Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NJ Physics NJ Physics: Mains Revision Test Physics Mechanics and Heat
Uploaded by
aOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NJ Physics NJ Physics: Mains Revision Test Physics Mechanics and Heat
Uploaded by
aCopyright:
Available Formats
MAINS REVISION TEST PHYSICS
MECHANICS and HEAT
S
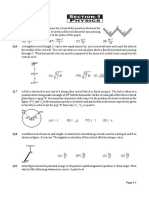
Q.1 A standing wave pattern is established in a string Q.4 A source of frequency f gives 5 beats/s when
as shown. The wavelength of one of the sounded with a source of frequency 200 Hz.
component traveling waves is: The second harmonic of same source gives 10
C
beats/s when sounded with a source of
I
frequency 420 Hz. The value of f is
(1) 200 Hz (2) 210 Hz
S
(3) 205 Hz (4) 195 Hz
6m
Q.5 A pipe open at both ends has a fundamental
Y
(1) 0.25m (2) 0.5m
S
resonant frequency = f. One-third length of the
(3) 1m (4) 4m
pipe is now immersed in a dense liquid, while
the upper end is kept open. The new
H C
Q.2 A wire having a linear density 0.1kg/m is kept
fundamental frequency of the air column in the
under a tension of 490 N. It is observed that it
I
pipe will be
P
resonates at a frequency of 400Hz and the next
(1) 3f (2) 2f / 3
higher frequency 450Hz. Find the length of the
S
(3) f / 3 (4) 3f / 4
wire
J
(1) 0.4m (2) 0.6m
Q.6 In the figure shown S is a source of constant
(3) 0.49m (4) 0.7m
Y
frequency and O is an observer moving with
N
constant velocity. The graph of frequency detected
Q.3 Two strings whose linear mass densities are 25
by observer v/s time is
gm·cm–1 and 9 gm·cm–1 are joined together.
H
The ratio of amplitude of reflected and incident
wave for the vibration waves is
P
1 1
(1) (2)
4 3
J
(1) (2)
9 3
(3) (4)
16 4
N (3) (4)
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
Mains Revision Test Mechanics and Heat NJ PHYSICS Page # 1
Q.7 An object of specific gravity is hung from a Q.10 As shown in figure two uniform rods of mass
massless string. The tension in the string is T. M and length L each are joined. What is the
The object is immersed in water so that one moment of inertia of system about an axis
half of its volume is submerged. The new perpendicular to plane through end A ?
S
tension in the string is A
2 1 2 1
(1) T (2) T
C
2 2
I
1 1 90°
(3) T (4) T C B
S
5ML2 7ML2
(1) (2)
3 3
Q.8 The ratio of the diameters of certain air bubble
Y
at the bottom and at the surface is 1 : 2. What 5ML2 7ML2
S
is the depth of the lake ? (3) (4)
12 12
(1 atmosphere = 10 m depth of water)
H C
(1) 80 m (2) 60 m Q.11 Momment of inertia I of a rod is given by
(3) 35 m (4) 70 m
I
relation I = I1 + ma2 + (m – b) c2 where m is
P
Q.9 A stone of mass of 16 kg is attached to a string I1a
mass. What is the dimension of
S
144 m long and is whirled in a horizontal smooth bc
J
surface. The maximum tension the string can (1) ML (2) ML2
withstand is 16 N. The maximum speed of (3) L2 (4) L
Y
revolution of the stone without breaking it, will
N
be : Q.12 A 6000 kg rocket set for a vertical flight. If the
(1) 20 ms–1 (2) 16 ms–1 exhaust speed of gases is 1000 m/s, how much
H
(3) 14 ms –1 (4) 12 ms–1 gas must be ejected per second to supply the
thrust needed to give the rocket an initial
P
upward acceleration of 20 m/s2:
(1) 90 kg/sec (2) 180 kg/sec
J
(3) 120 kg/sec (4) 9 kg/sec
N
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
Mains Revision Test Mechanics and Heat NJ PHYSICS Page # 2
Q.13 Small blocks of copper and steel are left out Q.17 A planet is at an average distance 'd' from the
overnight. In the morning, the copper feels sun and its average surface temperature is T.
colder to the touch than the steel. This is Assume that the planet receives energy only
because: from sun and loses energy only through
S
(1) The copper's temperature is lower radiation, from surface. Neglect atmospheric
(2) Copper is dense effects. Temperature T is proportional to
(3) Copper is a better thermal conductor (1) d2 (2) d–1/2
C
(4) Copper is a better electrical conductor (3) d1/2 (4) d1/4
I
Q.14 How many minimum ice cubes of mass 10 gm Q.18 A small ball of mass m is attached to two
at 0°C each should added to a glass containing identical spring each of spring constant K which
S
100 gm water at 20°C to bring it to 0°C ? are attached to floor and roof as shown. The
(1) 12 (2) 2 l
Y
(3) 3 (4) 25 spring have unstretched length . At what
S
2
distance from the ceiling will the ball remain in
Q.15 A Carnot engine working between 300 K and
equilibrium.
H C
600 K has a work output of 800 J per cycle.
What is the amount of heat energy supplied to
P I
the engine from the source in each cycle ? K
(1) 800 J (2) 1600 J
S
(3) 3200 J (4) 6400 J l m
J
K
Q.16 A ball A moving with certain velocity in positive
Y
x-axis collides with a stationary ball B. After
N
collision their direction of motion make angles
l Mg l Mg
and with the x-axis. The possible values – 1 1
H
(1) (2)
of and are 2 Kl 2 Kl
(1) = 30° and = – 45° Mg
P
Mg
(2) = 90° and = – 120° (3) (4) 2l
2K Kl
(3) =0° and = – 30°
(4) = 45° and = 0°
J
N
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
Mains Revision Test Mechanics and Heat NJ PHYSICS Page # 3
Q.19 In the shown figure the minimum value of F E E
required to move the block A away from the (1) (2)
R 2R
wall is
2E 3E
Massless, inextensible, (3) (4)
S
horizontal string R R
Fixed wall
B 1kg µ = 0.3 Q.22 Two particles are projected simultaneously
C
F from the same point on ground at angles 37º
I
Fixed horizontal A 3kg µ = 0.4 and 53º with horizontal with speed V and 2V
floor in the same vertical plane, then relative velocity
S
between them when both are in air (neglect the
17g 19g air resistance):
(1) (2)
15 10 (1) is always vertical
Y
(2) becomes zero once
S
23g 11g
(3) (4) (3) is changing continuously
10 10 (4) is constant
H C
Q.20 When a certain weight is suspended from a long Q.23 A projectile is thrown with a velocity of
uniform wire its length increases by 1 cm. If
I
20 m/s at an angle of 60° with the horizontal.
P
the same weight is suspended from another wire After how much time the velocity vector will
of the same material and length but having a
S
make an angle of 45° with the horizontal
diameter half of the first one, the increase in (take g = 10 m/s2)
J
length will be
(1) 0.5 cm (2) 2 cm 1
Y
(1) 3 sec. (2) sec.
(3) 4 cm (4) 8 cm 3
N
Q.21 A particle of mass m oscillates between P1 and (3) 2 sec. (4) ( 3 1) sec.
H
P2 inside of fixed smooth spherical shell of
radius R. At any instant the kinetc energy of
P
the particle is E. Then the force exerted by the
particle on the shell at this instant is :
J
P1 P2
N
P0
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
Mains Revision Test Mechanics and Heat NJ PHYSICS Page # 4
Q.24 Figure shows a particle P moving with constant Q.26 A particle is performing SHM on a straight line
velocity V along the positive x axis and four with amplitude 15 cm and time period 20s.
points a,b,c,d with their x and y coordinates. If Time taken by the particle to go from A to B
L1, L2 ,L3 and L4 are the magnitudes of angular through 'O' where AO = 12 cm and OB = 9
S
momentum of the particle about the points cm and O is point of equilibrium
a,b,c,d respectively then which of the following
is incorrect :
C
Y E E
a O
A B
I
(8,2) 12 cm 9 cm
c (1) 10 s (2) 5 s
S
(–2,1) 20 20
(3) s (4) s
6 3
Y S
b V d Q.27 A uniform wooden square board of side l is
(–2,–2) p (3,–2) kept on a frictionless horizontal surface such
H
that its distance from a vertical wall is 2l as
C
(1) L1 = L3 (2) L1 > L2
shown in figure. A man having mass equal to
(3) L2 = L4 (4) L1 > L4
I
the board is standing on the corner A of the
P
Q.25 P-V indicator diagram for a given sample of
board. If he moves to the centre O of the board
monoatomic ideal gas is shown in figure. The
S
then the distance of the centre of the board
average molar heat capacity of the system for
J
from the wall will become
the process ABCD is : (R is a universal gas
constant)
Y
l
N
p A
O
H
2p0 C D
2l
P
p0 B A
7l 9l
(1) (2)
4 4
J
V
V0 2V0 3V0
(5 2 1) (5 2 )
(3) l (4) l
3R 2 2 4
N
(1) 3R (2)
2
9R 9R
(3) (4)
4 2
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
Mains Revision Test Mechanics and Heat NJ PHYSICS Page # 5
Q.28 In the following figure, a sphere of radius 3 m
is in state of pure rolling on the plank. The
accelerations of the sphere and the plank are
indicated. The value of angular acceleration
S
is
2
a2 = 6 m/s
C
a1 = 3 m/s2
I
(1) 3 rad/s2
(2) 6 rad/s2
S
(3) 3 rad/s2 (opposite to the direction shown
in figure)
(4) 1 rad/s2
Q.29
Y S
One end of a 2.35 m long and 2.0 cm radius
aluminum rod (K = 235 W m–1 K–1) is held at
H C
20°C. The other end of the rod is in contact
I
with a block of ice at its melting point. The rate
P
(in kg s–1) at which ice melts is (Take latent
S
10
heat of fusion for ice as × 105 J.kg–1)
J
3
(1) 48 × 10–6 (2) 24 × 10–6
Y
(3) 2.4 × 10–6 (4) 4.8 × 10–6
Q.30
N
A carnot refrigerator operates between –3°C
H
and 27°C. How much work must be done so
as to extract 1 kJ of heat from the refrigerator?
P
(1) 100 J (2) 104 J
1000
J
(3) J (4) 900 J
9
N
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
Mains Revision Test Mechanics and Heat NJ PHYSICS Page # 6
You might also like
- Code - B: Test - 5 Test Series For NEET - 20Document26 pagesCode - B: Test - 5 Test Series For NEET - 20Naman kkNo ratings yet
- NEET Sample Paper-2Document26 pagesNEET Sample Paper-2Prejit PillaiNo ratings yet
- All India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-07 - NEET - 04-05-2023 - QuestionsDocument17 pagesAll India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-07 - NEET - 04-05-2023 - QuestionsMusical MaanishNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument19 pagesWavessundar77vish77No ratings yet
- Aipmt 2001Document16 pagesAipmt 2001GatiNo ratings yet
- 6436282bacd0d6001866219f - ## - AITS-08 - Paper-1 - Dropper NEET - 12-04-2023 - QuestionsDocument26 pages6436282bacd0d6001866219f - ## - AITS-08 - Paper-1 - Dropper NEET - 12-04-2023 - Questionsvision xeroxNo ratings yet
- Medical Entrance AIPMT PapersDocument15 pagesMedical Entrance AIPMT Paperssumit kumar0% (1)
- Equilibrium.: of FollowingDocument19 pagesEquilibrium.: of FollowingNeelMehtaNo ratings yet
- Aipmt 1998-2011Document293 pagesAipmt 1998-2011VideoGamesNo ratings yet
- FLT (Mains) 3Document10 pagesFLT (Mains) 3bheekha ramNo ratings yet
- NEETDocument32 pagesNEETSanjiv KumarNo ratings yet
- AIATSTYJMO2017T06 Solution PDFDocument24 pagesAIATSTYJMO2017T06 Solution PDFAditya VermaNo ratings yet
- NEET22-Intensive Program Test-9A-QADocument21 pagesNEET22-Intensive Program Test-9A-QABala ChinnappaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument30 pagesUntitledIram SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Nta Neet Abhyas MOCK TEST - 2Document45 pagesNta Neet Abhyas MOCK TEST - 2bapiNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains Mock Test 01 - Test Paper (Physics) - (Lakshya JEE 2023)Document10 pagesJEE Mains Mock Test 01 - Test Paper (Physics) - (Lakshya JEE 2023)Hacker KingNo ratings yet
- Neet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 8: PhysicsDocument15 pagesNeet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 8: PhysicsupsahuNo ratings yet
- JEE - Physics - Waves and SoundDocument16 pagesJEE - Physics - Waves and SoundSanjana KumariNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : J J J JDocument5 pagesPart - A (Physics) : J J J Jsusheel_uiitshimlaNo ratings yet
- RPET 2009 Physics 2Document12 pagesRPET 2009 Physics 2premsempireNo ratings yet
- Cet - 03 03 2024Document34 pagesCet - 03 03 2024sknoushad126No ratings yet
- AITS-Spot Test - VI - 13.03.2024Document20 pagesAITS-Spot Test - VI - 13.03.2024ntype795No ratings yet
- Test Series For Neet-2020Document15 pagesTest Series For Neet-2020kavyareddyNo ratings yet
- 5-Mar-2021 Test Solution CRT-16Document12 pages5-Mar-2021 Test Solution CRT-16Mihir RajNo ratings yet
- Class: 12 B1 B2 B3 Sub: PCM Date: 09-01-2022 Time: 3 Hours Phase Test-02 Marks: 300Document24 pagesClass: 12 B1 B2 B3 Sub: PCM Date: 09-01-2022 Time: 3 Hours Phase Test-02 Marks: 300Abhishek TekaleNo ratings yet
- PhySICS Paper With AnswerDocument5 pagesPhySICS Paper With Answersudhir_narang_3No ratings yet
- Alternating Currents - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0Document4 pagesAlternating Currents - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0dhruvapocof1No ratings yet
- 0102 Physics Paper With Answer MorningDocument5 pages0102 Physics Paper With Answer Morningspicypip123No ratings yet
- Q.paper CHA Full Test 07 NEET Badarpur (09!04!24) FT07Document21 pagesQ.paper CHA Full Test 07 NEET Badarpur (09!04!24) FT07bhaswatibanik01No ratings yet
- January 27 - MorningDocument12 pagesJanuary 27 - Morningadhyayan.learning.2021No ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper 1-10-2020Document160 pagesMock Test Paper 1-10-2020Parnava Pratihar V BINOY 64No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure TestDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure TestHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Neet Model Exam - All Units - 27-03-24Document46 pagesNeet Model Exam - All Units - 27-03-24Mehez KNo ratings yet
- Test Series For Neet-2020Document16 pagesTest Series For Neet-2020kavyareddyNo ratings yet
- Mock Test: PhysicsDocument11 pagesMock Test: PhysicsPrajakta ShettyNo ratings yet
- TANCET ME (Basic Engineering & Sciences) - Basic - Engg - and - SciencesDocument4 pagesTANCET ME (Basic Engineering & Sciences) - Basic - Engg - and - Sciencesrameshdurairaj81% (16)
- Test - Physics - Yakeen 2.0 - (2024) - MR SirDocument6 pagesTest - Physics - Yakeen 2.0 - (2024) - MR Sirhardiksingh4895No ratings yet
- Additional Content - PhysicsDocument9 pagesAdditional Content - Physicsnoname57754No ratings yet
- Jeem Sift Ii 7TH Jan 2020 PSK 22 02 2020 PDFDocument13 pagesJeem Sift Ii 7TH Jan 2020 PSK 22 02 2020 PDFBhart BansalNo ratings yet
- Oscillation and Waves - TEST - 17-02-24 - 02-17-2024-09-42-09-816 AMDocument3 pagesOscillation and Waves - TEST - 17-02-24 - 02-17-2024-09-42-09-816 AMyashvi.jain0507No ratings yet
- SATMock1 1Document12 pagesSATMock1 1JeetNo ratings yet
- Rathnavali Balika Vidyalaya Grade 13 Physics 2021 3rd Term Test Paper 6374b24ab8ca4Document10 pagesRathnavali Balika Vidyalaya Grade 13 Physics 2021 3rd Term Test Paper 6374b24ab8ca4shane heroNo ratings yet
- All Units - NEET - P + C + B - 26 - 06 - 22Document40 pagesAll Units - NEET - P + C + B - 26 - 06 - 22AshiqmonuNo ratings yet
- 640ccc774a2a28001898f001 ## AITS 04 Question Paper Yakeen 2 0 2023Document28 pages640ccc774a2a28001898f001 ## AITS 04 Question Paper Yakeen 2 0 2023wjgv4nwcz6No ratings yet
- Neet Full Test03Document25 pagesNeet Full Test03Ahkil NandaNo ratings yet
- AIPMT 2010 PrelimsDocument20 pagesAIPMT 2010 Prelimsarghadiproy012No ratings yet
- 3101 Physics Paper With Answer EveningDocument6 pages3101 Physics Paper With Answer Eveningspicypip123No ratings yet
- CST 9Document20 pagesCST 9aryaadarshsinghNo ratings yet
- AIEEE 2003 Questions PapersDocument20 pagesAIEEE 2003 Questions PapersAditya RamNo ratings yet
- GT Paper 23.03.2024Document23 pagesGT Paper 23.03.2024Notadi BoiNo ratings yet
- Physics: 25 (039:0:00 0 AM P) M M)Document25 pagesPhysics: 25 (039:0:00 0 AM P) M M)Priyansh RawatNo ratings yet
- 2701 Physics Paper With Answer MorningDocument5 pages2701 Physics Paper With Answer MorningnithinjothimuruganNo ratings yet
- AIM-Sample Paper-04Document22 pagesAIM-Sample Paper-04Bala ChinnappaNo ratings yet
- All India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-08 - NEET - 05-05-2023 - Questions - MorningDocument20 pagesAll India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-08 - NEET - 05-05-2023 - Questions - MorningMusical MaanishNo ratings yet
- 1-Puc Part2 NeetDocument69 pages1-Puc Part2 Neetmrlrdy13210% (1)
- 11 Full Syllabus Test - 04 (NEET) Physics: Write Answers in The Provided Space. MM: 720 (+4R, - 1W)Document17 pages11 Full Syllabus Test - 04 (NEET) Physics: Write Answers in The Provided Space. MM: 720 (+4R, - 1W)Suryakant AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 2007 Physics Paper With Ans EveningDocument4 pages2007 Physics Paper With Ans EveningAnarghya JainNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part C: Electromagnetic Fields IIFrom EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part C: Electromagnetic Fields IINo ratings yet
- Tech Mahindra Latest Placement Paper With Solution PDF 1Document36 pagesTech Mahindra Latest Placement Paper With Solution PDF 1aNo ratings yet
- Slide No Slide Detail Presenter Time (SECONDS)Document1 pageSlide No Slide Detail Presenter Time (SECONDS)aNo ratings yet
- ME Common Formulae - techKNOWcratDocument1 pageME Common Formulae - techKNOWcrataNo ratings yet
- Slide 1: Introduction: Good Afternoon Respected Judges On Dais We Are JNEC Jaguars 3.0 FromDocument1 pageSlide 1: Introduction: Good Afternoon Respected Judges On Dais We Are JNEC Jaguars 3.0 FromaNo ratings yet
- Tech Mahindra Latest Placement Paper With Solution PDF 1Document36 pagesTech Mahindra Latest Placement Paper With Solution PDF 1aNo ratings yet
- DVP 3.0Document1 pageDVP 3.0aNo ratings yet
- OEE Equipment Reliability-1 MachineDocument1 pageOEE Equipment Reliability-1 Machineapi-3835934No ratings yet
- 19 12 17 Physics ANSDocument6 pages19 12 17 Physics ANSaNo ratings yet
- UNIT3 ComplexDocument4 pagesUNIT3 ComplexaNo ratings yet
- First-Order Linear Differential Equations:: A Is An Equation of The FormDocument10 pagesFirst-Order Linear Differential Equations:: A Is An Equation of The FormRafi ZulfahmiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: JEE (Main+Advanced)Document1 pageSyllabus: JEE (Main+Advanced)aNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Common Mechanical TermsDocument4 pagesGlossary of Common Mechanical TermsaNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Tech Mahindra Placement Sample Paper 6Document10 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Tech Mahindra Placement Sample Paper 6PERFECTPARDHUNo ratings yet
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (Oee)Document11 pagesOverall Equipment Effectiveness (Oee)aNo ratings yet
- Casting Process Advantages and LimitationsDocument3 pagesCasting Process Advantages and LimitationsaNo ratings yet
- OEEDocument9 pagesOEEaNo ratings yet
- OEE Worksheet 021010Document1 pageOEE Worksheet 021010aNo ratings yet
- Mechanical-Engineering Gate2016.InfoDocument3 pagesMechanical-Engineering Gate2016.InfoHenryNo ratings yet
- Go-Kart Chassis's Design and Construction Based On Theoretical and Experimental FindingsDocument24 pagesGo-Kart Chassis's Design and Construction Based On Theoretical and Experimental FindingsSudersanSridhar100% (3)
- The Evaluation of Aerodynamic Drag of Go-Karts by Means of Coast Down Test and CFD AnalysisDocument31 pagesThe Evaluation of Aerodynamic Drag of Go-Karts by Means of Coast Down Test and CFD AnalysisJohn AriasNo ratings yet
- Me Mechanicalengineering - Com Diesel CycleDocument2 pagesMe Mechanicalengineering - Com Diesel CycleaNo ratings yet
- Me Mechanicalengineering - Com Otto CycleDocument1 pageMe Mechanicalengineering - Com Otto CycleaNo ratings yet
- CpsDocument22 pagesCpsAmal RajNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument4 pagesSampleaNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic EngineDocument2 pagesCryogenic EngineaNo ratings yet
- Company Name:-Dhananjay Enterprises College Guide: - Dr. Dhananjay R. Dolas Students: - Pavan Korde Pandurang Jadhav Gajanan KhandareDocument5 pagesCompany Name:-Dhananjay Enterprises College Guide: - Dr. Dhananjay R. Dolas Students: - Pavan Korde Pandurang Jadhav Gajanan KhandareaNo ratings yet
- Inspection Timings of M&M Clutch HousingDocument2 pagesInspection Timings of M&M Clutch HousingaNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document1 pageBook 1NiravNo ratings yet
- Common Answers: Design Engineers Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesCommon Answers: Design Engineers Interview QuestionsaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Practice QueestionsDocument2 pagesDBMS Practice QueestionsAbhibhava Bhatt VIII [E] 4No ratings yet
- Biology Transportation in PlantsDocument6 pagesBiology Transportation in PlantsTanaka ChirawuNo ratings yet
- Fangming Heng Thesis 2015Document147 pagesFangming Heng Thesis 2015keanshengNo ratings yet
- Example 6 1 Rectangular Water Tank DesignDocument7 pagesExample 6 1 Rectangular Water Tank DesignMesfin Derbew88% (104)
- Configure Ap Aruba ConsoleDocument2 pagesConfigure Ap Aruba ConsoleKule MemphisNo ratings yet
- Mcknight - Proposed Mastering Eq PDFDocument3 pagesMcknight - Proposed Mastering Eq PDFIordan Dan FfnNo ratings yet
- GravimetryDocument31 pagesGravimetrysvsaikumarNo ratings yet
- 17.alekhya Research ArticleDocument8 pages17.alekhya Research ArticleBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Excavators 1Document27 pagesExcavators 1Gold CubeNo ratings yet
- Training - Manual - Diagnostic - and - Troublesh CPC 202GDocument186 pagesTraining - Manual - Diagnostic - and - Troublesh CPC 202GGA AnnerNo ratings yet
- Properties in Shear: (Eg. Ssy 0.5sy)Document34 pagesProperties in Shear: (Eg. Ssy 0.5sy)Yusuf SahinNo ratings yet
- Maya Dynamics Basics:: MEL and ExpressionDocument33 pagesMaya Dynamics Basics:: MEL and ExpressionNguyễn HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD - Modify ToolbarDocument18 pagesAutoCAD - Modify ToolbarMarcusNo ratings yet
- Workbook Theory Grade Six SampleDocument4 pagesWorkbook Theory Grade Six SampleRobert TseNo ratings yet
- Explaining OPERCOM® Methodology in CommissioningDocument5 pagesExplaining OPERCOM® Methodology in Commissioningiman2222100% (2)
- Comba ODV-065R15E18J-GDocument1 pageComba ODV-065R15E18J-GGaga ChubinidzeNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion at An AngleDocument25 pagesProjectile Motion at An AngleKenneth Kent Stinson FloresNo ratings yet
- SmartPRO 5000U Plus ManualDocument10 pagesSmartPRO 5000U Plus ManualMugiranezaNo ratings yet
- Process Cooling System Chiller and Tower Sizing FormualsDocument2 pagesProcess Cooling System Chiller and Tower Sizing FormualsChuen Hau TanNo ratings yet
- Lista Ejercicios 3 PPEDocument25 pagesLista Ejercicios 3 PPEKarla HermorNo ratings yet
- Time-Domain Analysis of The Linear SystemsDocument32 pagesTime-Domain Analysis of The Linear SystemskamalNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Occlusal Contact Marking Indicators: Tanya P. BozhkovaDocument5 pagesComparative Study of Occlusal Contact Marking Indicators: Tanya P. BozhkovaMrinmayee ThakurNo ratings yet
- 33 KV Transmission Line Design Drawings PDFDocument265 pages33 KV Transmission Line Design Drawings PDFkapilsharma404No ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur B.Tech. I - I Sem. L C 4 2 Part-A LABDocument2 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Anantapur B.Tech. I - I Sem. L C 4 2 Part-A LABHappa1No ratings yet
- Simplicity Feature List Ver1.0 RevADocument25 pagesSimplicity Feature List Ver1.0 RevAbuk ipahNo ratings yet
- PIA B2 - Module 2 (PHYSICS) SubModule 2.1 (Matter) Final1Document17 pagesPIA B2 - Module 2 (PHYSICS) SubModule 2.1 (Matter) Final1samarrana1234679No ratings yet
- Storage Tanks Vessels Gas LiquidsDocument9 pagesStorage Tanks Vessels Gas Liquidswei wangNo ratings yet
- Asmi-52: 2/4-Wire SHDSL ModemDocument4 pagesAsmi-52: 2/4-Wire SHDSL ModemManuel FreireNo ratings yet
- Woodworking Plans - Childs RockerDocument16 pagesWoodworking Plans - Childs RockerBob Kowalski100% (1)
- Asme Se-165 2004Document25 pagesAsme Se-165 2004Kamalnath KpNo ratings yet