Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vertebral or Spinal Column or Spine: Science Skeletal System
Uploaded by
Christine Joy Daños0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views4 pagesThis consists of the skeleton that made up our skeletal system.
Original Title
Skeletal System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis consists of the skeleton that made up our skeletal system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views4 pagesVertebral or Spinal Column or Spine: Science Skeletal System
Uploaded by
Christine Joy DañosThis consists of the skeleton that made up our skeletal system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
2 zygomatic bones – cheekbones
Science nasal bones - which make up the bridge of
the bones,
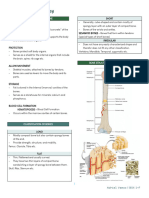
Skeletal System
lacrimal bones, palatine bones, the vomer,
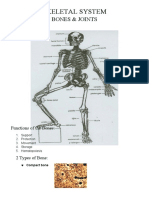
- Consists of 206 bones in an adult body the inferior nasal caonchae
- Ligaments, cartilage, joints and bones make up
20% of a person’s body mass
Bones hyoid bone – which sits just below the
mandible and does note connect with any
- Two sections: axial skeleton and appendicular other bone
skeleton
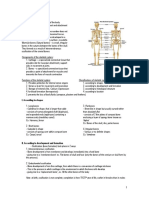
Axial skeleton-made of skull, vertebral Vertebral or spinal column or spine
column and thoracic cage - Comprised with 26 irregular bones that come
Appendicular skeleton – made more or together to form a flexible structure in a curvy s-
less of limbs shape, and this supports everything from the
skull to the pelvis
Axial skeleton - 5 sections:
Cervical vertebrae – at the top, first 7
- Skull
Thoracic vertebrae – the next 12
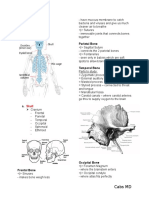
Made of 22 different bones Lumbar vertebrae - the remaining 5
Cranial bones – protects the brains - The vertebrae gets larger as we go down in
Facial bones- gives structure to the face order to support more and more weight
- Below the vertebrae we can find the sacrum
- Most of the bones in the skull are made up
which is 5 vertebrae fused together and lastly,
of flat bones and in the cranium these are
below the sacrum there is the coccyx otherwise
connected at serrated lines called sutures
known as tailbone, which is made of few tine
- Cranium – made of a vault and base vertebrae fused together.
- There are lots of ligaments keeping everything
-Base is divided into interior, middle, and In the spine together. the main ones are the
prosterior cranial fassae. Together these interior and prosterior longitudinal ligaments
produce the cranial cavity where the brain running down the front and back of the column
sits. from the neck to the sacrum.
- There are shorter ligaments that connect
- there are also ear cavity and nasal cavities adjacent vertebrae as well as intervertebral
as well as orbits which house the eye discs. These are the cushiony pads ,ade of a
nucleus pulposus which is the more elastic part
- there are 8 cranial bones – the frontal
surrounded by annulus fibrosus with lots of
bone, 2 large parietal bones, the occipital
collagen. These are found in between the each
bone, 2 temporal bone, sphenoid bone, and
vertebra acting as shock absorbers when we run
the ethmoid bone. These are connected with
and jump.
sutures- coronal, sagittal, lambnoid,
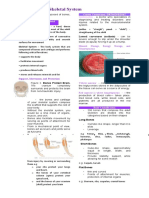
- Structure of vertebra: `\All have a body and a
squamous, occipitomastoid sutures
vertebral arch. The holes is called the vertebral
- foramina - holes that nerves and arteries foramen and the spinal cord passes through
and veins passes through. Most notably, the here. The vertebral arch is made of two pedicles
foramen magnum at the base of the skull and two laminae and from these project various
through which the spinal cord passes. processes. These are the spinous process, two
transverse processes, as well as the superior
- fourteen parts of the facial bones: and the inferior articular processes
- The vertebrae vary slightly depending on where
Mandible – lower jawbone they are found in the column:
Cervical vertebrae have spinous process that is
2 Maxillary bones- form the upper jaw and
very short a vertebral foramen that is large and
the part of the face
an additional transverse foramen to - Thin, flat bone, roughly triangular, and has three
accommodate vertebral arteries. borders, the superior, the medial or vertebral
Thoracic vertebrae have a spinous process that and the lateral or axillary
is long and points down and they also exhibit
structures called demifacets which connect to Upper limb
the ribs
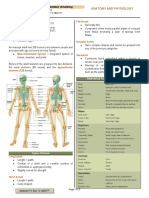
- Consists of arm, forearm and hand
Lumbar vertebrae being much larger have
pedicles and laminae that are short and thick, as Arm
well as other slight discrepancies.
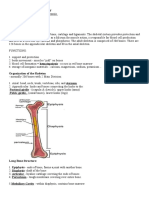
- We find the humerus, a typical long bone, with
Thoracic cage its greater and lesser tubercle, radial groove,
- Comprised of the sternum and the ribs as well medial and lateral epicondyle, radial and
as a lot of costal cartilage coronoid fossa, trochlea and capitulum
- Sternum is a flat bone right in the middle of the
thorax and it is made from three smaller bones Forearm
that have fused together. From top to bottom
- Two bones, the ulna and radius
these are the manubrium, the body and the
- These are connected all the way down by the
xiphoid process
interosseous membrane, a flexible ligament
There are 12 pairs of ribs that project from the vertebrae
Ulna
The first seven ribs attach directly to the sternum via
- Slightly longer, with its olecranon and coronoid
sections of costal cartilage and these are called true ribs
process
Then there are five pairs of false ribs, three of which
Radius
attach to the sternum indirectly, with costal cartilage from
ribs above, and then the last two are are called floating - Goes from wide to thin the other way, with a thin
ribs, because they don’t attach to the sternum at all head, the radial tuberosity, and a radial styloid
process
Ribs are flat bones that get longer going from one pair to
seven, and then shorter again from eight to twelve. Hand
- Has many separate bones
- The carpus, or the wrist, is made of eight short
Appendicular Skeleton
bones called carpals – these are scaphoid,
- Mainly just our limbs, there are other lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium,
components mention as well trapezoid, capitate and hamate
- 5 metacarpals, which make up the palm of the
hand, and they are simply named one through
five, from thumb to pinky.
Pectoral girdle - These connect to the phalanges, which are the
bones that make up the fingers. There are
- Comprised of the clavicle, or collarbone, and the
fourteen of these bones per hand, three per
scapula, or the shoulder blade, which together
finger, which are distal, middle, and proximal
give structure to the shoulder, thereby attaching
phalanges, except the thumb which has two, as
the upper limbs to the axial skeleton.
it has no middle phalanx
Clavicle
Pelvic Girdle
- Has a sternal end where it attaches to the
- Attaches the lower limbs to the axial skeleton
manubrium, and an acromial end, which joins
just like the pectoral girdle did for the upper
the scapula
limbs, although this one has far less mobility and
Scapula far more stability than the other.
- Starts at the sacrum, we described earlier, and
continues with two hip bones. These are made
of three separate bones at birth, which fuse to
become one by adulthood, but we still describe
the regions of the hip bone as being the ilium,
ischium, and pubis.
Lower limb
- Contains very thick bones, allowing us to run
and jump effectively.
Thigh
- Made of a single bone just like the arm, and this
one is called femur, which is the largest bone in
the body
- Here we see the head, with a small pit called
fovea capitis. Then the greater and lesser
trochanter, the intertrochanteric crest, the gluteal
tuberosity, linea aspera, medial and lateral
condyles, and epicondyles, intercondylar fossa
and patella
Leg
- Like the forearm, contains two bones, the tibia
and the fibula. Again, we see the interosseous
membrane between them
Tibia
We see the medial, and lateral condyle,
the intercondylar eminence, tibial
tuberosity, anterior border, medial
malleolus, and fibular notch
Fibula
Much thinner, with its head and lateral
malleolus
Foot
- Similar to the hand
- Tarsus, made of seven bones called tarsals. The
biggest two, the talus and calcaneus, make up
the ankle. Then there is the cuboid, the
navicular, and the medial, intermediate, and
lateral cuneiform bones.
- Next we see, the metatarsus, with five long
metatarsals, again numbered one through five
- Also like the hand we see 14 phalanges, three
per toe, except two the big toe, also known as
hallux.
\
You might also like
- Chapman Points Table PDFDocument3 pagesChapman Points Table PDFjwmeadow2401No ratings yet
- Chest Wall DeformitiesDocument19 pagesChest Wall Deformitiesmmkavitha9860% (5)
- UPSC Homoeopathy 2004 Question PaperDocument22 pagesUPSC Homoeopathy 2004 Question PaperDr. Kaarthika0% (1)
- Lab Report Skeletal SystemDocument9 pagesLab Report Skeletal SystemLiza Shi0% (1)
- Skeletal System: Skull Vertebral Column/spinal Cord Thoracic CageDocument7 pagesSkeletal System: Skull Vertebral Column/spinal Cord Thoracic Cagehannah peloniaNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review 3RDDocument7 pagesPointers To Review 3RDClarissa MontoyaNo ratings yet
- CHNCGDocument7 pagesCHNCGDANIEL LANCE NEVADONo ratings yet
- Zoology MidtermsDocument14 pagesZoology MidtermsJULIANNE ANACTANo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Physiology of Animals - Skeletal System.Document3 pagesAnatomy - Physiology of Animals - Skeletal System.Erica MaeNo ratings yet
- Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesAppendicular Skeletal SystemSOFIA ALEXIS MALIÑANANo ratings yet
- Spinal ColumnDocument2 pagesSpinal ColumnSOFIA ALEXIS MALIÑANANo ratings yet
- C5 Skeletal NotesDocument10 pagesC5 Skeletal NotesJocelyn AlunanNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiomechanics ReviewerJOHN EVAR LABASTILLANo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 5 - The Skeletal Systemnavalesmay1No ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton: Skull Hyoid Vertebral Column Thoracic Cage Parietal BoneDocument5 pagesAxial Skeleton: Skull Hyoid Vertebral Column Thoracic Cage Parietal BoneGabriel Joseph CabreraNo ratings yet
- VERTEBRAEDocument3 pagesVERTEBRAEstaceytuando10No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument35 pagesThe Skeletal SystemSamantha EllaineNo ratings yet
- Self Directed Module.3. BRAINSTEMDocument5 pagesSelf Directed Module.3. BRAINSTEMLouigie Marree Talento GarciaNo ratings yet
- MC I Modular Reviewer Skeletal SystemDocument21 pagesMC I Modular Reviewer Skeletal SystemSteiner LimNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 (SkeletalSystem)Document2 pagesLECTURE 3 (SkeletalSystem)ALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System TransesDocument11 pagesSkeletal System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Anatomy BonesDocument11 pagesAnatomy BonesDunkin DonutNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System For BMDocument13 pagesMusculoskeletal System For BMNepimuga OliverNo ratings yet
- Nursing AnaPhy-Skeletal System Axial SkeletonDocument29 pagesNursing AnaPhy-Skeletal System Axial SkeletonGail Chantel Spring PerlasNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Skeletal SystemDocument11 pages6.2 Skeletal SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- (Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFDocument7 pages(Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- LabSci1 Lab Ex15Document10 pagesLabSci1 Lab Ex15Hannah MondillaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal SystemSOFIA ALEXIS MALIÑANANo ratings yet
- Anatomical IntroductionDocument17 pagesAnatomical Introductionllazoozllbraa 7372No ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument11 pagesSkeletal SystemCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument62 pagesSkeletal SystemAlyza AlcazarinNo ratings yet
- Neuroana Topic 3 LectureDocument6 pagesNeuroana Topic 3 LecturexoNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal SystemJeremy KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesSkeletal SystemEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Column of DogDocument3 pagesVertebral Column of DogEmit Rosary PenetranteNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemIra George ArcillaNo ratings yet
- 3 General OsteologyDocument90 pages3 General Osteologyvbh8222No ratings yet
- 6.1 Skeletal SystemDocument4 pages6.1 Skeletal SystemEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Marian Diamond)Document34 pagesAnatomy (Marian Diamond)NHZANo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument2 pagesSkeletal SystemMa Khristina S WongNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LecDocument2 pagesAnaphy LecEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- SkeletalDocument21 pagesSkeletalKeith HiadgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 8 - Musculoskeletal SystemIbby HooriyaNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument3 pagesThe Musculoskeletal SystemCUARTERO, SHERYL ANNENo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument73 pagesSkeletal SystemUniversal DiscoveringNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesThe Skeletal SystemAarchi SinghNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson 4Document40 pagesSkeletal System Lesson 4Ella Nika FangonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Excitability Contractility Extensibility ElasticityDocument5 pagesElectrical Excitability Contractility Extensibility ElasticityMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System IyahDocument55 pagesThe Skeletal System IyahAnna R. DionisioNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesSkeletal SystemRachell AvecillaNo ratings yet
- Las Sses4 Q1 W5Document14 pagesLas Sses4 Q1 W5Joan AgranoNo ratings yet
- Hs 2Document5 pagesHs 2Elyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Information BookDocument15 pagesSkeletal System Information BookMartin SujaNo ratings yet
- LEC Orthopedic NursingDocument31 pagesLEC Orthopedic NursingAlthea Franz DuoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- Back Pain PDFDocument40 pagesBack Pain PDFsana shiekhNo ratings yet
- 7 - Skely AnatomyDocument3 pages7 - Skely AnatomyGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021Document13 pagesAssignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System ReviewerDocument3 pagesThe Skeletal System Reviewerkoshiaiko21No ratings yet
- 3 Musculoskeletal System-2020-10132Document11 pages3 Musculoskeletal System-2020-10132Горькое ДноNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - SKELETALSYSTEMDocument22 pagesChapter 5 - SKELETALSYSTEMGuenNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Test Score Card: A. Body Composition: Body Mass IndexDocument2 pagesPhysical Fitness Test Score Card: A. Body Composition: Body Mass IndexChristine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- List of Emergency Contact Numbers and Information Organization Contact # Contact PersonDocument2 pagesList of Emergency Contact Numbers and Information Organization Contact # Contact PersonChristine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- OLIVO - Lesson 3 History of Statistics QuizDocument2 pagesOLIVO - Lesson 3 History of Statistics QuizChristine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- PFA MODULE2 DanosDocument2 pagesPFA MODULE2 DanosChristine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Danos, Christine Joy V. November 16, 2020 IX - Archimedes Homeroom - Module 3Document3 pagesActivity 1: Danos, Christine Joy V. November 16, 2020 IX - Archimedes Homeroom - Module 3Christine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- OLIVO - Lesson-1-Statistics-Quiz (1)Document2 pagesOLIVO - Lesson-1-Statistics-Quiz (1)Christine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Branches of Statistics QuizDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Branches of Statistics QuizChristine Joy Daños100% (1)
- OLIVO - Lesson-1-Statistics-Quiz (1)Document2 pagesOLIVO - Lesson-1-Statistics-Quiz (1)Christine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- OLIVO - Lesson 3 History of Statistics QuizDocument2 pagesOLIVO - Lesson 3 History of Statistics QuizChristine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- 1Document10 pages1Christine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Branches of Statistics QuizDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Branches of Statistics QuizChristine Joy Daños100% (1)
- Pie Chart: September 18, 20 English 8Document1 pagePie Chart: September 18, 20 English 8Christine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- Business Math and Research (REVIEWER)Document2 pagesBusiness Math and Research (REVIEWER)Christine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- Key: Subject Yellow, Bold Verb Green, UnderlineDocument4 pagesKey: Subject Yellow, Bold Verb Green, UnderlineChristine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- PrayerDocument2 pagesPrayerGaizel Viesta AcostaNo ratings yet
- Triangle Inequality TheoremDocument2 pagesTriangle Inequality TheoremChristine Joy DañosNo ratings yet
- The Ostrich Biology Production and HealthDocument368 pagesThe Ostrich Biology Production and HealthMariela RivasNo ratings yet
- Estimating Sex of The Human Skeleton Based On Metrics of The SternumDocument7 pagesEstimating Sex of The Human Skeleton Based On Metrics of The SternumDenys PutraNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rodriguez Luke - 01-General-Body-Directional-TermsDocument24 pagesKami Export - Rodriguez Luke - 01-General-Body-Directional-TermsLuke RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Your Skeletal SystemDocument18 pagesThe Importance of Your Skeletal SystemChris DavisNo ratings yet
- Chest Mobility ExercisesDocument26 pagesChest Mobility ExercisesNimisha BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Thorax and Abdomen Muscle NotesDocument2 pagesThorax and Abdomen Muscle NotesJean OpallaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PDFDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PDFalexenneth canilaNo ratings yet
- Headtotoe 2Document5 pagesHeadtotoe 2api-675533626No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology by Dennis Munoz2Document1,273 pagesAnatomy and Physiology by Dennis Munoz2Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- Group 5 A.1 Axial BonesDocument7 pagesGroup 5 A.1 Axial BonesIsabella CariagaNo ratings yet
- Thoracic SurgeryDocument178 pagesThoracic SurgeryArthur Pendragon100% (1)
- Field Care of GameDocument19 pagesField Care of GameKen HouseNo ratings yet
- Final CBLM Core 1 Smoking, Pickling and SaltingDocument48 pagesFinal CBLM Core 1 Smoking, Pickling and SaltingCath Santos PanganNo ratings yet
- Moore's Clinically Oriented Anatomy 6th EdDocument4 pagesMoore's Clinically Oriented Anatomy 6th EdJohna Pauline Mandac67% (6)
- Radio Anatomy of The Thorax and Medias Tin Um 9-17Document113 pagesRadio Anatomy of The Thorax and Medias Tin Um 9-17Ditas ChuNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Practical Chest PhysiotherapyDocument198 pagesHandbook of Practical Chest PhysiotherapyKRUNAL BANGAL100% (2)
- Health AssessmentDocument2 pagesHealth AssessmentLee KimNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: By: Jasper C. Pilongo, M.DDocument110 pagesThe Skeletal System: By: Jasper C. Pilongo, M.Dash_zordickNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Notes For BS: Khyber Medical University Peshawar Prepared by DR, Raheel Ahmad Lecturer Pihms. PeshawarDocument84 pagesAnatomy Notes For BS: Khyber Medical University Peshawar Prepared by DR, Raheel Ahmad Lecturer Pihms. PeshawarShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 57 Anatomy and Surgical Access of The MediastinumDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 57 Anatomy and Surgical Access of The MediastinumAbeNo ratings yet
- Ln-4 The Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesLn-4 The Skeletal and Muscular SystemAnnie GraceNo ratings yet
- Skeleton Scavenger HuntDocument8 pagesSkeleton Scavenger Huntapi-278138513No ratings yet
- Bony Thorax PositioningDocument3 pagesBony Thorax PositioningMelanie RamdassNo ratings yet
- Syllabus SCSIDocument92 pagesSyllabus SCSIDcStrokerehab100% (1)
- Ch.8 - Axial & Appendicular SkeletonDocument72 pagesCh.8 - Axial & Appendicular SkeletonMeganNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 - MS1 Course Task Cu1Document3 pagesNCMB 312 - MS1 Course Task Cu1HeinzzzNo ratings yet