Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Communication and The 4 Models of Comunnication
Uploaded by
Kamil Dump0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCommunication involves the sharing of ideas between a sender and receiver using language, symbols, and actions. Effective communication is important for improving relationships and achieving goals. However, barriers like noise, psychological factors, and unclear language can interfere with clear communication. Several classic models of communication are discussed, including Aristotle's speaker-centered model, Shannon and Weaver's six-component model involving a sender, receiver, encoder, decoder, channel, and noise, and Schramm's model emphasizing a shared field of experience between parties.
Original Description:
Original Title
Introduction to Communication and the 4 Models of Comunnication
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCommunication involves the sharing of ideas between a sender and receiver using language, symbols, and actions. Effective communication is important for improving relationships and achieving goals. However, barriers like noise, psychological factors, and unclear language can interfere with clear communication. Several classic models of communication are discussed, including Aristotle's speaker-centered model, Shannon and Weaver's six-component model involving a sender, receiver, encoder, decoder, channel, and noise, and Schramm's model emphasizing a shared field of experience between parties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesIntroduction To Communication and The 4 Models of Comunnication
Uploaded by
Kamil DumpCommunication involves the sharing of ideas between a sender and receiver using language, symbols, and actions. Effective communication is important for improving relationships and achieving goals. However, barriers like noise, psychological factors, and unclear language can interfere with clear communication. Several classic models of communication are discussed, including Aristotle's speaker-centered model, Shannon and Weaver's six-component model involving a sender, receiver, encoder, decoder, channel, and noise, and Schramm's model emphasizing a shared field of experience between parties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Communication a.
Verbal - use of language or utter words
● it involves transaction: a person wants to talk to b. Nonverbal - body gestures and facial
someone because one needs something expression
● it is an intricate process of sharing ideas 2. Oral Dimension / Written Dimension
● the process of giving and receiving information a. Oral - imparts the message with proper
between a human source and a human receiver use of delivery
using words/language, symbols, and actions. b. Written - transcription of thoughts and
● came from the Latin word comunicare, meaning ideas
“to share” or “to make common” 3. Formal / Informal Dimensions
Why Effective Communication Matters? a. Formal - meticulous observation of
● Able to improve our relationships with others and appropriateness
achieve our goals in life. b. Informal - casual approach, no formalities
● It makes better people, & better people produce a 4. Intentional / Unintentional Dimensions
better world. a. Intentional - planning to say or on
● Besides the societal benefit, there are economic purpose
benefits of good communication as well. b. Unintentional - not intended or not in
● It is also an essential skill in leadership. purpose
Barriers to Communication Aristotle’s Model of Communication
● Mechanical - noise 1. considered as the first model of communication
● Psychological - state of mind that affects response which was proposed before 300 B.C.
to the message 2. the most widely accepted models of communication
● Semantic - technical words or jargons 3. Speaker-centered model
Do’s 4. can only be used in public speaking
● Know your audience 5 Primary Elements
● Speed in the first few moments 1. Speaker - the one who sends the message; the
● Stay within the allotted time active one
● Understand your message 2. Speech - the message
● Dry run 3. Occasion - event or time which it takes place
● Speak confidently but not aggressively 4. Audience - spectators or listeners
Don'ts 5. Effect - a change which is a result
● Never read Critical Elements of A Good Communicator
● Avoid use of jargons 1. Ethos - credibility of the speaker
● Empty space or dead air 2. Pathos - the way the audience react to the
● Don’t point your fingers speaker’s message
● Don’t overuse abbreviations 3. Logos - speaker’s message (facts, information and
● Don’t interrupt statements)
Miscommunication (Communication Breakdown) - failure to Aristotle - ancient Greek philosopher and polymath
communicate clearly Born 384 BC Stagira, Greece
Dimensions of Communication Died 322 BC Euboea Island Greece
Dimension - the amount of number of things that affects or Shannon and Weaver’s Model of Communication
influences 1. first and most influential models of communication.
2 Factors that can influence 4 Dimensions of 2. It was initially published in the 1948 paper "A
Communication Mathematical Theory of Communication" and
1. Culture - the set of shared practices that explains communication in terms of six basic
characterizes a certain group of people components: a source, an encoder, a channel,
2. Gender - what society considers appropriate for the noise, a decoder and the receiver.
men and women in terms of action and behavior. 3. Mother of all Models
4 Dimensions of Communication 4. Also known as Information Theory or Shannon
1. Verbal / Nonverbal Dimension Theory
6 Basic Components
1. Sender - or information source, transmits a
message
2. Encoder - or transmitter that is used to convert the
message into signals.
3. Channel - path or medium that carries the
transmitter to the receiver.
4. Noise - or disturbance
a. Internal - when the sender had a mistake
encoding their message
b. External - external hindrance
5. Decoder - or reception
6. Receiver - or destination, endpoint
Schramm's Model of Communication
1. It is a field of experience, it is everything that makes
a person unique.
2. It is an early and influential model of
communication.
Wilbur Schramm - father of Mass Communication, born
Marietta, Ohio in 1907 died in Hawaii in 1987
5 Components
1. Field of Experience - shared or common
knowledge of the speaker and the listener
2. Sender and Receiver - initiates the communication
and interprets the message
3. Message - or the content
4. Encoder and Decoder - Encoder is how the sender
processes the information they want to imply while
the decoder is how the receiver understands the
message.
5. Noise - interference external or internal
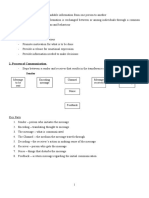
White’s Model of Communication
1. This is a circular and continuous communication,
this is why it is a cyclical model and not linear.
2. It is the concept of feedback, it is the speaker’s
perception of the listener’s response
8 Components
1. Thinking
2. Symbolizing
3. Expressing
4. Transmitting
5. Receiving
6. Decoding
7. Feedback
8. Monitoring
You might also like
- Signs That Your Partner Is NacissisticDocument4 pagesSigns That Your Partner Is NacissisticBlack BirdNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelegenceDocument43 pagesEmotional IntelegenceIvy AlzagaNo ratings yet
- Social Skills ChecklistDocument3 pagesSocial Skills ChecklistWilliamNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Document6 pagesOral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Katleya Balitaan75% (8)
- The Nonverbal Factor: Exploring the Other Side of CommunicationFrom EverandThe Nonverbal Factor: Exploring the Other Side of CommunicationNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Theory & Practice: Managing Employee Retention, Engagement, and CareersDocument15 pagesHuman Resource Theory & Practice: Managing Employee Retention, Engagement, and CareersMUHAMMAD TALATNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Oral-CommunicationDocument3 pagesReviewer Oral-CommunicationRyan100% (1)
- Oral Communication 1 Quarter Reviewer Nature of CommunicationDocument4 pagesOral Communication 1 Quarter Reviewer Nature of CommunicationIsabel De Leon100% (1)
- Oral Communication - ReviewerDocument4 pagesOral Communication - ReviewerSamsamNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument10 pagesPurposive CommunicationJee En Bee57% (7)
- FS1 Episode 4Document12 pagesFS1 Episode 4Alexis S. Duque50% (2)
- RPMS With Movs and Annotations JINKY MACALAGUING (Autosaved)Document104 pagesRPMS With Movs and Annotations JINKY MACALAGUING (Autosaved)Joey Orale100% (1)
- Purposive Communication-Lesson1Document20 pagesPurposive Communication-Lesson1Jerome BautistaNo ratings yet
- Hand Out For Midterm Exam in Oral CommDocument4 pagesHand Out For Midterm Exam in Oral CommRoland John MarzanNo ratings yet
- SCRAPBOOKDocument4 pagesSCRAPBOOKRachel Curato100% (1)
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocument3 pagesOral Comm Reviewerdingomez01No ratings yet
- ENG111Document5 pagesENG111Ciana SacdalanNo ratings yet
- Module 1&2 (Oral Comm)Document5 pagesModule 1&2 (Oral Comm)Lory TenorioNo ratings yet
- Humss 11 B1 Oral Comm Reviewer Unit 1Document2 pagesHumss 11 B1 Oral Comm Reviewer Unit 1JANIS ESPEJONo ratings yet
- Gec 115 Lec 1 - 2 Pre MidDocument3 pagesGec 115 Lec 1 - 2 Pre MidArchjune Aubrey AbellaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication LectureDocument18 pagesPurposive Communication LectureRandolf MartinezNo ratings yet
- TC Combined Notes Unit 1Document37 pagesTC Combined Notes Unit 1love goswamiNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication LT 1.1Document2 pagesOral Communication LT 1.1Eryka FloresNo ratings yet
- Oral Com and Fabm ReviewerDocument6 pagesOral Com and Fabm ReviewerEzra Mae ValdezNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm Reviewer - 1GDocument3 pagesOral Comm Reviewer - 1GJasken MabiniNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication PrelimDocument5 pagesPurposive Communication PrelimCrystal MaurinNo ratings yet
- Purcom Reviewer KVDGDocument11 pagesPurcom Reviewer KVDG06675354dNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes, Principles and EthicsDocument5 pagesCommunication Processes, Principles and Ethicsmarygrace carbonelNo ratings yet
- PRELIMS PCOMMS PoDocument6 pagesPRELIMS PCOMMS Polazarojohnvincent8No ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument4 pagesOral Communication ReviewerveraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Purposive Communication)Document13 pagesUnit 1 (Purposive Communication)Christine100% (2)
- Nature and Elements of CommunicationDocument17 pagesNature and Elements of CommunicationannahkaupaNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesOral CommunicationJulie Anne AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication ReviewerDocument10 pagesOral Communication ReviewerReychel LunaNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesOral CommunicationKaith Ashlee De LeonNo ratings yet
- PURPCOM PRELIMS ReviewerDocument11 pagesPURPCOM PRELIMS ReviewerPagodNo ratings yet
- DIASSDocument3 pagesDIASSLouanne LabataNo ratings yet
- Communication SkillsDocument6 pagesCommunication SkillsNikita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Oralcomm ReviewerDocument4 pagesOralcomm Reviewer예쁜SaichiNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesReviewer Oral CommunicationRyanNo ratings yet
- 1 The Components of The Communication ProcessDocument3 pages1 The Components of The Communication ProcessColleena CortesNo ratings yet
- Communication: Anil VermaDocument15 pagesCommunication: Anil Vermaaniket yadav0006No ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument5 pagesOral ComHanna BantinanNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER in PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATIONDocument9 pagesREVIEWER in PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATIONMikee Trisha Mae PonteNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication STUDY GUIDEDocument4 pagesPurposive Communication STUDY GUIDEjean ApostolNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument2 pagesPurcom Reviewergimboongaling489No ratings yet
- GEC 131 Puposive Comm Prelim CoverageDocument17 pagesGEC 131 Puposive Comm Prelim CoverageJohara BayabaoNo ratings yet
- English 4th QuarterDocument5 pagesEnglish 4th QuarterRae DizonNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument7 pagesCommunication ModelsKrystal NunezNo ratings yet
- Communication Is The Process of Expressing and Exchanging Information, Thoughts, Ideas and FeelingsDocument1 pageCommunication Is The Process of Expressing and Exchanging Information, Thoughts, Ideas and FeelingsMary Christine IgnacioNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerDesiree QuinioNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm NotesDocument7 pagesOral Comm NotesCandice FabrigaNo ratings yet
- PurCom MidtermsDocument5 pagesPurCom MidtermshaneenamaedediosNo ratings yet
- Midterms Reviewer For GE 5Document3 pagesMidterms Reviewer For GE 5Aquino, Jasmine C.No ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Module 1Document7 pagesPurposive Communication Module 1Reneli GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Bussinus Communication AhmadDocument43 pagesBussinus Communication AhmadIbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument8 pagesPurposive CommunicationPapsykatrinamaryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business CommunicationDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Business CommunicationAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document19 pagesWa0003.Lovis KumarNo ratings yet
- Learning at Home ProgramDocument5 pagesLearning at Home ProgramAldrin AldrinNo ratings yet
- Communication: Message To Be Sent Encoding Message Channel Message Received Message DecodingDocument4 pagesCommunication: Message To Be Sent Encoding Message Channel Message Received Message DecodingMyoMyanmarNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument2 pagesOral CommunicationKisumi ShiginoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Communication ModelsDocument2 pagesModule 5 Communication ModelsshahiraNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context First Quarter (Pointers) : 1. Schemata-DrivenDocument13 pagesOral Communication in Context First Quarter (Pointers) : 1. Schemata-DrivenMichael Jan BajenNo ratings yet
- Sample Module EditedDocument5 pagesSample Module EditedJayson GarciaNo ratings yet
- 20 Life Skills You Don't Get Taught in School: A Practical Guide to Personal Growth and SuccessFrom Everand20 Life Skills You Don't Get Taught in School: A Practical Guide to Personal Growth and SuccessNo ratings yet
- Lsel - Habit 5 (Draft 3)Document23 pagesLsel - Habit 5 (Draft 3)Gonzalez AndrewNo ratings yet
- Chap 12Document15 pagesChap 12Nguyen Thao Duy MaNo ratings yet
- GE - selfitisDocument5 pagesGE - selfitisTulika SahuNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Final Exams Part IIDocument3 pagesNCM 109 Final Exams Part IIsnay axieNo ratings yet
- Baludi - Term PaperDocument5 pagesBaludi - Term PaperBainalyn BaludiNo ratings yet
- Development of Human ResourcesDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Human ResourcesCarl Baytola RatesNo ratings yet
- Communication Satisfaction QuestionnaireDocument14 pagesCommunication Satisfaction QuestionnairePhương ThảoNo ratings yet
- AssafdefgDocument5 pagesAssafdefgRosela Mae BaracaoNo ratings yet
- Perdev Q2W8 PPT FinalDocument32 pagesPerdev Q2W8 PPT FinalJE RalynNo ratings yet
- Caress 1 1Document6 pagesCaress 1 1BOSSMEYJNo ratings yet
- AJGP 07 2020 Clinical Su Adult Survivors Childhood Trauma Fig 1Document1 pageAJGP 07 2020 Clinical Su Adult Survivors Childhood Trauma Fig 1PsihoEgo Coman CristinaNo ratings yet
- MyNotes Unit 1Document5 pagesMyNotes Unit 1prathmesh51chumbalkarNo ratings yet
- 6.scope of Educational PsychologyDocument7 pages6.scope of Educational PsychologyshiranthaNo ratings yet
- Distinction Between Social Change and Cultural ChangeDocument2 pagesDistinction Between Social Change and Cultural ChangeNikon SonuNo ratings yet
- Essay 11Document2 pagesEssay 11Siimanye Olumiyo JobelaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document16 pagesLesson 3Clea JunillerNo ratings yet
- Hes 008 - Sas 6Document2 pagesHes 008 - Sas 6Juliannah ColinaresNo ratings yet
- Socio-Cultural TraditionDocument7 pagesSocio-Cultural TraditionRosalinda GuingabNo ratings yet
- Elc ArgumentativeDocument6 pagesElc Argumentativenur iffHNo ratings yet
- Ogl 300 Project MangamentDocument4 pagesOgl 300 Project Mangamentapi-701146001No ratings yet
- Communication, Coaching, and Conflict SkillsDocument31 pagesCommunication, Coaching, and Conflict SkillsVrutika ShahNo ratings yet
- Impact of Organizational Culture On Organizational Performance (A Case Study of Federal Polytechic Offa, Kwara State)Document64 pagesImpact of Organizational Culture On Organizational Performance (A Case Study of Federal Polytechic Offa, Kwara State)lawal kola taofeeqNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Teacher Commitment On Student Achievement: A Case Study in IraqDocument5 pagesThe Effects of Teacher Commitment On Student Achievement: A Case Study in IraqSetiaji RahmawanNo ratings yet
- Teaching English As A Foreign LanguageDocument16 pagesTeaching English As A Foreign LanguageFebiana WardaNo ratings yet