Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LK 1 Deasy
Uploaded by
Hilmiwan Maulana Bhakti0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views38 pagesThis document provides an overview of 4 learning activities on the topic of English for public information:
1. Public notices - It discusses the definition, social function, characteristics, generic structure, and language features of public notices. Examples of different types of notices are also provided.
2. Posters and banners - It covers the definition, characteristics, generic structure, social/language function, and language features of posters and banners.
3. Graphic organizers - It addresses the definition, generic structure, social/language function, types (description, sequence, compare/contrast, cause/effect, problem/solution), and language features of graphic organizers.
4. Infographics - It gives a short description and
Original Description:
Lembar Kerja Pembelajaran
Original Title
LK 1 DEASY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of 4 learning activities on the topic of English for public information:
1. Public notices - It discusses the definition, social function, characteristics, generic structure, and language features of public notices. Examples of different types of notices are also provided.
2. Posters and banners - It covers the definition, characteristics, generic structure, social/language function, and language features of posters and banners.
3. Graphic organizers - It addresses the definition, generic structure, social/language function, types (description, sequence, compare/contrast, cause/effect, problem/solution), and language features of graphic organizers.
4. Infographics - It gives a short description and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views38 pagesLK 1 Deasy
Uploaded by
Hilmiwan Maulana BhaktiThis document provides an overview of 4 learning activities on the topic of English for public information:
1. Public notices - It discusses the definition, social function, characteristics, generic structure, and language features of public notices. Examples of different types of notices are also provided.
2. Posters and banners - It covers the definition, characteristics, generic structure, social/language function, and language features of posters and banners.
3. Graphic organizers - It addresses the definition, generic structure, social/language function, types (description, sequence, compare/contrast, cause/effect, problem/solution), and language features of graphic organizers.
4. Infographics - It gives a short description and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 38
LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri – Modul 1
Judul Modul ENGLISH FOR PUBLIC INFORMATION
Judul Kegiatan 1. PUBLIC NOTICE
Belajar (KB) 2. POSTERS AND BANNERS
3. GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS
4. INFOGRAPHIC
No Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban
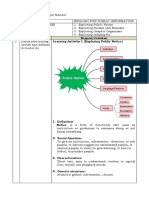
1 Daftar peta LEARNING ACTIVITY 1: PUBLIC NOTICE
konsep (istilah A. Introduction
dan definisi) di 1. Short Description.
modul ini Notice is a form of functional Text as intruction or guidance to
someone doing or not doing something.
2. Relevance.
3. Learning guide
a. Pre-activity: building background knowledge about notices.
b. Main Activity: Many activities encourage understanding and
enjoyment about notices.
c. Post-activity: Questioning, Discussion, Creating and
Presenting
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure
and lexico-grammatical features
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition of Notice
Notice is a form of functional Text as intruction or guidance
to someone doing or not doing something.
b. Social Function of Notice Text
The purpose of the notice is to announce or display
information to people.
- To give an intruction
- To give information
- To direction
- To warn
- To forbid
- To suggest
- To remind
c. Characteristics of Notice Text
- Short text (simple word, phrases, or clauses)
- Easy to understand
- Written in capital font
- Mostly use image/picture
d. Generic Structure of Public Notice
There are three parts of generic structure of public notice:
- Attention gather, this is optional
- Information
- Closure, this is optional. Closure is an act of closing
e. Language Features of Public Notice
- Using Imperative mood (imperative sentence). For
example (Run!, Get out!)
- Using Declarative reference (subject+verb)
- Spoken/written Language features
In spoken language, a. personal pronouns are often
used. b. The sentence structure of spoken language is
shorter and easier. c. Repetition and phrases. d.
Convensional tone is applied in spoken language. e.
Familiar words are mostly used. f. Fewer references to
previously stated infornation
In written language, a. personal pronouns are
infrequently used. b. The sentence is longer and harder.
c. The idead delivered through precise and varied
language. d. Applied formal tone. e. Rich and precise
vocabulary is implemented. f. Stated information may be
required.
f. Kind of Notice and their examples
- Command
- Caution
- Information
- Prohibition
- Warning
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
LEARNING ACTIVITY 2: POSTER AND BANNER
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
Poster is one of the communication media that is used to
convey a message or an information.
A banner is a typically rectangular advertisement placed on a
Web.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
a. Pre-activity: building background knowledge about poster
and banner
b. Main Activity: many activities encourage understanding and
enjoyment about poster and banner
c. Post-Activity: Questioning, Discussion, Creating, and
Presenting
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcome
a. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure
and lexico-grammatical features
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition of Poster and Banner
Poster is one of the communication media that is used to
convey a message or an information.
A banner is a typically rectangular advertisement placed on a
Web.
b. Characteristics of Poster and Banner
a) Generic Structure of Poster and Banner
Generic Structure of Poster
Header area
Title area
Author’s photo and address
Main area
Footer area
Background
Fonts
Generic Structure of Banner
Logo
Value Proposition
Body Copy
Image
Call to Action (CTA)
b) Social/Language Function of Poster and Banner
Function of Poster
Function of Bannes
c) Language Features of Poster and Banner
Language Feature of Poster
Short Text Element
Phareses and Active voice
Serif for text and san-serif font for title and Heading
(optional)
Language Features of Banner
Use Simple Present Tense
Subeject+verb+rest of sentence
Use simple phrases or statement
Look at me!
Readme! Ask me!
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Reference
LEARNING ACTIVITY 3: GRAPHIC ORGANIZER
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
A graphic organizer represents visual understanding that
structures information by organizing signifficant elements of a
notion or subject is a patterns using labels.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
a. Pre-activity, building background knowledge about graphic
organizer
b. Main activity, many activities encourage understanding and
enjoyment about graphic organizer
c. Post-activity, Analyze the funtion of each typ of graphic
organizers.
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure
and lexico-grammatical features
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Activities
a. Definition
A graphic organizer help teachers show and
explainrelationships between content and cubcontents and
how ther relate to ather areas.
b. Generic Structure
Titles, heading, and/or labels
Specific locations for information
Short descriptions (bullets or limited sentence)
c. Sosial/Language Function
The followings are some social functions for using graphic
organizer:
1. Tools for critical and creative thinking
2. Tools for organizing information
3. Tools for understanding information and relationships
4. Tools for depicting knowledge and understanding
5. Tools for self-learning
There are 5 types of graphic organizers:
Description
Sequence
Compare and Contrast
Cause and Effect
Problem and Solution
d. Language Features
1. Complect information.
2. Analytical, critical, planninh and creative thinking skills
are concerned.
3. The organizers are made to be easily edited, revised and
added.
4. Graphic organizers have multiple uses
5. Most graphic organizers use short word or phrases
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Reference
LEARNING ACTIVITY 4: INFOGRAPHICS
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
Infographics are essentially visual representations of
information. Commonly, they are utilized to tell stories, bring
ideas, or explore issue through a range of different infographics.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
a. Pre-activity: building background knowledge about
infographics
b. Main Activity: many activities encourage understanding and
enjoyment about infographics
c. Post-activity: Analyze the funtion of each typ of
infographics.
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure
and lexico-grammatical features
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition of Infographics
Infographics are essentially visual representations of
information. Commonly, they are utilized to tell stories,
bring ideas, or explore issue through a range of different
graphics.
b. Characteristics of Infographics
Clear Goals
Easy to Digest
Compelling Narrative
Unique Concept
Creative Design
Visual Focus-Not Text
c. Generic Structure of Infographics
Headline/Title
Beginning/Introduction
Middle/Main Infographic Content
End/Conclusion
Sources and Footnote
d. Social/Language Function of Infographics
Statistical Infographics
Informational Infographics
Timeline Infographics
Process Infographics
Geographic Infographics
Comparison Infographics
Hierarchical Infographics
List Infographics
e. Language Features Infographics
Informative, in general your aim is to bring clarity and
understanding
Engaging, stimulate them so that they will want to spend
time reading infographics
Accessible, communicate to the reader with the clearest
language.
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary and Reflection
2. Formative Test
3. Reference
2 Daftar materi 1. Language Features of Graphic Organizer
yang sulit
dipahami di
modul ini
3 Daftar materi 1. Graphic Organizer and Infographics
yang sering
mengalami
miskonsepsi
LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri – Modul 2
Judul Modul ENGLISH FOR PERSONAL COMMUNICATION
Judul Kegiatan 1. PERSONAL LETTER
Belajar (KB) 2. INVITATION
3. ANNOUNCEMENT
4. ADVERTISEMENT
No Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban
1 Daftar peta LEARNING ACTIVITY 1: PERSONAL LETTER
konsep (istilah A. Introduction
dan definisi) di 1. Short Description
modul ini Personal letter is a type of a letter, and is sent from one
individual to anothrer, is offten handwritten and send thought
the mail.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
d. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
e. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure
and lexico-grammatical features
f. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
Personal letter is a type of a letter, and is sent from one
individual to anothrer, is offten handwritten and send
thought the mail.
b. Generic Structure
- Date of writing
- Receiver
- Greeting form
- Ice breaker
- Main purpose
- Personal news
- Closing
- Complementary close/sign off
- Sender
c. Social/Language Function
d. Language Features
- Focus on exchanging personal curent news, feelings, and
conditions
- Use of pronouns, simple present tense, and past tense
- Use of date and adress
- Informam greeting or salutations
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Reference
5. Key answer
LEARNING ACTIVITY 2: INVITATION TEXT
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
An invitation may be formal on informal. It could be printed on
paper or sent via email.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure
and lexico-grammatical features
c. Skill
2. Learning Material and Learning Activities
a. Definition
An invitation Letter is a document that presents a formal
request for the presence of an individual, a group of people
or an organization at an event. An invitation may be formal
on informal. It could be printed on paper or sent via email.
An invitation can be used for a variety of events.
b. Generic Stucture
- Heading
- Recipent
- The content
- Formal phrase
- Reason on invitation
- Compilmentary sign/closing
- Sign off
- sender
c. Social Fuction
To invite someone attend/come an event.
d. Sosial/Language Features
- would you+infinitive
- would you like to + infinitive
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Reference
5. Key Answer
LEARNING ACTIVITY 3: ANNOUNCEMENT TEXT
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
An announcement is a statement made to the public or to the
media which gives infromation about something that has happened
or that will happen.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure and
lexico-grammatical features
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
An announcement is a statement made to the public or to the
media which gives infromation about something that has
happened or that will happen. The announcement of something
that has happened is the act of telling people about it. An
announcement in a publicplace, such as newspaper or the
window shop. An announcement can be spoken or written form.
It could be printed on paper or informed orally.
b. Generic Structure
- The puspose of announcement
- Day, Date, Time, Place
- Receiver
- Sender
c. Social function
Giving people some information
d. Social/language features
- Using simple present tense
- Using simple future tense
3. Discussion forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Reference
5. Key Answer
LEARNING ACTIVITY 4: ADVERTISEMENT TEXT
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
Advertising is a means of communication with the users of a
product or service.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure
and lexico-grammatical features
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
Advertising is a means of communication with the users of a
product or service. Advertisements are messages paid for by
those who send them and are intended to inform or influence
people who receive them. Advertising is always present,
though people may not be aware of it. In today's world,
advertising uses every possible media to get its message
through. It does this via television, print (newspapers,
magazines, journals etc), radio, press, internet, direct selling,
hoardings, mailers, contests, sponsorships, posters, clothes,
events, colours, sounds, visuals and even people
(endorsements).
b. Generic structure
- Topic
- Puspose
- Name of Product
- Users
c. Social function
- Giving an information
- To influence or to oersuade
- To give impression
d. Social/Language features
- The choice of word used related to necessary information
- Use indicate the target
- Precise, logical and courteous
- Suggesstion for the audience/reader/listener
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
4. Summary and Reflection
5. Formative Test
6. Reference
2 Daftar materi 1. Coherence and cohesion personal letter
yang sulit
dipahami di
modul ini
3 Daftar materi 1. Formal and Informal letter
yang sering
mengalami
miskonsepsi
LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri – Modul 3
Judul Modul ENGLISH FOR SOCIAL COMMUNICATION
Judul Kegiatan 1. DESCRIPTIVE TEXT 1 (PERSON AND ANIMALS)
Belajar (KB) 2. DESCRIPTIVE TEXT 2 (THING AND PLACE)
3. REPORT TEXT 1 (CLASSIFYING REPORT AND
COMPOSITIONAL REPORT)
4. REPORT TEXT 2 (COMPARATIVE REPORT AND
HISTORICAL REPORT)
No Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban
1 Daftar peta LEARNING ACTIVITY 1: DESCRIPTIVE TEXT 1 (PERSON
konsep (istilah AND ANIMALS)
dan definisi) di A. Introduction
modul ini 1. Short Description
Descriptive Text is a text that explains about what a person or
an animal, is like. It is about sensory experience, how
something looks, sounds, shapes.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold and apply religious value,
ethical calues, personal values and social values.
b. Knowledge, to analyze the contextual differences and
similarities between a number of descriptive texts in regard
to the social function, the text structure and the
lexicogrammatical features.
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Larning Activities
a. Definition
Descriptive Text is a text that explains about what a person
or an animal, is like. It is about sensory experience, how
something looks, sounds, shapes. Mostly it is about visual
experience, but description also deals with other kinds of
perception. It can be said that the descriptive text is a
meaningful text that describes particular person or animals.
It reveals the experience related to the sense, such as
appearance, shape, sound, taste is. In particular, it is a text
which says what a person or an animal is. Its purpose is to
give a visual picture of person, or animal being described,
such as My favourite teacher; Cockatoo (a specific bird) by
explaining the characteristics, appearance, physical features,
or anything relate to what the writer describes.
b. Social Funtion
- To give information about a particular entity by
describing its features, history, and special
characteristics.
- To give information about things by describing physical
attributes, behaviors, uses, etc.
c. Generic Struture
- Identification or general statements. It introduces or
identifies specific object (a person and animal).
- Descriptions: The parts of a text describe the object
characteristics, appeareances, personality, habits or
qualities
d. Language Features
- Focus on specific participants
- Use present tense
- Use linking verbs or relational process frequently (is, are,
has, have, belongs to)
- Use action verbs or material process and behavioural
process
- Use mental verb or mental process when describing
feelings
- Use nominal group frequently to describe
- Use adjective and adverbs to add information to nouns
and add information to verbs to provide more detailed
description about the topic
- Use adverbial phrases to add more information about
manner, place, or time and sometimes realized
inembedded clause which functions as circumstances
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Reference
LEARNING ACTIVITY 2: DESCRIPTIVE TEXT 2 (THING
AND PLACE)
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
Descriptive text is a meaningful text that describes and reveals
particular thing or place. The purpose of the text to give a visual
picture of a thing, such as my favourite books that describe
specific books.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold and apply religious value,
ethical calues, personal values and social values.
b. Knowledge, to analyze the contextual differences and
similarities between a number of descriptive texts in regard
to the social function, the text structure and the
lexicogrammatical features.
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activites
a. Definition
The description of things and places. It can be said that any
descriptive text is a meaningful text that describes and
reveals particular thing or place. The purpose of the text to
give a visual picture of a thing, such as my favourite books
that describe specific books, or a picture of a tourism place,
such as Komodo National Park by explaining its features,
forms, types, location, or anything related to what the writer
describes. The purpose of the descriptive text is clear, that is
to describe, represent or reveal an object, either abstract or
concrete.
b. Social Funtion
- To give information about a particular entity by
describing its features, history, and special
characteristics.
- To give information about things by describing physical
attributes, behaviors, uses, etc.
c. Generic Structure
- Identification
Identifies phenomenon to be described
- Description
Describes parts, qualities, or characteristics
d. Language Features
- Specific participant
- The use of the adjective (an adjective) to clarify the noun
- The use of simple present tense
- Action verb: verbs that show an activity
- Using passive voice
- Using noun phrase
- Using technical terms
- Using general and abstract noun
- Using conjunction of time and cause-effect
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
5. Key Answer
LEARNING ACTIVITY 3: REPORT TEXT 1 (CLASSIFYING
REPORT AND COMPOSITIONAL REPORT)
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
The term report text is also known as information report. Report
texts organize our experiences of the world for us; they are used to
record, organise, and store information relating to categories of
things.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold and apply religious value,
ethical calues, personal values and social values.
b. Knowledge, to analyze the contextual differences and
similarities between a number of report texts in regard to the
social function, the text structure and the lexicogrammatical
features.
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
There are so many text types that should be learned and
mastered not only by elementary level but also advance level
learners who need studying English. One of the text types is
report. The term report text is also known as information report.
Report texts organize our experiences of the world for us; they
are used to record, organise, and store information relating to
categories of things. Information reports are closely connected
to educational settings and workplaces; in particular, they are a
major vehicle for apprenticing individuals into the discourse
communities connected with science and technology.
b. Social Function
- Classifying report
To organise and describe a field or topic into a class and
subclass hierarchy
- Compositional Repost
To organise and describe a field or topic according to its part
(a part or whole part)
c. Generic Structure
- Title
- General statement
- Description
d. Language Future
- Use simple present tense
- Use action verb
- Use nouns and noun phrases
- Use linking verb
- Desciptive language
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Reference
5. Key Answer
LEARNING ACTIVITY 4: REPORT TEXT 2
(COMPARATIVE REPORT AND HISTORICAL REPORT)
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
Report texts organize our experiences of the world for us; they
are used to record, organise, and store information relating to
categories of things. Information reports are closely connected
to educational settings and workplaces; in particular, they are a
major vehicle for apprenticing individuals into the discourse
communities connected with science and technology.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to uphold and apply religious value, ethical calues,
personal values and social values
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functional, text structure
and lexico-grammatical features
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
Report texts organize our experiences of the world for us;
they are used to record, organise, and store information
relating to categories of things. Information reports are
closely connected to educational settings and workplaces; in
particular, they are a major vehicle for apprenticing
individuals into the discourse communities connected with
science and technology.
b. Social Function
- Comparative Report
To identify the similarities and differences between two
or more classes or things
- Historical Repost
To give information about the way things were in relation
to a particular historical period or site.
c. Generic Structure
On the basis of content, Comparative reports are typically
structured as follows:
- General Statement : It introduces entities to be compared
- Description: It contains the systematic analysis of
similarities and differences
On the other hand, Historical reports are typically structured
as follows:
- General Statement It Identifies historical period or site
And it defines and locates in time and place
- Description
Features or characteristics
Activities
Behaviours
Artefacts
Historical significance
d. Language Features
- Generalised participants are initially represented in simple
noun groups (E.g: Stars and Planets in text 1)
- Relating verbs that link an entity with its attributes
- Timeless present tense (with the exception of an historical
report)
- Attitudinal vocabulary is unusual as the emphasis is on
facts rather on opinions
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
2 Daftar materi 1. Language features of descriptive text
yang sulit
dipahami di
modul ini
3 Daftar materi 1. Types of report text
yang sering
mengalami
miskonsepsi
LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri – Modul 4
Judul Modul ENGLISH FOR ENTERTAINMENT
Judul Kegiatan 1. BIOGRAPHY
Belajar (KB) 2. HISTORICAL RECOUNT
3. FABLES
4. LEGENDS
No Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban
1 Daftar peta LEARNING ACTIVITY 1: BIOGRAPHY
konsep (istilah A. Introduction
dan definisi) di 1. Short Description
modul ini A biography, or simply bio, is a detailed description of a
person's life. It involves more than just the basic facts like
education, work, relationships, and death; it portrays a person's
experience of these life events. and may include an analysis of
the subject's personality.
2. Relevance
3. Learning guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold and apply religious value,
ethical calues, personal values and social values.
b. Knowledge, to analyze the contextual of Biography relevant
to the contexts of situation
2. Sub-Learning Outcomes
3. Learning Materials and Activities
a. Definition
Biographies are the one genre that can open their eyes and
hearts to people who have made a difference in the world.
They can learn about lives and eras of both the past and
present.
b. Function of Biography
To know a person’s story about his / her life outside of any
accomplishments this person may be known for and to give
lots of information easily and to educate the readers.
c. Characteristics of Biography
Biography is not written by subject and is always written in
third person. In other words, biographical texts are not made
by people who are being told their life history, but are told
by other people in the perspective of third people.
d. Grammar and language features
Use of simple past tense.
Temporal sequence and temporal conjunction are used as
s a link between one sentence with another sentence in
chronological order.
Focus on Specific participant In biography
Use of Action verbs. Group of words that describe
something that is actively done by a character.
Vocabularies in Biography Biography is closely related to
the journey of someone’s life.
e. Generic Structure
Orientation (introduction)
Events
Re-orientation (closing)
How to Write a Biographical Article From an Interview
- Choosing Your Subject and Angle
- Preparation and Interviewing Your Subject
- Planning and Drafting Your Article
- Revising and Editing
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
Bibliography
LEARNING ACTIVITY 2: HISTORICAL RECOUNT
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
Historical recount is closely related to the history of a place or
an object which is very memorable and considered important
throughout life. This type of the text is a kind of recount which
explains about the chronological events occurred in the past.
When you want you share your personal experience, then you
are trying to make your personal recount.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Laerning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold and apply religious value,
ethical calues, personal values and social values.
b. Knowledge, to figure out the historical recount in general.
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
Historical recount is concerned with a history of a place or
an object. Historical recount is closely related to the history
of a place or an object which is very memorable and
considered important throughout life. This type of the text is
a kind of recount which explains about the chronological
events occurred in the past.
b. Function of Historical recount
- To describe past historical experiences by retelling
chronological events by involving the important dates,
characters as well as the place of the events.
- To perform all-interpretive aspects in the historical
recount to be able to compile historical synthesis based
on the existence of careful research through the selection
of historical facts.
c. Characteristics of Historical Recount
- Retelling the past historical events
- Upholding the history of a place or an object
- Written scientifically or imaginatively
- Purposing to informing or entertaining (can be both)
d. Generic Structure
- Orientation (introduction)
- Events
- Re-orientation (closing)
e. Grammar and language features
- The participant of historical recount must be specific, it
could involve persons, animals or things)
- The of use correct pronouns referring to the participants
of the text.
- It deals with the use of material processes or actions
verbs.
- It uses some adverb phrased to mention location, manner,
and frequency, such as in the afternoon, carefully, and
never.
- It used the past tense in the sentences because historical
recount tells the readers about past events,
- It also requires the use of adjectives to describe the
objects.
- The use of evaluative words are absolutely needed to
assess the significance of something,
- The historical recount should be focusing on the ordered
events which were signaled by the use of time
connections like after that, ,after, before, finally, etc
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Tests
4. Bibliography
LEARNING ACTIVITY 3: FABLES
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
A fable is a fictional story, poems or prose, with a specific
moral or lesson that is conveyed to the reader.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold, and put into action religious,
moral, and ethical values, integrity, accountability,
independence, tolerance, care, mutual respect, peace, and
collaboration in daily lives.
b. Knowledge, to obtain a number of fable with contextually
different social functions, text structures, and lexico-
grammatical features.
c. Skill
2. Learning materials and Learning activities
a. Description
A fable is a story featuring animals, plants or forces of nature
which are aanthropomorphized (given human qualities). A
fable always ends with a moral value which was intended as
the lesson. This is the lesson that is intended to be learnt
through reading the story. Fables can relate to everyone and
connect us with other culture. They are often passed into our
culture as myths or legends and are used to teach us about
morals.
b. Function of Fables
- To entertain or to amuse the readers about the interesting
story
- To convey moral messages or lessons to the readers,
especially for children to behave morally in the world to
understand the values of the culture in which they are
written.
c. Characteristics of Fable
- Using at least one character makes a bad decision
- Using simple plot and character
- Involving a character who is sly or clever
- Using animals or elements of nature (non-human
characters)
- Containing a moral or lesson which can be found in the
end of the story
- Using personification
- Containing a funny and amusing story
- Reflecting cultural beliefs
d. Generic Structure
- Orientation (introduction)
- Complication
- Resolution
e. Grammar and language features
- Using commn and nonspecific setting
- Often taking place outside
- Using past action verb: Climbed, Turned, Brought
- Using specific noun as pronoun of person, animal in the
story. Example: The king, the queen, etc.
- Using adjectives which are for noun phrase. Example:
Long black, hair, two red apples, etc.
- Using time connectives and Conjunctions to arrange the
events. Examples: Then, before, after, soon, etc.
- Using adverbs and adverbial phrase to show the location
of events. Examples: here, in the mountain, ever after,
etc.
- Using dialogue to elicit an emotional response from the
reader.
- Using Past Tense
- Ending in happy resolution
- Using of variety of simple, compound and complex
sentences
f. Common animal characters used in fables
g. Moral values of the fable
- Persuasion is better than force
- Liars may give themselves away
- Make hay while the sun shines
- Don’t just follow the crowd
- Pride can be costly
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Bibliography
LEARNING ACTIVITY 4: LEGENDS
A. Introduction
1. Short Description
A legend is “a story or narrative that lies somewhere between
myth and historical fact and which, as a rule, is about a
particular figure or person.” Traditionally, a legend is a
narrative that focuses on a historically or geographically
specific figure, and describes his exploits. Similar to a myth, a
legend can provide an etymological narrative, often filling in
historical gaps.
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold, and put into action religious,
moral, and ethical values, integrity, accountability,
independence, tolerance, care, mutual respect, peace, and
collaboration in daily lives.
b. Knowledge, to obtain a number of legend with contextually
different social functions, text structures, and lexico-
grammatical features.
c. Skill
2. Learning materials and Learning activities
a. Definition
A legend is a story about human events or actions that has
not been proved nor documented in real history. Legends are
retold as if they are real events and were believed to be
historical accounts. Legend can relate to everyone and
connect us with other culture. They are often passed into our
culture as myths or legends and are used to teach us about
morals. Legends are about people and their actions or deeds.
The people lived in more recent times and are mentioned in
history.
b. Function of Legend
- To present the story of human actions in such a way that
they are perceived by the the listeners or readers to be
true (in literature).
- To entertain or to amuse the readers about the interesting
story (in general)
c. Characteristics of Legend
- A legend is a set in specific place or time
- The main character is often heroic
- The main character is a human, not a God
- A legend is a fictional story Usually there is some
historical truth at the heart of every legend
- Heroes perform great deeds with their strength and their
intelligence. Exaggeration is usually involved in retelling
deeds.
- Heroes often give up dreams of happiness to help others
Legend
- The hero is real but some parts of the story are not
completely true. They have been stretched or expanded
upon.
- Handed down through generation
- The story was told orally and turned into literary
masterpieces
d. Generic Structure
- Orientation (introduction)
- Complication
- Resolution
- Re-orientation
e. Grammar and language features
- The use of Adjective that form the noun phrase.
- Time connectives and conjunction.
- The use of adverb and adverbial phrases to indicate the
location of the incident or events.
- The use of action verbs in the past tense.
- The used of saying verbs that mark remarks.
- The use of thinking verbs.
- The use of dialogue to elicit an emotional response from
the reader
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. Bibliography
2 Daftar materi 1. Written in formal language
yang sulit 2. Written in chronological order
dipahami di
modul ini
3 Daftar materi 1. Social function and the aims of Biographi
yang sering 2. Wether historical recount is fiction or a history
mengalami
miskonsepsi
LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri – Modul 5
Judul Modul ENGLISH FOR PRACTICAL USE
Judul Kegiatan 1. PROCEDURE TEXT (MANUAL)
Belajar (KB)
2. PROCEDURE TEXT (RECIPE)
3. PROCEDURE TEXT (ITINERARY)
4. NEWS ITEM
No Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban
1 Daftar peta LEARNING ACTIVITY 1: PROCEDURE TEXT (MANUAL)
konsep (istilah A. Introduction
dan definisi) di 1. Short description
modul ini 2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold, and put into action religious,
moral, and ethical values, integrity, accountability,
independence, tolerance, care, mutual respect, peace,
collaboration, and nationalism
b. Knowledge, to analyse the contextual differences and
similarities between a number of Procedure texttexts in
regard to the social functions, by showing the evidence from
the texts (expressions, sentences, paragraphs, etc) in fluent
and lexicogrammatically accurate spoken and written
English.
c. Skill
2. Learning Material and learning activities
a. Definition
What is procedure text?
Procedure text is a text that explains or helps us how to
make or to use something.
What is Manual?
Manual alternatively referred to as documentation or end-
user documentation, a manual is a book or pamphlet that
contains information about a program or piece of
hardware. For example, a computer case may come with
documentation explaining what sizes of motherboard it
can hold. Or, a video game may come with a manual
explaining how to play it.
b. Social Function of Manual as A type of Procedure Text
- It is used to describe how something is done in
sequenced steps.
- It provides a series of steps in sequence that explain the
readers how to do something while allowing them to
reach the outcome successfully.
- The communicative purpose of the text is to tell the steps
of making or doing something
c. Generic Structure of Manual
- Goal/aim.
- Materials/equipments
- Steps/methods.
d. Significant Lexico-grammatical Features
- Generally using simple present tense.
- Using adverbial of sequence or using temporal adjective.
- Using imperative sentences or command.
- Using action verbs.
- Using conjunctions to link a process to another process.
- Using adverb of time to express details of time.
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. References
4. Formative Test
LEARNING ACTIVITY 2: PROCEDURE TEXT (RECIPE)
A. Introduction
1. Short description
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
a. Pre-activity, building background knowledge about
procedure texts.
b. Main activity, Many activities encourage understanding and
enjoyment while you are comprehending the materials about
procedure texts.
c. Post-activity, Questioning, Discussion, Creating, and
Presenting.
B. Main Section
1. Learning outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold, and put into action religious,
moral, and ethical values, integrity, accountability,
independence, tolerance, care, mutual respect, peace,
collaboration, and nationalism
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functions, text structures,
and lexico-grammatical features of procedure text in regard
to the contexts of situation.
c. Skill
2. Learning Material and learning activities
a. Definition of Recipe
Procedure text is the text which gives the steps or procedures
on how to do something. Generally speaking, a recipe is a
list of ingredients and a set of instructions that tell you how
to cook something. In procedure texts the focus is on
systemically explaining a logal sequence of action or steps.
There are some different procedure texts serving different
purposes. Recipe is one of the common procedural texts. A
recipe is a list of ingredients and a set of instructions that tell
you how to cook something. A recipe is usually divided into
ingredients and methods. Each stage plays a role in
explaining what we need or what precisely we have to do
next.
b. Generic Structure of Recipe
- Goal/aim
- Ingredients
- Steps/Method
c. Social/Language Function of Recipe
- Recipe is used to describe how food is completely made
or cooked through a sequence of series.
- Communicative purpose of recipe is to describe how
food is completely made through a sequence of actions
or steps.
d. Language Features of Recipe
- Noun or noun groups
- Conjunctions
- Action verbs
- Imperatives
- Adverbial
- Vocabulary
- The language in recipe is supposed to be clear and
precise.
- Present tense is generally used in recipe.
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
5. Answer Key
LEARNING ACTIVITY 3: PROCEDURE TEXT (ITINERARY)
A. Introduction
1. Short description
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
a. Pre-activity, building background knowledge about itinerary.
b. Main activity, Many activities encourage understanding and
enjoyment while you are comprehending the materials about
itinerary.
c. Post-activity, Questioning, Discussion, Creating, and
Presenting.
B. Main Section
1. Learning outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold, and put into action religious,
moral, and ethical values, integrity, accountability,
independence, tolerance, care, mutual respect, peace,
collaboration, and nationalism
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functions, text structures,
and lexico-grammatical features in regard to the contexts of
situation.
c. Skill
2. Learning Material and learning activities
a. Definition
Itinerary can be defined as a route or plan or guide book of
travel. It usually contains any information dealing with travel
or journey such as schedule of visit (vacation), time, dates,
transportation, and other information. Itinerary is defined as
a schedule of events relating to a planned travel which is
generally including destinations to be visited at a specified
time and the means of transportation to move between those
destinations.
b. Generic Structure
c. Social/ language function
- To make a well-prepared program or travel
- To make an effective journey or travel
- To be a guideline in spending time during travelling
d. Language Features
- Use simple present tense
- Use action verb
- Use simple sentence or phrase
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
5. Answer Key
LEARNING ACTIVITY 4: NEWS ITEM
A. Introduction
1. Short description
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
a. Pre-activity, building background knowledge about news
item texts.
b. Main activity, many activities encourage understanding and
enjoyment while you are comprehending the materials about
news item texts.
c. Post-activity, Questioning, Discussion, Creating, and
Presenting.
B. Main Section
1. Learning outcomes
a. Attitude, to internalize, uphold, and put into action religious,
moral, and ethical values, integrity, accountability,
independence, tolerance, care, mutual respect, peace,
collaboration, and nationalism
b. Knowledge, to analyze the social functions, text structures,
and lexico-grammatical features in regard to the contexts of
situation.
c. Skill
2. Learning Material and learning activities
a. Definition of News Item Text
News item text is a text that tells the readers, listeners or
viewers about events of the day. The events in news item
text should be considered newsworthy or important. News
item is one example of authentic materials that can be used
in teaching and learning process. Through news item text
students can be easily enganged with the materials because
they are viewing articles and news that are happening around
them. Additionally, the authentic nature of the material
presents a broad spectrum of vocabulary and sentence
structures.
b. Generic Structure of News Item
- Main Events / Newsworthy event(s)
- Elaboration / Background event(s)
- Resource of Information (Source).
c. Social/Language Function of News Item
The social function of news item text is to inform the
readers, listeners or viewers about newly received or
noteworthy information, especially about recent or important
events.
d. Language Features of News Item
- Using action verbs
- Using saying verb
- Using passive voice
- Using adverb
- Using Past tense in explaining news events. But if it is a
fact that until now still happen or still in the form of fact,
then can use simple present tense.
- The language in news item is supposed to be clear and
precise.
3. Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
5. Answer Key
2 Daftar materi 1. Generic structure of itinerary
yang sulit
dipahami di
modul ini
3 Daftar materi 1. Social Function of itinerary
yang sering
mengalami
miskonsepsi
LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri – Modul 6
Judul Modul ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC CONTEXT
Judul Kegiatan 1. ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION TEXTS
Belajar (KB) 2. HORTATORY EXPOSITION TEXTS
3. EXPLANATION TEXTS
4. DISCUSSION TEXT
No Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban
1 Daftar peta LEARNING ACTIVITY 1: ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION
konsep (istilah TEXTS
dan definisi) di A. Introduction
modul ini 1. Description
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude
b. Knowledge
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
Analytical Exposition belongs to argumentative texts.
Through this type of texts, the writer/speaker elaborates
his/her idea about the phenomenon surrounding. His/her
purpose is to convince the audience that his/her idea is an
important matter.
b. Generic Structures
- Thesis: Introducing the topic and indicating the writer‘s
point of view.
- Argument: Explaining the argument to support the
writer‘s position. The number of arguments may vary,
but each argument must be supported by evidence and
explanation.
- Reiteration: Restating the writer‘s point of view / to
strengthen the thesis. We can make conclusion in
reiteration.
c. Social Function
An Analytical Exposition is intended by the writer/speaker:
To convince the audience that his/her idea is an important
matter.
d. Language Features
Grammatical points that are most often used:
- Use of internal conjunction
- Use of causal conjunction
- Use of the Simple Present Tense
- Use of relational process
- Use of compound and complex sentences
- Use of words that link argument
Vocabulary
Pronunciation
Common expressions Expressions
- The following are the reasons why….. / ðə ˈfɒl.əʊ.ɪŋ ər
ðə ˈriː.zən waɪ/
- Based on the arguments above, …… /beɪst ɒn ðə
ˈɑːgjʊmənts əˈbʌv/
Discussion Forum
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
5. Answer key
LEARNING ACTIVITY 2: HORTATORY EXPOSITION
TEXTS
A. Introduction
1. Description
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude
b. Knowledge
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
Hortatory Exposition belongs to argumentative texts. In this
type of texts, the writer/speaker includes several opinions
about certain things to strengthen the main idea of the text.
Hortatory Exposition proposes recommendations as the
concluding paragraph. The writer/speaker influences the
reader that something should or should not be the case or be
done.
b. Generic Structure
A Hortatory Exposition consists of three main components:
Thesis: Statement or announcement of concerned issue.
Arguments: Reasons for concern that will lead to
recommendation.
Recommendation: Statement of what should or should not
happen or be done based on the given arguments.
c. Social Function
A Hortatory Exposition is intended by the writer/speaker: To
persuade the audience that something should or should not
be the case or be done.
d. Language Features
Grammatical points that are typical of this text type:
- Use of The Simple Present Tense
- Use of passive sentences
- Use of modals and adverb: certainly, surely, etc.
- Use of subject pronoun (e.g. I and we)
- Use of temporal connectives an causal connectives
- Use of evaluative language
Mini-Dictionary [Vocabulary]
Common Expressions
- The following are the reasons why….. /ðə ˈfɒl.əʊ.ɪŋ ər
ðə ˈriː.zən waɪ/
- Based on the arguments above, … /beɪst ɒn ðə
ˈɑːgjʊmənts əˈbʌv/
- I think we should …
- …is important to …
- It could be argued that …
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
5. Answer key
LEARNING ACTIVITY 3: EXPLANATION TEXTS
A. Introduction
1. Description
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude
b. Knowledge
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
Texts. Explanation texts can be said as one of the most
complicated types as they could be a combination of other
text types such as descriptive text, procedure text, and
argumentative texts. Explanations detail and logically
describe the stages in a process, such as the rainbow, or how
a car engine works. Quite often, especially in its written
version, this text type appears with a picture complement to
support clarity.
b. Generic Structure
General statement; stating the phenomenon issues which
are to be explained.
Sequenced explanation; stating a series of steps which
explain the phenomena.
Concluding statement.
c. Social Function
An Explanation Text is intended by the writer/speaker: To
explain the audience how and why something works or
happens.
d. Language Features
The grammatical points that are typical of this text type:
- Use of passive voice pattern
- Use of the Simple Present Tense
- Use of technical terms
- Use of words that show cause and effect
- Use of abstract noun
- Use of action verb
- Use of noun phrases
Mini-Dictionary [Vocabulary]
Common Expressions
- For example /fɔːr ɪgˈzɑːmpl/
- These include /ðiːz ɪnˈkluːd/ For instance / fɔːr
ˈɪnstəns/
- As shown by … /æz ʃəʊn baɪ/…
- … Such as … … /sʌʧ æz/; /sʌʧ əz/
- On the other hand, … /ɒn ði ˈʌðə hænd/, …
- Including ….. /ɪnˈkluːdɪŋ/ …..
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
5. Answer key
LEARNING ACTIVITY 4: DISCUSSION TEXT
A. Introduction
1. Description
2. Relevance
3. Learning Guide
B. Main Section
1. Learning Outcomes
a. Attitude
b. Knowledge
c. Skill
2. Learning Materials and Learning Activities
a. Definition
Discussion text is a text which presents a problematic
discourse. This problem is discussed from different points of
view. It presents pro and contra opinion on certain issue.
b. Generic Structure
General statement to introduce the audience to the topic
of discussion – it can include a question and the view of
the author can be expressed here (called the discussion‘s
thesis)
A series of paragraphs that have points for and against the
topic – the text may have paragraphs on the for side
followed by paragraphs on the against side, and within the
paragraphs there should be evidence to support the point
of view.
A concluding paragraph that sums up the discussion and
gives the opinion of the author of the text.
c. Social Function
A Discussion Text is intended by the writer/speaker to
present (at least) two points of view about issue or problem;
to present arguments from differing points of view about
issue or problem.
d. Language Features
The grammatical points that are typical of this text type:
- Use of the Simple Present Tense
- Use of medium to high degrees of modality.
- Use of quoted and reported speech to support
arguments.
- Use of passive voice to change focus of sentences.
- Focus on beginning of sentences.
- Use of complex combination of clauses.
- Use of complex sentences.
Mini-Dictionary [Vocabulary]
Common Expressions
- Let's begin/start with ... /lets bɪˈɡɪn/; / lets stɑːt wɪð/ /
- This might mean /ðɪs maɪt miːn/
- Some people say /sʌm ˈpiː.pəl seɪ/
- Others argue /ˈʌðəz ˈɑːgjuː/
- On the one hand,…/ɒn ðə wʌn hænd/
- As far as I'm concerned,… /æz fɑːr æz aɪm kənˈsɜːnd/
- I think /aɪ θɪŋk/
- In my opinion,… /ɪn maɪ əˈpɪnjən/
- As far as I know,… /æz fɑːr æz aɪ nəʊ/
- In my view /ɪn maɪ vjuː/
C. Closing Section
1. Summary
2. Reflection
3. Formative Test
4. References
5. Answer key
2 Daftar materi 1. Make an argument and supported argument
yang sulit 2. Complex combination of clauses
dipahami di
modul ini
3 Daftar materi 1. Social function of analytical exposition texts and Hortatory
yang sering Exposition Text
mengalami
miskonsepsi
You might also like
- Artificial Intelligence High Technology PowerPoint TemplatesDocument48 pagesArtificial Intelligence High Technology PowerPoint Templatesaswin100% (1)
- Madeline Decker - Ci 403 - Just Mercy Unit Lesson PlansDocument35 pagesMadeline Decker - Ci 403 - Just Mercy Unit Lesson Plansapi-355737575No ratings yet
- 5 ThesisStatementDocument70 pages5 ThesisStatementJohn Tristan Miguel AlairNo ratings yet
- Module Graphic OrganizerDocument11 pagesModule Graphic OrganizerrobertoNo ratings yet
- Steam Education PowerPoint TemplatesDocument48 pagesSteam Education PowerPoint TemplatesRobi IlhamNo ratings yet
- DLL in Mil 4.27.23Document4 pagesDLL in Mil 4.27.23Glenn PrestozaNo ratings yet
- M2 Empowerment TechnologyDocument36 pagesM2 Empowerment TechnologyJohn keyster Alonzo67% (3)
- Lesson 1:: The Arts in Computer-Generated Images and Handheld Mobile DevicesDocument41 pagesLesson 1:: The Arts in Computer-Generated Images and Handheld Mobile DevicesAngelo Liwanag100% (2)
- Ericca Garrison DMGT 706Document189 pagesEricca Garrison DMGT 706reginarowlandNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriDocument6 pagesLK 1 - Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiriwayansomadana34No ratings yet
- Modul 1 Profesional PPG Bahasa InggrisDocument18 pagesModul 1 Profesional PPG Bahasa InggrisSiti NurzulianaNo ratings yet
- LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: Judul Modul English For Public Information Judul Kegiatan Belajar (KB)Document4 pagesLK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: Judul Modul English For Public Information Judul Kegiatan Belajar (KB)Goris FarisiNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Modul I English For Public InformationDocument4 pagesLK 1 Modul I English For Public InformationAnto BuddyNo ratings yet
- Nur Annisa MR - LK - 1.modul 1 Profesi - Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesNur Annisa MR - LK - 1.modul 1 Profesi - Bahasa InggrisNur Annisa Mei RizkiNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 1Document6 pagesLK 1 - Modul 1oyongNo ratings yet
- LK 1.1 Modul Profesional 1 Bahrul AlamDocument5 pagesLK 1.1 Modul Profesional 1 Bahrul AlamBahrul AlamNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 - Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul1 Yerni Hida SiagianDocument31 pagesLK 0.1 - Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul1 Yerni Hida SiagianYerni Hida SiagianNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri English For Public InformationDocument3 pagesLK 0.1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri English For Public InformationAna AthiyahNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Williantika RahayuDocument5 pagesLK 1 - Williantika RahayuWilliantika RahayuNo ratings yet
- Eneng Siti Fatonah LK 1 Modul 1 ProfesionalDocument5 pagesEneng Siti Fatonah LK 1 Modul 1 ProfesionalSiti FatonahNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Modul 1 English For Public InformationDocument7 pagesLK 1 Modul 1 English For Public Informationjauhar muttaqinNo ratings yet
- LK 1.1 MODUL 1 - Ajeng Dewi WulandariDocument5 pagesLK 1.1 MODUL 1 - Ajeng Dewi WulandariPetrichorNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 NURMI LELI Modul 1-6 PROFESIONALDocument51 pagesLK 0.1 NURMI LELI Modul 1-6 PROFESIONALNurmi LeliNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Profesional English For Public InformationDocument4 pagesLK 1 - Profesional English For Public InformationAnto Buddy100% (1)
- LK 0.1 Modul 1 Bahasa Inggris - Frian SaputraDocument5 pagesLK 0.1 Modul 1 Bahasa Inggris - Frian SaputraFrian SaputraNo ratings yet
- LK 1 ProfesionalDocument24 pagesLK 1 ProfesionalLheni MeilanNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 1 English For Public Infomation - 201506473786 Syamsul BahriDocument6 pagesLK 1 - Modul 1 English For Public Infomation - 201506473786 Syamsul Bahriabu Hanifah100% (1)
- LK 1 - Profesional - Bahasa Inggris - Modul 1Document5 pagesLK 1 - Profesional - Bahasa Inggris - Modul 1adi100% (2)
- LK 0.1 - ProfesionalDocument24 pagesLK 0.1 - ProfesionalYulia Nur IstiqomahNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Modul 1Document4 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Modul 1Angyar SulaemanNo ratings yet
- LK.1.1 Modul 1-6 (Profesi) - Misna NurbaytiDocument31 pagesLK.1.1 Modul 1-6 (Profesi) - Misna NurbaytiMisna Noerbayti100% (1)
- Modul 1 ProfesionalDocument3 pagesModul 1 ProfesionalSiti HartatikNo ratings yet
- LK 1.1 Modul 1 Prof Edit RikaDocument5 pagesLK 1.1 Modul 1 Prof Edit RikaNila FermitaNo ratings yet
- LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: Modul Profesional 1Document5 pagesLK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: Modul Profesional 1ainul yaqinNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 1 ProfesionalDocument5 pagesLK 1 - Modul 1 ProfesionalAbdul KarimNo ratings yet
- LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriDocument4 pagesLK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriFenny IndrianiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 - Utami Fauziyah - Bahasa Inggris - 002Document77 pagesLK 0.1 - Utami Fauziyah - Bahasa Inggris - 002Utami FauziyahNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Modul 1Document6 pagesMindmap Modul 1Iyut PitrianyNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri Aniza PuspitaDocument9 pagesModul 1 LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri Aniza PuspitaAniza PuspitaNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Profesional Modul 1Document5 pagesLK 0.1 Profesional Modul 1Devi Eva FianyNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri LK. 01 Modul 1 NurlailaDocument7 pagesTugas Mandiri LK. 01 Modul 1 NurlailaNurlaila 1234No ratings yet
- LK Profesional 1&2 - Atikah RosminiDocument8 pagesLK Profesional 1&2 - Atikah Rosminiatikah rosminiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 - Modul 1 - Fitri Maulidiyani - Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesLK 0.1 - Modul 1 - Fitri Maulidiyani - Bahasa InggrisFitri MaulidiyaniNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 PPG Bahasa InggrisDocument9 pagesLK 0.1 PPG Bahasa InggrisAnnah SwanNo ratings yet
- LK-1-Modul 1 - Profesional - Medi Heri SaputraDocument11 pagesLK-1-Modul 1 - Profesional - Medi Heri Saputramedyputra100% (1)
- LK 0. 1 - Profesional-Modul 1Document4 pagesLK 0. 1 - Profesional-Modul 1KESMAS KUYNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Profesional English For Personal CommunicationDocument3 pagesLK 1 - Profesional English For Personal CommunicationAnto BuddyNo ratings yet
- No Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban Learning Activity 1 (Exploring Public Notice)Document7 pagesNo Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban Learning Activity 1 (Exploring Public Notice)Win_die88No ratings yet
- LK 1.1 Modul 1 ProfesionalDocument3 pagesLK 1.1 Modul 1 ProfesionalDwi WahyuniNo ratings yet
- LK 1-Modul 1Document5 pagesLK 1-Modul 1mita mustikaNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Profesional Modul 1Document49 pagesLK 0.1 Profesional Modul 1Yundi NenohaiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Profesional Dan Pedagogik - Hemin Yundi Mus NenohaiDocument49 pagesLK 0.1 Profesional Dan Pedagogik - Hemin Yundi Mus NenohaiYundi NenohaiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 MODUL 1 Bhs InggrisDocument9 pagesLK 0.1 MODUL 1 Bhs InggrisArieNo ratings yet
- Dwi LK 1 - Modul 1 PrefesionalDocument5 pagesDwi LK 1 - Modul 1 PrefesionalIKHWANNUL IHSANNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Profesional Modul 1Document6 pagesLK 1 Profesional Modul 1Farra PramitaNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 1 PrefesionalDocument5 pagesLK 1 - Modul 1 PrefesionalTaufik AnsyariNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul 1 ProfesionalDocument5 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul 1 ProfesionalErma Ardy WijayantiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 - Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - YAYAH ASIAH NDocument19 pagesLK 0.1 - Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - YAYAH ASIAH NSMPN 3 cikarangpusatNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 1Document5 pagesLK 1 - Modul 1Hani WahyuniartiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 MODUL PROFESIONAL 1 - Arina Silfiyati RohimahDocument14 pagesLK 0.1 MODUL PROFESIONAL 1 - Arina Silfiyati RohimahArina Silfiyati RohimahNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Modul 1Document7 pagesLK 1 Modul 1Kholied MawardiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 - Modul1Document7 pagesLK 0.1 - Modul1muhalib alibNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri Modul Bahasa Inggris 1 Tedi KurniawanDocument8 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri Modul Bahasa Inggris 1 Tedi KurniawanKoko KurniaNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Profesional (Modul 1)Document6 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Profesional (Modul 1)Marwani umarNo ratings yet
- Profesional - Modul 1Document6 pagesProfesional - Modul 1agustina kurnianingsihNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul1Document12 pagesLK 1 - Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri-Modul1Tulip Yuni Rosyani PutriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Group 3Document29 pagesLesson 12 Group 3BASTASA PAULONo ratings yet
- Using Charts and Graphs in The Classroom: Visual Effects and Data InterpretationDocument25 pagesUsing Charts and Graphs in The Classroom: Visual Effects and Data InterpretationaeidazahiliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6: Modeling, Evaluation, and VisualizationDocument14 pagesLecture 6: Modeling, Evaluation, and VisualizationGabrielle Joshebed AbaricoNo ratings yet
- How Valuable Is Company's Data?: What Is Business Intelligence?Document26 pagesHow Valuable Is Company's Data?: What Is Business Intelligence?Arindam MondalNo ratings yet
- Empowerment TechnologiesDocument5 pagesEmpowerment TechnologiesMIRISH FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Chipinge and Chimanimani Evaluation Report PDFDocument54 pagesChipinge and Chimanimani Evaluation Report PDFtendai EngromNo ratings yet
- Jungle TemplateDocument38 pagesJungle TemplatevladymirNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Science - QuoraDocument15 pagesWhat Is Data Science - Quorabksreejith4781No ratings yet
- Plantilla Powerpoint de VacaDocument44 pagesPlantilla Powerpoint de Vacaangel7293No ratings yet
- Data and Information VisualizationDocument27 pagesData and Information Visualizationcharlotte899No ratings yet
- English8 q2 Mod3 CompareandContrastSameTopicinDifferentMultimodalTexts v2Document26 pagesEnglish8 q2 Mod3 CompareandContrastSameTopicinDifferentMultimodalTexts v2Ma'am CharleneNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Tech 12 Week 3 - 4Document18 pagesEmpowerment Tech 12 Week 3 - 4Kenjie JaboneroNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technology: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document20 pagesEmpowerment Technology: Quarter 1 - Module 1Kian Junsay Tan100% (1)
- Unit 3 - Economies As Social SystemsDocument9 pagesUnit 3 - Economies As Social SystemsHannah CuerdoNo ratings yet
- Future Dusk Portfolio by SlidesgoDocument40 pagesFuture Dusk Portfolio by SlidesgoNATALIA ALSINA MARTINNo ratings yet
- Q4 Module 3Document20 pagesQ4 Module 3Krd lyricNo ratings yet
- At The End of The Session, The Students Are Expected ToDocument25 pagesAt The End of The Session, The Students Are Expected ToRYSON ARMADA100% (1)
- Group 2 - Group Discussion - Introduction To Data AnalyticsDocument20 pagesGroup 2 - Group Discussion - Introduction To Data AnalyticsTiara Indah SariNo ratings yet
- BSCADocument39 pagesBSCAROOMA SALEEMNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 InfographicDocument3 pagesGrade 5 Infographic1030246No ratings yet
- HALT130-1-Jan-Jun2019-FA2 Memo-CD-V.5-05032019Document14 pagesHALT130-1-Jan-Jun2019-FA2 Memo-CD-V.5-05032019obanguestfarmNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Organizational StructureDocument5 pagesDissertation On Organizational StructureBuyPapersOnlineBaltimore100% (1)
- Y1b4vrjwr - Week 22 - English 7Document6 pagesY1b4vrjwr - Week 22 - English 7alvaran jillianNo ratings yet