Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Glycolysis and cellular respiration overview
Uploaded by
Paul Paniza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesOriginal Title
General Zoology Module 1 Lesson 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesGlycolysis and cellular respiration overview
Uploaded by
Paul PanizaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
INTRODUCTION
- Glucose as an Energy Source
o broken down through cellular respiration
o to eventually produce adenosine triphosphate
used to power the different metabolic processes in animal cells
- Cellular Respiration
1. Pathway 1 (Aerobic Pathway) -> produces higher ATP
a. Glycolysis (can occur aerobically or anaerobically, does not require O2
b. Transitional Reaction
c. Krebs Cycle
d. Oxidative Phosphorylation
i. Electron Transport Chain
ii. Chemiosmosis
2. Pathway 2 (Anaerobic Pathway) -> produces lesser ATP
a. Lactic Acid Fermentation
i. Glycolysis
ii. NAD+ Regeneration
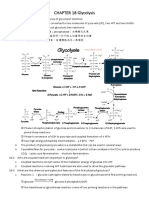
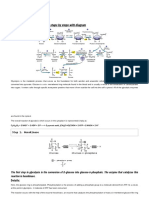
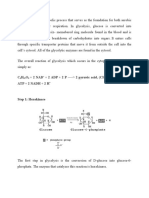
GLYCOLYSIS
- Nutshell:
o Glucose is broken down into pyruvate and ATP
I. Energy Investment Phase (2 G3P MOLECULES)
1. Phosphorylation
START:
One Glucose Molecule
ENZYME:
Hexokinase
DESCRIPTION:
invests some ATP in order to gain more ATP later on
a phosphate group from ATP will be added to a glucose molecule
END:
Glucose 6-phosphate
2. Isomerization
START:
Glucose 6-phosphate
ENZYME:
Phosphoglucoisomerase
END:
Fructose 6-phosphate
3. Phosphorylation
START:
Fructose 6-phosphate
ENZYME:
Phosphofructokinase
DESCRIPTION:
a phosphate group from ATP will be added to fructose 6-
phosphate
END:
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
4. Cleavage
START:
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
ENZYME:
Aldolase
DESCRIPTION:
splits into two (2) different structures
END:
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
5. Isomerization
START:
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)
ENZYME:
Isomerase
DESCRIPTION:
transforms DHAP molecule into another G3P molecule
END:
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
II. Energy Harvesting Phase
6. Oxidation/Dehydrogenation and Phosphorylation
START:
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
ENZYME:
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) Dehydrogenase
DESCRIPTION:
hydrogen is released and binds to NAD+ to form NADH
a phosphate from the cytoplasm combines with G3P
END:
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
7. Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
START:
1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
ENZYME:
Phosphoglycerate Kinase
DESCRIPTION:
BPG releases a phosphate group
the phosphate group binds to an ADP molecule turning it into an
ATP molecule
END:
3-Phosphoglycerate (3-PGA)
ATP molecule
8. Isomerization
START:
3-Phosphoglycerate (3-PGA)
ENZYME:
Phosphoglycerate Mutase
END:
2-Phosphoglycerate (2-PGA)
9. Dehydration
START:
One Glucose Molecule
ENZYME:
Hexokinase
DESCRIPTION:
invests some ATP in order to gain more ATP later on
a phosphate group from ATP will be added to a glucose molecule
END:
Glucose 6-phosphate
You might also like
- Chapter 5: Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument10 pagesChapter 5: Carbohydrate Metabolismrose100% (1)
- 10 Steps Glycolysis ExplainedDocument8 pages10 Steps Glycolysis Explaineddani2703No ratings yet
- Non-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseFrom EverandNon-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Chapter 11. Metabolism of CarbohydrateDocument35 pagesChapter 11. Metabolism of CarbohydrateMohd RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathways: Catabolic Pathways Anabolic PathwaysDocument38 pagesMetabolic Pathways: Catabolic Pathways Anabolic PathwaysEhtisham AslamNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Krebs CycleDocument5 pagesGlycolysis Krebs Cyclemarites ValdezNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Wps OfficeDocument24 pagesGlycolysis Wps Officekristel ann matela100% (1)
- Notes From Langman's Medical EmbryologyDocument13 pagesNotes From Langman's Medical EmbryologyJeane Irish Paller Egot92% (12)
- Carbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)Document25 pagesCarbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)DIPENDRA KUMAR KUSHAWAHANo ratings yet
- Glycolysis 14 40Document4 pagesGlycolysis 14 40ehnzdhmNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: NotesDocument15 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: Notesarmin509No ratings yet
- Summary of Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument1 pageSummary of Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationMariser ReyesNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument22 pagesGlycolysisjason misticaNo ratings yet
- 13 - Glycolysis TEAM438Document28 pages13 - Glycolysis TEAM438Haze MNo ratings yet
- 1st Half of Glycolysis To Kreb CycleDocument2 pages1st Half of Glycolysis To Kreb CycleDoreen Shane CabigonNo ratings yet
- Glycolytic PathwayDocument17 pagesGlycolytic PathwayramchinnaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec ReviewerDocument25 pagesBiochem Lec ReviewerBarlaan Raniela Marie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis:: The Central Pathway of Glucose DegradationDocument23 pagesGlycolysis:: The Central Pathway of Glucose DegradationMohammad Noman AkramNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Carbohydrates NotesDocument21 pagesMetabolism of Carbohydrates NotesRhen Shane GivertasNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018Document136 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018N A Anggriani WulandariNo ratings yet
- Biochem Term PaperDocument8 pagesBiochem Term Paperakanksha awasthiNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Aerobic Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesGroup 5 - Aerobic Cellular Respirationditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration: General BiologyDocument12 pagesAerobic Respiration: General BiologyV KimNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM ReviewerDocument48 pagesBIOCHEM ReviewerMarie GdlNo ratings yet
- CELLULAR RESPIRATION BiologyDocument59 pagesCELLULAR RESPIRATION BiologyNur SafirahNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis Generates ATPDocument37 pagesCellular Respiration: Glycolysis Generates ATPPrince Kyle R. DolosoNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis PresentationDocument34 pagesGlycolysis PresentationAl LimNo ratings yet
- Asy GlycolysisDocument69 pagesAsy GlycolysisErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Bio - Active Learning - Cellular Respiration & FermentationDocument24 pagesBio - Active Learning - Cellular Respiration & FermentationnurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism HandoutDocument9 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Handoutwendydeveyra7No ratings yet
- 10 Steps GlycoDocument7 pages10 Steps GlycoRhianne Grace CastroNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: First Stage of Cellular Respiration You Will Need: M1-M4, M11 Coloured Pens/pencils (4 Preferred) TextbookDocument48 pagesGlycolysis: First Stage of Cellular Respiration You Will Need: M1-M4, M11 Coloured Pens/pencils (4 Preferred) TextbookAshmeet MahanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 18 GlycolysisDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 18 Glycolysis楊畯凱No ratings yet
- GlucolysisDocument11 pagesGlucolysisMohamed SalahNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: Step 1: HexokinaseDocument6 pagesGlycolysis: Step 1: HexokinaseAirra RamosNo ratings yet
- ASB0204 Chap 7 - CidDocument42 pagesASB0204 Chap 7 - CidZulhelmiNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument46 pagesGlycolysisaishwaryatidke754No ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants: Chapter - 4Document9 pagesRespiration in Plants: Chapter - 4Monica BaiNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument12 pagesGlycolysisenrico andrionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document23 pagesChapter 14nhocnho_1993No ratings yet
- Slides GlicóliseDocument10 pagesSlides GlicóliseTãhsìn Ãhsäñ SãrkãrNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration GlycolysisDocument1 pageCellular Respiration GlycolysisReigne CuevasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Hour 1Document31 pagesCellular Respiration Hour 1DamiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Metabolism 3 Glycolysis ISUDocument25 pagesCarbohydrates Metabolism 3 Glycolysis ISUsjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY1Document2 pagesBIOLOGY1rainrulletNo ratings yet
- BCH 312 Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument6 pagesBCH 312 Pentose Phosphate PathwayMARYJANE NZUBECHUKWU NJOKUNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument9 pagesGlycolysisIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- CHE 311 Lecture 4 GlycolysisDocument28 pagesCHE 311 Lecture 4 Glycolysisisaac mwanzaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis ProcessDocument7 pagesGlycolysis ProcessBlister CountNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Energy Metabolism and Membrane Physiology of The ErythrocyteDocument5 pagesChapter 9 - Energy Metabolism and Membrane Physiology of The ErythrocyteAira UsiNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Glucose, Glycogen: Biochemistry-II (MIC-403)Document16 pagesMetabolism of Glucose, Glycogen: Biochemistry-II (MIC-403)zainmaryamNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis 3MD (3)Document48 pagesGlycolysis 3MD (3)gostrider0093sNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of carbohydrates via glycolysis pathwayDocument18 pagesMetabolism of carbohydrates via glycolysis pathwayhiNo ratings yet
- Zoology AssignmentDocument9 pagesZoology AssignmentBiba JaanNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument7 pagesGlycolysisTahirat NasiruNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesAerobic Cellular RespirationTasneem MaruhomNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis-StryerDocument36 pagesGlycolysis-StryerAngelikaOdimerNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics & Metabolism GuideDocument56 pagesBioenergetics & Metabolism GuideAww AddNo ratings yet
- 2 GlycolysisDocument41 pages2 Glycolysislou765500No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationKEITHLYN EIZEL RAMITERRENo ratings yet
- Paniza, P - Synthesis PaperDocument5 pagesPaniza, P - Synthesis PaperPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Journal No. 1: My StoryDocument1 pageJournal No. 1: My StoryPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Module 1 Arthropoda and EchinodermataDocument5 pagesGeneral Zoology Module 1 Arthropoda and EchinodermataPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Module 1 ChordataDocument4 pagesGeneral Zoology Module 1 ChordataPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- English Multimodal Presentation ScriptDocument2 pagesEnglish Multimodal Presentation ScriptPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Module 1 Mollusks and AnnelidaDocument3 pagesGeneral Zoology Module 1 Mollusks and AnnelidaPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- English Multimodal Presentation ScriptDocument2 pagesEnglish Multimodal Presentation ScriptPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Paniza, P - Synthesis PaperDocument5 pagesPaniza, P - Synthesis PaperPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Module 1 Platyhelminthes and NematodaDocument1 pageGeneral Zoology Module 1 Platyhelminthes and NematodaPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Group D7 BIO 31.02 Project ProposalDocument1 pageGroup D7 BIO 31.02 Project ProposalPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Module 1 Lesson 1-2.5Document5 pagesGeneral Zoology Module 1 Lesson 1-2.5Paul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and cellular respiration overviewDocument3 pagesGlycolysis and cellular respiration overviewPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- General Zoology Module 1 Lesson 1-2.5Document5 pagesGeneral Zoology Module 1 Lesson 1-2.5Paul PanizaNo ratings yet
- BIO 31.02 Project Correlates Local Bat Species With Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesBIO 31.02 Project Correlates Local Bat Species With Climate ChangePaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- LAMP Assay ROC Curve AnalysisDocument15 pagesLAMP Assay ROC Curve AnalysisPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- LAMP Assay ROC Curve AnalysisDocument15 pagesLAMP Assay ROC Curve AnalysisPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Group D7 Module 1 Computation ExerciseDocument17 pagesGroup D7 Module 1 Computation ExercisePaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- COAM - November Bonding Session Project TimelineDocument2 pagesCOAM - November Bonding Session Project TimelinePaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Faith Narrative Paniza Theo11LLDocument3 pagesFaith Narrative Paniza Theo11LLPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Paniza - EnGL 11 Task On After The Last SkyDocument15 pagesPaniza - EnGL 11 Task On After The Last SkyPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Group D7 BIO 31.02 Project ProposalDocument1 pageGroup D7 BIO 31.02 Project ProposalPaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- Paniza - EnGL 11 Informative Essay OutlineDocument3 pagesPaniza - EnGL 11 Informative Essay OutlinePaul PanizaNo ratings yet
- August 24,2017: Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9Document3 pagesAugust 24,2017: Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9Josal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- 2 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH Reviewer 2Document4 pages2 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH Reviewer 2manuelNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps of GlycolysisDocument3 pages10 Steps of GlycolysisHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Gene Silencing: Presented byDocument23 pagesGene Silencing: Presented byRouf Ahmad100% (1)
- Bioinformatics: Network Analysis: Flux Balance Analysis and Metabolic Control AnalysisDocument52 pagesBioinformatics: Network Analysis: Flux Balance Analysis and Metabolic Control AnalysisGiulio MilaneseNo ratings yet
- SLK-Science-Grade-8-Q4W2Document24 pagesSLK-Science-Grade-8-Q4W2Ellen QuiseoNo ratings yet
- Modern and Convensional Wound Dressing To Interleukin 1 and Interleukin 6 in Diabetic WoundDocument2 pagesModern and Convensional Wound Dressing To Interleukin 1 and Interleukin 6 in Diabetic WoundGilang yuanggaNo ratings yet
- Photosenthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesPhotosenthesis and Cellular RespirationMonkey D. AilaNo ratings yet
- ბეტა ამილოიდი და ტაუ ცილა ალცჰაიმერის დაავადების პათოგენეზშიDocument1 pageბეტა ამილოიდი და ტაუ ცილა ალცჰაიმერის დაავადების პათოგენეზშიEMD GROUPNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson 1.1Document16 pagesBiology Lesson 1.1Crystal Joy BondadNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Packet Heaven WalkerDocument5 pages9.2 Packet Heaven WalkerHNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-8-QUARTER-4-MODULE-2Document23 pagesSCIENCE-8-QUARTER-4-MODULE-2eljentabzNo ratings yet
- Uploads571457146589cell Growth and Reproduction Key Study Guide PDFDocument12 pagesUploads571457146589cell Growth and Reproduction Key Study Guide PDFDiego GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Aberrations (Reprint of Cytogenetic and Genome Research 2004) by G. Obe (Editor), A. T. Natarajan (Editor)Document397 pagesChromosome Aberrations (Reprint of Cytogenetic and Genome Research 2004) by G. Obe (Editor), A. T. Natarajan (Editor)alokNo ratings yet
- Assertion An Reasion (Final File)Document3 pagesAssertion An Reasion (Final File)s.yagyan prasad acharyNo ratings yet
- GLYCOLYSISDocument6 pagesGLYCOLYSISCatherine AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Biology Set 3Document6 pagesBiology Set 3Chong AiklongNo ratings yet
- Duan, 2021Document26 pagesDuan, 2021farihameetsworldNo ratings yet
- AP FRQsDocument10 pagesAP FRQsanson3225877976No ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration MSDocument52 pagesEnergy and Respiration MSWaheed SherazNo ratings yet
- TPJ 12652Document12 pagesTPJ 12652xprakashNo ratings yet
- Core CH 27 Molecular GeneticsDocument6 pagesCore CH 27 Molecular GeneticsTSZ YAN CHEUNGNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1Document4 pagesBiochemistry 1Beatriz SilvaNo ratings yet
- A World That Stay Normally Hidden From Our Eyes But Matter A Lot To UsDocument11 pagesA World That Stay Normally Hidden From Our Eyes But Matter A Lot To UsVîñàý PãtêlNo ratings yet
- The SH2 Domain and Kinase Activity of JAK2 Target JAK2 To Centrosome and Regulate Cell Growth and Centrosome AmplificationDocument22 pagesThe SH2 Domain and Kinase Activity of JAK2 Target JAK2 To Centrosome and Regulate Cell Growth and Centrosome AmplificationkshariqmNo ratings yet
- Normal and Anomalous Mitosis in CellDocument7 pagesNormal and Anomalous Mitosis in CellIrish Claire Molina TragicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Mutation and CancerDocument43 pagesChapter 14 Mutation and CancerCharlieHuangNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument10 pagesBiochemistryArjayle Airobail LlevadoNo ratings yet
- Biomg 1350 - Fall 2012 Preliminary Exam 3Document3 pagesBiomg 1350 - Fall 2012 Preliminary Exam 3Lauren PriscoNo ratings yet