Professional Documents
Culture Documents
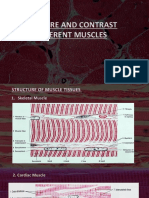
Tabular Difference Between Smooth and Skeletal Muscles
Uploaded by
Nouman Shahzad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesSkeletal muscles are striated, contain sarcomeres, and have fast myosin ATPase activity and calcium ion-induced contraction. Smooth muscles lack striations and sarcomeres, have slow myosin ATPase activity and calcium ion-induced contraction, and exhibit stress relaxation and latch mechanisms. The key differences between skeletal and smooth muscles are their structural organization, speed and regulation of contraction, and degree of voluntary control.
Original Description:
Original Title
Tabular difference between smooth and skeletal muscles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSkeletal muscles are striated, contain sarcomeres, and have fast myosin ATPase activity and calcium ion-induced contraction. Smooth muscles lack striations and sarcomeres, have slow myosin ATPase activity and calcium ion-induced contraction, and exhibit stress relaxation and latch mechanisms. The key differences between skeletal and smooth muscles are their structural organization, speed and regulation of contraction, and degree of voluntary control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesTabular Difference Between Smooth and Skeletal Muscles
Uploaded by
Nouman ShahzadSkeletal muscles are striated, contain sarcomeres, and have fast myosin ATPase activity and calcium ion-induced contraction. Smooth muscles lack striations and sarcomeres, have slow myosin ATPase activity and calcium ion-induced contraction, and exhibit stress relaxation and latch mechanisms. The key differences between skeletal and smooth muscles are their structural organization, speed and regulation of contraction, and degree of voluntary control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
PHYSIOLOGY ASSIGNMENT
SKELETAL MUSCLES SMOOTH MUSCLES
Striation
Cells are striated. Cells are not striated.
Fibers
Fibers larger than those in smooth muscles. Fibers smaller than those in skeletal muscles.
Attachment
Ends of actin filament are attached to Z disc. Ends of actin filament are attached to dense
bodies.
Sarcomere
Sarcomere is present. No sarcomere is present.
Myosin ATPase
Myosin ATPase activity is very fast. Myosin ATPase activity is very slow.
Initiation Of Contraction
The initiation of contraction in response to The initiation of contraction in response to calcium
calcium ions is much faster than in smooth ions is much slower than in skeletal muscles.
muscles.
Regulatory Hormone
Troponin is the regulatory protein that binds Calmodulin is the regulatory protein that binds
calcium. calcium.
Cross Bridge
Cross bridges remain attached to the actin Fraction of time that the cross bridges remain
filament for a short fraction of time. attached is greatly increases.
Gap Junction
No gap junctions are present. Gap junctions are present.
Level Of Control
Skeletal muscles are voluntary. Smooth muscles are involuntary.
Source Of Calcium
Source of calcium is Sarcoplasmic reticulum. Source of calcium is sarcoplasmic reticulum and
ECF.
Membrane Potential
Membrane potential in resting stage is -90 Membrane potential in resting stage is about -50 to
mV. -60mV.
Force Of Muscle Contraction
The force of muscles contraction is 3 to 4 It is greater than that of skeletal muscles as great
Kg /cm2. as 4 to 5 Kg/cm2.
Stress Relaxation Response
They inhibit stress _relaxation response. They exhibit stress_ relaxation response.
Voltage Gated Channels
They have more voltage gated sodium They have far more voltage gated calcium channels
channels and very few voltage gated calcium and very few voltage gated sodium channels.
channels.
Depolarization
Depolarization cannot occur without action Multi-unit smooth muscles can depolarize without
potential. action potential.
Latch Mechanism
There is no latch mechanism for prolong There is latch mechanism for prolong holding of
holding of contraction of skeletal muscles. contraction of smooth muscles.
Energy Consumption
Energy consumed to maintain contraction is The energy consumed to maintain contraction is
300 times greater than the comparable miniscule due to latch mechanism.
smooth muscles.
Neuroeffector Junction
The vesicles of the autonomic nerve fiber Forms so called diffused junctions nerve fibers
ending contains acetylcholine in some fibers innervate the outer layer and varicosities
and norepinephrine in other fibers. distributed along there.
You might also like
- Dr. Niranjan Murthy H L: Asst. Prof., Dept. of Physiology Sree Siddhartha Medical College & Hospital, TumkurDocument17 pagesDr. Niranjan Murthy H L: Asst. Prof., Dept. of Physiology Sree Siddhartha Medical College & Hospital, Tumkurnirilib100% (1)
- Anaphy Midterm ReviewerDocument38 pagesAnaphy Midterm ReviewerJoshua UveroNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument2 pagesCell PhysiologyQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Summary Lab 2: 2+ IntracellularDocument15 pagesLab Manual Summary Lab 2: 2+ IntracellularSmartunblurrNo ratings yet
- Assignment of PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAssignment of PhysiologySalman aliNo ratings yet
- Smooth Muscle Explained FreeDocument22 pagesSmooth Muscle Explained FreeOmphile DansonNo ratings yet
- Muscle 1Document53 pagesMuscle 1mem734094No ratings yet
- Collection of Muscle Physilology QuestionsDocument33 pagesCollection of Muscle Physilology QuestionskamaluNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: B. Pimentel, M.D. University of Makati - College of NursingDocument71 pagesThe Muscular System: B. Pimentel, M.D. University of Makati - College of Nursingapi-19824701No ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle ContractionDocument16 pagesSkeletal Muscle ContractionHasnain AsifNo ratings yet
- 07 Human Physiology The Muscular SystemDocument68 pages07 Human Physiology The Muscular SystemsuNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Lecture 1DDocument7 pagesMuscular System Lecture 1DShane PascualNo ratings yet
- Calcium PumpDocument3 pagesCalcium PumpmcwnotesNo ratings yet
- Smooth MuscleDocument33 pagesSmooth MuscleDorin PathakNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Different Muscles: Human Physiology 20368038 V. Nishanthi BCMBDocument11 pagesCompare and Contrast Different Muscles: Human Physiology 20368038 V. Nishanthi BCMBThamizh Arasi VinayagamNo ratings yet
- Physiology QuestionsDocument51 pagesPhysiology QuestionskamaluNo ratings yet
- 7B Muscles, Movement and The Heart 7B CheckpointDocument8 pages7B Muscles, Movement and The Heart 7B CheckpointsalmaNo ratings yet
- Possible Mechanism For Regulation of The Latch PhenomenonDocument3 pagesPossible Mechanism For Regulation of The Latch PhenomenonKyle OrtegaNo ratings yet
- S1 OtotDocument46 pagesS1 OtotJauhar FirdausNo ratings yet
- Smooth MuscleDocument51 pagesSmooth Musclefilza farheenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document7 pagesChapter 7Kei GauranoNo ratings yet
- 6 Contraction of Skeletal MuscleDocument109 pages6 Contraction of Skeletal MuscleHaslinNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Reporters: Butad, Rhena Christine M. Yabana Maria FeDocument31 pagesMuscular System: Reporters: Butad, Rhena Christine M. Yabana Maria FeRhena Christine Omega MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Locomotion & Movement (Muscles)Document41 pagesLocomotion & Movement (Muscles)DEEPANKAR SAHANo ratings yet
- Collection of Muscle Physilology QuestionssDocument36 pagesCollection of Muscle Physilology QuestionsskamaluNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture On Nerve Physiology by Dr. RoomiDocument12 pages3rd Lecture On Nerve Physiology by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument6 pagesMuscular SystemTricia Mae LlerenaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MusclesDocument7 pagesSkeletal MusclesAhmed OudahNo ratings yet
- Neuro Muscular Junction NNDocument68 pagesNeuro Muscular Junction NNAnak AyamNo ratings yet
- Cellular Physiology of Nerve and Muscle - 2024Document84 pagesCellular Physiology of Nerve and Muscle - 2024Bilgehan BölekNo ratings yet
- 5 - Contraction of Skeletal MusclesDocument27 pages5 - Contraction of Skeletal MusclessadaffardoosNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Skeletal, Smooth and Cardiac MuscleDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Skeletal, Smooth and Cardiac MuscleksbabarNo ratings yet
- General Mechanism of Muscle ContractionDocument22 pagesGeneral Mechanism of Muscle ContractionAnuya Kulkarni-DeoNo ratings yet
- G. Muscle Physiology - 1Document45 pagesG. Muscle Physiology - 1Milimo MweembaNo ratings yet
- Action Potential in Smooth MuscleDocument22 pagesAction Potential in Smooth Muscleaswad mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Physiology NotesDocument26 pagesPhysiology NotesThao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Anaphy)Document8 pagesChapter 6 (Anaphy)Gerald SouribioNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular JunctionDocument10 pagesNeuromuscular JunctionAfeefuddin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 6.muscular TissueDocument40 pages6.muscular Tissuemero wowNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physiology NotesDocument20 pagesMuscle Physiology NotesPisiform90100% (1)
- Investigation of Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle ContractionDocument14 pagesInvestigation of Mechanisms of Skeletal Muscle Contractiongeddy D.No ratings yet
- Fizobioqimia FinalDocument12 pagesFizobioqimia FinalTamar PertiaNo ratings yet
- Muscles 1Document25 pagesMuscles 1sairash.khan23No ratings yet
- 4.2 Muscle PhysiologyDocument72 pages4.2 Muscle PhysiologySurvin KandhariNo ratings yet
- Muscle DentalDocument74 pagesMuscle Dentalapi-3710331No ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument49 pagesMuscle PhysiologyNauval Zilal FananyNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Mechanism of Muscle ContractionDocument38 pages10.2 Mechanism of Muscle ContractionDaksha yashaNo ratings yet
- Muscularsyst EM: Actin and Myosin MyofilamentsDocument16 pagesMuscularsyst EM: Actin and Myosin MyofilamentsCatherine Joy delos SantosNo ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesThe Muscular SystemKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- Muscul Arsystem: Skeletal MuscleDocument5 pagesMuscul Arsystem: Skeletal MuscleGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Review - Animal Motor SystemsDocument4 pagesReview - Animal Motor SystemskjhNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument7 pagesPhysiologyLe Maurice CiminiNo ratings yet
- Skeletal MuscleDocument72 pagesSkeletal Musclekiedd_0467% (3)
- Bio 215 Topic 5 MusclesDocument88 pagesBio 215 Topic 5 MusclesYara BeainiNo ratings yet
- Smooth Muscle ContractionDocument9 pagesSmooth Muscle Contractionchelmarkromagos64No ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- The Sodium Theory Revisited: Or 45 Years of a Full Time Cnrs NeurophysiologistFrom EverandThe Sodium Theory Revisited: Or 45 Years of a Full Time Cnrs NeurophysiologistNo ratings yet
- Stress Management: Multiple-Choice Self-Assessment Questions Answer GuideDocument3 pagesStress Management: Multiple-Choice Self-Assessment Questions Answer GuideSonu Yadav100% (1)
- Neurophysiology of Nerve Impulses: Physioex 9.0 Review Sheet ExerciseDocument6 pagesNeurophysiology of Nerve Impulses: Physioex 9.0 Review Sheet ExerciseAna Lucia BerganzaNo ratings yet
- Perio Lec.9 Pathogenesis o Periodontal DiseasesDocument32 pagesPerio Lec.9 Pathogenesis o Periodontal DiseasesزينNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.2 Organelle QuizDocument3 pagesWorksheet 1.2 Organelle QuizCyndel TindoyNo ratings yet
- Senses Blood Exp HeartDocument134 pagesSenses Blood Exp HeartJustine May S. ColicoNo ratings yet
- Heat Shock Proteins in The Immune System - Robert J. BinderDocument186 pagesHeat Shock Proteins in The Immune System - Robert J. BinderHari NugrohoNo ratings yet
- LAS 1 Final Sem - Earth and Life 11-ABM 2 (Az Baclig)Document4 pagesLAS 1 Final Sem - Earth and Life 11-ABM 2 (Az Baclig)Az BacligNo ratings yet
- Class 9th ScienceDocument5 pagesClass 9th ScienceEntertainment VediosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy SEQDocument15 pagesAnatomy SEQfast-track for n2021No ratings yet
- Linguistics S2 (L1 Neuro-Linguistics)Document11 pagesLinguistics S2 (L1 Neuro-Linguistics)ChakibNo ratings yet
- Bio f4 Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesBio f4 Endocrine SystemE-SKUUL ACADEMYNo ratings yet
- A Methodical Approach To Interpreting The Platelet Parameters of The Complete Blood CountDocument11 pagesA Methodical Approach To Interpreting The Platelet Parameters of The Complete Blood CountAlex YohanaNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of Sepsis - 2021 Update - Part 2, Organ Dysfunction and AssessmentDocument13 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Sepsis - 2021 Update - Part 2, Organ Dysfunction and AssessmentValerie ZimmermannNo ratings yet
- GLYCOLYSISDocument6 pagesGLYCOLYSISHAZEL SANDRONo ratings yet
- Wilco - HummingbirdDocument2 pagesWilco - HummingbirdThom BarrettNo ratings yet
- LOPERAMIDEDocument3 pagesLOPERAMIDEfaye kimNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Estudio Farmacognostico de P.oleraceaDocument5 pages5.1 Estudio Farmacognostico de P.oleraceaNatalia OlmosNo ratings yet
- YCB Level 1 - Aasanas & Practical Exam SyllabusDocument13 pagesYCB Level 1 - Aasanas & Practical Exam Syllabusriddhee100% (1)
- Unit 4 - Bioinspired EngineeringDocument24 pagesUnit 4 - Bioinspired EngineeringANURAG ASHISH KHATNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury Concept MapDocument1 pageAcute Kidney Injury Concept MapKEn PilapilNo ratings yet
- Biology: Biology Is The Scientific Study of LifeDocument64 pagesBiology: Biology Is The Scientific Study of LifeJohn HenryNo ratings yet
- 5.0 LeukopoiesisDocument37 pages5.0 LeukopoiesisJunior SataNo ratings yet
- Session #8 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document5 pagesSession #8 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G INo ratings yet
- BIOL3530 - Developmental Biology, RegenerationDocument2 pagesBIOL3530 - Developmental Biology, RegenerationNida ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga: LIQUIZONE Chemistry ReagentsDocument2 pagesDaftar Harga: LIQUIZONE Chemistry ReagentsVictoria AnnaNo ratings yet
- Spa PPT - FinalDocument45 pagesSpa PPT - FinalShivam DwivediNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.8 SL Respiration QuestionsDocument9 pagesTopic 2.8 SL Respiration QuestionsIzabella Rea100% (1)
- UntitledDocument37 pagesUntitledclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Centrioles, Centrosomes, and CiliaDocument16 pagesCentrioles, Centrosomes, and Ciliathebrotherhood2014No ratings yet
- Pharmacology SlidesDocument1,377 pagesPharmacology SlidesFritzel Pallon SusbillaNo ratings yet