Professional Documents
Culture Documents
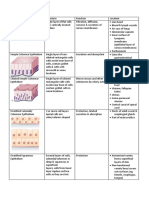
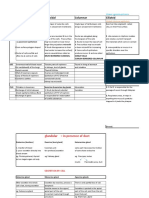
Number of Layers or Category Shape of Cells
Uploaded by
Gwen Llanes Ambrona0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Table of Tissues
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesNumber of Layers or Category Shape of Cells
Uploaded by
Gwen Llanes AmbronaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Number of Layers or Category Shape of Cells
Simple (Single layer of cells) Squamous
Cuboidal
Columnar
Stratified (More than one layer of cells) Squamous
o Nonkeratinized (moist)
o Keratinized
Cuboidal (very rare)
Columnar (very rare)
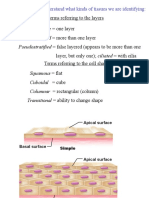
Pseudostratified (Modification of simple epithelium) Columnar
Transitional (Modification of stratified epithelium) Roughly cuboidal to columnar when not stretched and squamous-like when stretched
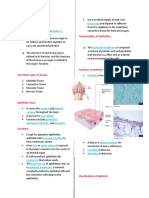
Structure Function Location
Simple Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium Single layer of flat, often Diffusion Lining of blood vessels
hexagonal cells; the nuclei Filtration and the heart
appear as bumps when viewed Some secretion Lymphatic vessels
in cross section because the Some protection against Alveoli of the lungs
cells are so flat friction Portions of the kidney
tubules
Lining of serous
membranes of body
cavities (Pleural,
Pericardial, Peritoneal)
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Single layer of cube-shaped Secretion and absorption Kidney tubules
cells; some cells have microvilli by cells of the kidney Glands and their ducts
(kidney tubules) or cilia (terminal tubules Choroid plexuses of the
bronchioles of the lungs) Secretion by cells of brain
glands and choroid Lining of terminal
plexuses bronchioles of the lungs
Movement of particles Surfaces of the ovaries
embedded in mucus out
of the terminal
bronchioles by ciliated
cells
Simple Columnar Epithelium Single layer of tall, narrow cells; Movement of particles Glands and some ducts
some cells have cilia out of the bronchioles of Bronchioles of the lungs
(bronchioles of the lungs; the lungs by ciliated cells Auditory tubes
auditory tubes; uterine tubes, Partially responsible for Uterus
and uterus) or microvilli the movement of oocytes
(intestines) through the uterine tubes Uterine tubes
by ciliated cells Stomach
Secretion by cells of the Intestines
glands, the stomach, and Gall bladder
the intestines Bile ducts
Absorption by cells of the Ventricles of the brain
intestines
Pseudostratified Columnar Single layer of cells; some cells Synthesize and secrete Lining of nasal cavity
Epithelium are tall and thin and reach the mucus onto the free Nasal sinuses
free surface, and others do not; surface and move mucus Auditory tubes
the nuclei of these cells are at (or fluid) that contains Pharynx
different levels and appear foreign particles over the Trachea
stratified; the cells are almost surface of the free Bronchi of the lungs
always ciliated and are surface and from
associated with goblet cells that passages
secret mucus onto the free
surface
Stratified Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Several layers of cells that are Protects against abrasion Keratinized – outer layer
cuboidal in the basal layer and Forms a barrier against of the skin
progressively flattened toward infection Nonkeratinized – mouth,
the surface; the epithelium can Reduces loss of water throat, larynx,
be nonkeratinized (moist) or from the body esophagus, anus, vagina,
keratinized; in nonkeratinized inferior urethra, and
stratified squamous epithelium, corneas
the surface cells retain a nucleus
and cytoplasm; in keratinized
stratified epithelium, the
cytoplasm of cells at the surface
is replaced by a protein called
keratin, and the cells are dead
You might also like
- Chapter 4 TissueDocument7 pagesChapter 4 TissueVince De PanoNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity4 Tissues PDFDocument6 pagesLec Activity4 Tissues PDFYda Maxine PalmaNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 TissuesDocument15 pagesWEEK 4 TissuesMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Type of Epithelium CellDocument3 pagesType of Epithelium CellHo Shi XianNo ratings yet
- Part2 Histology Mock ExamDocument16 pagesPart2 Histology Mock ExamAyana Bustamante GabionNo ratings yet
- Human Tissues Structure, Function and LococationDocument4 pagesHuman Tissues Structure, Function and Lococationxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Type of Epithelium Illustration Characteristics Location FunctionDocument7 pagesType of Epithelium Illustration Characteristics Location FunctionRjosheNo ratings yet
- Epithelia N Connective FunctionsDocument2 pagesEpithelia N Connective Functionsmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Terms Referring To The LayersDocument21 pagesTerms Referring To The Layerskyle swayNo ratings yet
- Bio2 - 4.02 - Animal Growth & Development - Tissues and Nutritional AssessmentDocument57 pagesBio2 - 4.02 - Animal Growth & Development - Tissues and Nutritional AssessmentMARKIEL JUSTINE DOMOSMOGNo ratings yet
- Lecture EpithelialTissuesDocument21 pagesLecture EpithelialTissuesJeddhie MoraNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue7Document33 pagesEpithelial Tissue7api-242868690No ratings yet
- Apr 1Document9 pagesApr 1KEISHA CZARELLE POBRENo ratings yet
- Terms Referring To The LayersDocument23 pagesTerms Referring To The LayersPraneetha NouduriNo ratings yet
- Histology Table ReviewerDocument4 pagesHistology Table ReviewerDaNicaRaylaNo ratings yet
- Histology of EpitheliumDocument24 pagesHistology of EpitheliumAshfaq Abdali AhmadNo ratings yet
- Title: Tissues: Simple Squamous EpitheliumDocument12 pagesTitle: Tissues: Simple Squamous EpitheliumManelli Faten Buenaventura100% (1)
- 4 - TissuesDocument103 pages4 - TissuesAngel Alexis BiasonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesLesson 2 TissuesRodefe AmitNo ratings yet
- Ex 6a Epithelial TissuesDocument21 pagesEx 6a Epithelial Tissuesسجود صافيNo ratings yet
- هيستوDocument5 pagesهيستوAli HigazyNo ratings yet
- ZOOLEC (Tissues Table)Document6 pagesZOOLEC (Tissues Table)JOHN ANDREW EVIANo ratings yet
- Os 201 Histo Lab CellsDocument33 pagesOs 201 Histo Lab CellsJoyce TLeeNo ratings yet
- GUMAPAC. Lab Act 4 Epithelial TissuesDocument5 pagesGUMAPAC. Lab Act 4 Epithelial TissuesClifford CastaritasNo ratings yet
- Simple EpitheliumDocument64 pagesSimple EpitheliumRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument86 pagesEpithelial TissuesElena ArvanitiNo ratings yet
- 07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterDocument12 pages07 Structural Organism in Animal Ncert MasterexercisestartNo ratings yet
- Slides 06 CellularStructure CellBiologyDocument14 pagesSlides 06 CellularStructure CellBiologyCamila HerreraNo ratings yet
- Henle Loop Fenestrated CapillaryDocument27 pagesHenle Loop Fenestrated CapillarymcwnotesNo ratings yet
- 3 Tissues in The Human Body 22864Document11 pages3 Tissues in The Human Body 22864Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-REVIEWER-Practical ExamDeity Ann ReuterezNo ratings yet
- Epithelial, Conective and Adipose LECTURE2Document84 pagesEpithelial, Conective and Adipose LECTURE2rideroftorchNo ratings yet
- Epithelium Tissue Q&ADocument5 pagesEpithelium Tissue Q&ANo NameNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 2: CellsDocument67 pagesAP Biology Unit 2: Cellsapi-292966101No ratings yet
- Histology AssignmentDocument6 pagesHistology AssignmentBryan LebasnonNo ratings yet
- General Zoology-Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesGeneral Zoology-Midterm ReviewerELIZA NICOLE ATANo ratings yet
- Anatomy All in One?Document244 pagesAnatomy All in One?hp9zgxv7tgNo ratings yet
- Epithelium HÖ 2022-23Document65 pagesEpithelium HÖ 2022-23fiston ishimweNo ratings yet
- The Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan KianiDocument74 pagesThe Epithelium: By: Maj Rizwan Kianiviya7No ratings yet
- Histology - Epithelial TissuesDocument4 pagesHistology - Epithelial TissuesKrissa OmandamNo ratings yet
- General Histology FinalDocument60 pagesGeneral Histology FinalDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Animal Cells and TissueDocument13 pages2.3 Animal Cells and TissueDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- Histo 1 PDFDocument14 pagesHisto 1 PDFSamantha Cruz BlancoNo ratings yet
- 1.epithelium, Connective Tissues, Cell JunctionsDocument21 pages1.epithelium, Connective Tissues, Cell JunctionsbrihaspathiacademyNo ratings yet
- Squamous Cuboidal Columnar CiliatedDocument5 pagesSquamous Cuboidal Columnar CiliatedVaishalee 17No ratings yet
- Lecture 19 Urinary Sys BIOL3571 F2023Document55 pagesLecture 19 Urinary Sys BIOL3571 F2023thesoccerprince.10No ratings yet
- 96 (1) Tissue and OrgansDocument81 pages96 (1) Tissue and OrgansbillNo ratings yet
- Bio 1Document13 pagesBio 1Jorellie PetalverNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument72 pagesThe Cellbir.email013No ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument32 pagesAnaphy Reviewerpatientsafety100% (1)
- Epithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumDocument3 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Location of EpitheliumVanyVillegasNo ratings yet
- JI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 9-10Document2 pagesJI UNIT 2 Complete Notes - 9-10Shubham PawadeNo ratings yet
- LP1 - Cells - TissuesDocument36 pagesLP1 - Cells - Tissuesstephcruz0726No ratings yet
- Embryo HistologyDocument14 pagesEmbryo HistologyshmirtbNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes 2Document13 pagesHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 A. Prokaryotic Cells Low-Power Lens Is Being UsedDocument4 pagesExperiment 5 A. Prokaryotic Cells Low-Power Lens Is Being UsedJing WenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESDocument13 pagesChapter 4 ANAPHY NOTESShannelle SinciocoNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY 1 2022 Materials Part 3Document29 pagesHISTOLOGY 1 2022 Materials Part 3Mutahir AliNo ratings yet
- Task #2 - Image AnalysisDocument2 pagesTask #2 - Image AnalysisGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Task #4 - Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageTask #4 - Interview QuestionsGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Activity 1Document1 pageLesson 1 Activity 1Gwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Task #1 - Communication ModelDocument1 pageTask #1 - Communication ModelGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Task #3 - Process QuestionsDocument1 pageTask #3 - Process QuestionsGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Readings in Visual ArtsDocument2 pagesReadings in Visual ArtsGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Task #4Document1 pageTask #4Gwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Activity 1Document2 pagesLesson 2 Activity 1Gwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Task #1Document1 pageTask #1Gwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Common Characteristics of Most Types of Epithelial Tissue AreDocument2 pagesCommon Characteristics of Most Types of Epithelial Tissue AreGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Task #2Document1 pageTask #2Gwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Global Glocal TeacherDocument1 pageGlobal Glocal TeacherGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Reflection (Freedom Writers Movie)Document1 pageReflection (Freedom Writers Movie)Gwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- M1 The Human OrganismDocument4 pagesM1 The Human OrganismGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Liability or Equity Instrument of Another Entity" by The International Accounting StandardsDocument1 pageLiability or Equity Instrument of Another Entity" by The International Accounting StandardsGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Consumerism and HappinessDocument1 pageConsumerism and HappinessGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Asf 1101Document2 pagesAsf 1101Gwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Body Image Read and ReflectDocument1 pageBody Image Read and ReflectGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Ignatian DiscernmentDocument1 pageIgnatian DiscernmentGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- FORUMDocument1 pageFORUMGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet
- Dear GodDocument1 pageDear GodGwen Llanes AmbronaNo ratings yet