Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1
Uploaded by
api-649746233Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1
Uploaded by
api-649746233Copyright:
Available Formats
GO TOs
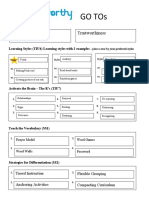
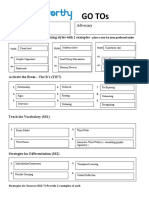
Core Values (TIU3)
Acceptance Trustworthiness
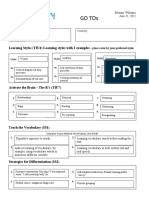
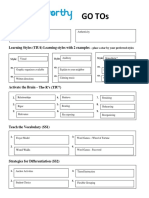
Learning Styles (TIU4) Learning styles with 2 examples – place a star by your preferred styles
Style Visual Style Auditory Style Kinesthetic
Create easily memorable
: ex. : ex. mnemonic devices : ex. Hands on projects
Well organized and brightly
color coated powerpoints
ex. ex. Call and answer response. I say ex.
something and have the class Learning stations
Handout packets or physical repeat it
Activate the Brain – The R’s (TIU7)
1. RELATIONSHIPS 4. retrieve 7. retaining
2. 5. 8.
rigor routing rehearsing
3. 6. 9.
relevance Re-exposing reorganizing
Teach the Vocabulary (SS1)
1. Frayer Models 3. Word games
2. 4.
Word Walls Wheel of Fortune
Strategies for Differentiation (SS2)
Strategies for Success (SS2-7) Provide 2 examples of each
1. Tiered instruction 3. Flexible grouping
2. Anchoring Activities 4. Compacting curriculum
Strategies for Success (SS2-7) – Provide 2 examples of each
Example 1 Example 2
Think-Pair-Share: Teacher poses a question. Four Corners: Students move to their favorite
Cooperative Grouping Students think about the answer then pair up corner, teacher poses a question, and the students
with a neighbor and share with the class then talk about it with each other before sharing
with the class
Graphic Organizers
Anchor Charts Fishbone Graphic Organizer
Advanced Organizers
Analogy Venn diagram
Similarities / Differences
T-Chart Venn Diagrams
Summarizing &
Notetaking 3-2-1 summary: 3 big ideas, 2 examples, 1 Note graphic sheet. Everyone’s notes look
conclusion the same and just fill in.
Cues & Questions “Remember this name; it may be important” “what do you already know about ____?”
Blooms Verbs (SS8 and SS9)
Create Assess, Defend, rate, predict, recommend. “Assess what you already know about this topic.” “Defend
your opinion on ____.” “Rate the books from least favorite to favorite.” “Predict what will happen in the
APPS: next part.” “if you were in the story what would you recommend to one of the characters?”
Evaluate Design, hypothesize, develop, collect, plan. “Design your own.” “Hypothesize what you think will
happen.” “Develop a story about…” “Collect data on…” “make sure you remain quiet while you plan
what you are going to write.”
APPS:
Analyze Compare, Contrast, relate, write, separate. “Compare and contrast the two stories.” “Try to
relate a conflict in your life with the conflict in the story.” “Write down 5 words to help you
memorize this new concept.” “Separate the numbers into categories.”
APPS:
Demonstrate, choose, practice, sketch, solve. “Demonstrate how to properly wash your
Apply hands.” “Choose the best word that goes in the blank.” “Practice walking quietly and single
file.” “Sketch a picture of a clock.” “Solve this math problem and review with your partner.”
APPS:
Understand Explain, summarize, express, review, discuss. “Explain why this happened.” “Summarize
the plot.” “Express how this made you feel.” “Review the vocabulary list.” “Discuss with a
neighbor…”
APPS:
Remember Tell, list, match, memorize, identify. “Tell me what you already know about this.”
“List three things you remember from the story.” “Match the definitions to the word.”
“Memorize these key words.” “Identify the main character in this story.”
APPS:
Four Questions to redirect behavior (CBM5)
1.
Excuse me, what are you doing?
2.
What are you supposed to be doing?
3.
Are you doing it?
4.
What are you going to do to be successful?
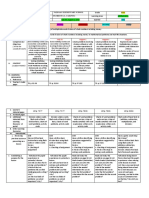
Modifications and Accommodations (E6)
Quantity
Time
Level of Support
Adapt the number of items that the Adapt the time allotted and allowed for learning, Increase the amount of personal assistance to
learner is expected to learn or the number task completion, or testing.
keep the student on task, to reinforce or prompt
of activities students will complete prior to the use of speci c skills. Enhance adult-student
assessment for mastery.
For example:
relationships; use physical space and
environmental structure.
For example:
Individualize a timeline for completing a task;
pace learning di erently (increase or decrease) For example:Assign peer buddies, teaching
Reduce the number of social studies for some learners.
assistants, peer tutors, or cross-age tutors.
terms a learner must learn at any one Specify how to interact with the student or how
time. Add more practice activities or to structure the environment.
worksheets.
Input
Di culty
Output
Adapt the way instruction is delivered to Adapt the skill level, problem type, or the rules on Adapt how the student can respond to
the learner.
how the learner may approach the work.
instruction.
For example:
For example:
For example:
Use di erent visual aids, enlarge text, plan Allow the use of a calculator to gure math Instead of answering questions in writing, allow a
more concrete examples, provide hands- problems, simplify task directions, or change verbal response. Use a communication book for
on activities, place students in rules to accommodate learner needs.
some students, or allow students to show
cooperative groups, pre-teach key knowledge with hands-on materials.
concepts or terms before the lesson.
Participation
Notes:
Adapt the extent to which a learner is
actively involved in the task.
For example:
In geography, have a student hold the
globe, while others point out locations.
Ask the student to lead a group. Have the
student turn the pages while sitting on
your lap (kindergarten).
ffi
ff
fi
ff
fi
Suggestions for working with Students in Poverty (E12)
1. Provide access to computers, magazines, newspapers, and books so low-income students can see 4. Students who live in poverty may not always know the correct behaviors for school
situations. At home, they may function under a different set of social rules. Take time to
and work with printed materials. School may be the only place where they are exposed to print
explain the rationale for rules and procedures in the classroom.
2. Keep your expectations for poor students high. Poverty does not 5. Be careful about the school supplies you expect students to purchase. Keep
mean ignorance. your requirements as simple as you can for all students.
3. 6.
Don’t make comments about your students’ clothes or belongings unless Do not require costly activities. For example, if you require students
they are in violation of the dress code. to pay for a field trip, some of them won’t be able to go.
Reading Strategies to Strengthen Literacy Skills (R8)
Strategy name When / how to use it Define it
1. Before during after. Individually, small
Alphabet Matching Match upper case to lower case, match letter to sound,
groups, whole class
2.
Reader’s Theater During, small groups Promotes fluency through students reading orally their lines
or parts of the story or script.
3. Graphic organizer for students to organize their ideas into a
Paragraph Hamburger Before, during, after. Individually, small groups, whole class. cohesive paragraph.
Making content comprehensible for ELL students (R9)
Write at least 3 strategies / techniques that you could easily implement in your classroom for your content
1. Prepare the lesson
Graphic organizers, Marginal notes, Jigsaw reading
2. Build background
Personal dictionaries, content word wall, word sorts
3. Make verbal communication understandable
Think aloud, model, multimedia like PowerPoints
4. Learning strategies (this one should be easy!)
I wonder wall, question cube, word splash
5. Opportunities for interaction
Groupings, four corners, wait time
6. Practice and application
Hands on practice, manipulative, working w partners
7. Lesson delivery
Objectives stated and posted, students engagement, pacing
8. Review and assess
Paraphrasing, assessment, evaluation
You might also like
- Grammar Practice Simplified: Guided Practice in Basic Skills (Book A, Grades 2-3): Nouns, Verbs, Capital Letters, Periods, Question Marks, and MoreFrom EverandGrammar Practice Simplified: Guided Practice in Basic Skills (Book A, Grades 2-3): Nouns, Verbs, Capital Letters, Periods, Question Marks, and MoreNo ratings yet
- Go ToDocument4 pagesGo Toapi-522314038No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-513026137No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1-1-1-1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1-1-1-1api-619042264No ratings yet
- 1-23-21 Teachworthy Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1 1 1Document4 pages1-23-21 Teachworthy Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1 1 1api-538319698No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-519369060No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-507711757No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1Document6 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1api-581800326No ratings yet
- Go To Page 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page 1 1api-648403099No ratings yet
- Go To Page - 021921tribittDocument4 pagesGo To Page - 021921tribittapi-541257444No ratings yet
- July22 Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesJuly22 Go To Page Word Fillable 11api-519819549No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-535372256No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1api-525369598No ratings yet
- Go To Page 9Document4 pagesGo To Page 9api-506322496No ratings yet
- Go To Page WebDocument4 pagesGo To Page Webapi-519411182No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable HallDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable Hallapi-612496910No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-520915806No ratings yet
- The Go To Page Word Fillable - TWDocument4 pagesThe Go To Page Word Fillable - TWapi-537263106No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word FillableDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillableapi-554659963No ratings yet
- Go To Page - YarrituDocument4 pagesGo To Page - Yarrituapi-521274759No ratings yet
- Current Go ToDocument4 pagesCurrent Go Toapi-627806836No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable ADocument5 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable Aapi-568975076No ratings yet
- Go To Page CampbellDocument4 pagesGo To Page Campbellapi-608432067No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-517957053No ratings yet
- Go To Page - JarrodDocument5 pagesGo To Page - Jarrodapi-558650571No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1api-537777991No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1api-554381190No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1api-616973358No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument5 pagesGo To Pageapi-531987317No ratings yet
- Go To Page 1 1 1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page 1 1 1 1 1api-514926981No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-CompleteDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-Completeapi-621043961No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable Final DraftDocument5 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable Final Draftapi-615036882No ratings yet
- LGW Go To Page Word FillableDocument4 pagesLGW Go To Page Word Fillableapi-713776286No ratings yet
- Go To Page CompletedDocument4 pagesGo To Page Completedapi-516915537No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument5 pagesGo To Pageapi-589972069No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-527233824No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1 1 1api-541675053No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 3Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 3api-549434479No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-622195317No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-558579882No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-557782254No ratings yet
- Lisa Sebock S4s-CombinedDocument5 pagesLisa Sebock S4s-Combinedapi-679144934No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-522117714No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-CompleteDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-Completeapi-601782495No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-616396340No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 - 1api-612529167No ratings yet
- My Go To Page 1Document4 pagesMy Go To Page 1api-582829530No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument5 pagesGo To Pageapi-618128891No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 1 1 2Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 1 1 2api-556271109No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-518962709No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 Janet Scott 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 Janet Scott 1api-518809610No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-587187814No ratings yet
- Go To PageDocument4 pagesGo To Pageapi-522340206No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable 11Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable 11api-515746239No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document5 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-570575701No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1websiteDocument4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1websiteapi-588745842No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-577792181No ratings yet
- GTP ExportDocument4 pagesGTP Exportapi-480969929No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1api-565429351No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1Document4 pagesGo To Page Word Fillable-1 1 1api-554646785No ratings yet
- Biology in The Secondary School From The StudentsDocument9 pagesBiology in The Secondary School From The StudentsBikash GaintaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 6th Grade (Mixed Lesson)Document6 pagesLesson Plan 6th Grade (Mixed Lesson)Vlad VargauNo ratings yet
- Acr-Araling Panlipunan - Marlon C. RufoDocument10 pagesAcr-Araling Panlipunan - Marlon C. RufoMarlon C. RufoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Cittizenship & DiversityDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 Cittizenship & Diversitynickoh28No ratings yet
- Computer Science Personal StatementsDocument1 pageComputer Science Personal Statementsmohammed KhalidNo ratings yet
- Festivals of Aklan, Cebu and Batangas 7Document3 pagesFestivals of Aklan, Cebu and Batangas 7Chichan S. Soreta100% (1)
- Guidelines On The Preparation of PIVOT I D E A Lesson Exemplars RM No. 296 s.2020Document61 pagesGuidelines On The Preparation of PIVOT I D E A Lesson Exemplars RM No. 296 s.2020Jonathan Marc Fule Castillo100% (1)
- WEEK1Document3 pagesWEEK1Riza GusteNo ratings yet
- Advanced Psychology SyllabusDocument7 pagesAdvanced Psychology SyllabusMark GanitanoNo ratings yet
- Dll-q1-Math (July 30-August 3, 2018)Document6 pagesDll-q1-Math (July 30-August 3, 2018)Florecita CabañogNo ratings yet
- (Re - Work) Employee-to-Employee Facilitator Prep GuideDocument2 pages(Re - Work) Employee-to-Employee Facilitator Prep GuidesoniacinhaNo ratings yet
- Activity Plan 2 Name CardsDocument3 pagesActivity Plan 2 Name Cardsapi-491640675No ratings yet
- Gaya Belajar Dan Prestasi Belajar Kimia Siswa Sma: Iceng Hidayat, A. Rachaman Ibrahim Meydian ElytasariDocument7 pagesGaya Belajar Dan Prestasi Belajar Kimia Siswa Sma: Iceng Hidayat, A. Rachaman Ibrahim Meydian ElytasariRefita Ega IINo ratings yet
- Dilation - FormalDocument14 pagesDilation - Formalapi-355095027No ratings yet
- Flexible Teacher in The 21ST CenturyDocument2 pagesFlexible Teacher in The 21ST CenturyJonathan Magalong100% (1)
- Unit I Lesson 1 - Introduction To Understanding Culture Society PoliticsDocument23 pagesUnit I Lesson 1 - Introduction To Understanding Culture Society PoliticsRachel DaliuagNo ratings yet
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan - BadmintonDocument4 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan - BadmintonVianca Mae Agullo100% (1)
- Guide in Making The CreedDocument2 pagesGuide in Making The CreedLaedyn Faye IsipNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 Recognizing and of A WholeDocument7 pagesGrade 1 Recognizing and of A WholeMark LariosaNo ratings yet
- Ran-Ras Presentation FinalDocument19 pagesRan-Ras Presentation Finalapi-231978749100% (1)
- Systematic Approach To Teaching: 1. Establishing Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesSystematic Approach To Teaching: 1. Establishing Learning ObjectivesMar Francis RicoNo ratings yet
- PCE Preparation Action PlanDocument4 pagesPCE Preparation Action PlanAamena MultaniNo ratings yet
- Sales Force Motivation: An IntroductionDocument1 pageSales Force Motivation: An Introductionvinku25No ratings yet
- Curriculum For One Year B.Ed. (Secondary) Programme-National Council For Teacher Education (NCTE)Document33 pagesCurriculum For One Year B.Ed. (Secondary) Programme-National Council For Teacher Education (NCTE)rajendra kumar devarapalliNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 4 q1 w3Document4 pagesDLL Mathematics 4 q1 w3kathleenjane100% (1)
- Grade 2 EAGLEDocument4 pagesGrade 2 EAGLEKimberly Beltran MasiddoNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal: Maligaya National High School Brgy. Maligaya, Palayan City, Nueva EcijaDocument5 pagesProject Proposal: Maligaya National High School Brgy. Maligaya, Palayan City, Nueva EcijaRoland RodriguezNo ratings yet
- FLCT Evaluation 2Document4 pagesFLCT Evaluation 2Palomar AnnabelleNo ratings yet
- Learning Based On Designing Research Into Designing As An Educational Paradigm PDFDocument267 pagesLearning Based On Designing Research Into Designing As An Educational Paradigm PDFJuan Pablo DueñasNo ratings yet
- Careers As ActionDocument22 pagesCareers As ActionFernanda Cavalheiro Ruffino RauberNo ratings yet