Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digestive Systems Anatomy
Uploaded by
MARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views13 pagesOriginal Title
PPT Chapter 2h - Digestive system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views13 pagesDigestive Systems Anatomy
Uploaded by
MARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEACopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
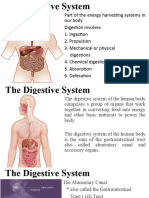
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Consist of musculomembranous tube
extending from the mouth to the anus.
Its function are:
1. Ingestion
2. Grinding
3. Digestion
4. Absorption of nutrients
5. Elimination of solid waste
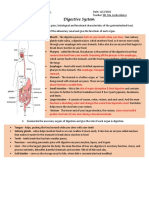
Anatomy and physiology of the
digestive system
1. Mouth 5. Small intestines
2. Pharynx 6. Large intestines
3. Esophagus 7. Rectum
4. Stomach 8. anus
1. Mouth
Responsible
for the initial (mechanical)
breakdown of food
Serves as prehensile (grasping) mechanism
Defensive and offensive weapon
2. Pharynx
Common passage for food and air
3. Esophagous
Musculomembranous tube extending the
pharynx and the stomach
4.Stomach hollow, pear shaped,
muscular digestive organ.
a. Simple stomach – Produces
hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen.
Divided into:
1. Cardia(entrance)
2. Fundus(body)
3. Pylorous(termination)
b. Compound stomach
1. Reticulum(honeycomb) – most anterior and
smallest section of the compound stomach. Receives
heavy matter in food and acts as a liquid reservoir to
soften materials (2gallons)
2. Rumen(paunch) – largest part of the compound
stomach, site of microbial digestion. Also called
fermentation vat. (40gallons)
3. Omasum (Many plies) – filled with muscular
laminae. Laminae is studded with short, blunt
papillae that grind roughage before it enters the
abomasum (5gallons)
4. Abomasum (true stomach) – secretes gastric enzyme
and hydrochloric acid (7gallons)
5.Smallintestines – primary organ for
absorption of nutrients
1.Duodeum – closely attached to the
stomach, contains the pancreas
2.Jejunum – about 90% of the small
intestines
3.Ileum – the last part of the small
intestines
6. Large intestines – it extends from
the termination of ileum to the anus
a. Cecum(Cul-de-sac) – somewhat comma
shaped and lies to the right of the
median plane
b. Colon– differes from the small intestine
in the it is larger, sacculated and has
longitudinal bands and more fixed
position.
7.Rectum – Terminal part of the
intestines. It is the organ of
storage
8.Anus – terminal part of the
alimentary system
Avian Digestive System
1. Beak/bill– adopted for rapid picking of
small particles of feeds
2. Esophagous – most birds have an enlarged
area in the esophagus called crop:
a. Serve as an ingesta holding and moistening
reservoir
b. Allow breakdown reaction of salivary
amylase
c. Fermentation
3. Proventriculus– true stomach of poultry,
produces digestive enzymes
4. Gizzard (ventriculus) – thick muscular walled
area to physically reduce particle size of
ingesta. Contains grit (small stone or hard
particles)
5. Small intestines
6. Cecaand large intestines – Contains 2 blind
pouch called ceca as compared to mammals
cecum. Ceca and large intestines are site of
water resorption.
7. Cloaca,vent,anus – eliminates waste products
Process of Rumination
Re-gargitation
Re-mastication
Re-ensalivation
Re-swallowing
You might also like
- Lea 417 510 2011Document121 pagesLea 417 510 2011Oliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition and FeedingDocument29 pagesAnimal Nutrition and FeedingMaster MenteNo ratings yet
- Genbio2-Lesson 2-Nutrient Procurement and Processing Part 2Document45 pagesGenbio2-Lesson 2-Nutrient Procurement and Processing Part 2yvetteNo ratings yet
- Module 2c Anatomy and Physiology (Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary, and Reproductive Systems)Document63 pagesModule 2c Anatomy and Physiology (Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary, and Reproductive Systems)Erik BaldadoNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Endocrine SystemDocument36 pagesDigestive and Endocrine SystemAldrei Vina Pauleah BorjaNo ratings yet
- Stomach in VertebratesDocument6 pagesStomach in VertebratesTuhinNo ratings yet
- The four types of animal digestive systemsDocument7 pagesThe four types of animal digestive systemsPEARL ALPHA MAE MATURANNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Gastro Intestinal SystemDocument13 pagesStructure and Functions of The Gastro Intestinal SystemhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Anat 25 GItract EDocument10 pagesAnat 25 GItract EAnonymous H0JCjweaQANo ratings yet
- Project Free Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesProject Free Digestive Systemfelina.duran001No ratings yet
- Digestive Systems of Vertebrates and InvertebratesDocument7 pagesDigestive Systems of Vertebrates and InvertebratesClexandrea Dela Luz Corpuz100% (1)
- Heterotrophic nutrition: how organisms obtain foodDocument10 pagesHeterotrophic nutrition: how organisms obtain foodNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Lab Ex 3 CDocument7 pagesLab Ex 3 Cs.manuel.kyrraaliahNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ZooDocument9 pagesDigestive System Zooshisuinara1810No ratings yet
- The Digestive ProcessDocument2 pagesThe Digestive ProcessHopeNo ratings yet
- 1.study of Physiological Functions of Digestive System of Farm AnimalsDocument58 pages1.study of Physiological Functions of Digestive System of Farm AnimalsKashifNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 2021Document29 pagesDigestive System 2021fashion20trendsNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandDocument5 pagesLABORATORY EXERCISE The Gastrointestinal System With Accessory GlandGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Document3 pagesDigestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Kaikiyi Sykay PachecoNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaDocument9 pagesLab Exercise Digestive System Bautista Maria LuisaEricka ElloNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio de La Via Digestiva BajaDocument15 pagesLaboratorio de La Via Digestiva BajaDanna Lopez RamosNo ratings yet
- ch34 DigestiveDocument7 pagesch34 DigestiveAldi RegarNo ratings yet
- Ruminant Digestive System: Ms. ZubiateDocument13 pagesRuminant Digestive System: Ms. ZubiateJuleika S. Sierra100% (1)
- DigestiveDocument5 pagesDigestivealayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Types of Digestive SystemsDocument15 pagesTypes of Digestive SystemsshakiraNo ratings yet
- Monogastric: Single-Chambered StomachDocument4 pagesMonogastric: Single-Chambered StomachFarhan Rezki MNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science W5.1Document3 pagesEarth and Life Science W5.1Kurt AJ ColacionNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Chapter SummaryDocument58 pagesLife Processes Chapter SummaryAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument43 pagesDigestive SystemDaniella100% (2)
- Digestive System Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesDigestive System Lecture NotesIvan FernandezNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Lec 2Document2 pagesNCM 105 Lec 2Rizaga, Carlos BenedictNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument34 pagesDigestive SystemJJ Almagro100% (1)
- Digestive System NewDocument26 pagesDigestive System NewJonathan Farne CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Know The Parts of Digestive System:: B. Type of Digestion That Occurs in Each Part?Document3 pagesKnow The Parts of Digestive System:: B. Type of Digestion That Occurs in Each Part?rswonickNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of The Different Livestock Systems: By: Kristy BairdDocument24 pagesA Comparison of The Different Livestock Systems: By: Kristy BairdReynaldy ChristianNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ReviewerDocument6 pagesDigestive System ReviewerAspyn OvardNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestina L Tract: (Digestive System)Document56 pagesGastrointestina L Tract: (Digestive System)Josephine AcioNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Overview: Parts and FunctionsDocument62 pagesDigestive System Overview: Parts and FunctionsKeturah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Zoology (The Book 1)Document48 pagesZoology (The Book 1)sweetnutellaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesDigestive SystemShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Practical - 3 Identifying The Digestive System of Farm AnimalDocument44 pagesPractical - 3 Identifying The Digestive System of Farm AnimalSharfan AhamedNo ratings yet
- 1-digestive-systemDocument1 page1-digestive-systemRussel GuratNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive SystemChristine Joyce S. CruzNo ratings yet
- The flow of digestionDocument5 pagesThe flow of digestionUsita, Zackary, T.No ratings yet
- Nutrition NotesDocument8 pagesNutrition NotesAbidan Patrick (COOL DUDE PRO)No ratings yet
- The human digestive system in 40 charactersDocument15 pagesThe human digestive system in 40 charactersUzma SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Tugas Biology Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesJawaban Tugas Biology Digestive Systemaulia nurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About the Human Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesEverything You Need to Know About the Human Digestive SystemLegendary NinjaNo ratings yet
- Organs of Alimentary Tract and Accessory Organs. Digestion Begins in The Mouth or Oral Cavity. It Contains 32 Teeth ThatDocument4 pagesOrgans of Alimentary Tract and Accessory Organs. Digestion Begins in The Mouth or Oral Cavity. It Contains 32 Teeth ThatRhea Mae PerezNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive SystemFrancisco D. AndaquigNo ratings yet
- Lab Act DigestiveDocument8 pagesLab Act DigestiveJhia TorreonNo ratings yet
- Zoo 1 PPT 9 Digestive (2015)Document31 pagesZoo 1 PPT 9 Digestive (2015)Zucc mahnutNo ratings yet
- Agri Assignment 2Document9 pagesAgri Assignment 2mahek sachadevNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention for the Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesStrategic Intervention for the Digestive SystemKarla Javier PadinNo ratings yet
- 4thQ Week1 PPT DigestiveDocument49 pages4thQ Week1 PPT DigestiveGeronimo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Digestion & AbsorptionDocument13 pagesDigestion & AbsorptionU Than HanNo ratings yet
- Monogastric Digestive System ExplainedDocument9 pagesMonogastric Digestive System ExplainedAlex AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- #13 Digestive System - OllanasDocument9 pages#13 Digestive System - OllanasKirsten AletheaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and Functions in 40 CharactersDocument7 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and Functions in 40 CharactersKerwin LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2g - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 2g - Respiratory SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2f - Lymphatic SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 2f - Lymphatic SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2j - Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesChapter 2j - Reproductive SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Module 2e - The Cardiovascular SystemDocument13 pagesModule 2e - The Cardiovascular SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2i - Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 2i - Urinary SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Introduction to Animal ScienceDocument13 pagesIntroduction to Animal ScienceMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Module 2d - The Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesModule 2d - The Nervous SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Module 2b - The Skeletal SystemDocument11 pagesModule 2b - The Skeletal SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Module 2a - Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument3 pagesModule 2a - Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- Module 2c - The Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesModule 2c - The Muscular SystemMARC LOUIE F. BARNACHEANo ratings yet
- English 8 Lesson 1 & 2 PDFDocument29 pagesEnglish 8 Lesson 1 & 2 PDFNina Romina Navalta40% (5)
- BUSINESS PLAN FORMATrawDocument18 pagesBUSINESS PLAN FORMATrawChaaaNo ratings yet
- Grade11 Q4 M1 OAP LO2 Processing Concoctions and ExtractsDocument22 pagesGrade11 Q4 M1 OAP LO2 Processing Concoctions and ExtractsRodel Desabille100% (1)
- Coyote and The Buffalo - + + + + + + + + + + + + + - : Peet-Za (Curled-Hairs) - (Document4 pagesCoyote and The Buffalo - + + + + + + + + + + + + + - : Peet-Za (Curled-Hairs) - (Aaniya LalaniNo ratings yet
- GREIDADocument67 pagesGREIDAadrian montenegroNo ratings yet
- Natamax BDocument6 pagesNatamax Bshivani_singh_18No ratings yet
- Bharathi Fssai 5 YearsDocument4 pagesBharathi Fssai 5 Yearspavan kumar T RNo ratings yet
- Workshop Third TermDocument4 pagesWorkshop Third TermMariaVictoriaTorresTamaraNo ratings yet
- For Beginners - Tartine Country RecipeDocument8 pagesFor Beginners - Tartine Country RecipeBrava PizzaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Main IdeaDocument4 pagesAssessment Main IdeaMARIA SANDOVAL FLORESNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs ExercíciosDocument3 pagesModal Verbs ExercíciosSandra Patrícia Miranda da Silva100% (1)
- 2ND Quarter Exam Grade 3 Math Sample OnlyDocument2 pages2ND Quarter Exam Grade 3 Math Sample OnlyKram Jerets100% (3)
- How To Have An Enid Blyton SummerDocument8 pagesHow To Have An Enid Blyton SummerKeith userNo ratings yet
- Grammar Unit 5: Can, Can't, Could, Couldn'tDocument2 pagesGrammar Unit 5: Can, Can't, Could, Couldn'tsofiagg33100% (2)
- Segundo Bgu Scientific Project 2 Week 2Document3 pagesSegundo Bgu Scientific Project 2 Week 2GTA SAN 208No ratings yet
- 03 - Grammarway 3 - Flashcards PDFDocument138 pages03 - Grammarway 3 - Flashcards PDFБюро переводовNo ratings yet
- Proposal Chapter1 3 Moringa Leaves With Cucumber Ice Cream 11 2proposalDocument28 pagesProposal Chapter1 3 Moringa Leaves With Cucumber Ice Cream 11 2proposalRhed Tombaga100% (1)
- Swot Analysis of Amul: "The Taste of India"Document4 pagesSwot Analysis of Amul: "The Taste of India"NehaBajajNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Value PropositionDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Value PropositionBerlynne Mae BouquiaNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses VIIIDocument1 pageFuture Tenses VIIIKaterina PetrovaNo ratings yet
- English Book II: 1. The Dying SunDocument17 pagesEnglish Book II: 1. The Dying SunMuhammad Arslan Muhammad Arslan100% (1)
- Nestle SA Nutrition Health and Wellness StrategyDocument3 pagesNestle SA Nutrition Health and Wellness StrategyantovnaNo ratings yet
- Breanna Honohan Resume UpdatedDocument3 pagesBreanna Honohan Resume Updatedapi-455017712No ratings yet
- English Idioms That Describe RelationshipsDocument24 pagesEnglish Idioms That Describe RelationshipsAmirah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 Nutr484Document11 pagesCase Study 2 Nutr484api-644004752No ratings yet
- Creating Shared Value Sustainability Report 2022 en PDFDocument63 pagesCreating Shared Value Sustainability Report 2022 en PDFDal TaylorNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Major Foodborne Illnesses Caused by Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi and ParasitesDocument37 pagesTopic 2 Major Foodborne Illnesses Caused by Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi and Parasitesedison aguilarNo ratings yet
- Robert Kuok Hock NienDocument11 pagesRobert Kuok Hock NienYan Sham0% (1)
- Lesson Plan On NutritionDocument4 pagesLesson Plan On NutritionJENNY MAY SUDAY100% (1)
- TTM Febrero 2018 PDFDocument32 pagesTTM Febrero 2018 PDFEugenia Martínez DireneNo ratings yet