Professional Documents
Culture Documents
States of Matter and Atomic Structure
Uploaded by
Rebecca Beron Resadas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesOriginal Title
ADGE2.1 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesStates of Matter and Atomic Structure
Uploaded by
Rebecca Beron ResadasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
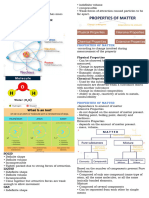
Vocabulary: States of Matter
Atoms- indivisible
Molecules- composed of two or more atoms STATES OF MATTER
combined
Ions- Particles with charged
Protons- Positive charged
Neutron- Neutral
Electron- Negative charged
Bosons- a whole energy spins
Fermions- half energy spins
Higgs Boson- The Higgs field
Gluon- Strong force
Photon- Electromagnetic force Solid- closely packed, restricted motion
Z & W-Boson- Weak force Liquid- far apart with free movement (flow)
Gas- very far apart, free movement
Quarks- in every quark an equivalent of the (chaotic)
anti-particle Plasma- highly charged particles with
extremely high kinetic energy
Mesons- 2 quarks Bose Einstein Condensate- superfluid,
Pentaquarks- 5 quarks flowing without friction, simulate conditions
Dibaryon- 6 quarks same in black holes
Monatomic- composed of just one atom Properties of Matter
Diatomic- composed of only two atoms of According to change involved during
the same or different chemical elements measurement of the property
(O2, CO)
Physical Properties- no change in
Homonuclear Diatomic- consists of two composition takes place
atoms of same element combined (H2, N2,
O2, and all halogens) Chemical Properties- change in
composition occurs
Heteronuclear Diatomic- consists of two
atoms of different elements chemically According to dependence on amount of
combined (HCl, HF) matter
Cations- Positive charges Extensive Property- depend on the
Anions- Negative charges amount of material like mass, length and
volume
Intensive Property- depend on the quality
of material like odor, color, density,
solubility, boiling point, melting point,
electrical conductivity
CHEM 225- Lesson 1: Matter & Its Properties Page 1
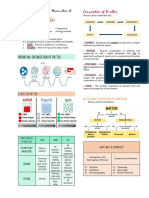
Based on the number of components Separation Methods
present
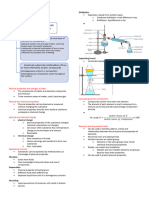
Filtration
Pure Substance- a single substance either
an element or compound with definite Separate a solid from liquid in a
composition and properties heterogeneous mixture using a filtering
membrane
Mixtures- made of blend of elements and
compounds.
Based on the number of kinds of atoms
present
Elements- pure substances that are made
up of only one kind of atom Distillation
Compounds- pure substances that are Separate a liquid in a homogeneous mixture
made up of two or more kinds of atoms
Based on the uniformity of composition and
properties
Homogeneous mixtures- has a uniform
composition and exhibits same properties in
different parts of mixtures
Magnetic separation
Heterogeneous mixtures- non uniform
composition and its properties vary in Separate a magnetic solid from a
different parts of mixtures heterogeneous mixture
Decantation
Separate a solid from a liquid in a
heterogeneous mixture based on gravity
CHEM 225- Lesson 1: Matter & Its Properties Page 2
Sublimation
Separate a volatile solid from a non-volatile
solid
CHEM 225- Lesson 1: Matter & Its Properties Page 3
You might also like
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Inbound 4695793937270644090Document6 pagesInbound 4695793937270644090joshuatimothylaoNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM ReviewerDocument6 pagesGENCHEM ReviewerChricellFNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Chem A4 SizeDocument12 pagesWeek 5 Chem A4 SizeKrisha Mae PalomarNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 Long Exam 1 Reviewer: Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesChem 16 Long Exam 1 Reviewer: Key Conceptsdesperateboy100% (1)
- Chem1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument3 pagesChem1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- Genchem1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenchem1 ReviewerCrystal Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- CHEM (no formula)Document4 pagesCHEM (no formula)palacioaya28No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFYING MATTER AND ITS PROPERTIESDocument2 pagesCLASSIFYING MATTER AND ITS PROPERTIESCarl Zeus TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Different Molecular Attraction Different Molecular Arrangement StatesDocument4 pagesDifferent Molecular Attraction Different Molecular Arrangement StatesGeraldine ManaloNo ratings yet
- M1W1 Understanding Matter and Chemical ChangeDocument6 pagesM1W1 Understanding Matter and Chemical ChangePrincess Diane AgripaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGeneral Chemistry Topic 1 ReviewerNishka CarabeoNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEMISTRY 1 1stDocument4 pagesGEN CHEMISTRY 1 1strenmarseyerNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryRhea Kristine C. MateoNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its Properties & Atomic Structure: IsotopesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its Properties & Atomic Structure: IsotopesCharles BarcelonNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem - Matter ReviewerDocument2 pagesGen Chem - Matter Reviewerjellyjelly458No ratings yet
- Matter Unit NotesDocument7 pagesMatter Unit NotesAnonpcNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience ReviewerIT'S JAY STEPHEN0% (1)
- Matter and Its Components - 1Document6 pagesMatter and Its Components - 1TenacityNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument70 pagesCHEMISTRYF E R N A NNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry: Unit 1 - The Particle Nature of MatterDocument5 pagesIB Chemistry: Unit 1 - The Particle Nature of MattermjohnmccNo ratings yet
- BrudaDocument6 pagesBrudaemmalin2025No ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1 - P1 - MatterDocument21 pagesChemistry Unit 1 - P1 - MatterMelina BazarNo ratings yet
- FGFDGFDGDocument5 pagesFGFDGFDGEXONOOT YTNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic: Classifying MatterDocument11 pagesAtoms and The Periodic: Classifying MattercharlieNo ratings yet
- Gen Chemistry 1: Same AsnDocument3 pagesGen Chemistry 1: Same Asnjames BernalNo ratings yet
- Chem (Lec)Document2 pagesChem (Lec)Dalgom's WifeNo ratings yet
- MATTER AND ITS COMPONENTS EXPLAINEDDocument7 pagesMATTER AND ITS COMPONENTS EXPLAINEDTenacityNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesDocument2 pagesLesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Hierarchal Organization of MatterDocument9 pagesHierarchal Organization of MatterChelsea Fyana PulmanoNo ratings yet
- Iyakan Ko ToDocument5 pagesIyakan Ko ToSantos, John Christian Rogelio M.No ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument3 pagesChem ReviewerShane PangatoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaDocument75 pagesChemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaJESPHER GARCIANo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Gen Science)Document3 pagesReviewer (Gen Science)Sophia LantinNo ratings yet
- 1 ChemistryDocument13 pages1 ChemistryAlexandra EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument11 pagesPeriodic TableMichelle AlarcioNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties 2. Chemical Properties: Dependent On The Amount of Matter Mass Weight Thickness Surface AreaDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties 2. Chemical Properties: Dependent On The Amount of Matter Mass Weight Thickness Surface AreaPrinces CornelNo ratings yet
- Gen Chame LecDocument9 pagesGen Chame LecAlloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYkhayceemeade2No ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument18 pagesIntroduction To ChemistryViktor Mikhael Roch BarbaNo ratings yet
- Sections 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4,1.5Document17 pagesSections 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4,1.5gchanjrNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5Ann Margaret Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- 1 Matter and Its Properties ...Document65 pages1 Matter and Its Properties ...Akira SatoūNo ratings yet
- Gen-ChemDocument12 pagesGen-ChemGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Properties and Structure of MatterDocument17 pagesModule 1 Properties and Structure of Matterisaheqq12No ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Matter, States, and PropertiesDocument3 pagesChemistry 1: Matter, States, and Propertieskeith herreraNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 CHEMISTRY HandoutsDocument3 pagesGrade 7 CHEMISTRY HandoutsCestlavi Santos100% (1)
- Chemistry IGCSE Rev PackDocument39 pagesChemistry IGCSE Rev Packرهام کاظمیNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Chemistry ExplainedDocument15 pagesFoundations of Chemistry ExplainedfuckyouNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Year MTDocument12 pagesChemistry 1st Year MTENo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Stoichiometric Relationships PDFDocument7 pagesTopic 1 Stoichiometric Relationships PDFAshwinNo ratings yet
- scienceDocument1 pagescienceandreacaswNo ratings yet
- Chem LabDocument10 pagesChem LabJenna RosalesNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Study of ChemistryDocument7 pagesIntroduction to the Study of ChemistryMark Julius Felix PagudNo ratings yet
- Pure Substance and Mixtures Study GuideDocument2 pagesPure Substance and Mixtures Study GuideAlexiandria MaggayNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes - Preliminary 2021 4Document35 pagesChemistry Notes - Preliminary 2021 4Sejal SinhaNo ratings yet
- BASIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLESDocument7 pagesBASIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLESBhabi BarrugaNo ratings yet
- Title and Author Method Used Research Findings Conclusion and Limitation of The StudyDocument1 pageTitle and Author Method Used Research Findings Conclusion and Limitation of The StudyRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- GE 101 Exercise - Philosophical Perspectives of The SelfDocument2 pagesGE 101 Exercise - Philosophical Perspectives of The SelfRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- States of Matter and Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesStates of Matter and Atomic StructureRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Human Resource RebeccaDocument6 pagesHuman Resource RebeccaRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Types and Assumptions in ResearchDocument2 pagesHypothesis Types and Assumptions in ResearchRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Retailers AssociationDocument14 pagesThe Philippine Retailers AssociationRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis 1Document6 pagesSwot Analysis 1Rebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Name: Time/Day: THF 10:30-12:00 Subject: International Marketing Instructor: Mrs. Virginia B. Cabarlo Test I. Fill in The BlanksDocument1 pageFinal Examination Name: Time/Day: THF 10:30-12:00 Subject: International Marketing Instructor: Mrs. Virginia B. Cabarlo Test I. Fill in The BlanksRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Twenty: Reaction PaperDocument13 pagesChapter Twenty: Reaction PaperRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1Rebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Shiela Mae DamarillosDocument4 pagesSubmitted By:: Shiela Mae DamarillosRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Resume 21Document2 pagesResume 21Rebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Name: Time/Day: THF 10:30-12:00 Subject: General Psychology Instructor: Mrs. Virginia B. CabarloDocument2 pagesFinal Examination Name: Time/Day: THF 10:30-12:00 Subject: General Psychology Instructor: Mrs. Virginia B. CabarloRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research: Bsba - IiiDocument7 pagesMarketing Research: Bsba - IiiRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Employment Background Checks Is To Flag Any Criminal Convictions in AnDocument2 pagesEmployment Background Checks Is To Flag Any Criminal Convictions in AnRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1Rebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- RLC Strategy, SWOT & Finance Report: Real Estate Developer AnalysisDocument2 pagesRLC Strategy, SWOT & Finance Report: Real Estate Developer AnalysisRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Name: Time/Day: THF 10:30-12:00 Subject: International Marketing Instructor: Mrs. Virginia B. Cabarlo Test I. Fill in The BlanksDocument1 pageFinal Examination Name: Time/Day: THF 10:30-12:00 Subject: International Marketing Instructor: Mrs. Virginia B. Cabarlo Test I. Fill in The BlanksRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Retailers AssociationDocument14 pagesThe Philippine Retailers AssociationRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Advertising Finals (Shie)Document9 pagesAdvertising Finals (Shie)Rebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Becay BecayDocument18 pagesBecay BecayRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Pilar Municipality Peace Order Council Resolution Endorsing Police Officer ApplicantsDocument2 pagesPilar Municipality Peace Order Council Resolution Endorsing Police Officer ApplicantsRebecca Beron Resadas100% (3)
- Submitted By:: Shiela Mae DamarillosDocument4 pagesSubmitted By:: Shiela Mae DamarillosRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- General PsychologyDocument2 pagesGeneral PsychologyRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Adhoc ResolutionDocument2 pagesAdhoc ResolutionRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management (MM4) : Submitted By: Rebecca B. ResadasDocument3 pagesMarketing Management (MM4) : Submitted By: Rebecca B. ResadasRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Retailers AssociationDocument14 pagesThe Philippine Retailers AssociationRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument4 pagesArt AppreciationRebecca Beron ResadasNo ratings yet
- Physics Week 1-14Document360 pagesPhysics Week 1-14Archit GatadeNo ratings yet
- Distance From A Point To A Line - WikipediaDocument9 pagesDistance From A Point To A Line - WikipediaDenes MarschalkoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics (BT-201) B.Tech. I Year CO - 01 Unit I - Quantum PhysicsDocument39 pagesEngineering Physics (BT-201) B.Tech. I Year CO - 01 Unit I - Quantum PhysicsAbhishek ThakralNo ratings yet
- 2 - Physical Quantities and Measurements1 - Physical Quantities & UnitsDocument27 pages2 - Physical Quantities and Measurements1 - Physical Quantities & UnitsCHARLES CHIMZNo ratings yet
- Vibration FinalDocument20 pagesVibration FinaljaysamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structural Analysis: Lecture 1 Vesna Terzic, PH.DDocument18 pagesAdvanced Structural Analysis: Lecture 1 Vesna Terzic, PH.DBilly JimenezNo ratings yet
- Science Past PaperDocument16 pagesScience Past PaperCrissCross SSNo ratings yet
- Applied Mechanics CH 1Document11 pagesApplied Mechanics CH 1Tushar KiranNo ratings yet
- Units and Measurements-1 MCQSDocument69 pagesUnits and Measurements-1 MCQSmairaj2No ratings yet
- Solids and Semi-Conductors Energy BandsDocument12 pagesSolids and Semi-Conductors Energy Bandssuneel SaiNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics Concepts (Good) PDFDocument707 pagesSolid State Physics Concepts (Good) PDFDielectric MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Base FeaturesDocument42 pagesSheet Metal Base FeaturesAnil VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Jack KowmanNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis I Assignment Solutions: James C. RobinsonDocument26 pagesFunctional Analysis I Assignment Solutions: James C. Robinsonarvind lakshmi ranjanNo ratings yet
- 10 Wave OpticsDocument5 pages10 Wave OpticsSimon PradeepNo ratings yet
- Shade Your Id Number. On The Orange BookletDocument1 pageShade Your Id Number. On The Orange BookletCharles AugustusNo ratings yet
- Odd Even FunctionsDocument6 pagesOdd Even FunctionsJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- How Zero-Point Energy Can Become an Energy SourceDocument76 pagesHow Zero-Point Energy Can Become an Energy SourceAkshaya Kumar RathNo ratings yet
- Module3 MCQDocument2 pagesModule3 MCQLukkuman ANo ratings yet
- Jee 31dec2023 QP MorDocument10 pagesJee 31dec2023 QP MorphychemgodNo ratings yet
- Discrete Symmetries and Violation: From Experiment To TheoryDocument5 pagesDiscrete Symmetries and Violation: From Experiment To TheorylaliloNo ratings yet
- INO12 Lecture 01 2012-04-20Document46 pagesINO12 Lecture 01 2012-04-20О. Энх-АмгаланNo ratings yet
- Nature of ForceDocument14 pagesNature of ForceShiela CarabidoNo ratings yet
- Physic Lab 6Document10 pagesPhysic Lab 6api-463453187No ratings yet
- Waves Lecture SlidesDocument23 pagesWaves Lecture SlidesHania SheikhNo ratings yet
- Physics Foundation MSc Entrance Exam PrepDocument18 pagesPhysics Foundation MSc Entrance Exam Prepsreejitha KNo ratings yet
- JAN 24 Batch: Pre Mock - 02Document3 pagesJAN 24 Batch: Pre Mock - 02Quazi Sahil HossainNo ratings yet
- MCQ Question Answers Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in A PlaneDocument8 pagesMCQ Question Answers Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in A PlaneDisha Tripathi - 10-ENo ratings yet
- The Two-Body Problem: Classical Dynamics Michaelmas 2014Document3 pagesThe Two-Body Problem: Classical Dynamics Michaelmas 2014ram kumarNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument31 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For Scientistsramy thaerNo ratings yet