Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DLP Q4 W4D4
Uploaded by
LA Lloyd Arvin MontesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DLP Q4 W4D4
Uploaded by
LA Lloyd Arvin MontesCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region V – Bicol
DIVISION OF CAMARINES NORTE
SAN LORENZO RUIZ NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Mampurog, San Lorenzo Ruiz
DAILY LESSON School SAN LORENZO RUIZ NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL Grade Level GRADE
PLAN 10
Grade 10 Teacher LA LLOYD ARVIN E. MONTES Learning Area SCIENCE
Date and Time May 25, 2023 Quarter 4th
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards The learners demonstrate understanding of how gases behave based on the motion and
relative distances between gas particles.
B. Performance
Standards
C. Learning Investigate the relationship between:
Competencies/ a. volume and pressure at constant temperature of a gas;
Objectives b. volume and temperature at constant pressure of a gas;
c. explains these relationships using the kinetic molecular theory. S10MT-IV-a-b-21
1. Relate properties of gases to kinetic molecular theory
II.CONTENT (Subject KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY
Matter/Lesson)
III.LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References Science 10 Learner’s Materials
1. Teacher’s Guide Page 268-269
Pages
2. Learner’s Material Page 391-393
Pages
3. Textbook Pages
4. Additional Materials
from Learning
Resources
B. Other Learning
Resources
IV.PROCEDURES Activities
A. ELICIT
Ask the learners to describe the two figures above.
1. ENGAGE Learners view video presentation of Charles’ Law for them to have an idea about the
lesson.
Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7ZpuMBk f1Ss&t=99s
2. EXPLORE Group the learners into four. Each group will perform the activity in every learning station.
STATION 1: JET- PROPELLED BALLOON
Guide Questions:
1. Explain why the balloons shoots along the thread at a speed using the concept of the gas
laws.
2. What does this proved regarding the compressibility of gases?
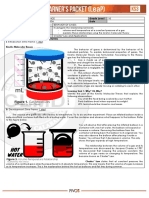
STATION 2: THE RISING WATER
Guide Questions:
4. What happened to the level of the water inside the glass?
5. What caused this to happened?
6. If the rim of the glass was raised above the surface of the water, what might have
happened? Let the learners present their output.
3. EXPLAIN Ask a volunteer from each group to explain their answers in front of the class.
4. ELABORATE The teacher discusses the key concept.
Kinetic Molecular Theory states that:
a. Gases are composed of molecules. The distances from one molecule to another
molecule are far greater than the molecules’ dimensions. These molecules can be
considered as spherical bodies which possess negligible mass and volume.
b. Kinetic Molecular Theory states that: Gases are composed of molecules. The distances
from one molecule to another molecule are far greater than the molecules’ dimensions.
These molecules can be considered as spherical bodies which possess negligible mass
and volume.
c. Gas molecules are always in constant random motion and they frequently collide with
one another and with the walls of the container. Collision among molecules are perfectly
elastic, that is, energy may transfer from molecule to molecule as the result of collision but
the total energy of all the molecules in the system remains the same/constant.
d. There is a neither attractive nor repulsive force between or among gas molecules.
e. Movement of gas molecules is affected by temperature. The average kinetic of the
molecules is directly related to the temperature of gas
5. EVALUATE Direction: Identify and underline the possible weakness or flaws in the postulates.
Write TRUE if the postulate is accurate and FALSE if the postulate is flawed.
1. A gas consists of a collection of small particles traveling in straight line motion and
obeying Newton’s Laws.
2. The molecules in a gas occupy negligible volume.
3. Collisions between molecules are perfectly elastic (that is, no energy is gained nor lost
during the collision).
4. There are negligible, attractive, or repulsive forces between molecules.
5. The average kinetic energy of a molecule is constant.
6. EXTEND Give other practical applications of Gas Laws.
V. REMARKS
Prepared by:
LA LLOYD ARVIN E. MONTES
Teacher I
Noted:
LUNINGNING B. ACAL
School Principal I
You might also like
- Boyle's Law 7 E's Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesBoyle's Law 7 E's Lesson PlanGelCess Paroan75% (12)
- Polarity of Molecules DLPDocument4 pagesPolarity of Molecules DLPMELANIE IBARDALOZA91% (11)
- First Quarter (Week 1) : What I Need To Know?Document5 pagesFirst Quarter (Week 1) : What I Need To Know?Angelina Lumbre100% (1)
- Poblacion Bagumbayan, Sultan KudaratDocument2 pagesPoblacion Bagumbayan, Sultan KudaratSheena DalguntasNo ratings yet
- Thermowell Velocity Calculations: Company: Tag No: Project No: Date: Reference: RevDocument2 pagesThermowell Velocity Calculations: Company: Tag No: Project No: Date: Reference: RevFatoni Gea AirlanggaNo ratings yet
- April 26Document4 pagesApril 26Dare QuimadaNo ratings yet
- April 25Document4 pagesApril 25Dare QuimadaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryGarren Jude Aquino100% (1)
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument6 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayPretzelParkNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular ForcesDocument6 pagesIntermolecular ForcesJohn Nerlo Dequiña100% (1)
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument3 pagesPolarity of MoleculesRyan Dave MacariayNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory May-11Document5 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory May-11Omhar CeresNo ratings yet
- KMT Module 1 G10Document11 pagesKMT Module 1 G10cedrickjamesarestaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 DLL Week 1Document7 pagesGen Chem 2 DLL Week 1Tristan PereyNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - LeDocument10 pagesWeek 3 - LeRodney BarbaNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 DLLDocument7 pagesGen Chem 2 DLLAnalynAsuncionAtaydeNo ratings yet
- DLL Physical ScienceDocument8 pagesDLL Physical ScienceMarjorie BrondoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science M3Document22 pagesPhysical Science M3Ma WiNo ratings yet
- Physical Science NOV. 20-22, 2019 DLPDocument2 pagesPhysical Science NOV. 20-22, 2019 DLPJedidiah Jara QuidetNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 3 Day 2Document2 pagesPhysical Science Week 3 Day 2daniel loberizNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 10 Week2Document3 pagesQ4 Science 10 Week2Edison Caringal50% (2)
- Gas Law - DLP 10Document7 pagesGas Law - DLP 10cherrymaeregalario2001No ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 DAILY LESSON LOGDocument8 pagesGen Chem 2 DAILY LESSON LOGMaricriz Bioco100% (1)
- Syllabus in Science 9: Talisay, Camarines NorteDocument3 pagesSyllabus in Science 9: Talisay, Camarines NorteMaria Faye MarianoNo ratings yet
- PHY SCI DLP Q3 Week 2Document15 pagesPHY SCI DLP Q3 Week 2Radish CucumberNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DLL1Document8 pagesPhysical Science DLL1Gracie O. ChingNo ratings yet
- DLL Nov 14 Ionic and Covalent BasesDocument4 pagesDLL Nov 14 Ionic and Covalent Baseshelen grace cabalagNo ratings yet
- SDLP-Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument6 pagesSDLP-Kinetic Molecular TheoryJessica SudioNo ratings yet
- L.P For ApplicationDocument12 pagesL.P For ApplicationRommelyn RosasNo ratings yet
- PolarityDocument3 pagesPolarityLalaine SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Els 1 6 4 19Document2 pagesEls 1 6 4 19Mark Kevin Villareal100% (2)
- Week 2 - LeDocument10 pagesWeek 2 - LeRodney BarbaNo ratings yet
- Grade Level Grade 10 Quarter/Domain Week & Day No Date: Daily Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesGrade Level Grade 10 Quarter/Domain Week & Day No Date: Daily Lesson PlanDiana Jane GudesNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 2 PsDocument4 pagesSummative Test 2 PsKennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Gases Lesson1 - 12Document97 pagesChapter 3 Gases Lesson1 - 12Julius Salas100% (1)
- 7E ModelDocument5 pages7E ModelFlorante-Melanie TagubaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Lesson Plan WK 3Document4 pagesYear 10 Lesson Plan WK 3RhemaNo ratings yet
- Dll. MATTER - DAY5.WEEK2.melting.3RDQDocument4 pagesDll. MATTER - DAY5.WEEK2.melting.3RDQjunalyn franciscoNo ratings yet
- Sample LE PS W3 ADocument8 pagesSample LE PS W3 AJoseph GutierrezNo ratings yet
- DLL Chem Dec02Document4 pagesDLL Chem Dec02Rosallie Caaya-NuezNo ratings yet
- Q4-Science 10 - Wk1-DLLDocument5 pagesQ4-Science 10 - Wk1-DLLaprilyn gamboaNo ratings yet
- Atoms Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesAtoms Lesson PlanCindirella Galos100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson PlanMaria Joylyn DivinoNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Gases LPDocument5 pagesGetting To Know Gases LPkimmymantos022No ratings yet
- Con Chem 1st QT W2 D1Document3 pagesCon Chem 1st QT W2 D1TEREMIE JOSEPH OBADONo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q3 Week 2 - DLL BausinDocument4 pagesScience 8 Q3 Week 2 - DLL Bausinsheryll BausinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mechanical EnergyDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Mechanical EnergyNorma Lyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Behavior and Properties of GasesDocument3 pagesBehavior and Properties of Gasesjohnpaul.ducducanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science MidtermDocument6 pagesPhysical Science MidtermYvonne De Venecia MalicdemNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Intermolecular Forces of Attarction 11 Hubble Ocampo Mark Gil P.Document5 pages1.2 Intermolecular Forces of Attarction 11 Hubble Ocampo Mark Gil P.Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Q3-PS-Week 6-March 4-8, 2024Document4 pagesQ3-PS-Week 6-March 4-8, 2024Joan MarieNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument5 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryFatima Ybanez Mahilum-LimbagaNo ratings yet
- (KE) Exploring The Structure and Function of Life LPDocument6 pages(KE) Exploring The Structure and Function of Life LPKaye EstrellaNo ratings yet
- SEL SCI Grade 9 Early 3rd Quarter B JabeenDocument6 pagesSEL SCI Grade 9 Early 3rd Quarter B JabeenJhon Excell SanoNo ratings yet
- PolarDocument6 pagesPolarShermaine GenistonNo ratings yet
- 7s Lesson PlanDocument5 pages7s Lesson PlanCristwin Quinio100% (1)
- DLP in Polarity of MoleculesDocument9 pagesDLP in Polarity of MoleculesCyrex BuladoNo ratings yet
- Dll. MATTER - DAY5.WEEK2.CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER.3RDQDocument4 pagesDll. MATTER - DAY5.WEEK2.CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER.3RDQjunalyn franciscoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q3 Module 1Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q3 Module 1Cess BagtasNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science 12Document2 pagesLesson Plan in Earth and Life Science 12Ryl MitchNo ratings yet
- Survey of Progress in Chemistry: Volume 2From EverandSurvey of Progress in Chemistry: Volume 2Arthur F. ScottNo ratings yet
- DLP Q4 W4D5Document1 pageDLP Q4 W4D5LA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- DLP Q3 W4D3Document2 pagesDLP Q3 W4D3LA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- DLP Q3 W2D2Document2 pagesDLP Q3 W2D2LA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- DLP Q3 W1D2Document3 pagesDLP Q3 W1D2LA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- OHSP LM Week 9 10 7 ScienceDocument2 pagesOHSP LM Week 9 10 7 ScienceLA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Science WarDocument1 pageScience WarLA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For DemoDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics For DemoLA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science PT 2Document8 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science PT 2LA Lloyd Arvin MontesNo ratings yet
- World Journal of Pharmaceutical ResearchDocument14 pagesWorld Journal of Pharmaceutical ResearchDevanandDongreNo ratings yet
- IJSO 2013 Experiment TaskA QuestionsDocument11 pagesIJSO 2013 Experiment TaskA QuestionsmpecthNo ratings yet
- Shrinkage Limit Test Lab ManualDocument2 pagesShrinkage Limit Test Lab ManualmmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 OscillationsDocument54 pagesChapter 14 OscillationsPathmanathan Nadeson100% (1)
- WWW Slipnot ComDocument2 pagesWWW Slipnot ComjuankeplerNo ratings yet
- Computational Study of Uctuating Motions and Cluster Structures in Gas-Particle OwsDocument25 pagesComputational Study of Uctuating Motions and Cluster Structures in Gas-Particle OwsMuhammad Adnan LaghariNo ratings yet
- Weak Acid Vs Strong Base TitrationDocument9 pagesWeak Acid Vs Strong Base Titrationgovindshankarq9No ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument9 pagesChemistry ProjectSreedhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Report of Hospital BuldingtDocument35 pagesStructural Analysis Report of Hospital BuldingtPrasanth Nair50% (2)
- Short Circuit CalculationsDocument7 pagesShort Circuit CalculationsMohamedNo ratings yet
- Seismic Analysis of Multistorey Building With Floating Column by Using TabsDocument11 pagesSeismic Analysis of Multistorey Building With Floating Column by Using TabshemolandNo ratings yet
- Ecss Q ST 70 16c (1december2020)Document94 pagesEcss Q ST 70 16c (1december2020)Tanishq DwivediNo ratings yet
- Back Presure Valve in PCP or SRPDocument15 pagesBack Presure Valve in PCP or SRPShubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Pile Integrity Tester Model Comparison: Pit-X, Pit-X2, Pit-V and Pit-FvDocument5 pagesPile Integrity Tester Model Comparison: Pit-X, Pit-X2, Pit-V and Pit-FvDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICK100% (1)
- Pappas - Energy Simulation of A DSF - A Process Using CFD and EnergyPlusDocument8 pagesPappas - Energy Simulation of A DSF - A Process Using CFD and EnergyPlusHamo HamoNo ratings yet
- 20 6 LightDocument22 pages20 6 LightUbaid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Reference ManualDocument27 pagesLubricant Reference ManualNguyen Tien Quy100% (6)
- Project NTPCDocument43 pagesProject NTPCShubham CronosNo ratings yet
- Night Vision Technology Seminar PresentationDocument19 pagesNight Vision Technology Seminar PresentationRam VBITNo ratings yet
- Hardness Conversion Chart 3 PDFDocument3 pagesHardness Conversion Chart 3 PDFmuthuswamy77No ratings yet
- Slaking Characteristics of Geomaterials in Direct Shear TestDocument197 pagesSlaking Characteristics of Geomaterials in Direct Shear TestnihajnoorNo ratings yet
- Chimney DesignDocument13 pagesChimney DesignUhong Lai100% (1)
- 4.13C - Hückel MO Theory - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument4 pages4.13C - Hückel MO Theory - Chemistry LibreTextsKanhai LeishangthemNo ratings yet
- bst161 FullDocument23 pagesbst161 FullchkznzjwfsNo ratings yet
- Vibration Svinkin PDFDocument13 pagesVibration Svinkin PDFyin hoe ongNo ratings yet
- G8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureDocument49 pagesG8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Availability Analysis (Second Law Analysis)Document47 pagesAvailability Analysis (Second Law Analysis)Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Physics As Level Book (2022-2023)Document492 pagesPhysics As Level Book (2022-2023)AMNA MOAZZAMNo ratings yet
- Shigley Solve Cap. 5 &6Document63 pagesShigley Solve Cap. 5 &6Johnny SanchezNo ratings yet