Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HAPP 111 Laboratory Exam Reviewer
Uploaded by
Don Aldrich Santos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesLab EXAM reviewer Study Well
Original Title
HAPP-111-Laboratory-Exam-Reviewer (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLab EXAM reviewer Study Well
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesHAPP 111 Laboratory Exam Reviewer
Uploaded by
Don Aldrich SantosLab EXAM reviewer Study Well
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
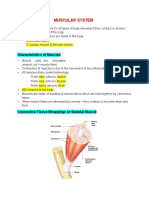
Exercise 5: Muscular System Exercise 6: Nervous System
• Structure of Skeletal Muscle • Brain
o Connective tissue coverings o Cerebrum – the largest part of the
▪ Epimysium – muscle brain
▪ Perimysium – fasciculus ▪ Frontal lobe – emotions,
▪ Endomysium – muscle voluntary movements
fiber ▪ Parietal lobe – sensations
o Sarcomere – basic unit of a ▪ Occipital lobe – vision
myofibril ▪ Temporal lobe – auditory,
o Muscle Fiber filaments smell, memory
▪ Actin – thin filament o Cerebellum – coordination of
▪ Myosin – thick filament movement, posture, balance, fine
o Organelles motor movement, motor learning
▪ Sarcolemma – cell o Brainstem – life sustaining
membrane in muscle functions; most primitive part
▪ Sarcoplasm – cytoplasm ▪ Midbrain
in muscle ▪ Pons – movement
▪ Sarcoplasmic reticulum – coordination
releases calcium ions ▪ Medulla oblongata –
o Striations breathing, heartbeat; most
▪ A band – appears thicker caudal structure
due to actin-myosin o Diencephalon
overlap ▪ Epithalamus – emotional
▪ I band – appears thinner and visceral response to
due to absence of myosin odors
▪ Z disk – boundary ▪ Thalamus – influences
between sarcomeres moods and detects pain
• Steps in Muscle Contraction ▪ Hypothalamus – controls
o Generation of Action Potential pituitary gland
from CNS
o Action potential reaches the nerve
end, releasing neurotransmitter Exercise 7: Peripheral Nervous System
(acetylcholine)
o Acetylcholine binds to a receptor in • Somatic Senses – single receptors embedded
sarcolemma in skin or muscle tissue
o Gated sodium ion channel opens; o Thermoreceptors – detect hot, cold,
influx of sodium ions and changes in the temperature
o Depolarization triggers release of o Propioceptors – sense the
calcium ions contraction or tension of a muscle
o Calcium binds to troponin organ
o Troponin-tropomyosin moves away • Special Senses – involve elaborate sense
from myosin-binding site organs
o ATP hydrolysis forms cross bridges o Photoreceptors – light sensitive
o Actin and myosin pull each other receptors found inside the eye
• Phases of Muscle Contraction (Skeletal o Chemoreceptors – sensitive to odor
Muscles) and taste and can be found in
o Latent Phase olfactory bulb and taste buds
o Contraction Phase
o Relaxation Phase
Exercise 8: Blood, the Endocrine, and Lymphatic o Luteinizing hormone – stimulates
Systems cells that produces testosterone and
progesterone
• Erythrocytes (RBC) – carries gases using o Follicle-stimulating hormone –
hemoglobin; last for 120 days initiates development of ova
• Leukocytes (WBC) – immunity against o Prolactin – initiates milk secretion
diseases o Thyroxine – regulates body
o Granulocytes metabolism
▪ Eosinophil – involved in o Calcitonin – decreases calcium
immunity against parasitic level in the blood
infections o Parathormone – maintains or
▪ Neutrophil – first line of increases the calcium level in the
defense for bacterial blood
infection o Aldosterone – increase sodium
▪ Basophil – releases levels and decreases potassium
histamine levels in the blood
o Agranulocytes o Melatonin – regulates the body’s
▪ Lymphocytes – present in circadian rhythm
viral infections; involved o Insulin – decreases sugar level in
in adaptive immunity the blood by converting glucose to
▪ Monocytes – important in glycogen
chronic infection; turns o Glucagon – increases sugar level in
into macrophages after the blood by releasing stored
diapedesis occurs glycogen
• Thrombocytes – needed for clotting process o Testosterone – responsible for male
• Endocrine Glands secondary sex characteristics
o Pituitary Gland – master gland; o Estrogen – responsible for female
secretes hormones to control other secondary sex characteristics
glands o Progesterone – stimulates secretion
o Thyroid Gland – found in the of nutrients for early zygote
throat; secretes thyroxine and • Lymphatic Structures
calcitonin o Lymphatic Vessels – structures that
o Parathyroid Gland – four glands collect lymph from different parts
found in the posterior of the thyroid of the body
gland; secretes parathormone o Lymph Nodes – small, round
o Adrenal Gland – found in the organs found along lymphatic
superior portion of the kidneys; vessels that filters the lymph
secretes epinephrine o Tonsils – structures found in the
o Pancreas – found in the abdominal throat that can fight infections.
area posterior to stomach; secretes o Thymus – location of maturation of
insulin and glucagon the immune cells T cells
o Thymus Gland – found in the chest o Spleen – structure in the left
anterior to the heart; secretes hypochondriac region responsible
thymosine for destroying worn out RBCs
o Pineal Gland – found in the middle
of the brain; secretes melatonin
• Hormones
o Antidiuretic hormone – constrict
the blood vessels and decrease
urine
o Oxytocin – stimulates uterine
contraction during labor
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to The Pineal Gland (The Third Eye) And Its FunctionFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Pineal Gland (The Third Eye) And Its FunctionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Review - Animal Motor SystemsDocument4 pagesReview - Animal Motor SystemskjhNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 and 2 GenhistoDocument4 pagesTopic 1 and 2 GenhistoShiina MashiroNo ratings yet
- OT 212 - NotesDocument4 pagesOT 212 - Notesno nameNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesBIOLOGY-Skeletal and Muscular SystemSilverNo ratings yet
- Muscular System ManuscriptDocument21 pagesMuscular System ManuscriptOdds BinalayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document6 pagesChapter 8Yna Mae C. De LeonNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesMuscular SystemDOROLA CRIS JANELICA R.No ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System: Rodina Rivera-Gorospe, M.DDocument44 pagesAutonomic Nervous System: Rodina Rivera-Gorospe, M.DPogo LocoNo ratings yet
- Psyco104 Hayward Ch3 OnlineDocument51 pagesPsyco104 Hayward Ch3 OnlineyaoyingNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System-Lacsamana NotesDocument13 pagesEndocrine System-Lacsamana NotesNOEL ANGELO LACSAMANANo ratings yet
- S1 OtotDocument46 pagesS1 OtotJauhar FirdausNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System-1Document46 pagesAutonomic Nervous System-1a-tldNo ratings yet
- Craniosacral OsteopathyDocument100 pagesCraniosacral OsteopathyHossein Khorrami100% (1)
- Neurology 1Document47 pagesNeurology 1Sonu CanNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument9 pagesMusclesYulia RestyNo ratings yet
- NEURO 3.04 ANSLimbic System HypothalamusDocument10 pagesNEURO 3.04 ANSLimbic System HypothalamusMarlon BauagNo ratings yet
- System: Musculo Muscle Tissue:: A&P Muscle Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument23 pagesSystem: Musculo Muscle Tissue:: A&P Muscle Anatomy & PhysiologyjhnnolanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System TransesDocument5 pagesEndocrine System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemRoeisa SalinasNo ratings yet
- 7 MuscleDocument3 pages7 MuscleprincessstephNo ratings yet
- o Brain, Spinal Cord - o Cranial Nerves, Spinal Nerves - o Sympathetic o ParasympatheticDocument33 pageso Brain, Spinal Cord - o Cranial Nerves, Spinal Nerves - o Sympathetic o ParasympatheticLance CarandangNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Chapter 1 2Document6 pagesANAPHY Chapter 1 2BSN1C John Ashley PastorizoNo ratings yet
- ANS PharmacologyDocument181 pagesANS Pharmacologywizgrace12No ratings yet
- Kuliah Pengantar Fisiologi Neuromuskuloskeletal 2021Document43 pagesKuliah Pengantar Fisiologi Neuromuskuloskeletal 2021rifkaNo ratings yet
- Animal Hormones PDFDocument11 pagesAnimal Hormones PDFAin HusnaNo ratings yet
- 051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla CatecholaminesDocument4 pages051 Endocrinology Physiology Adrenal Medulla Catecholaminesیوسف رمضانNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument16 pagesMuscular Systemjgabiran02No ratings yet
- Unit Xii - Animal Physiology Ii: Reproductive, Nervous, Digestive, Muscular SystemsDocument40 pagesUnit Xii - Animal Physiology Ii: Reproductive, Nervous, Digestive, Muscular SystemsangelaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Reviewer - BAYLONDocument16 pagesReproductive System Reviewer - BAYLONElijah Joaquin Payumo BaylonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer 2.0Document7 pagesAnatomy Reviewer 2.0Angeline VegaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer 2.0Document7 pagesAnatomy Reviewer 2.0Angeline VegaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer 2.0Document7 pagesAnatomy Reviewer 2.0Angeline VegaNo ratings yet
- Sci Nervous and Endocrine RVWRDocument5 pagesSci Nervous and Endocrine RVWRNhovie Claire FlorencioNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesMuscular SystemMelanie SablayNo ratings yet
- First Eaxam SlidesDocument49 pagesFirst Eaxam SlidesYousef Ahmad2No ratings yet
- General Biology Lesson 13Document13 pagesGeneral Biology Lesson 13GUCOR, LOVELY SHANE C.No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer - BAYLONDocument6 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer - BAYLONElijah Joaquin Payumo BaylonNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenbio2 ReviewerLovely QuezonNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System - 4: Chapter - 5 Lecture - 11Document53 pagesThe Nervous System - 4: Chapter - 5 Lecture - 11Noor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of MusculosceletalDocument119 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of MusculosceletalIrgi PutraNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument61 pagesMuscle TissueCatherine Joy SalongaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 2Document18 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 2Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Osmosis High-Yield Physiology - Medicalstudyzone - Com (Sürüklenen)Document87 pagesOsmosis High-Yield Physiology - Medicalstudyzone - Com (Sürüklenen)Dilay MercimekNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFDocument22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFannora daffaNo ratings yet
- Kidneys: The Urinary SystemDocument25 pagesKidneys: The Urinary SystemStella LopeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System DivisionsDocument52 pagesNervous System DivisionsJohn Toni OrtizNo ratings yet
- Anaphy 1aDocument7 pagesAnaphy 1aFheonna De La PeñaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Endocrine Physiology: Vaclav - Hampl@lf2.cuni - CZDocument45 pagesGeneral Principles of Endocrine Physiology: Vaclav - Hampl@lf2.cuni - CZfrankminNo ratings yet
- Grad SmoothMuscleDocument18 pagesGrad SmoothMuscleF ParikhNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology2021Document19 pagesEndocrine Physiology2021saimon reyNo ratings yet
- Similarities N Differences of Facilitated Diffusion N Active TransportDocument24 pagesSimilarities N Differences of Facilitated Diffusion N Active TransportEddy LooNo ratings yet
- Cell-N-Genetics-2008 TerbaruDocument38 pagesCell-N-Genetics-2008 TerbaruRaja DarmawanNo ratings yet
- hypothal-hypof disorders part1 - копияDocument176 pageshypothal-hypof disorders part1 - копияElena Borş MorariNo ratings yet
- Neurohistology Lecture 3 Endocrine SystemDocument32 pagesNeurohistology Lecture 3 Endocrine Systemisicheipraise3No ratings yet
- 5 Physiological Bases of BehaviorDocument69 pages5 Physiological Bases of BehaviorNikhil VelagapudiNo ratings yet
- Muscle 1Document53 pagesMuscle 1mem734094No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledDdsNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemJustGellaiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine Systemden mNo ratings yet
- Cayanan Gio Lance T. Statistics and Probability q3 w2 Written WorkDocument1 pageCayanan Gio Lance T. Statistics and Probability q3 w2 Written WorkDon Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- And Probability Q3 W2 Performance TaskDocument1 pageAnd Probability Q3 W2 Performance TaskDon Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document8 pagesExperiment 3Don Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- The Microscope Reviewer in MLSPDocument5 pagesThe Microscope Reviewer in MLSPDon Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Narrative EssayDocument3 pagesLesson 10 Narrative EssayDon Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - 21st CenturyDocument15 pagesQuarter 1 - 21st CenturyDon Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- q3 Basic CalculusDocument8 pagesq3 Basic CalculusDon Aldrich SantosNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument35 pagesPancreasPaskalisNo ratings yet
- Psych-K Practical ApplicationsDocument10 pagesPsych-K Practical Applicationsdeluca4482% (17)
- Renal Nursing ReviewerDocument8 pagesRenal Nursing ReviewerGeraldine Waje100% (2)
- Faith HealingDocument23 pagesFaith Healingcreamyfrappe0% (1)
- Lab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel ElectrophoresisDocument22 pagesLab 7 - DNA Fingerprinting and Gel ElectrophoresisAmy HollingsworthNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal-SignedDocument3 pagesResearch Proposal-Signedapi-410826283No ratings yet
- Significance of The Structure of Human SkeletonDocument5 pagesSignificance of The Structure of Human SkeletonTodirenche LarisaNo ratings yet
- #NephJC CTscan TranscriptDocument22 pages#NephJC CTscan TranscriptSatrio Budi WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Psychological Intervention To Improve Attention ADHD ChildDocument5 pagesThe Role of Psychological Intervention To Improve Attention ADHD ChildRia WindikaNo ratings yet
- PlaintDocument20 pagesPlaintSaige DriverNo ratings yet
- Applications of Nanomaterials in Biology and MedicineDocument87 pagesApplications of Nanomaterials in Biology and MedicinePhạm Việt Dũng100% (1)
- 5 ElementDocument4 pages5 ElementkayrodeNo ratings yet
- Speck - X-Ray Contrast Media - Overview, Use and Pharmaceutical AspectsDocument134 pagesSpeck - X-Ray Contrast Media - Overview, Use and Pharmaceutical AspectsSimona Mariana DutuNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAnesthesia Drug Studyczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- Elias On 1983Document3 pagesElias On 1983JesusCordoba100% (2)
- The Scoring Clinical Index For OnychomycosisDocument4 pagesThe Scoring Clinical Index For OnychomycosisPatricia Avalos C.No ratings yet
- Bob Beck Lecture - Take Back Your PowerDocument42 pagesBob Beck Lecture - Take Back Your Powerprobiermalaus100% (1)
- Endocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesEndocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDani Anyika100% (1)
- Breathing and RespirationDocument5 pagesBreathing and RespirationPriyansh PatelNo ratings yet
- Measurement ScalesDocument6 pagesMeasurement ScalesRohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2015 Coca-Cola MENA Scholarship ApplicationDocument15 pages2015 Coca-Cola MENA Scholarship ApplicationMehroze MunawarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Study Guide - Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 3ed PDFDocument245 pagesClinical Case Study Guide - Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 3ed PDFraquelbibi0% (1)
- Assessment Standard 4 Traits Employability Skills TESTDocument5 pagesAssessment Standard 4 Traits Employability Skills TESTnurse1990No ratings yet
- Management of Acquired Maxillary Defects Partially Edentlous PDFDocument129 pagesManagement of Acquired Maxillary Defects Partially Edentlous PDFRamy Khalifa AshmawyNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic Management of Obstetric: HaemorrhageDocument52 pagesAnaesthetic Management of Obstetric: Haemorrhagerevathidadam55555No ratings yet
- LO Dan WO Cardio Week 4 (Jumat)Document38 pagesLO Dan WO Cardio Week 4 (Jumat)Alan Dwi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Pharamcology Unit 10 AnswersDocument13 pagesPharamcology Unit 10 AnswersLovren YoungNo ratings yet
- Report CapsicumDocument105 pagesReport CapsicumRina WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Politeknik Ungku Omar: Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi MalaysiaDocument9 pagesPoliteknik Ungku Omar: Kementerian Pengajian Tinggi Malaysiaazmir100% (3)
- Goljan Errata SheetDocument11 pagesGoljan Errata SheetVishala MishraNo ratings yet