Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ada 6 Learning Styles
Uploaded by
Adriana PatOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ada 6 Learning Styles
Uploaded by
Adriana PatCopyright:
Available Formats
en
ig c
ll e
e
t
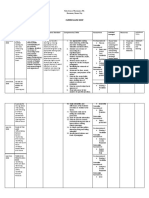
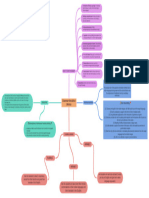
n The term intelligence has
traditionally been used to refer to
I
performance on certain tests .
,
However IQ tests may be related Ap
t
to metalinguistic knowledge than i
.
Specific abilities thought to
t
communicative ability The kind of
predict success in language
u
ability measured by a traditional
learning.
ed
IQ test may be a strong predictor The most widely used aptitude tests have
when it comes to learning that been the Modern Language Aptitude Test
involves language analysis and ( )
MLAT and the Pimsleur Language Aptitude
rule learning . Battery PLAB ( ). All measure the ability to 1)
identify and memorize new sounds , 2)
understand the function of particular
words in sentences , 3) figure out
grammatical rules from language samples
and 4) remember new words .
styl
e
g
n
s
in
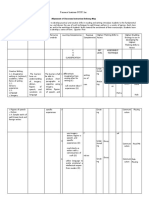
It describes an individual s natural habitual and ' , ,
, ,
ra
preferred way of absorbing processing and
retaining new information and skills Reid ( , 1995).
e
LLearners can be dividen in field independent or
,
field dependent according to whether they
tend to separate details from the general
background or tend to see thing more
holistically .
rso
e
P
ilan
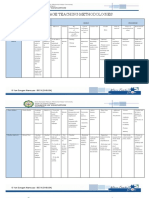
Several personality characteristics
have been proposed as likely to affect
t
second language learning such as
, , -
y
inhibition learner anxiety self
,
confidence self esteem empathy - , ,
dominance talkativeness , ,
responsiveness etc , .
Individual
differences
in second
language
ziL
e z
learning
t
at
J ,zaíD h
ezeM a
S
E
U
Instrumental motivation :
T
n
u
H o i l & Juli
t
language learning for immediate
.
a
IT T A
e
or practical goals
Integrative motivation language :
learning for personal growth and
cultural enrichment .
el i e
D
M
b f
r
N
s
e
T
n
Learner beliefs can be strong
I A
V
raeL
mediating factors in their
A TI O N
experience in the classroom.
Recent research on learner beliefs about the role of
grammar and corrective feedback in second language
learning shows a mismatch between students and
' . ,
teachers views Thus learners instructional preferences will '
influence the kind of strategies teachers should use .
uis
q it
c i
a
o
f
n
o
It has been hypothesized that there is
tity
eg
a critical period for second language
n
' ,
e
Learners identities impact on what acquisition called the Critical Period
.
dI
they can do and how they can Hypothesis It claims that there is a
participate in classrooms this , time in human development changes
naturally affects how much they in the human brain which affect the
.
can learn Identities could eventually nature of language acquisition .
lead to their isolation and to
restricted or less powerful
participation in the class comunity .
Toohey (2000) argues that
indentities change over time it s , '
important that the class provides
learning oportunites for every
student .
, .& , . (2011).
. . 53-75
Lightbown P Spada N How languages
are learned Oxford Pp
You might also like
- Japanese Nihongo First StepDocument183 pagesJapanese Nihongo First Stepg0nchan78% (9)
- Mycenaean Greek: 1 OrthographyDocument5 pagesMycenaean Greek: 1 Orthographynico-rod1No ratings yet
- My Korean 2Document503 pagesMy Korean 2valery herrera100% (2)
- Grade 08 English With Answer KeyDocument7 pagesGrade 08 English With Answer KeyKanyesha HesedortNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English Grade 10 by Lyra Z. AustriaDocument17 pagesLesson Plan in English Grade 10 by Lyra Z. Austrialyra z austria67% (3)
- DLL Grade 8 EnglishDocument4 pagesDLL Grade 8 EnglishCrisanta Panes Bolero100% (1)
- K3V DT PartsDocument1 pageK3V DT Partssolserengsa100% (1)
- English 7 - Quarter 4Document17 pagesEnglish 7 - Quarter 4Angelica NobletaNo ratings yet
- L4 - The Lion King - Teacher Notes - American English PDFDocument12 pagesL4 - The Lion King - Teacher Notes - American English PDFdorinaNo ratings yet
- Le Francais en CinquiemeDocument166 pagesLe Francais en CinquiemeWaly Sow100% (1)
- UI Is CommunicationDocument13 pagesUI Is CommunicationEverett McKayNo ratings yet
- Episode 7 Writing My First Lesson Plan PDFDocument15 pagesEpisode 7 Writing My First Lesson Plan PDFZoey DutcheeNo ratings yet
- Unpacked CG G2 Q1Document11 pagesUnpacked CG G2 Q1Laith Austin T. GalagarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Speaking - Key Terms - GlossaryDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Speaking - Key Terms - GlossaryAishaNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Eng4 DLL (W2)Document12 pagesQ3 - Eng4 DLL (W2)Gracezyl ManlangitNo ratings yet
- Acp English Class 3Document8 pagesAcp English Class 3Chinmayee MishraNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in Grade 10Document5 pagesCurriculum Map in Grade 10Jovy LazonaNo ratings yet
- 2.6.2 Ip 2.6.2Document10 pages2.6.2 Ip 2.6.2jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- 3RD Meeting MaterialDocument14 pages3RD Meeting MaterialKadek DitoNo ratings yet
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q4 - W4 - D4Document9 pagesDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q4 - W4 - D4Lotcel Alcantara SugatanNo ratings yet
- Cuadro Comparativo Methods 2ND LG AcquisitionDocument18 pagesCuadro Comparativo Methods 2ND LG AcquisitionBraian Maximiliano GarcésNo ratings yet
- 2.6.1 Ip 2.6.1Document10 pages2.6.1 Ip 2.6.1jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Iplan L3.2.2Document4 pagesIplan L3.2.2jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Iplan L3.2.2-ADocument4 pagesIplan L3.2.2-Ajayson reyesNo ratings yet
- DLL wk5Document30 pagesDLL wk5Cher MariaNo ratings yet
- DLL Template For TeachersDocument6 pagesDLL Template For TeachersAika A. RochaNo ratings yet
- Seminario de San Jose: Diary Curriculum MapDocument8 pagesSeminario de San Jose: Diary Curriculum MapKARLO MARKO VALLADORESNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Evan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- 1st Q WEEK 3 ALL SUBJECTS DAY 3Document6 pages1st Q WEEK 3 ALL SUBJECTS DAY 3FiLresh OcLarit - LlorenNo ratings yet
- Cidam TemplateDocument2 pagesCidam TemplateEph FurNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Grade 7Document16 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 7Mary Grace CorpuzNo ratings yet
- DLL All Subjects 2 q4 w4 d4Document9 pagesDLL All Subjects 2 q4 w4 d4Abegail E. EboraNo ratings yet
- Dolor Cidam CreativeDocument8 pagesDolor Cidam CreativeDOLORFEY L. SUMILENo ratings yet
- Tacticas de Evaluacion KevinDocument3 pagesTacticas de Evaluacion KevinEliana RoscelyNo ratings yet
- English 8 - Quarter 1Document9 pagesEnglish 8 - Quarter 1Angelica NobletaNo ratings yet
- Language Teaching MethodologiesDocument10 pagesLanguage Teaching MethodologiesG-yan Dungan MamuyacNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in English 1Document1 pageSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in English 1John Mark BulahNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: I. ObjectivesEvan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- Mae Ann Curriculum Map Grade 7Document2 pagesMae Ann Curriculum Map Grade 7Mae Ann Miralles PiorqueNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 DLL. Q4 W5 Day 1Document5 pagesGrade 2 DLL. Q4 W5 Day 1Rhonalyn Patrimonio GirayNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson Planapi-584849024No ratings yet
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Plan Grade: 11: 1. Creative WritingDocument8 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Plan Grade: 11: 1. Creative WritingJemay YutragoNo ratings yet
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q4 - W4 - D4Document9 pagesDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q4 - W4 - D4Princess Diane Jade AgnisNo ratings yet
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q4 - W2Document49 pagesDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q4 - W2JayD'z Mini RabbitryNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 Iplan Lesson 2 LO2-3Document4 pages2.1.3 Iplan Lesson 2 LO2-3jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- 2.1.2 Iplan Lesson 2 LO2-2Document4 pages2.1.2 Iplan Lesson 2 LO2-2jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 DLL - Lesson 13 - Week 4Document2 pagesGrade 3 DLL - Lesson 13 - Week 4Aria JinzihanNo ratings yet
- MG DLLDocument8 pagesMG DLLTintin Dimalanta LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ESPDocument7 pagesSyllabus ESPErfiansyah Bagus RiyadiNo ratings yet
- DLL - All Subjects 2 - Q4 - W5 - D1Document6 pagesDLL - All Subjects 2 - Q4 - W5 - D1Lougiebelle DimaanoNo ratings yet
- (Arranged by Amt/Rbt) (Based On Amt/Rbt Classification) Refer To The Melc Given by DepedDocument12 pages(Arranged by Amt/Rbt) (Based On Amt/Rbt Classification) Refer To The Melc Given by DepedRogieMae Dela Cruz SantosNo ratings yet
- Caparing TableDocument4 pagesCaparing TableNgọc HồNo ratings yet
- Grammar Translation MethodDocument1 pageGrammar Translation MethodNguyen Ngoc YenNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris I: (Teknik Informatika/Sistem Komputer)Document18 pagesBahasa Inggris I: (Teknik Informatika/Sistem Komputer)Kadek DitoNo ratings yet
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapDocument4 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment MapcaroleNo ratings yet
- DLL All Subjects 2 q4 w4 d4Document9 pagesDLL All Subjects 2 q4 w4 d4HEYA YANGNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 English Syllabus 4th QuarterDocument15 pagesGrade 7 English Syllabus 4th QuarterJonel CarballoNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in English 7Document4 pagesCurriculum Map in English 7John Resty P. AsoyNo ratings yet
- нэгж хичээл 11 ангиDocument13 pagesнэгж хичээл 11 ангиБаатар Бат-ЭрдэнэNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Evaluation ToolDocument2 pagesMonitoring and Evaluation ToolCamelle Medina100% (1)
- Knowledge: The Factor Condition of Knowing Something With Familiarity Gained Through Experience or AssociationDocument5 pagesKnowledge: The Factor Condition of Knowing Something With Familiarity Gained Through Experience or AssociationShen EugenioNo ratings yet
- DLLL English 9Document5 pagesDLLL English 9Dail Ramyel PanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17Document6 pagesLesson 17elmerNo ratings yet
- English Core Learning Area Standard: QUARTER 1: Philippine Oral LoreDocument4 pagesEnglish Core Learning Area Standard: QUARTER 1: Philippine Oral Lorejg.mariane102No ratings yet
- Proiectare CL 7 NouDocument22 pagesProiectare CL 7 NouoleseaNo ratings yet
- CIDAM - EappDocument3 pagesCIDAM - EappTintin ArcalasNo ratings yet
- Unit Planner IepsDocument4 pagesUnit Planner Iepsapi-407279500No ratings yet
- RPT t5 - Bahasa InggerisDocument8 pagesRPT t5 - Bahasa InggerisfikriNo ratings yet
- Delphi Study NotesDocument36 pagesDelphi Study NotesRianNo ratings yet
- Ela Grade Three GuidanceDocument57 pagesEla Grade Three Guidanceapi-266473918No ratings yet
- Listado de Verbos Irregulares10 - 11Document1 pageListado de Verbos Irregulares10 - 11Sebastian GuerreroNo ratings yet
- NLEPT Catalogue PDFDocument121 pagesNLEPT Catalogue PDFHëłľ Śç BøÿNo ratings yet
- I Hate English CourseworkDocument6 pagesI Hate English Courseworkf67m6abx100% (2)
- A Written Test 2Document6 pagesA Written Test 2Alice WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Example Lesson Plan Name Student Profile: Topic: Aims::: Hercules Chipps TravelDocument5 pagesExample Lesson Plan Name Student Profile: Topic: Aims::: Hercules Chipps TravelLiz BiggsNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Special EducationDocument6 pagesUnit 4: Special Educationdong nganNo ratings yet
- Speech CommunitiesDocument4 pagesSpeech CommunitiesIntan SiraitNo ratings yet
- Apuntes 1Document9 pagesApuntes 1Iván Bote MerinoNo ratings yet
- TocharianDocument28 pagesTocharianebi18750No ratings yet
- Imaginary Homelands Salman RushdieDocument7 pagesImaginary Homelands Salman Rushdierazataizi444No ratings yet
- Mona Baker - Contextualization in Trans PDFDocument17 pagesMona Baker - Contextualization in Trans PDFBianca Emanuela LazarNo ratings yet
- Gerund or InfinitiveDocument4 pagesGerund or Infinitivesmail ajramiNo ratings yet
- The Bayeux Tapestry Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesThe Bayeux Tapestry Lesson Planapi-316613415No ratings yet
- Rajib Mall Lecture NotesDocument84 pagesRajib Mall Lecture NotesAnuj NagpalNo ratings yet
- Jadual Pameran 29 APRIL 2019 Foyer SMK Bandar Sungai PetaniDocument1 pageJadual Pameran 29 APRIL 2019 Foyer SMK Bandar Sungai PetanirohizahNo ratings yet
- An Analysis On Word Search in Conversation Between Non-Native Speaker and Native Speaker of EnglishDocument13 pagesAn Analysis On Word Search in Conversation Between Non-Native Speaker and Native Speaker of EnglishShierly Diana Da CostaNo ratings yet
- GMAT Verbal - TestDocument14 pagesGMAT Verbal - TestArjunSahooNo ratings yet
- Principles of Language Learning and Teaching (Longman) - Chapter 8: Cross Linguistic Influence and Learner LanguageDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Language Learning and Teaching (Longman) - Chapter 8: Cross Linguistic Influence and Learner LanguageLuis Rodriguez Zalazar100% (1)