Professional Documents
Culture Documents
For Genetic
Uploaded by
SUAREZ DIOSCOROOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
For Genetic
Uploaded by
SUAREZ DIOSCOROCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetics - study of how genes control development
Gene - basic physical & functional unit of heredity
- made up of DNA
- act as instructions to make proteins
Proteins - Large organic molecules, Always contain nitrogen
- Essential to the structure and function of living things
- Made up of smaller units called ‘amino acids’.
Enzymes - are one of the most important groups of proteins
- They speed up and control all chemical reactions within the body
Types of enzymes - Intracellular enzymes: occur inside cells, where they speed up and
control metabolic reactions
- Extracellular enzymes: produced by cells, but catalyze reactions
outside the cell (e.g. digestion)
Difference DNA & RNA - RNA contains the sugar ribose, while DNA contains the slightly
different sugar deoxyribose (a type of ribose that lacks one oxygen
atom)
Chemical composition - Double heleix (Back bone), has Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine and
Adenine and structure of DNA
Chemical composition - Single heleix (back bone), has Guanine, Cytosine, Uracil and Adenine
and structure of RNA
DNA - known as the chemical basis of heredity
RNA main function - The central dogma of molecular biology suggests that the primary
role of RNA is to converts the information stored in DNA into
proteins.
WHY DO CELL DIVIDE? - Repair of damaged tissue, Growth of an organism, Replace old and
dying cells.
Cell death - >50 billion cells die in our body /day (called programmed cell)
APOPTOSIS - A type of cell death in which a series of molecular steps in a cell lead
to its death.
NECROSIS - unprogrammed form of cell death
CELL DIVISION - MITOSIS, MEIOSIS & BINARY FISSION
Mitosis - The process cells use to make exact replicas of themselves
- observed in almost all the body’s cells, including eyes, skin, hair, and
muscle cells.
Meiosis - In this type of cell division, sperm or egg cells are produced instead of
identical daughter cells as in mitosis
Binary Fission - Single-celled organisms like bacteria replicate themselves for
reproduction
Types of Binary Fission - Irregular, Longitudinal, Transverse & Oblique
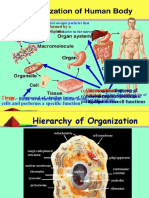
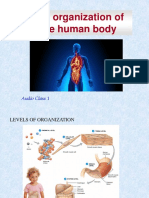
cell - the smallest unit that can live on its own and that makes up all living
organisms and the tissues of the body
Chromatids - In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-
like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of
DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that
support its structure
Chromosome - A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic
material of an organism. Most eukaryotic chromosomes include
packaging proteins called histones which, aided by chaperone
proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its
integrity
Why is proper protein production so important?
Protein has many roles in your body. It helps repair and build your body's tissues, allows metabolic
reactions to take place and coordinates bodily functions. In addition to providing your body with a
structural framework, proteins also maintain proper pH and fluid balance.
You might also like
- The Biology of HomosexualityDocument201 pagesThe Biology of HomosexualityIsis Bugia100% (1)
- LECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesDocument11 pagesLECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesGGonzales KarlaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesTristan Arambulo100% (1)
- Cell PhysiologyDocument52 pagesCell Physiologyhafsah sidi abdullahi100% (4)
- Biology NotesDocument20 pagesBiology NotesDannesa ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 - Chapter 2Document20 pagesScience Form 1 - Chapter 2Beevy GB85% (39)
- End of Quiz: GE 107 - Science, Technology, and Society - A11 Final Examination (Ge 107)Document5 pagesEnd of Quiz: GE 107 - Science, Technology, and Society - A11 Final Examination (Ge 107)christian Jay HorseradaNo ratings yet
- M3 Science (Summer Notes) : Unit 1: Biology (Tissues, Organs, and Systems)Document27 pagesM3 Science (Summer Notes) : Unit 1: Biology (Tissues, Organs, and Systems)Muskan HomeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Cell: Parts FunctionsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Animal Cell: Parts FunctionsconfuseciousNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Cellular Organisation of The Body: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDocument79 pagesChemical and Cellular Organisation of The Body: Dr. Garry NiedermayerWeng Sze TingNo ratings yet
- Operational Health Physics Training (Moe)Document32 pagesOperational Health Physics Training (Moe)senorafiore9517No ratings yet
- Structural Organization in Animals - Cell Organelle, Tissues, Organ System ADocument7 pagesStructural Organization in Animals - Cell Organelle, Tissues, Organ System AMohammad Ali Sikder RamimNo ratings yet
- Atom Molecule - Formed by A Group of AtomsDocument46 pagesAtom Molecule - Formed by A Group of AtomsrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- Lect10F1 Cell Nucleus 2011Document9 pagesLect10F1 Cell Nucleus 2011phicho5781No ratings yet
- Cell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceDocument48 pagesCell Energy: Earth and Life ScienceCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Types of CellsDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - Types of CellsSage Of WholesomenessNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument75 pagesReviewerKurt SecretarioNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument3 pagesBody SystemsA R F I J U LNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Cell Organelles and FunctionDocument43 pagesWeek 4 - Cell Organelles and FunctionDesiree Pescasio DimasuayNo ratings yet
- The Organization of The Human BodyDocument83 pagesThe Organization of The Human BodyEstherLarrosaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer: Animal CellDocument1 pageReviewer: Animal CellJosua GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biology Checkpoint Topics Part 1Document36 pagesBiology Checkpoint Topics Part 1esteban ferrada silvaNo ratings yet
- We Are CellsDocument2 pagesWe Are CellsYoufre YTNo ratings yet
- Dr. Alvi Milliana Risma Aprinda K. UIN Maliki MalangDocument90 pagesDr. Alvi Milliana Risma Aprinda K. UIN Maliki MalangFaridNo ratings yet
- Zoo101 (Lec) Assignment - Cell Growth and ReproductionDocument11 pagesZoo101 (Lec) Assignment - Cell Growth and ReproductionJanaCasandra ManitiNo ratings yet
- Organelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)Document6 pagesOrganelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Rev1Document6 pagesAnaphy Rev1antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerAnn Fenelope AniscoNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Exam - General BiologyDocument12 pages1st Summative Exam - General BiologyAgatha AquinoNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument13 pagesAnaphyCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnaphy ReviewerRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Cell BiologyDocument43 pagesChapter 1-Cell Biologyapi-374357No ratings yet
- Cells Can Be Classified Into 2Document5 pagesCells Can Be Classified Into 2Angela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologybobadillamarie156No ratings yet
- Cell Structure.Document9 pagesCell Structure.Feranmi AkinboboyeNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization in Animal ComplexibilityDocument93 pagesLevels of Organization in Animal ComplexibilityRion BaiganNo ratings yet
- All About Animal Cells: Presentation byDocument32 pagesAll About Animal Cells: Presentation byMarifer Dapat100% (1)
- AnatomyDocument6 pagesAnatomygreatkill07No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document8 pagesUnit 1Azeem FaizalNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues, and OrgansDocument11 pagesCells, Tissues, and OrgansHugo LauNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Proteins Are TH-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageSCIENCE Proteins Are TH-WPS OfficeNicole Jade MallorcaNo ratings yet
- Biology PDFDocument66 pagesBiology PDFPrathyusha KunaparajuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cells and Their FunctionsDocument18 pagesUnit 2 Cells and Their FunctionsAndreaNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- Biochem The Celleluar Basis of LifeDocument21 pagesBiochem The Celleluar Basis of Lifealmira garciaNo ratings yet
- La CélulaDocument4 pagesLa CélulaMarianela Quesada EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & OrganizationDocument7 pagesCell Structure & OrganizationMaryam ShahidNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AnatomyDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Anatomydesbest100% (1)
- Human Anatomy Major Organs of The BodyDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy Major Organs of The BodyKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument77 pagesLevels of OrganizationHyu Dum FakNo ratings yet
- Physio Compiled NotesDocument9 pagesPhysio Compiled Notesthtu.sint.swuNo ratings yet
- Biology Capsule PDFDocument15 pagesBiology Capsule PDFShubhneetNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Human Body and NutritionDocument8 pagesOrganisation of Human Body and NutritionAngela Gutierrez GomezNo ratings yet
- CG - Y9 - 02-03 Levels of Organisation & Cell StructureDocument39 pagesCG - Y9 - 02-03 Levels of Organisation & Cell StructureCharlotte BurkeNo ratings yet
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDocument37 pagesZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisation in AnimalsDocument30 pagesCell Organisation in Animalsputeri 93100% (2)
- Chapter 1 GED BioDocument52 pagesChapter 1 GED BioKhant ZawNo ratings yet
- 2.3 BiologyDocument12 pages2.3 BiologykaryanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument13 pagesCell Structure and FunctionNatalie KwokNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 March 2009Document36 pagesLecture 1 March 2009api-19824406No ratings yet
- Bioinformatics - Derived Databases: How Do We Carry Out 1 and 2 ?Document25 pagesBioinformatics - Derived Databases: How Do We Carry Out 1 and 2 ?Kiki IsabelNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle, Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Cycle, Mitosis Worksheetrosellevalerio2014No ratings yet
- Happ Week 2 TransesDocument7 pagesHapp Week 2 TransesJohn TacordaNo ratings yet
- 6 DCB 7 CD 5Document89 pages6 DCB 7 CD 5rechinNo ratings yet
- Acquisition of New Genes - FinalDocument23 pagesAcquisition of New Genes - FinalAbhi Sachdev100% (2)
- Jurnal 1 - PreBreeding - S.K. Jain and OmprakashDocument10 pagesJurnal 1 - PreBreeding - S.K. Jain and OmprakashZAKIAH SYAHIDAHNo ratings yet
- 2010 SPN BL Rez MALDI TOFDocument12 pages2010 SPN BL Rez MALDI TOFSergey SidorenkoNo ratings yet
- Book PDFDocument569 pagesBook PDFprabhudevmvNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis Hand-OutDocument4 pagesPedigree Analysis Hand-OutCatNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document25 pagesPresentation 1Saurav Suman100% (1)
- TB cellsignalfrq 65696c9ef1baf2.65696ca0f11c56.93457589 加水印Document11 pagesTB cellsignalfrq 65696c9ef1baf2.65696ca0f11c56.93457589 加水印y77811766No ratings yet
- Cell Biology1Document4 pagesCell Biology1Ashlee TalentoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 24: Genetic EngineeringDocument15 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 24: Genetic Engineeringmaria matsuokaNo ratings yet
- Reactivation of The Cell Cycle in Terminally Differentiated CellsDocument111 pagesReactivation of The Cell Cycle in Terminally Differentiated CellsSouravChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Principles of Drug DiscoveryDocument11 pagesPrinciples of Drug Discovery23103086No ratings yet
- Murine Germinal Center B Cells Require Functional Fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3 Signaling For Igg1 Class-Switch RecombinationDocument10 pagesMurine Germinal Center B Cells Require Functional Fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3 Signaling For Igg1 Class-Switch RecombinationAycaNo ratings yet
- 02 WholeDocument205 pages02 WholeGhecrea GrigoreNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- Forensic OdontologyDocument40 pagesForensic OdontologyUma DatarNo ratings yet
- Punjab - Expansion and StrengtheningDocument32 pagesPunjab - Expansion and StrengtheningdrAbdulGhaffarNo ratings yet
- PG Syllabus 2019Document1,065 pagesPG Syllabus 2019afreen.hussain0910No ratings yet
- G10Q3 BiodiversitylasDocument4 pagesG10Q3 BiodiversitylasMichael TuyayNo ratings yet
- 1-3 San Joaquin Reflection PaperDocument3 pages1-3 San Joaquin Reflection PaperJeremy RefugiaNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesMendelian Genetics Worksheet PDFgil100% (1)
- Bacterial Associations With LegumesDocument27 pagesBacterial Associations With LegumesJorgeAngeliniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT by FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Document14 pagesChapter 24 Biology 2nd Year - Prof. Ijaz Ahmed Khan Abbasi (Lecturer Biology PGC) Notes - MDCAT by FUTURE DOCTORS - Touseef Ahmad Khan - 03499815886Tauqeer Ahmad100% (1)
- 3.THPT CHV 2023bclDocument5 pages3.THPT CHV 2023bcl04 Nguyễn Ngọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Goodwin and Guzes Psychiatric Diagnosis 7Th Edition Carol S North Full ChapterDocument51 pagesGoodwin and Guzes Psychiatric Diagnosis 7Th Edition Carol S North Full Chapterdennis.gaver763100% (9)