Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 7 - Quarter 3 Learning Activity Sheet - Week 5 To 8 Polygon and Circle I. Objectives
Uploaded by
Myra Ramirez RamosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 7 - Quarter 3 Learning Activity Sheet - Week 5 To 8 Polygon and Circle I. Objectives
Uploaded by
Myra Ramirez RamosCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: ________________________ Section: _________ The formula for the number of diagonals 𝒅 is
𝒏 (𝒏 − 𝟑 )
Grade 7 – Quarter 3 𝒅=
𝟐
Learning Activity Sheet – Week 5 to 8
The number of diagonals for a quadrilateral will be
POLYGON AND CIRCLE
𝒏(𝒏 − 𝟑) 𝟒(𝟒 − 𝟑 ) 𝟒 (𝟏)
𝒅= = = =𝟐
I. OBJECTIVES 𝟐 𝟐 𝟐
At the end of the lesson, the students are able to:
a. Illustrate polygons: (a) convexity, (b) angles and (c) The diagonals of the quadrilateral in the previous
sides;
̅̅̅̅̅ or 𝑌𝑀
figure are 𝑀𝑌 ̅̅̅̅̅ and ̅̅̅̅
𝐷𝑋 or ̅̅̅̅
𝑋𝐷 .
b. Exterior and interior angles of a polygon; and
c. Illustrate a circle and the terms related to it: radius, A polygon can also be Convex or Concave
diameter, chord, center, arc central angle and polygon. A convex polygon has its all diagonals in
inscribed angle. the interior of the polygon. A Concave polygon has at
least one diagonal exterior of the polygon.
II. KEY CONCEPTS Convex Polygon Concave Polygon
A. POLYGON
A polygon is a geometric figure formed by joining
the endpoints of at least three line segments.
A polygon can be regular or irregular. Regular
polygons have congruent sides & congruent interior
angles. Irregular polygons don’t have congruent
sides or angles.
The table below shows the names of polygons
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is
which are common to most of us.
determined by the formula
Polygon Number of Sides/Angles
(𝒏 − 𝟐) ∙ 𝟏𝟖𝟎°
Triangle 3
Quadrilateral 4
The measure of an interior angle of a regular
Pentagon 5
polygon is given by
Hexagon 6
(𝒏 − 𝟐) ∙ 𝟏𝟖𝟎°
Heptagon 7
𝒏
Octagon 8
Nonagon 9
The measure of an exterior angle of a regular
N-gon n-sides polygon is given by
𝟏𝟖𝟎° − 𝒎𝒆𝒂𝒔𝒖𝒓𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝒊𝒏𝒕𝒆𝒓𝒊𝒐𝒓 𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒍𝒆
The figures below are both hexagon but one is
regular and the other is irregular.
Example:
Regular Hexagon Irregular Hexagon
A regular polygon has 8 sides. 𝑛 = 8
a. Sum of the interior angles:
(𝑛 − 2) ∙ 180° = (8 − 2) ∙ 180°
= (6) ∙ 180°
= 1 080°
Aside from the sides and angles, a polygon has a b. Measure of the interior angles:
vertex and diagonal. Diagonals are line segments (𝑛−2)∙180° (8−2)∙180°
drawn from one of the vertex to the other vertices. =
𝑛 8
(6)∙180°
=
8
1 080°
=
8
= 135°
c. Measure of the exterior angles:
The vertices of the triangle are 𝐴, 𝐵 and 𝐶 . The 180° − 𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑟 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒
angles are 𝐴, 𝐵 and 𝐶 . The sides are ̅̅̅̅
𝐴𝐵 or ̅̅̅̅
𝐵𝐴, ̅̅̅̅
𝐴𝐶 = 180° − 135°
or ̅̅̅̅
𝐶𝐴 and ̅̅̅̅
𝐵𝐶 or ̅̅̅̅
𝐶𝐵. A triangle has no diagonal. = 45°
B. CIRCLE ___6. You can draw a diagonal outside of a
A circle is a closed figure containing points which concave polygon.
are equidistant to the center. A circle can be named a. True b. False c. Maybe
using its center. ___7. The interior ∠s of a 12-gon measures __.
a. 150° b. 180° c. 90°
___8. The exterior ∠s of a 12-gon measures __.
a. 180° b. 150° c. 30°
___9. What is the sum of the interior angles of a
triangle?
a. 60° b. 180° c. 30°
___10. The interior angle of a regular pentagon
measures ____.
a. 72° b. 108° c. 540°
a. Center – the point located at the middle of the
circle. The center of the circle is point 𝑃. B. Use the given figure below. Write the letter of your
b. Radius – a line segment drawn from the center to answer on the space provided in each item.
any point on the circle. A circle can have many
radius (radii). The radii of circle 𝑃 are 𝑃𝑂 ̅̅̅̅, 𝑃𝐴
̅̅̅̅, 𝑃𝑅
̅̅̅̅
̅̅̅̅̅
and 𝑃𝑀.
c. Diameter – a line segment whose endpoints are
points on the circle. It passes through the center.
The diamters of circle 𝑃 are 𝑀𝑂 ̅̅̅̅̅/𝑂𝑀
̅̅̅̅̅ and 𝐴𝑅̅̅̅̅/𝑅𝐴
̅̅̅̅.
d. Chord – a line segment whose endpoints are
points on the circle. The chords in the circle are
̅̅̅̅̅/𝑅𝑀
𝑀𝑅 ̅̅̅̅̅, 𝑀𝑂
̅̅̅̅̅/𝑂𝑀
̅̅̅̅̅ and 𝐴𝑅
̅̅̅̅/𝑅𝐴
̅̅̅̅.
e. Arc – is a part of a circle that consists of points on
the circle whose endpoints are on the circle. Some
of the arcs of circle 𝑃 are 𝑂𝐴 ̂ and 𝐴𝑅𝑀 ̂ . You can
trace the part of the circle that will connect the ___1. Which is the center of the circle?
given points. a. N b. O c. S
f. Central Angle – an angle of a circle with its vertex ___2. Which of the following is a diameter?
located on the circle and the sides are radii of the a. ̅̅̅̅
𝑆𝑁 b. ̅̅̅̅̅
𝑂𝑀 ̅̅̅̅
c. 𝑆𝑇
circle. Some of the central angles of circle 𝑃 are
___3. Which of the following is NOT a chord?
∠𝐴𝑃𝑂 and ∠𝑅𝑃𝑀.
a. ̅̅̅̅
𝑂𝑇 b. ̅̅̅̅
𝑃𝑅 c. ̅̅̅̅̅
𝑀𝑇
g. Inscribed Angle – an angle of a circle whose
vertex is a point on the circle and its sides are ___4. The part of the circle tracing from 𝑅 to 𝑁
chords of the circle. The inscribed angle of circle 𝑃 is a __________.
is ∠𝑃𝑅𝑀 or ∠𝑀𝑅𝑃. ∠𝑅𝑀𝑂 or ∠𝑂𝑀𝑅 is also an a. diameter b. radius c. arc
inscribed angle. ___5. How many radii are there in circle 𝑂?
a. 5 b. 4 c. 3
___6. How many chords are there in circle 𝑂?
III. Activities
a. 4 b. 1 c. 2
A. Select the best answer by writing the letter of the
correct answer on the space provided for each item. ___7. ∠𝑆𝑇𝑀 is a/an ___________.
a. central ∠ b. center c. inscribed ∠
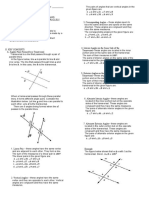
___1. A polygon is a closed geometric figure. ___8. Which point is exterior of circle 𝑂?
a. True b. False c. Maybe a. 𝑁 b. 𝑄 c. 𝑂
___2.Which has the least number of sides?
___9. Which of the following is a central angle?
a. octagon b. pentagon c. dodecagon
a. ∠𝑁𝑂𝑇 b. ∠𝑆𝑇𝑀 c. ∠𝑇𝑆𝑁
___3. Part of a polygon drawn from the vertex to
̂ is a _______
___10. 𝑆𝑀𝑁
another non-adjacent vertex.
a. semi-circle b. major arc c. minor arc
a. diagonal b. side c. interior ∠
___4. Decagon has ___ diagonals.
a. 40 b. 10 c. 35
___5. The sum of interior ∠s of a 12-gon is ___.
a. 1 080° b. 180° c. 1 800°
ANSWER KEY
A.
1. A
2. B
3. A
4. C
5. C
6. A
7. A
8. C
9. B
10. B
B.
1. B
2. A
3. A
4. C
5. B
6. A
7. C
8. B
9. A
10. A
You might also like
- Teaching Guide Catchup G7 InterventionDocument2 pagesTeaching Guide Catchup G7 InterventionIra Odette AndresNo ratings yet
- Dependent vs Independent VariablesDocument7 pagesDependent vs Independent VariablesmarvieroseNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Materials IN Mathematics 7: Addition and Subtraction of PolynomialsDocument8 pagesStrategic Intervention Materials IN Mathematics 7: Addition and Subtraction of PolynomialsEulamarie PadlanNo ratings yet
- Basic Education Assistance For Mindanao: Learning GuideDocument34 pagesBasic Education Assistance For Mindanao: Learning GuideJC RiveraNo ratings yet
- Using Geometric Figures to Solve Real-Life ProblemsDocument3 pagesUsing Geometric Figures to Solve Real-Life ProblemsLavander BlushNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Daily Lesson Log Week2Document5 pagesMath 7 Daily Lesson Log Week2Ederlyn LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Tos 1ST Quarter Pre-Test 2020-2021Document4 pagesTos 1ST Quarter Pre-Test 2020-2021Donabel CariosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Evaluating Algebraic ExpressionDocument14 pagesLesson Plan Evaluating Algebraic ExpressionNimfa MalizaNo ratings yet
- REMAINDER THEOREM SUDOKU 4x4Document3 pagesREMAINDER THEOREM SUDOKU 4x4Judith MendozaNo ratings yet
- Central Angle and Intercepted ArcDocument4 pagesCentral Angle and Intercepted ArcEric de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Dll-Cot Multiplication of IntegersDocument7 pagesDll-Cot Multiplication of IntegersRizaneth Gay Mirar100% (1)
- Math 9 Learning CompetencyDocument6 pagesMath 9 Learning CompetencyCassandra Niña NaviaNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document2 pagesDay 2jennelyn malaynoNo ratings yet
- DEMONSTRATIONlessonplanDocument6 pagesDEMONSTRATIONlessonplanLovely VillasNo ratings yet
- Geometric Relations Daily LessonDocument2 pagesGeometric Relations Daily LessonRusshel Jon Llamas Macalisang100% (1)
- The mean, median and mode in the middleDocument7 pagesThe mean, median and mode in the middleLilibeth SearesNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math: Multiplying polynomialsDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Math: Multiplying polynomialsKez Max100% (1)
- Math 7 Summative Test 3Document3 pagesMath 7 Summative Test 3OSZEL JUNE BALANAYNo ratings yet
- Multiplication of Binomial To BinomialDocument5 pagesMultiplication of Binomial To BinomialMelisa May Ocampo AmpiloquioNo ratings yet
- Circle and Its PartsDocument7 pagesCircle and Its PartsAngelen RegaroNo ratings yet
- Tos Grade 8Document3 pagesTos Grade 8Martin BaccayNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippineskikoy20No ratings yet
- 3 M9 Summative Test Tos Q1Document4 pages3 M9 Summative Test Tos Q1Sharon PascualNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Teaching Mathematics Grade 9Document3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Teaching Mathematics Grade 9ERIX VALMADRIDNo ratings yet
- 6.1.3 Permutations of N Different Objects Taken R at A TimeDocument1 page6.1.3 Permutations of N Different Objects Taken R at A TimeCikgu Fayruzz NaseerNo ratings yet
- Principal Roots of Rational and Irrational Week 6Document13 pagesPrincipal Roots of Rational and Irrational Week 6Khenchy FalogmeNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Mathematics 7 CMDocument3 pages3rd Quarter Mathematics 7 CMJeff LacasandileNo ratings yet
- The Following Are The Steps in Constructing Perpendicular Bisector of A Segment Using A Compass and A StraightedgeDocument4 pagesThe Following Are The Steps in Constructing Perpendicular Bisector of A Segment Using A Compass and A StraightedgeAnjelo Amar BarcenasNo ratings yet
- G8DLL Q2W3 LC24-25Document13 pagesG8DLL Q2W3 LC24-25Reina Chenna SaulongNo ratings yet
- SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsDocument9 pagesSDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsZyra CabarleNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in Mathematics 7 Q2 1Document1 pagePerformance Task in Mathematics 7 Q2 1Mariel Pastolero100% (1)
- Sequences: Generate and Describe Patterns SSP - M10AL - Ia - 1Document2 pagesSequences: Generate and Describe Patterns SSP - M10AL - Ia - 1Emyren ApuyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Law of Cosines: February 2019Document10 pagesLesson Plan For Law of Cosines: February 2019Denmark SantosNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 10 Weekly PlanDocument2 pagesMathematics 10 Weekly PlanRochelle100% (1)
- DLL - July29-31 Deductive-InductiveDocument3 pagesDLL - July29-31 Deductive-Inductiveerrol rustia100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized CotDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized CotLeizel Samson100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Undefined TermsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Undefined TermsJinkee F. Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios of Special AnglesDocument12 pagesTrigonometric Ratios of Special AnglesPaulNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Solving Problems On Real Numbers-1Document2 pagesActivity Sheet Solving Problems On Real Numbers-1Eunice Ortile100% (1)
- Secondary Student'S Permanent Record: Maramba National High SchoolDocument2 pagesSecondary Student'S Permanent Record: Maramba National High SchoolErold TarvinaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Roots Using DiscriminantDocument3 pagesNature of Roots Using DiscriminantTser SueNo ratings yet
- Math7 Las Q4-1Document82 pagesMath7 Las Q4-1sheryl manuelNo ratings yet
- LAS Math 7 q4Document6 pagesLAS Math 7 q4DenNo ratings yet
- WLP - Grade 8Document13 pagesWLP - Grade 8Jean DelaNo ratings yet
- DLP For Demojul232019Document5 pagesDLP For Demojul232019Catherine SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Math 9 Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesDetailed Math 9 Lesson PlanGraceRasdas0% (1)
- DLL LCDocument5 pagesDLL LCSisa Vargas Mabuyao100% (1)
- Lesson Plan of Operations of Radicals 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan of Operations of Radicals 2zaira acejoNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level: GdistributionsDocument16 pagesSchool Grade Level: GdistributionsJeemark Naceel AlojadoNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification Math 7 1 Quarter (2018-2019) : Topic Item No. No. of Items PercentageDocument1 pageTable of Specification Math 7 1 Quarter (2018-2019) : Topic Item No. No. of Items PercentageJudy Ann SottoNo ratings yet
- MATH10 QUARTER 2 Week 2 DLLDocument8 pagesMATH10 QUARTER 2 Week 2 DLLkich100% (2)
- Math 7 - Summative Week 678Document2 pagesMath 7 - Summative Week 678Brian MaryNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Quarterly Test Q3 SOLODocument4 pagesMath 10 Quarterly Test Q3 SOLOERICK HUTAMARESNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan Math 8 COT 1 SY 2021-2022Document8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Math 8 COT 1 SY 2021-2022BERNIE EMPIMONo ratings yet
- m7q4l5 Analyzinginterpreting and Rawing Conclusions From Graphics and Tabular Forms EditedDocument8 pagesm7q4l5 Analyzinginterpreting and Rawing Conclusions From Graphics and Tabular Forms EditedMark Anthony M Tolentino100% (1)
- Absolute Value Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAbsolute Value Lesson PlanRhea AloNo ratings yet
- Pivot 4a Budget of Work (Bow) in MathematicsDocument3 pagesPivot 4a Budget of Work (Bow) in MathematicsMarife Faustino GanNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument4 pagesPerformance TaskGwen MarielleNo ratings yet
- g7 Polygons Interior and Exterior AnglesDocument40 pagesg7 Polygons Interior and Exterior AnglesTenten Peter100% (1)
- PolygonDocument3 pagesPolygonasep habibulohNo ratings yet
- Parents' Permit: Name and Signature of Parent/GuardianDocument1 pageParents' Permit: Name and Signature of Parent/GuardianJanine Elizabeth AbelNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 3 4 MATH 7 Geometry TransversalDocument2 pagesQ3 WEEK 3 4 MATH 7 Geometry TransversalMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Project MSF: Impact of Modular Instruction To The Level of Academic Performance of Selected LearnersDocument10 pagesProject MSF: Impact of Modular Instruction To The Level of Academic Performance of Selected LearnersMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Q4 Las Week 1 3Document13 pagesQ4 Las Week 1 3Myra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 PROJECT AN ASSESSMENT TOOL POST TEST EditedDocument2 pagesGRADE 7 PROJECT AN ASSESSMENT TOOL POST TEST EditedMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Q3 WEEK 1 2 MATH 7 Geometry AnglesDocument10 pagesQ3 WEEK 1 2 MATH 7 Geometry AnglesMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- M7 LAS Q2 Wk3Document2 pagesM7 LAS Q2 Wk3Myra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 3rd Quarter MATHDocument5 pagesGRADE 10 3rd Quarter MATHMyra Ramirez Ramos0% (2)
- Semi - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Addition of PolynomialsDocument4 pagesSemi - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Addition of PolynomialsMyra Ramirez Ramos57% (7)
- Lesson Plan DemoDocument8 pagesLesson Plan DemoMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Semi - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Addition of PolynomialsDocument4 pagesSemi - Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Addition of PolynomialsMyra Ramirez Ramos57% (7)
- LP Addition of PolynomialsDocument4 pagesLP Addition of PolynomialsMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Lis Urgent ReportDocument1 pageLis Urgent ReportMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 3rd Quarter MATHDocument5 pagesGRADE 10 3rd Quarter MATHMyra Ramirez Ramos0% (2)
- Glossary GeometryDocument3 pagesGlossary GeometryMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 7 PERIODIC EXAMDocument5 pagesMATHEMATICS 7 PERIODIC EXAMMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Schools Division of Nueva Ecija Fourth Periodical Examination Mathematics 7Document5 pagesDepartment of Education Schools Division of Nueva Ecija Fourth Periodical Examination Mathematics 7Myra Ramirez Ramos0% (1)
- Equivalent Record Form: Region Iii-Central LuzonDocument1 pageEquivalent Record Form: Region Iii-Central LuzonMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Bullying ResearchDocument3 pagesBullying ResearchMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Multiplication of PolynomialsDocument1 pageMultiplication of PolynomialsMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument1 pageNetworkMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Long Test MathDocument3 pages2nd Grading Long Test MathMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Long Test MathDocument3 pages2nd Grading Long Test MathMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Long Test MathDocument3 pages2nd Grading Long Test MathMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Long Test MathDocument3 pages2nd Grading Long Test MathMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument115 pagesForce and MotionMyra Ramirez Ramos90% (10)
- 2nd Grading 1st Long TestDocument2 pages2nd Grading 1st Long TestMyra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- 4th PT MATH 8Document10 pages4th PT MATH 8Myra Ramirez RamosNo ratings yet
- Problems 4301 4400 Crux CompressedDocument43 pagesProblems 4301 4400 Crux CompressedAnonymous j6r5KRtrH2No ratings yet
- Humongous Book of Trigonometry ProblemsDocument1,157 pagesHumongous Book of Trigonometry Problemsallan.villegasNo ratings yet
- Inscribed AnglesDocument22 pagesInscribed AnglesLeo Rene Astacaan LeonidaNo ratings yet
- ENGG DRAWING MCQsDocument17 pagesENGG DRAWING MCQsprashmceNo ratings yet
- Velocity Analysis-Instantaneous Center MDocument7 pagesVelocity Analysis-Instantaneous Center MSuman_SamadderNo ratings yet
- Drill Ex 7 Answers Nq4nucgDocument48 pagesDrill Ex 7 Answers Nq4nucgdevang tank100% (2)
- NetsDocument4 pagesNetsDtdc SenthlNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 8studentDocument371 pagesMaths Grade 8studentsharmasanjivNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Cbse Official Practice Papers With Marking SchemeDocument83 pagesClass 10 Maths Cbse Official Practice Papers With Marking Schemeabin dpsNo ratings yet
- CGP Year 2 Maths WorkoutDocument3 pagesCGP Year 2 Maths Workoutrsaber231No ratings yet
- COT-1-SOLID-FIGURES Grade 6Document5 pagesCOT-1-SOLID-FIGURES Grade 6MARIGRACE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- F3 First Term Revision Set 1 2023Document12 pagesF3 First Term Revision Set 1 2023TAN LAU GUAN HONG MoeNo ratings yet
- MYP4 Coordinate Goemetry (Sheet 2)Document7 pagesMYP4 Coordinate Goemetry (Sheet 2)Mohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Ukcat Abstract ReasoningDocument2 pagesUkcat Abstract ReasoningEnzo Valendino100% (1)
- 3 Math6Q3Week1Document25 pages3 Math6Q3Week1Dhan MangmangonNo ratings yet
- Triangle 3Document12 pagesTriangle 3Vilas ShindeNo ratings yet
- 4.7 Solving Problems With Inverse Trig Functions (Slides 4-To-1) PDFDocument5 pages4.7 Solving Problems With Inverse Trig Functions (Slides 4-To-1) PDFhakomoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Maths Foundation FlashcardsDocument7 pagesEdexcel Maths Foundation FlashcardsPetar GeorgievNo ratings yet
- IMO Class-8 Level 2 (12-02-2017)Document6 pagesIMO Class-8 Level 2 (12-02-2017)KamalNo ratings yet
- GURUKUL BHARAT DPP:- COMPLEX NO EXERCISESDocument7 pagesGURUKUL BHARAT DPP:- COMPLEX NO EXERCISESKumar AtthiNo ratings yet
- 152ag - Engineering GraphicsDocument2 pages152ag - Engineering GraphicsSaikrishna sidduNo ratings yet
- E2Qdif CDocument2 pagesE2Qdif CLucas ShazNo ratings yet
- Lecture #6: Complex 3D Modeling With Polygon MeshDocument9 pagesLecture #6: Complex 3D Modeling With Polygon MeshvirtuaclassNo ratings yet
- A Teen Age Boy Wrote HisDocument3 pagesA Teen Age Boy Wrote Hisapi-19562657No ratings yet
- CES3Document2 pagesCES3Achietots CabarioNo ratings yet
- 4 Sector and ArcsDocument21 pages4 Sector and ArcsWrath100% (1)
- Hsslive-Xi-Maths-Qb-10. STRAIGHT LINESDocument5 pagesHsslive-Xi-Maths-Qb-10. STRAIGHT LINESheizzenclovNo ratings yet
- GAUSS LAW (Assignment - 2) - 1Document6 pagesGAUSS LAW (Assignment - 2) - 1Kaustubh PurohitNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter Examination in Math 10Document4 pages3RD Quarter Examination in Math 10Enrico EusebioNo ratings yet
- Week 3 (Vector Addition)Document51 pagesWeek 3 (Vector Addition)Aris Dwyane M PascualNo ratings yet