Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6.3 - 5 Factors That Affect Reaction Rates OH Teacher
Uploaded by
Michelle Ng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views6 pagesOriginal Title
6.3 - 5 Factors that Affect Reaction Rates OH teacher
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views6 pages6.3 - 5 Factors That Affect Reaction Rates OH Teacher
Uploaded by
Michelle NgCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Name: _______________
Date: ________________
SCH4U Factors that Affect Reaction Rates
1. Concentration
2. Surface Area
3. Catalyst
4. Temperature
5. Nature of Reactant
Rate of Reaction = frequency of collisions x fraction of effective collisions.
1. Nature of Reactant
No. of Molecules
Ea(Mg Ea(Cu Energy
) )
Maxwell-Boltzmann Distribution Curve
By changing the reactants, the activation energy is lowered
or raised. Lower activation energy results in a higher
number of molecules that have the right energy for the
reaction. This increases the fraction of effective collisions.
Name: _______________
Date: ________________
Ea(Cu
)
Copper (least reactive)
Ea(Mg
)
magnesium (more
reactive)
By lowering the activation energy, the reaction will go quickly, because
less energy is required to proceed in this reaction.
Example:
Magnesium will react faster with HCl than copper.
Name: _______________
Date: ________________
2. Concentration
Ea
Increasing concentration increases the number of molecules that
collide. This increases the distribution curve vertically, thereby
increasing the area under the curve. This will increase the frequency
of collisions, which increases the reaction rate.
Name: _______________
Date: ________________
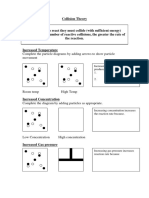
3. Surface Area
Ea
Increasing surface area increases the number of molecules that collide.
This increases the distribution curve vertically, thereby increasing the
area under the curve. This will increase the frequency of collisions,
which increases the reaction rate.
4. Temperature
No. of Molecules
Ea
By increasing temperature the average kinetic energy is
increased. This means the area under the curve beyond the
activation energy increases. More molecules have the
energy to react. This change increases the fraction of
Name: _______________
Date: ________________
effective collisions (area under the curve) and the frequency
of collisions (more energy = more collisions).
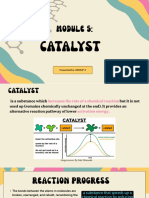
5. Catalyst
No. of
Molecules
Ea(cat) Ea(uncat) Energy
By adding a catalyst, the activation energy is lowered.
Lower activation energy results in a higher number of
molecules that have the right energy for the reaction. This
increases the fraction of effective collisions.
Name: _______________
Date: ________________
By lowering the activation energy, the reaction will go quickly, because
less energy is required to proceed in this reaction.
HW Q 1-8 pg. 296
You might also like
- Sterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 2, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Physics Practice Questions: Vol. 2, High Yield College Physics Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- SCH4U 5 Factors That Affect Reaction Rates HandoutDocument2 pagesSCH4U 5 Factors That Affect Reaction Rates HandoutMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Rate of ReactionDocument9 pagesChapter 9 Rate of ReactionEykNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory Questions WorksheetDocument2 pagesCollision Theory Questions WorksheetRohith GudatiNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument21 pagesKineticsMo_Bash1No ratings yet
- C8 Rates of ReactionDocument25 pagesC8 Rates of Reactionshayaanzaman0No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CHM476 (Part 2)Document15 pagesChapter 2 CHM476 (Part 2)PUTRI DAYANA BATRIESYA ABDUL HANIFNo ratings yet
- Module 4 EdittedDocument22 pagesModule 4 EdittedMARIE ANN DIAMANo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Factors Affecting The RORDocument15 pagesLesson 4 - Factors Affecting The RORAvNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology in Chemistry: Title: Collision Theory (Simulation)Document10 pagesInformation and Communication Technology in Chemistry: Title: Collision Theory (Simulation)z890% (1)
- Answers Rates of ReactionDocument1 pageAnswers Rates of Reactionkaran79No ratings yet
- Reaction Rate 2024Document47 pagesReaction Rate 2024Peter KiwanukaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Handout - Studentcopy - 2023Document12 pagesTopic 6 Handout - Studentcopy - 2023钱俊翰No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Reaction RateDocument8 pagesFactors Affecting The Reaction RateReanne Mae BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Gen - Chem 2 Q3 Module6 7Document16 pagesGen - Chem 2 Q3 Module6 7Kenneth HernandezNo ratings yet
- 6.1.2 Collision Theory: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pages6.1.2 Collision Theory: Learning ObjectivesaurennosNo ratings yet
- Activity SheetDocument3 pagesActivity Sheetjanice alquizar100% (1)
- Rates of ReactionDocument6 pagesRates of ReactionAnuki PereraNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory QuizDocument1 pageCollision Theory QuizMaricel YamatNo ratings yet
- Kinetics RevisionDocument3 pagesKinetics Revisionpline13579No ratings yet
- iGCSE - Chem - Worksheet 20 - RatesDocument3 pagesiGCSE - Chem - Worksheet 20 - Rateskashif mohammedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics Module 2Document16 pagesChemical Thermodynamics Module 2Francis LeovicNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Reaction RatesDocument4 pagesWeek 4 Reaction RatesFil IlaganNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reactions 18 April 2024Document46 pagesRate of Reactions 18 April 2024Amahle KudaNo ratings yet
- CatalystDocument26 pagesCatalystrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Gen. Chemistry 2Document5 pagesGen. Chemistry 2pinedaisleNo ratings yet
- Rates of Reactions Notes and Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesRates of Reactions Notes and Practice QuestionsEustina MumbireNo ratings yet
- Collision TheoryDocument6 pagesCollision TheorySherenaiah GacoteNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Chem NotesDocument2 pagesTopic 6 Chem NotesEmma SingerNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Module N0. 2 - Alvarez Jenita V 3 1 1Document19 pagesPhysical Science - Module N0. 2 - Alvarez Jenita V 3 1 1Mariene SabordoNo ratings yet
- Q4 Module 4 CompressedDocument2 pagesQ4 Module 4 CompressedFELIX ROBERT VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- 2014 Collision Theory PresentationDocument28 pages2014 Collision Theory PresentationLorato MokgethiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-1 Rate of Chemical Reactions - StudentDocument30 pagesChapter 1-1 Rate of Chemical Reactions - StudentDhayan KomanthakkalNo ratings yet
- Q3 PS MODULE5 Wk5Document12 pagesQ3 PS MODULE5 Wk5EVA YUNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistrytesting nameNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.3: Kinetics I: 2.3 (A) Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionDocument4 pagesTopic 2.3: Kinetics I: 2.3 (A) Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionLinaNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Choose The Correct Word To Fill in Each Blank in The Paragraphs Below To ReinforceDocument3 pagesInstructions: Choose The Correct Word To Fill in Each Blank in The Paragraphs Below To ReinforceSupicha BuabanNo ratings yet
- Eche0807 at C1Document6 pagesEche0807 at C1Hema LataNo ratings yet
- Physci Catalyst 101Document34 pagesPhysci Catalyst 101Kyuptonite KimNo ratings yet
- Collision TheoryDocument50 pagesCollision TheoryJulie CabusaoNo ratings yet
- Kinetics 6.1 Assess Q's 1Document9 pagesKinetics 6.1 Assess Q's 1Kenny ZhangNo ratings yet
- Q4 W7 8 Sci10 LawDocument8 pagesQ4 W7 8 Sci10 LawBa BengNo ratings yet
- Cohesive DeviceDocument10 pagesCohesive Devicemoralesmarkfrancis9No ratings yet
- 2ND Term S2 Chemistry... - 2Document44 pages2ND Term S2 Chemistry... - 2Adelowo Daniel100% (2)
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - WEEK 4Document13 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - WEEK 4RODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
- Chapter Test B: Teacher Notes and Answers 17Document7 pagesChapter Test B: Teacher Notes and Answers 17Mmf 123 JanNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document24 pagesModule 4MARIE ANN DIAMANo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry: Topic 6 Chemical KineticsDocument18 pagesIb Chemistry: Topic 6 Chemical KineticsThe Entangled Story Of Our WorldNo ratings yet
- The Rate of Chemical Reaction - NotesDocument6 pagesThe Rate of Chemical Reaction - Notesshawaiz.m.malik2010No ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction 2Document13 pagesRate of Reaction 2MalaysiaBoleh100% (9)
- SPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 1Document37 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 1kslpeter87No ratings yet
- Physical Science - Week 28Document4 pagesPhysical Science - Week 28Mira VeranoNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: I. ObjectivesRemar Jhon PaineNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Chemistry Chapter 6 Rate of Reaction 2Document41 pagesCheat Sheet Chemistry Chapter 6 Rate of Reaction 2yinkaNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory: Complete The Particle Diagrams by Adding Arrows To Show Particle MovementDocument2 pagesCollision Theory: Complete The Particle Diagrams by Adding Arrows To Show Particle MovementRob Gama50% (2)
- Kinetics SL (Answers)Document13 pagesKinetics SL (Answers)ŁØNo ratings yet
- Physical Change: Chemical ReactionsDocument9 pagesPhysical Change: Chemical ReactionsAishi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rates: The Collision TheoryDocument6 pagesRates: The Collision TheorymunzarinNo ratings yet
- 5 5+Collision+Model+StudentDocument4 pages5 5+Collision+Model+StudentJannah ElmaghrabyNo ratings yet
- T2A1 MCQsDocument32 pagesT2A1 MCQsGadgetGlitchKillNo ratings yet
- Definitions: 13.3 Classifying HydrocarbonsDocument12 pagesDefinitions: 13.3 Classifying HydrocarbonsMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Answers - Chapter13Document34 pagesAnswers - Chapter13Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- 11.1 Galvanic CellsOH 2019Document6 pages11.1 Galvanic CellsOH 2019Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- 8.4 and 9.2 Buffers and The Common Ion Effect StudentDocument3 pages8.4 and 9.2 Buffers and The Common Ion Effect StudentMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Solving Equilibrium Problems For Bases (SCH4U)Document3 pages8.3 Solving Equilibrium Problems For Bases (SCH4U)Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Oxidation Numbers OH Teacher 2020Document19 pages10.2 Oxidation Numbers OH Teacher 2020Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Balancing by Half Reaction 2020Document30 pages10.3 Balancing by Half Reaction 2020Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The Elements: Appendix CDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table of The Elements: Appendix CMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 9.2 Solubility Equilibria TeacherDocument4 pages9.2 Solubility Equilibria TeacherMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Appendix B: Supplemental Practice ProblemsDocument7 pagesAppendix B: Supplemental Practice ProblemsMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Le Chatelier Notes StudentDocument6 pages7.4 Le Chatelier Notes StudentMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Appendix DDocument4 pagesAppendix DMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Math and Chemistry: Appendix EDocument6 pagesMath and Chemistry: Appendix EMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: Answers To Numerical Chapter and Unit Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesAppendix A: Answers To Numerical Chapter and Unit Review QuestionsMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 6.2 The Rate Law OH TeacherDocument5 pages6.2 The Rate Law OH TeacherMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Chemical Kinetics Student HODocument4 pages6.1 Chemical Kinetics Student HOMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Notes StudentDocument2 pages7.1 Notes StudentMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.1 OHDocument5 pagesChapter 5.1 OHMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CH 12 Worksheet 1-3 - DocDocument8 pagesMicrosoft Word - CH 12 Worksheet 1-3 - DocMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Polymers Notes 2020Document6 pages2.3 Polymers Notes 2020Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- 4.1chemical Bonding HandoutDocument4 pages4.1chemical Bonding HandoutMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Dble Bonded Func GP Ketones Aldehydes C Acids Oh 2018Document9 pages1.4 Dble Bonded Func GP Ketones Aldehydes C Acids Oh 2018Michelle NgNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry Questions CorrectedDocument2 pagesCalorimetry Questions CorrectedMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Quantum Mechanical ModelDocument4 pages3.2 Quantum Mechanical ModelMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- 4.1chemical Bonding TeacherDocument5 pages4.1chemical Bonding TeacherMichelle NgNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 MIDTERM ExamDocument2 pagesPhysics 1 MIDTERM ExamKent Paul Camara UbayubayNo ratings yet
- Catalogue - Bertin - Complet - NHP - Eng WebDocument40 pagesCatalogue - Bertin - Complet - NHP - Eng WebWELLINGTON VASCONCELOSNo ratings yet
- Engine Oil: Randi Adtia - BDM Pacific Lubritama IndonesiaDocument32 pagesEngine Oil: Randi Adtia - BDM Pacific Lubritama IndonesiarandiNo ratings yet
- Carburetor TypesDocument24 pagesCarburetor TypesHAMZA YOUSAFNo ratings yet
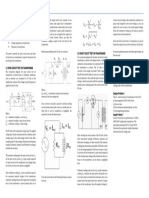
- Transformers - Open Circuit Test and Short Circuit TestDocument1 pageTransformers - Open Circuit Test and Short Circuit TestAdriel BayNo ratings yet
- 0 - IEC62933-2-1 BESS - TestesDocument90 pages0 - IEC62933-2-1 BESS - TestesPethra Brito100% (1)
- LPG Gas Unit Conversion Values - KG, Litres, MJ, KWH & MDocument14 pagesLPG Gas Unit Conversion Values - KG, Litres, MJ, KWH & MAwat JassimNo ratings yet
- Diagrama 5Document1 pageDiagrama 5Joaquin FernandezNo ratings yet
- TORNADO® Rotary Lobe PumpsDocument20 pagesTORNADO® Rotary Lobe PumpsbvmilNo ratings yet
- AvatarON E8331M DG G3 2Document2 pagesAvatarON E8331M DG G3 2barryNo ratings yet
- 2V Series: 2/2 Way Solenoid ValveDocument2 pages2V Series: 2/2 Way Solenoid Valveremus popescuNo ratings yet
- Exercicis GEODocument17 pagesExercicis GEOJoan PerelloNo ratings yet
- LPG GAS Bank Calculation SampleDocument1 pageLPG GAS Bank Calculation SampleVasanth Kumar VNo ratings yet
- General Vendor ListDocument11 pagesGeneral Vendor ListMohamed RefaatNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter Exam in EnglishDocument4 pages4TH Quarter Exam in EnglishJean HugoNo ratings yet
- Zilmet Heat Exchanger Lit Piece 1Document9 pagesZilmet Heat Exchanger Lit Piece 1Andone GigiNo ratings yet
- Natasha Nur Ananda: 1 PendahuluanDocument12 pagesNatasha Nur Ananda: 1 Pendahuluandr.rizkypmNo ratings yet
- 17th ACM - Dist CHT PresnDocument27 pages17th ACM - Dist CHT PresnaminwahiNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int As Level Physics ElectricityDocument17 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int As Level Physics Electricityandhi soesiloNo ratings yet
- S770 Hyd STD V-1603Document2 pagesS770 Hyd STD V-1603Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Scheduled Maintenance and Inspection Program SummaryDocument10 pagesScheduled Maintenance and Inspection Program SummaryVincent LefeuvreNo ratings yet
- EHV Profile Comprehensive (Compatibility Mode)Document60 pagesEHV Profile Comprehensive (Compatibility Mode)Hari HaranNo ratings yet
- Stabilizer Cylinder - Side Shift - Eu - D7430Document2 pagesStabilizer Cylinder - Side Shift - Eu - D7430hastaNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-5Document112 pagesElectricity: Very Short Answer Type Questions-Pg-5Vansh kumar bhushanNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument21 pagesPhysics ProjectKanmani SathiachandranNo ratings yet
- Mech Valvetronic-Engine-Technology ppt-1Document16 pagesMech Valvetronic-Engine-Technology ppt-1Anil Göwđa100% (1)
- LT36147 Diesel Pro Installation InstructionsDocument15 pagesLT36147 Diesel Pro Installation InstructionsSaidul AminoNo ratings yet
- PWM Controller For ZVS Half Bridge: EaturesDocument41 pagesPWM Controller For ZVS Half Bridge: Eaturesalex castroNo ratings yet
- 1 Principles of Heat TransferDocument8 pages1 Principles of Heat TransferArchana A SNo ratings yet
- Market Monitor Eu Jan To Mar23 Jun23Document7 pagesMarket Monitor Eu Jan To Mar23 Jun23The International Council on Clean TransportationNo ratings yet