henrl Becqueral in 1896
A wave havving high frequencY
and nom a s s particle
No change in and A
Nuclear Fusion Combining of two lighter nucdei to form a heavy nucleus
Splitting of heavy nucleus into 2 or more lighter nuclei Nuclear fission
General Tormula CHan-2
1.
From unsaturated nydrocarbons
IeparduOn
From alky halides
saturated Alkanes5
Substitution Reaction Halogenation
Combustion
Chemical properties
Isomerisation
Aromatization
yclic polymerisation or etnyne
General formula CaHan
Decarboxylation of aromatic acids Preparation
From Alkymes
Reduction of Phenol
O m d i k nalides
NItration Preparation
From vidinal dihalides
|Sulphonatlon
Electrophilicsubstitution reactions Fromalcohols by acldicdehydration
Halogenation
Chemical properuees
Benzene Aromatic Hydrocarbons Alkenes Additionof dihydrogen
Frledal- Crafts alkylation
AAdditon of halogens
Addiion redcuon
Tosymmetrical alkene
Addition of hydrogen nalldes
Combustion
chemicalproperties 1 o unsymmetical ne
Unsaturated
ortho and Para directing groups
OH, -NH2 CH, CaHs Monosubstituted Benzene
Addition of water
-NO2,-CN, -CHO, -coOH Meta directing groups
Polymerisation
General formula CaHan-2
F r o m calcium carbide
epardu
From vicinal dihalides
Alkyness
Additlon of dihydrogen
Chemlcal properties Addition reaction AOdition or naiogens
Additlon of hydrogen halldes
You might also like
- NucleiDocument3 pagesNucleijaisinghrajput2146No ratings yet
- Mass Defect and Binding EnergyDocument1 pageMass Defect and Binding EnergyMichelle nananaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 NucleiDocument14 pagesChapter 13 Nucleisnv vnsNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Radius: Important Formulae Application ofDocument2 pagesS.NO. Radius: Important Formulae Application ofNitin RanaNo ratings yet
- Im 1482154379 PDFDocument23 pagesIm 1482154379 PDFramlakhanNo ratings yet
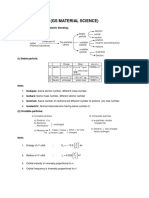
- (Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingDocument23 pages(Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingramlakhanNo ratings yet
- NucleiDocument8 pagesNucleipoojanbhojan1No ratings yet
- Dual Nature Radiation - MatterDocument1 pageDual Nature Radiation - Mattersarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Transfer of Electrons Between Atoms With ADocument1 pageTransfer of Electrons Between Atoms With AameenallyNo ratings yet
- 25 Nuclear Physics: OutlineDocument21 pages25 Nuclear Physics: OutlineeltytanNo ratings yet
- Oxo AQAGCSE P7 ws01 XxaannDocument3 pagesOxo AQAGCSE P7 ws01 XxaannParam BhimaniNo ratings yet
- Unit07 Edexcel International Gcse 9 1 Physics P220to257Document38 pagesUnit07 Edexcel International Gcse 9 1 Physics P220to257Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- PG 1Document1 pagePG 1Faizal HafizNo ratings yet
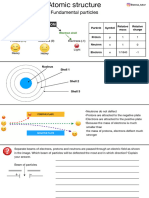
- Structure of The Atom: Sub-Atomic Particles Atomic Models Characteristics of AtomDocument1 pageStructure of The Atom: Sub-Atomic Particles Atomic Models Characteristics of AtomJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Nuclei - Mind Maps - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document1 pageNuclei - Mind Maps - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)npmishra9818No ratings yet
- Nuclei For CBSE Physics Class XII Revision NotesDocument4 pagesNuclei For CBSE Physics Class XII Revision NotesKuldeep HoodaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear and Particle Physics: 3 Year Junior Honours CourseDocument11 pagesNuclear and Particle Physics: 3 Year Junior Honours CourseoomganapathiNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: - The Atom NucleusDocument1 pageGeneral Chemistry: - The Atom NucleusKristineNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Nuclei ExplainedDocument13 pagesAtoms and Nuclei ExplainedHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics Chapter: Structure and PropertiesDocument40 pagesNuclear Physics Chapter: Structure and PropertiesShakir KhattakNo ratings yet
- Revision-Map Chapter 4Document1 pageRevision-Map Chapter 4Megha BishtNo ratings yet
- P11 Dual Nature Radiation - MatterDocument1 pageP11 Dual Nature Radiation - Matterpujansonani677No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Neutron Diffraction On Magnetic MaterialsDocument40 pagesAn Introduction To Neutron Diffraction On Magnetic MaterialsAde MulyawanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics - Mind Map - Lakshya NEET 2024Document1 pageNuclear Physics - Mind Map - Lakshya NEET 2024aanyakaurchonaNo ratings yet
- Colorful Pastel Decimals Math Maze WorksheetDocument2 pagesColorful Pastel Decimals Math Maze WorksheetJessa FerrerNo ratings yet
- Chemi Chapter 3Document4 pagesChemi Chapter 3俊恒No ratings yet
- Together When Positive Charges Repel Each Other?": - "Why Do Protons StayDocument23 pagesTogether When Positive Charges Repel Each Other?": - "Why Do Protons StayIvanah Mae AcloNo ratings yet
- Nuclei Arihant CBSE ChapterwiseDocument21 pagesNuclei Arihant CBSE ChapterwiseMRIDUL SINGH SOAMNo ratings yet
- Struktur AtomDocument5 pagesStruktur AtomCheryl Koeswara 1005033No ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument11 pagesNuclear Physics NotesMichelle nananaNo ratings yet
- 1 Fundamental+particles ScriptDocument1 page1 Fundamental+particles Scriptaria.choudharyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 Notes BundleDocument37 pagesChemistry Paper 1 Notes Bundleemilysacre123No ratings yet
- Modern Physics CH 12Document29 pagesModern Physics CH 12pingjin010No ratings yet
- The Nucleosynthesis of Chemical ElementsDocument14 pagesThe Nucleosynthesis of Chemical ElementsCraig Juliene NavaltaNo ratings yet
- The mass of a nucleus and nuclear stabilityDocument25 pagesThe mass of a nucleus and nuclear stabilityhema maliniNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument17 pagesAtomic PhysicsOrangess GirlNo ratings yet
- Lattice: Ionic and Cao CsiDocument2 pagesLattice: Ionic and Cao CsiUlrichJohnSuplitoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure AnalysisDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure AnalysisMaydline MarbunNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Mind MapDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure Mind Mapa8257448No ratings yet
- ConductorsDocument7 pagesConductorsEshita RoyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FissionDocument1 pageNuclear FissionKevin Haworth0% (1)
- Atomic Structure NotesDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure NotesArti DeviNo ratings yet
- Guide For Nuclide ChartDocument2 pagesGuide For Nuclide ChartRufino RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Binding Energy and Nuclear StabilityDocument8 pagesBinding Energy and Nuclear StabilityJamila RaniNo ratings yet
- Topic 8: Nuclear Physics: - NucleusDocument13 pagesTopic 8: Nuclear Physics: - NucleusHamzah Arman HusniNo ratings yet
- Fusion RouteDocument26 pagesFusion RouteEdward MillerNo ratings yet
- Concept Map ChemistryDocument2 pagesConcept Map ChemistryLester PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Radiation ElementsDocument8 pagesIntroduction to Radiation ElementsAjimKe'enNo ratings yet
- Nuclei - Short Notes - VIJETA SERIES CLASS-12THDocument2 pagesNuclei - Short Notes - VIJETA SERIES CLASS-12THAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Nuclear Physics by Imran AzizDocument187 pagesAdvanced Nuclear Physics by Imran AzizDr.Imran AzizNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument11 pagesAtomic StructureananyahatesithereNo ratings yet
- Intro To Neutron ScatteringDocument191 pagesIntro To Neutron ScatteringEleni MitsiNo ratings yet
- Algebra-Based Physics II: Dec. 3: Chap 31 Nuclear Physics and RadioactivityDocument24 pagesAlgebra-Based Physics II: Dec. 3: Chap 31 Nuclear Physics and RadioactivityazureusNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument30 pagesNuclear PhysicsAreeshaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument65 pagesNuclear ChemistrySriram GangulaNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic Theory Elements and CompoundsDocument10 pagesDalton's Atomic Theory Elements and CompoundsSamantha DumagpiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear StructureDocument37 pagesNuclear StructureNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch. 44: Quarks, Leptons and The Big Bang The Fundamental ParticlesDocument4 pagesCh. 44: Quarks, Leptons and The Big Bang The Fundamental ParticlesvaibhavdkNo ratings yet
- Chapter Thirteen Nuclei: Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesChapter Thirteen Nuclei: Page 1 of 8MT๛ LUCIFERNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition Voet Test Bank DownloadDocument21 pagesFundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition Voet Test Bank Downloadmatildaphelim4g8100% (36)
- Galozinc 1180Document48 pagesGalozinc 1180Pramod SherkarNo ratings yet
- On The Applicability of Flory-Huggins Theory To Ternary Starch-Water-Solute SystemsDocument10 pagesOn The Applicability of Flory-Huggins Theory To Ternary Starch-Water-Solute SystemsjuarsrdNo ratings yet
- Sopha-2021-Investigation To The Optimum Amount of CA, MG and S For The Cultivation of Shallot in Alluvial SoilDocument6 pagesSopha-2021-Investigation To The Optimum Amount of CA, MG and S For The Cultivation of Shallot in Alluvial SoilGinaAliyaSophaNo ratings yet
- Nickel MPS 300 1Document12 pagesNickel MPS 300 1Francisco BocanegraNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Types of SolidDocument4 pagesCHEM-Types of SolidMark Joseph PulintanNo ratings yet
- Iliade 453:2019 - Clen MethodDocument7 pagesIliade 453:2019 - Clen MethodMonirNo ratings yet
- Wound DressingDocument42 pagesWound DressingAbdulazeez Abdulmalik100% (1)
- Well Test Standards WTS 3.8 Coflexip Hoses: Global ManualDocument9 pagesWell Test Standards WTS 3.8 Coflexip Hoses: Global ManualEmmanuel100% (1)
- Carbonized Rice Hull: Ronnie O. NaagDocument18 pagesCarbonized Rice Hull: Ronnie O. NaagRonnie NaagNo ratings yet
- Silicone Elastomers: UV-Cure Silicone RubberDocument12 pagesSilicone Elastomers: UV-Cure Silicone Rubberzaryab khanNo ratings yet
- CBQ ChemDocument35 pagesCBQ ChemIniya RajasekharNo ratings yet
- Product Overview. Polymer Dispersions For Architectural CoatingsDocument6 pagesProduct Overview. Polymer Dispersions For Architectural CoatingsLong An DoNo ratings yet
- Ferrite Processing: Powder Preparation-Raw Materials SelectionDocument66 pagesFerrite Processing: Powder Preparation-Raw Materials Selection吳尚謙No ratings yet
- NCHE111 Study Guide 2024Document96 pagesNCHE111 Study Guide 2024sibulelemathandabuzo1No ratings yet
- Behaviour of NINL Blast Furnace With 100% Calibrated Lump Iron OreDocument9 pagesBehaviour of NINL Blast Furnace With 100% Calibrated Lump Iron OreROWHEITNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan Air Boiler: OlehDocument35 pagesPengolahan Air Boiler: OlehPuput MawartiNo ratings yet
- Surface TensionDocument21 pagesSurface TensionVarun Sudarsanan80% (5)
- % Chapter 27: Molecular GeneticsDocument39 pages% Chapter 27: Molecular Geneticsdds uwuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SS2 Second TermDocument5 pagesChemistry SS2 Second TermKel FelixNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Matters Ch16 Textbk ANSDocument2 pagesChemistry Matters Ch16 Textbk ANSZeneon63% (8)
- 9 ICSE Chemistry Full Test SECTION I (40 Marks) Attempt All Questions From This SectionDocument3 pages9 ICSE Chemistry Full Test SECTION I (40 Marks) Attempt All Questions From This SectionYash SharmaNo ratings yet
- USING MANGOSTEEN RIND AS A PIGMENT IN A MULTIPURPOSE MAKEUP IntroDocument4 pagesUSING MANGOSTEEN RIND AS A PIGMENT IN A MULTIPURPOSE MAKEUP IntroKimberly SisonNo ratings yet
- BS 60079-10-2Document30 pagesBS 60079-10-2Ade KalejaiyeNo ratings yet
- Automotive Lubricants Reference Book (Caines, Arthur J. Haycock, Roger F. Hillier Etc.)Document775 pagesAutomotive Lubricants Reference Book (Caines, Arthur J. Haycock, Roger F. Hillier Etc.)André MenezesNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends Multiple Choice 2012-07-13Document9 pagesPeriodic Trends Multiple Choice 2012-07-13أحمد إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Handbook PDFDocument29 pagesChemistry Handbook PDFAer ZNo ratings yet
- PRC-II Lab ManualDocument41 pagesPRC-II Lab ManualRana Asad AliNo ratings yet
- Study The Hardness of Water and To Determine The Presence of Different IonsDocument11 pagesStudy The Hardness of Water and To Determine The Presence of Different IonsasohanadcNo ratings yet
- DURMAT Flux Cored Wires For Wear Protection Rev 10 RedDocument28 pagesDURMAT Flux Cored Wires For Wear Protection Rev 10 RedandreasNo ratings yet