Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Can Only Be Observed As Matter Undergoes A Physical Change: General Chemistry 1
Uploaded by
Genelyn Alano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pagereviewer
Original Title
General Chemistry 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentreviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageCan Only Be Observed As Matter Undergoes A Physical Change: General Chemistry 1
Uploaded by
Genelyn Alanoreviewer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
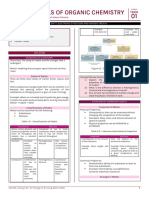
GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 the melting temperature of iron or
the freezing temperature of water,
can only be observed as matter
NATURE AND STATES OF MATTER undergoes a physical change
I. THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTER
Law of Constant Proportion
All things of the same type have the
same proportions of the elements
that compose them
Four Basic Principles of Particles of the
Particle Model of Matter
1. Matter is made of tiny particles
2. There are empty space between the
particles
3. The particles are in constant motion
4. There are forces that act between
the particles
MATTER AND ITS PROPORTIES
Properties – characteristics that enable us to
distinguish on substance from
another
Light and resistant
Transparent
Fragile
Elastic
Flexible
Strong and Resistant
1. Physical Properties
characteristics of matter that is not
associated with a change in its
chemical composition
examples of physical properties:
density, color, hardness, melting
and boiling points, and electrical
conductivity
density and color, without
changing the physical state of the
matter observed
You might also like
- Chapter 1 OutlineDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Outlinedill1233No ratings yet
- Module Shs Chem1Document4 pagesModule Shs Chem1Ansel SotnasNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter Lesson 1Document39 pagesProperties of Matter Lesson 1mika3laac0sta14No ratings yet
- Module Shs Chem1Document4 pagesModule Shs Chem1Ansel SotnasNo ratings yet
- What Are Physical Properties of Matter?Document32 pagesWhat Are Physical Properties of Matter?Tomasian100% (1)
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument19 pagesIntroduction To ChemistryDianne Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEWER Lesson 1Document3 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 1 REVIEWER Lesson 1jjjangchunNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 L1 W1Document51 pagesChem 1 L1 W1Desire JoyNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- Chem1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument3 pagesChem1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument25 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesJose Gilberto De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeDocument12 pagesChemistry: Matter and ChangeMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument3 pagesGen ChemJanice RiliNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem MatterDocument58 pagesGen Chem MatterKC KayeNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY I Midterms ReviewerDocument15 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY I Midterms ReviewerAJ Santos100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument13 pagesLesson 1: Matter and Its Propertiesricky100% (1)
- 04 Unit 2. Matter and EnergyDocument29 pages04 Unit 2. Matter and EnergyKevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 NotesBlaster OneNo ratings yet
- MLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyDocument15 pagesMLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyfuckyouNo ratings yet
- 01 04 JournalDocument3 pages01 04 JournalAkshay KarthikNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1Document6 pagesStudy Guide 1Rochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument12 pagesGen ChemGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Basic Concepts About Matter: Area Chemistry/Science What Is Being Studied EmphasisDocument9 pagesChapter 1. Basic Concepts About Matter: Area Chemistry/Science What Is Being Studied EmphasisYhena ChanNo ratings yet
- Matter Group 2: I. Definition of Matter and Its ExampleDocument8 pagesMatter Group 2: I. Definition of Matter and Its ExampleMichael S LeysonNo ratings yet
- All in OneDocument232 pagesAll in Onemelese teshomeNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Gen Chem 1 1Document3 pagesWeek 1 Gen Chem 1 1Cedrick GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Week - 2 - States of Matter and PropertiesDocument22 pages2024 - Week - 2 - States of Matter and Propertieskarokamil243No ratings yet
- 1 Properties of MatterDocument24 pages1 Properties of MatterCarlben Jan RadaNo ratings yet
- (Chem30) Trans Unit 1Document4 pages(Chem30) Trans Unit 1katey perryNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Chapter 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement ChemistryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Chapter 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement ChemistryGIAN CARLONo ratings yet
- Bab 5 Tingkatan 1Document14 pagesBab 5 Tingkatan 1foryourhonour wongNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument2 pagesGen Chembrie calixtroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 Properties of MatterDocument12 pagesLesson 13 Properties of MatterKrish D.No ratings yet
- Module 1 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument16 pagesModule 1 Matter and Its PropertiesPatricia GallegoNo ratings yet
- L1 Introduction of Gen Chem 1Document5 pagesL1 Introduction of Gen Chem 1John Mark Clouie PlacaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of MatterDocument14 pagesPhysical Properties of MatterSoso AnoosNo ratings yet
- Colorful and Fun Science Safety Rules PresentationDocument21 pagesColorful and Fun Science Safety Rules Presentationkimallison shinNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ChemistryDocument26 pagesFundamentals of ChemistryGulane, Patrick Eufran G.No ratings yet
- Chem Unit 2Document1 pageChem Unit 2xelzzlimNo ratings yet
- 1 Week Notes To Solid Properties of MatterDocument2 pages1 Week Notes To Solid Properties of MatterPinaka ShungaNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument40 pagesMatterMarianne B. HingpesNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem NatennnDocument5 pagesGen Chem NatennnAriaane Grace DaquioagNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes (Midterms)Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes (Midterms)John Henry PahilangaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document60 pagesModule 1 Lesson 107 JAVIER LLYOD GENELSON B.No ratings yet
- Matter, Measurement, and Problem SolvingDocument26 pagesMatter, Measurement, and Problem SolvingBiruk BtNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Particle Nature of MatterDocument67 pagesUnit 9 Particle Nature of Mattermiguelcastillo212301No ratings yet
- Example: Sun or Any StarDocument3 pagesExample: Sun or Any StarNiki KevinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1anurag777.class9No ratings yet
- Group 2 Properties of MaterialsDocument24 pagesGroup 2 Properties of MaterialsjohnpaulshobayanNo ratings yet
- Materials Properties CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesMaterials Properties CharacteristicsIvandelist XNo ratings yet
- CIC Journalism ContestDocument9 pagesCIC Journalism ContestBag the Old HagNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Matter and Materials Booklet Part 1Document38 pagesGR 10 Matter and Materials Booklet Part 1tcd11ytNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Hapter Atter and Hange: Chemistry 1-2 Mr. ChumbleyDocument33 pagesHapter Atter and Hange: Chemistry 1-2 Mr. Chumbleyshahad mohammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyDocument26 pagesChapter-2 - Matter-and-EnergyJam BermejoNo ratings yet
- CHE 1-2 Chapter 1 NotesDocument33 pagesCHE 1-2 Chapter 1 NotesCherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 (GC 1) Activity Sheet 1.2: Powered by OLOPSC Home-Based SchoolingDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 (GC 1) Activity Sheet 1.2: Powered by OLOPSC Home-Based SchoolingJert MasangkayNo ratings yet
- 05 - SPSF1 07 B5Document14 pages05 - SPSF1 07 B5Anonymous RfKC0LciBK0% (1)
- 05 - SPSF1 07 B5Document14 pages05 - SPSF1 07 B5intan rohaidaNo ratings yet
- 19 64148 Form5Document1 page19 64148 Form5Genelyn AlanoNo ratings yet
- Acad Rec FormatDocument1 pageAcad Rec FormatGenelyn AlanoNo ratings yet
- CLO 1 EditedDocument3 pagesCLO 1 EditedGenelyn AlanoNo ratings yet
- CLO 1 EditedDocument3 pagesCLO 1 EditedGenelyn AlanoNo ratings yet
- 19 13404 Form5 PDFDocument1 page19 13404 Form5 PDFGenelyn AlanoNo ratings yet