Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells Revision - Csecc Bio
Uploaded by
nikeiraawer10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views6 pagesOriginal Title
CELLS REVISION_ CSECC BIO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views6 pagesCells Revision - Csecc Bio
Uploaded by
nikeiraawer1Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
C E L L S
Cells are the basic units of protozoa and multicellular organisms.
FUNCTIONS OF CELL STRUCTURES
Cell membrane - surrounds cells, controls what leaves and enter cell
Cytoplasm- gel-like substance that fills cell and contains cell
organelles
Cell wall - made of cellulose, surround plant cells and gives shape
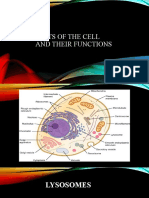
CELLS ORGANELLES
These are membrane enclosed structures with specific functions.
Nucleus- control centre of cell, responsible for production of
proteins and cell division.
Mitochondria - respiration occurs here.
Chloroplast - contains chlorophyll, photosynthesis occurs here.
Vacuole - fluid filled structure
- fluid contains cell sap
- contains sugar and other substances
- help maintain firmness of cell
Endoplasmic reticulum- responsible for making large molecules in
cell
Ribosome - production of proteins
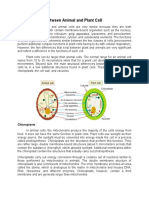
COMPARISON OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
feature Plant cell Animal cell
Cell wall present absent
Chloroplast present absent
Vacuole Large and permanent Small and temporary
Cytoplasm This layer under cell Fills cell
wall
Starch granules present absent
Glycogen absent present
Mitochondria present present
Nucleus present present
Ribosomes present present
VIRUSES, BACTERIA AND FUNGI
CELL ORGANIZATION
Specialized Cells
=> helps efficiency and divides labour
Examples of specialized ANIMAL Cells
- Ciliated epithelial cell - lines respiratory tract, helps trap dust
particles
- Red blood cells - carry oxygen to blood
- Phagocytes - kills pathogens (disease causing organisms)
Examples of specialized PLANT Cells
- Palisade Cell - photosynthesis
- Xylem Cell - transports water and minerals
- Phloem Cell - Transports sugar and other foods
TISSUE - identical cells that work together to perform a specific
function.
Eg. in animals, muscles and nerves. Eg. in plants, xylem vessel,
palisade layer
ORGANS- different tissues that work together to perform a specific
function
Eg. in animals, heart, lung. Eg. in plants, leaf, root, stem
ORGAN SYSTEM - a number of organs which are coordinated to
perform specific functions.
Eg. in animals, digestive system, transport system
Eg. in plants, root system, leaves on a tree
ORGANISM - complex organisms are made up of a number of organ
systems. Eg. human or mango tree
THE AMOEBA
Structures
Protoplasm - made up of two layers, ectoplasm and endoplasm
(contains all cell organelles).
Food vacuole - bubble of water surrounding a food particle,
enclosed by a cell membrane.
Contractile Vacuole - controls amounts of water present in
protoplasm.
Pseudopodia - used for movement and for feeding
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
DIFFUSION
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low
concentration. HIGH TO LOW.
Importance in living organisms.
- Food diffuses from inside intestines into blood capillaries.
- Gases from respiration diffuses across cell membranes into
mitochondria
- Oxygen diffuses from lungs into capillaries and red blood cells
OSMOSIS
The movement of water molecules from a dilute solution to a
concentrated solution through a SEMI-PERMEABLE MEMBRANE.
Importance in living organisms.
- Water moves across cell membranes by osmosis.
- In plants, osmosis is important because it helps water move up
the plant, from cell to cell.
TERMS TO REMEMBER
Plasmolysis – the process by which a cell loses water, this will happen
in a concentrated solution.
Flaccid – a cell which has become soft because of water loss. If a
plant loses its firmness, it will begin to wilt.
Turgid – a cell which is firm due to gaining water.
You might also like
- Short Notes Form 4 Biology (Chapter 1-4)Document6 pagesShort Notes Form 4 Biology (Chapter 1-4)Ema Fatimah75% (8)
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 2Document93 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 2leelijye100% (1)
- Cell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet: Structure/Function Cell PartKimora BrooksNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument8 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- The Cell Is The Basic Unit of Life. Biologist Learned About Cellular Structure by Using Light and Electron MicroscopeDocument80 pagesThe Cell Is The Basic Unit of Life. Biologist Learned About Cellular Structure by Using Light and Electron MicroscopeAnonymous JcdSmM3No ratings yet
- 2 CellsDocument31 pages2 CellsRashed NadaNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Plant and Animal CellDocument28 pages2.6 Plant and Animal Cellthethtarhoney12No ratings yet
- 21 1 Cellfunction 120529002534 Phpapp02Document29 pages21 1 Cellfunction 120529002534 Phpapp02HARINI A/P SARAVANAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Cell Sturucture)Document86 pagesChapter 1 (Cell Sturucture)faatin najihaNo ratings yet
- Biology Study GuideDocument35 pagesBiology Study GuideJuliana Gortaire EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Bio NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument106 pagesCell Structure and Cell Organisationwienna1987No ratings yet
- 2.1 - Cell FunctionDocument29 pages2.1 - Cell Functionliefeng81100% (2)
- CHAPTER 2 Plant CellDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 2 Plant CellAiman Haikal100% (1)
- SMA 11-1 CellsDocument111 pagesSMA 11-1 Cellsnur aulia100% (1)
- Session 2: Cells - The Basic Units of Life: WWW - Learnxtra.co - ZaDocument5 pagesSession 2: Cells - The Basic Units of Life: WWW - Learnxtra.co - ZaKaylaNo ratings yet
- O Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsDocument10 pagesO Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsTakudzwa ZvidzaNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument26 pagesCELLKush HarianiNo ratings yet
- 21 1 Cellfunction 120529002534 Phpapp02Document29 pages21 1 Cellfunction 120529002534 Phpapp02HARINI A/P SARAVANAN MoeNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsYukiNo ratings yet
- w1 Introduction of CellsDocument60 pagesw1 Introduction of CellsNur Bahiyah Binti Abdul Wahab IPGKTINo ratings yet
- Bio F4 KSSM Chapter 2-DLPDocument102 pagesBio F4 KSSM Chapter 2-DLPNurasyikin SaidinNo ratings yet
- Cell Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument43 pagesCell Fundamental Unit of LifeTeam goreNo ratings yet
- Cell and Its FunctionDocument26 pagesCell and Its FunctionMarielle MatunogNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument37 pagesCELLSsuggaballNo ratings yet
- E18f338b CellsDocument42 pagesE18f338b CellsMohammad Abdullah KNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Cell Analogy 2015Document52 pagesChapter 2-Cell Analogy 2015Nor HarlinawatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?Document5 pagesChapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?HeroNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Structure FunctionDocument124 pages1 Cell Structure FunctionIntoy, Stephanie Mae100% (1)
- A Tour of The CellDocument15 pagesA Tour of The CellMegan GohNo ratings yet
- 10 CMH Human and Social Biology: CellsDocument28 pages10 CMH Human and Social Biology: CellsScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledlgNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?Document6 pagesWhat Is A Cell?Waleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- 2 BioenergeticsDocument27 pages2 BioenergeticshanniemaelimonNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesMd AurangjebNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Function: CellsDocument8 pagesCell Structures and Function: CellsChardean Gel BaclaanNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument6 pagesThe CellshaniahNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument3 pagesCellsSamuel MohammedNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Function 2012Document69 pagesCell Structure and Function 2012gpranay4100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Cell Structure & Function Unit 1: Cell: The Unit of LifeDocument41 pagesChapter 3: Cell Structure & Function Unit 1: Cell: The Unit of LifeMark Harwell Rifo100% (1)
- The Basic Unit of Living MatterDocument13 pagesThe Basic Unit of Living MatterNawabKNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocument54 pagesCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Functions of A CellDocument4 pagesFunctions of A CellyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled Documentsumedhasaha09No ratings yet
- C1Document256 pagesC1azfdin100% (4)
- Study Notes - Topic 1 A'sDocument11 pagesStudy Notes - Topic 1 A'sJenniffer SmithNo ratings yet
- Cells 4THDocument70 pagesCells 4THKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Chpter 2Document10 pagesBiology Notes Chpter 2Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- CellDocument16 pagesCellanantchouhdary1709No ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology NotesDocument30 pagesYear 11 Biology NotesafeefaNo ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Biology Note About CellsDocument17 pagesBiology Note About CellsEK TubeNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Summary NotesDocument5 pagesCell Structure Summary NotesLayan MahasnehNo ratings yet
- Golgi ApparatusDocument4 pagesGolgi ApparatusalecNo ratings yet
- 4 - Cell JunctionsDocument25 pages4 - Cell JunctionsKhdhir M. Salem100% (1)
- Struktur Sel Dan OrganelDocument33 pagesStruktur Sel Dan OrganelSeptian IksanNo ratings yet
- 04 Vesicle TransportDocument35 pages04 Vesicle TransportAnonymous vhjGsvpNo ratings yet
- General Biology Act NotebookDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology Act NotebookSheene MariquinaNo ratings yet
- (The Ecosystem) I. Objectives: A Detailed Lesson PlanDocument16 pages(The Ecosystem) I. Objectives: A Detailed Lesson PlanAlezandraNo ratings yet
- GB1Q1W2L1Document5 pagesGB1Q1W2L1ANDREI ESCOTILLONNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The CELLDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The CELLlorelie asisNo ratings yet
- Review On Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesReview On Animal and Plant CellLadymae GalolaNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Cell Biology and BiochemistryDocument8 pagesRelationship Between Cell Biology and BiochemistryLydia OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document38 pagesModule 1Rochelle BambaNo ratings yet
- Lakhmir Singh Biology Class 9 Solutions CH 2Document7 pagesLakhmir Singh Biology Class 9 Solutions CH 2DarshilNo ratings yet
- Prok A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProk A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsAMADO JR BANAWANo ratings yet
- Genetics: Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisDocument60 pagesGenetics: Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisPatches24 Patches24No ratings yet
- 5th Sem Syllabus BotanyDocument3 pages5th Sem Syllabus BotanyAdnan BandayNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and OrganellesDocument50 pagesCell Structures and OrganellesKhristian de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Exercise 4 - Anatomy of The Cell and Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesThe Cell: Exercise 4 - Anatomy of The Cell and Cell Divisionwpwalker1No ratings yet
- Protein TargetingDocument10 pagesProtein TargetingdwigusmalawatiNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Create Your Own Model Analogy of The Cell and Its OrganellesDocument2 pagesInstructions: Create Your Own Model Analogy of The Cell and Its OrganellesColein FranleighNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Their Function By. Reyster Pavia 3c Week 3 ReportingDocument24 pagesCell Structure and Their Function By. Reyster Pavia 3c Week 3 ReportingWina MaeNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Is The Basis of Reproduction For Every OrganismDocument3 pagesCell Division Is The Basis of Reproduction For Every OrganismAlliah MendozaNo ratings yet
- Act 1 W Ks Cell Structure OrganellesDocument4 pagesAct 1 W Ks Cell Structure OrganellesKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Science 9th Chapter 5 Cell Biology NotesDocument4 pagesScience 9th Chapter 5 Cell Biology NotesavanishNo ratings yet
- Fronda Exam in Adveanced Cell Mol Bio 12072021Document6 pagesFronda Exam in Adveanced Cell Mol Bio 12072021Jericho D. FrondaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan About CellDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan About CellRichard ServoNo ratings yet
- Pages From Human Biology, 15th EditionDocument44 pagesPages From Human Biology, 15th EditionSzutsTamasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 & 10 - Endomembrane System I & IIDocument8 pagesLecture 9 & 10 - Endomembrane System I & IILujainNo ratings yet