Professional Documents
Culture Documents
g2pt1 Heavy Reinforced Concrete, Pre-Stressed Concrete and Steel Construction
Uploaded by
Evrylle Jariol0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesOriginal Title
g2pt1 Heavy Reinforced Concrete, Pre-stressed Concrete and Steel Construction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesg2pt1 Heavy Reinforced Concrete, Pre-Stressed Concrete and Steel Construction
Uploaded by
Evrylle JariolCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
3.1.
1 SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS
3.4 REINFORCED CONCRETE FLOOR SYSTEMS
3.4.2 REINFORCED CONCERETE BEAMS
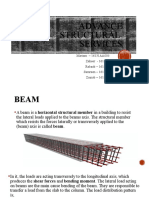
A Beam - a structural member, resting on
supports usually at its ends, which supports
transverse loads. The loads that act on the beam,
as well as the weight of the beam itself, tend to
bend rather than lengthen or shorten it. A girder is
a term applied to a beam that supports one or
more smaller beams, as concentrated loads.
3.43.1.1 SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS
REINFORCED CONCRETE FLOOR SYSTEMS
3.4.2 REINFORCED CONCERETE BEAMS
Beams may be classified as:
a. Simple beams - These are beams having a single span with a
support at each end, there being no restraint at the supports.
b. Cantilever beams - These are beams that are supported at one
end only, or they may be that portion of beams projecting beyond
one of its supports.
c. Continuous beams -These are beams resting on more than two
supports. The term “semi-continuous” is also frequently used in
reinforced-concrete. It refers to a beam having two spans with
little or no restraint at the two extreme ends of the beam. The end
span of a continuous beam, where little or restraint is provided at
the end support, is referred to as a semi-continuous beam.
3.4 REINFORCED CONCRETE FLOOR SYSTEMS
3.1.1 SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS
3.4.3 TYPES OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAMS
1. Rectangular beams
2. T – beams - When a reinforced concrete floor slab
and its supporting
beam (or girder) are built at the same
time and thoroughly tied together, a
part of the slab may be considered to
act with upper part of the beam in
compression. This form of a beam is
called a T- beam.
3. Beam with Compression Reinforcement - These are beams with
reinforcement in the compression as well as the tension side of the
beam, hence they are also called double reinforced beams. In this
type of beam no bent up bars are required. Beams with compression
reinforcement are used when the cross-sectional dimensions of the
beam are limited by architectural or structural conditions so that
there is an insufficient concrete area for the compressive stresses.
3.4 REINFORCED CONCRETE FLOOR SYSTEMS
3.1.1 SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS
4. Cantilever Beams
The tensile reinforcement is located at top of the beam and inverted
U-stirrups are provided.
5. Hollow box girders
These are double reinforced beams used for long spans. In order to
reduce the dead load (the weight of the beam) it is hollowed in the
center of the section. Diaphragms are provided at intervals
throughout the length of the beam.
6. Beam Brackets or Corbels
Short beam extensions from columns used to support rafters or
trusses.
You might also like
- Beam DesignDocument46 pagesBeam DesignAnik Sarker100% (1)
- Bota PrintDocument8 pagesBota PrintFraterPrierius100% (5)
- Material Approval FormDocument1 pageMaterial Approval Formsomjitsahani75% (8)
- 3 STRUCTURAL DESIGN 1 (Structural Elements)Document15 pages3 STRUCTURAL DESIGN 1 (Structural Elements)John Amir A Aguilar100% (1)
- Types of Structural FormsDocument21 pagesTypes of Structural FormsCorwyn Byrne88% (8)
- Beam and Its Types: BY Aravindkumar BDocument15 pagesBeam and Its Types: BY Aravindkumar BYogendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Columns Beams SlabsDocument48 pagesColumns Beams SlabsWilson Muguro100% (1)
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Types of Active Structures: A Presentation ONDocument26 pagesTypes of Active Structures: A Presentation ONSakshi MiglaniNo ratings yet
- Petronas Technical Standards: Load-Out and Sea-Fastening For Upstream FacilitiesDocument26 pagesPetronas Technical Standards: Load-Out and Sea-Fastening For Upstream FacilitiesAbhishek Gupta100% (1)
- Housing Typologies & Development in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesHousing Typologies & Development in The Philippinesmaria lourdes bautista100% (1)
- Manpower Equipment Schedule Sistona VellarimoDocument2 pagesManpower Equipment Schedule Sistona VellarimoKirby LabadanNo ratings yet
- CH3 Analysis of Statically Determinate TrussesDocument39 pagesCH3 Analysis of Statically Determinate TrussesKong VisalNo ratings yet
- TES Tank Foundation Method of StatementDocument10 pagesTES Tank Foundation Method of StatementAishah AliasNo ratings yet
- Timber Gridshells - Architecture, Structure and Craft (PDFDrive) PDFDocument359 pagesTimber Gridshells - Architecture, Structure and Craft (PDFDrive) PDFBernardus RayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BEAMDocument25 pagesChapter 1 BEAMDawit TesfayNo ratings yet
- Structural DetailsDocument28 pagesStructural Detailssatish budihalNo ratings yet
- Different Loads of StructuresDocument21 pagesDifferent Loads of StructuresXristell SalutNo ratings yet
- Stuctural Elements - EscalatorDocument47 pagesStuctural Elements - EscalatorPrakhar VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5-Topic 1 - Analysis of BeamsDocument21 pagesLesson 5-Topic 1 - Analysis of BeamsNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- BeamDocument10 pagesBeamfifieeNo ratings yet
- Analysis For External Reactions and Internal Stress Resultants of Statically Determinate StructuresDocument5 pagesAnalysis For External Reactions and Internal Stress Resultants of Statically Determinate StructuresJanice RamonNo ratings yet
- RSW 03 Concrete Beams and SlabsDocument7 pagesRSW 03 Concrete Beams and SlabsarpigaoNo ratings yet
- Ass Unit 2Document17 pagesAss Unit 2Samreen Khan100% (1)
- Spardha Mehta - Report On Bulk Active StructuresDocument18 pagesSpardha Mehta - Report On Bulk Active StructuresSpradha Mehta100% (1)
- 25 AsmitaS Long Span TrussesDocument18 pages25 AsmitaS Long Span TrussesAsmita SutarNo ratings yet
- ASS Unit 2 HalfDocument29 pagesASS Unit 2 HalfSamreen KhanNo ratings yet
- Cables & Arches NotesDocument2 pagesCables & Arches NotesHamza MujahidNo ratings yet
- 2 TRUSSES My Notes-1Document3 pages2 TRUSSES My Notes-1Ishmael ChikomoNo ratings yet
- Types of Structures and LoadsDocument17 pagesTypes of Structures and LoadsRyan Forayo BosngonNo ratings yet
- Structural ElementsDocument24 pagesStructural ElementsDivya chowdary100% (1)
- Module 1.1Document5 pagesModule 1.1ChuckieNo ratings yet
- Column, Beams and Roof FramingDocument74 pagesColumn, Beams and Roof FramingNathanniel Pogado GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Ar 373 BT 3 ReviewerDocument11 pagesAr 373 BT 3 ReviewerMelvin AlarillaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structures: Amatul Wasey 14131AA001Document27 pagesAdvanced Structures: Amatul Wasey 14131AA001amatul waseyNo ratings yet
- Beam StructureDocument6 pagesBeam StructureEdi YantoNo ratings yet
- Beam (Structure)Document4 pagesBeam (Structure)OgwoGPNo ratings yet
- Teori Dasar StrukturDocument32 pagesTeori Dasar StrukturPAK RINo ratings yet
- المشروع النهائيDocument46 pagesالمشروع النهائيAbdallah BohasheshaNo ratings yet
- Beam 1Document5 pagesBeam 1saheed tijaniNo ratings yet
- Beam and Wall InteractionDocument15 pagesBeam and Wall Interactionmikailadam656No ratings yet
- 2 TRUSSES My NotesDocument3 pages2 TRUSSES My Notestinotaku58No ratings yet
- Lecture 2. ReviewDocument53 pagesLecture 2. ReviewJien Ryle Lungtad PatunobNo ratings yet
- Beam (Structure)Document6 pagesBeam (Structure)Alfredo RomeroNo ratings yet
- BT ReviewerDocument5 pagesBT ReviewerNerinel Coronado0% (1)
- Page 1 Structural AssignmentDocument2 pagesPage 1 Structural AssignmentPatricia BraganzaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Truss PDFDocument8 pagesBasics of Truss PDFKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Nota Structure-TrussDocument8 pagesNota Structure-TrussSiti NurfatinNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.1 Beams Loads and Stresses - MACALINTALDocument2 pagesDiscussion 2.1 Beams Loads and Stresses - MACALINTALROMELYN MACALINTALNo ratings yet
- Bldgtec 3 Reading 3Document4 pagesBldgtec 3 Reading 3Danilo V. RavinaNo ratings yet
- Kishan. Gunesegeran - Inti International University NilaiDocument16 pagesKishan. Gunesegeran - Inti International University NilaikaronaNo ratings yet
- Shell Roof and Membrane Structures1Document32 pagesShell Roof and Membrane Structures1yaminisreevalliNo ratings yet
- Beam (Structure) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesBeam (Structure) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHare Krishna jhaNo ratings yet
- Trabeated System - PresentationDocument51 pagesTrabeated System - Presentationveena100% (1)
- Struktur Beton Ii: Jurusan Teknik Sipil Fakultas Teknik Universitas MataramDocument6 pagesStruktur Beton Ii: Jurusan Teknik Sipil Fakultas Teknik Universitas MataramTotok_CBSNo ratings yet
- ColumnsDocument38 pagesColumnsRamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3znabu asefaNo ratings yet
- Advance Structure System PDFDocument55 pagesAdvance Structure System PDFmaaz siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Truss System: Arbaminch UniversityDocument55 pagesTruss System: Arbaminch UniversityHaileyesus EsubalewNo ratings yet
- Types of ColumnDocument14 pagesTypes of Columnanbarasan0No ratings yet
- Civil Topic 008: Basic Information of Beam Details.: So, First We Start With What Is Beam?Document7 pagesCivil Topic 008: Basic Information of Beam Details.: So, First We Start With What Is Beam?honaNo ratings yet
- Beam, Frame TrussDocument3 pagesBeam, Frame TrussKrishna MyakalaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document4 pagesLec 4Muhammad Suhaib Uz Zaman KhanNo ratings yet
- Bridges - Presentation - For StudentsDocument14 pagesBridges - Presentation - For StudentsHANINNo ratings yet
- Bridges and Their TypesDocument8 pagesBridges and Their TypesAbhishek PawarNo ratings yet
- DSR ReportDocument29 pagesDSR Report13 Vedant DamodareNo ratings yet
- ACI Guidelines For Reinforced ConcreteDocument18 pagesACI Guidelines For Reinforced ConcreteJhyl AquinoNo ratings yet
- Art App Module 5B Elements and Principles of Visual Arts and Mediums and TechniquesDocument24 pagesArt App Module 5B Elements and Principles of Visual Arts and Mediums and TechniquesEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- Art App Module 5 Elements and Principles of Visual Arts and Mediums and TechniquesDocument52 pagesArt App Module 5 Elements and Principles of Visual Arts and Mediums and TechniquesEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- Art App Module 5A Elements and Principles of Visual Arts and Mediums and TechniquesDocument34 pagesArt App Module 5A Elements and Principles of Visual Arts and Mediums and TechniquesEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- Prelim ArtappDocument3 pagesPrelim ArtappEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- Prelim ArtappDocument3 pagesPrelim ArtappEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- ReportingDocument6 pagesReportingEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- Cwts ReportingDocument2 pagesCwts ReportingEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- Six Notions of ArtDocument6 pagesSix Notions of ArtEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- Prelim Art App2Document3 pagesPrelim Art App2Evrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- Article Iii Bill of RightsDocument3 pagesArticle Iii Bill of RightsAnonymous 7rl8EWAuBBNo ratings yet
- Artcile IiDocument3 pagesArtcile IiEvrylle JariolNo ratings yet
- ATE NOTES - Waterways TransportationDocument43 pagesATE NOTES - Waterways Transportationnavneet kalantriNo ratings yet
- Long Span Rail Case History 1Document2 pagesLong Span Rail Case History 1Hossein DoudiNo ratings yet
- Specifications and LegendsDocument1 pageSpecifications and LegendskimberlyjoyregaladoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Earth Work and Mass Hual Diagram)Document24 pagesLecture 3 (Earth Work and Mass Hual Diagram)Moneer MohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document59 pagesChapter 5Haile GuebreMariamNo ratings yet
- MG Constructions and Interior Quotation - D Group LayoutDocument3 pagesMG Constructions and Interior Quotation - D Group LayouthimavanthNo ratings yet
- Sudha GadDocument23 pagesSudha GadPravin MasalgeNo ratings yet
- Rock Mechanics QuestionnairesDocument5 pagesRock Mechanics QuestionnairesElyssa Michelle Caringas MicuaNo ratings yet
- Vidy-Laussane Folded Plate CasestudyDocument6 pagesVidy-Laussane Folded Plate CasestudyAjay KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Manila ANCESTRAL HOUSESDocument15 pagesManila ANCESTRAL HOUSESGideon NavarroNo ratings yet
- Hd605-7e0 S - N 10732-Up - Lubrication Piping, Rear (2 - 2) (#10732-)Document2 pagesHd605-7e0 S - N 10732-Up - Lubrication Piping, Rear (2 - 2) (#10732-)Maria Elena MessemakerNo ratings yet
- Concrete Name B3,5 B5 B7,5 B10 B12,5 B15 B20 B22,5 B25 B30 B35 B40 B45 B50 B55 B60 B65 B70 B80 B90 B100 M50 M75 M100 M125 M150 M200 M250 M300 M350 M400 M450 M500 M600 M650 M700 M800 R R R R EDocument7 pagesConcrete Name B3,5 B5 B7,5 B10 B12,5 B15 B20 B22,5 B25 B30 B35 B40 B45 B50 B55 B60 B65 B70 B80 B90 B100 M50 M75 M100 M125 M150 M200 M250 M300 M350 M400 M450 M500 M600 M650 M700 M800 R R R R ENGUYEN LAMNo ratings yet
- Building and Construction MaterialsDocument121 pagesBuilding and Construction MaterialsElena NoveskaNo ratings yet
- Ceiling Reflected Plan Ceiling Reflected Plan Ceiling Reflected PlanDocument1 pageCeiling Reflected Plan Ceiling Reflected Plan Ceiling Reflected Plandomin domNo ratings yet
- Technical Data: What Is A CT Chamber?Document2 pagesTechnical Data: What Is A CT Chamber?birhanuNo ratings yet
- Bill of Quantities-TenderDocument12 pagesBill of Quantities-TenderbhartiNo ratings yet
- Agreements 2018Document165 pagesAgreements 2018Martin OkaraNo ratings yet
- BUS SHELTER - PLAN-BlDocument2 pagesBUS SHELTER - PLAN-Blchiranjeevi OMSNo ratings yet
- Primary School: First Floor PlanDocument1 pagePrimary School: First Floor PlanSimrah MatheenNo ratings yet
- Firestop Joint Spray CFS-SP WB: Technical Data ApplicationsDocument5 pagesFirestop Joint Spray CFS-SP WB: Technical Data ApplicationsBiprojit HoreNo ratings yet
- Mix Design For Concrete Grade M 25Document3 pagesMix Design For Concrete Grade M 25Omar Marghani SalmaNo ratings yet
- Av 813 W (1-Av)Document1 pageAv 813 W (1-Av)SrStrikeNo ratings yet
- Sika® ViscoCrete® - Sika ConcreteDocument4 pagesSika® ViscoCrete® - Sika Concretemanuel agostinhoNo ratings yet