Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mil Reviewer
Mil Reviewer
Uploaded by
aldrin josephOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mil Reviewer
Mil Reviewer
Uploaded by
aldrin josephCopyright:
Available Formats
MIL REVIEWER THE DANGER OF DESENSITIZATION
WHAT IS DESENSITIZATION?
What is COMMUNICATION?
DOES IT STILL MAKE A SOUND? DESENSITIZATION
The gift of BEING HEARD! ● To react less.
● To be less affected.
COMMUNICATION ● To be less sensitive.
● From the latin term communicare, which means “to share”
or “to impart” or from the latin word communis, which NORMALIZATION - is when the mass media continually
roughly means “working together.” reinforce certain behavioral patterns of exposure until they
become automatic habit.
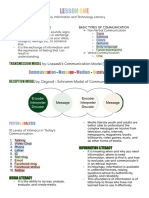
Communication Process Through Models
TRANSMISSION MODEL AUTOMATICITY - it is a state where our minds operate
● representation of communication as an attempt to answer without a conscious effort from us.
the question “Who says what to whom, through what
medium, and with what effect?” When we are emotionally desensitized, we reach our empathy
● Relatively straightforward. limit.
RITUAL OR EXPRESSIVE MODEL DESENSITIZATION
● the communication is ritualized because the meaning is To not experience an emotional response to something after
suggested more than explicitly stated and the repeated exposure to it.
understanding of it, though connotative, is mutual.
“EVERYTHING THAT IS REPETITIVE EVENTUALLY
PUBLICITY MODEL LOSES ITS POWER”
● the communication involves audiences as “spectators”
rather than participants or information receivers. MOVIE AND TELEVISION REVIEW AND
● Attention is the measure of how successful the CLASSIFICATION BOARD (MTRCB)
communication has transpired. Mission: To encourage value-based media and entertainment
culture
RECEPTION MODEL
● communication as an open process, which means that Vision: To provide age-appropriate media as an indispensable
messages sent and received are open to various tool for moral recovery and nation building
interpretations based on context and the culture of the
receiver. MEDIA CRITERIA MEDIA RATINGS
● Encoder - produces and sends messages T - Theme ● RATED G
● RATED PG
● Decoder - receives and interprets messages L - Language ● RATED SPG
N - Nudity
MEDIA S - Sex ● RATED G
● The main ways that large numbers of people receive V - Violence ● RATED PG
● RATED 13
information and entertainment that is internet, newspapers, H - Horror ● RATED 16
periodicals, magazines, journals, billboards, film. D - Drugs ● RATED 18
● Means of distributing texts and messages to a large mass
of people. “G” or GENERAL AUDIENCE● RATED–XSuitable for all ages. Does
not contain anything unsuitable for children, and safe to be
INFORMATION viewed without adult guidance or supervision.
● As a broad term that can cover data, knowledge derived
from study, experience, or instruction, signals or symbols. “PG” or PARENTAL GUIDANCE – Parental Guidance may
contain some adult material but may be permissible for children
LITERACY to watch under the guidance and supervision of a parent or an
● Equivalent to a skill adult.
● Ability to identify, understand, interpret, create, and
communicate using printed and written materials “SPG” or STRONG PARENTAL GUIDANCE – May
associated with varying contexts. contain more serious topic and theme. May not be advisable for
children to watch thus requiring greater parental responsibility.
WHAT IS OUR SUBJECT ALL ABOUT?
MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY Age-verification process:
G - no need for age-verification
MEDIA LITERACY PG - patron below 13 years old should be accompanied by a
● When you understand and use various media forms to responsible adult
access information, you consider yourself media literate. R -13 - no patron below 13 years old
R -16 - no patron below 16 years old
R -18 - no patron below 18 years old
RATED X - not for public exhibition.
INFORMATION LITERACY 8 TYPOLOGY OF MEDIA LITERACY
● Able to recognize when information is needed and to LANDI ECS
locate, evaluate, effectively use, and communicate it in its
various formats. ACQUIRING FUNDAMENTALS
● There are other people and physical entities aside from one
TECHNOLOGY LITERACY self.
● Able to utilize different “digital technology, LANGUAGE ACQUISITIONS
communication tools or networks to locate, evaluate, use, ● Recognizing speech sounds, signs, symbols, and gestures.
and create information.”
NARRATIVE ACQUISITIONS
● Recognizing the difference between fiction and non-
fiction.
DEVELOPING SKEPTICISM
Discounting claims in ads.
Psychological Pricing
Charm/Odd Pricing
Charm Pricing/ Odd Pricing - This involves using pricing that
ends in 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. In charm pricing, the left digit is
reduced from a round number by one percent.
BOGOF
BUY ONE GET ONE FOR FREE - this is the pricing strategy
in which customers pay the full price for one product or service
to get another for free.
Comparative Pricing
Comparative Pricing - Placing expensive next to standard. It is
tagged as the most effective psychological pricing strategy. This
is simply involves offering two similar products simultaneously
but making one product’s price much more attractive than the
other.
Discount Pricing
Discount Pricing - The strategy where you mark down the
prices of your merchandise. The goal of a discount pricing
strategy is to clear old inventory from your business and
increase sales.
Prestige Pricing
Prestige Pricing - it is the complete opposite of odd or
charming pricing because it involves making all numerical
values into rounded figures. It will give a sense of superiority to
the product.
INTENSIVE DEVELOPMENT
● Strongly motivated to seek out information that you are
skeptic about.
EXPERIENTIAL EXPLORING
● Strongly motivated to seek out different contents and
narratives.
● You are finding your interest.
CRITICAL APPRECIATION
● Accepting messages on their own terms then evaluating
them within that sphere.
● Processing and articulating the message.
SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
● Taking a moral stand.
● Believing that the message you will give can make a
constructive impact on society.
You might also like
- Computer Systems Servicing Week 5 and 6Document39 pagesComputer Systems Servicing Week 5 and 6aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Computer System Servicing - Week 2Document32 pagesModule 2 - Computer System Servicing - Week 2aldrin joseph100% (1)
- Pulling The Plug On The Car Industry The Dismal State of Germany's Army Debt On The Nile How To Conduct A Sex SurveyDocument88 pagesPulling The Plug On The Car Industry The Dismal State of Germany's Army Debt On The Nile How To Conduct A Sex SurveyEconomist MagazineNo ratings yet
- MODULE-3 - Computer System Servicing Week 3Document45 pagesMODULE-3 - Computer System Servicing Week 3aldrin joseph100% (3)
- DIAGNOSTIC TEST Contemporary WorldDocument2 pagesDIAGNOSTIC TEST Contemporary Worldaldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Creatve Writing Module Week 2Document9 pagesCreatve Writing Module Week 2aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Module 5-6 Empowerment Technology-Week 5 - 6Document27 pagesModule 5-6 Empowerment Technology-Week 5 - 6aldrin joseph100% (9)
- Sdoquezon Adm SHS11 Abm BM M3 PDFDocument29 pagesSdoquezon Adm SHS11 Abm BM M3 PDFaldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Dona Adela Export v. TIDCORPDocument2 pagesDona Adela Export v. TIDCORPLili MoreNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet PDFDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet PDFaldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument3 pagesPerformance Task in Statistics and Probabilityaldrin joseph100% (2)
- ORAL-COMMUNICATION Module Week 2Document14 pagesORAL-COMMUNICATION Module Week 2aldrin joseph100% (3)
- Solution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th by ArensDocument15 pagesSolution Manual For Auditing and Assurance Services 17th by ArensMarsha Johnson100% (31)
- 5443 Global Supply Chain ManagementDocument22 pages5443 Global Supply Chain Managementdouglas gacheru ngatiiaNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 4: Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumDocument14 pagesProf Ed 4: Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumApril Jay BacalaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Issues in Accounting: Solution ManualDocument17 pagesContemporary Issues in Accounting: Solution ManualDamien SmithNo ratings yet
- Mil Weel 3-4Document14 pagesMil Weel 3-4NOEMI AMADORNo ratings yet
- A-Detailed-Lesson-Morales AppetizerDocument6 pagesA-Detailed-Lesson-Morales Appetizeraldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Slaughter House Rs. 237.20 Million Feb-2021Document21 pagesSlaughter House Rs. 237.20 Million Feb-2021Saeed AkhtarNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION Week 5 And6Document10 pagesPURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION Week 5 And6aldrin joseph100% (1)
- GEC-PC Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesGEC-PC Midterm ReviewerSarah Mae EmbudoNo ratings yet
- MIL RevDocument7 pagesMIL Revsydneyroxas03No ratings yet
- 1stq Mil NotesDocument18 pages1stq Mil NotesJim Adrian FloresNo ratings yet
- Clientele and Audiences in CommunicationDocument17 pagesClientele and Audiences in CommunicationGalpo, Timothy John PabalanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 13 Professionals and Practitioners in CommunicationDocument30 pagesLesson 13 Professionals and Practitioners in CommunicationPauline Mae PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Resto CommunicationDocument4 pagesResto Communicationaaron villatuyaNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument6 pagesMIL ReviewerConsificGamingNo ratings yet
- SICRITDocument26 pagesSICRITShann Brenan DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument20 pagesBusiness Communicationphyothantaung1231No ratings yet
- Medinfolit 1Document7 pagesMedinfolit 1JASIS JULIA NOELYN V.No ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument10 pagesPurposive CommunicationMa. Cristina GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral ComDocument2 pagesReviewer in Oral ComMarjorie PabloNo ratings yet
- CALP FocusDocument14 pagesCALP FocusArham ShahNo ratings yet
- MIL PresentationDocument56 pagesMIL PresentationAgent 47No ratings yet
- Purposive CmmunicationDocument10 pagesPurposive Cmmunicationno nameNo ratings yet
- Skill Set For Engineers: By: Prof. Mayur M.Sevak & DR - Darshan DalwadiDocument67 pagesSkill Set For Engineers: By: Prof. Mayur M.Sevak & DR - Darshan Dalwadipatel JeetNo ratings yet
- PurpComm Lesson 1 5 DoneDocument16 pagesPurpComm Lesson 1 5 DoneErain Angellie LatayNo ratings yet
- Communication in Extension New Version Final Na NiiiiiiiiiiiDocument38 pagesCommunication in Extension New Version Final Na NiiiiiiiiiiiNancy Mercado AglionesNo ratings yet
- Notes For MITL (Lesson 1)Document2 pagesNotes For MITL (Lesson 1)Nicolette Dream GreenNo ratings yet
- Transmedi A Storytel L I NGDocument43 pagesTransmedi A Storytel L I NGyomismo0023No ratings yet
- PC (MT)Document5 pagesPC (MT)kerstin alcantaraNo ratings yet
- Back TO Schoo L!: Welcome..Document31 pagesBack TO Schoo L!: Welcome..Hugh Maxwell DumagoNo ratings yet
- EL 120 ReviewerDocument6 pagesEL 120 Reviewercharlot besasNo ratings yet
- Funda4 - CommunicatingDocument2 pagesFunda4 - CommunicatingbondadluiNo ratings yet
- Management of Global CommunicationsDocument19 pagesManagement of Global CommunicationssagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter. CHAPTER 1 01Document60 pagesChapter. CHAPTER 1 01Pauline Ann Gerona PetalcorinNo ratings yet
- Media Information Literacy ReviewerDocument8 pagesMedia Information Literacy ReviewerAlexia SamonteNo ratings yet
- L2 - Communication Process and Roadblocks - RepairedDocument17 pagesL2 - Communication Process and Roadblocks - RepairedDrishti RNo ratings yet
- Purcom Reviewer KVDGDocument11 pagesPurcom Reviewer KVDG06675354dNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument323 pagesBusiness CommunicationRadhika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Communication (CS)Document52 pagesLesson 1 - Communication (CS)Yassine BouzekriNo ratings yet
- Ged106 - Lesson 4 5 2Document3 pagesGed106 - Lesson 4 5 2Micaela De JesusNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication q1 LP 6Document7 pagesOral Communication q1 LP 6MICHAEL MORILLONo ratings yet
- Mil (Reviewer) - 013124Document6 pagesMil (Reviewer) - 013124nanamiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Media TechDocument33 pagesUnit 1 Media TechCarlos TabangayNo ratings yet
- MIL Topics 3 4Document38 pagesMIL Topics 3 4yashun491No ratings yet
- 1 - Business Communication in The Digital AgeDocument9 pages1 - Business Communication in The Digital AgeSilk Zambujil CanlasNo ratings yet
- Digital and Media Literacy ReviewerDocument6 pagesDigital and Media Literacy ReviewerKaira RazonNo ratings yet
- MediaDocument3 pagesMediagutierrezcharlesedmar2324No ratings yet
- DCM2020 Campaign Planbook DeckDocument29 pagesDCM2020 Campaign Planbook DeckcaitdalinNo ratings yet
- PurposivecommunicationDocument60 pagesPurposivecommunicationCalvin HilaryNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context Module 5 - Week 5Document7 pagesOral Communication in Context Module 5 - Week 5Jan MykaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01: Introduction To Public SpeakingDocument91 pagesLecture 01: Introduction To Public SpeakingAaryaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Communication Processes: Message/CodeDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Communication Processes: Message/Code꧁ΛПGΣᄂ꧂No ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerrDocument6 pagesMIL ReviewerrIsha GuroNo ratings yet
- BC Module 1Document55 pagesBC Module 1supriyajay02csNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication - NotesDocument5 pagesPurposive Communication - NotesMiraijinNo ratings yet
- Introduction CPLDocument22 pagesIntroduction CPLDr. Shweta KumariNo ratings yet
- 4 Comm Strategies and Comm For Various PurposesDocument2 pages4 Comm Strategies and Comm For Various PurposesTrixie Ann MenesesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MILDocument4 pagesModule 1 MILwelpNo ratings yet
- The Media and The Literacies:: Media Literacy, Information Literacy, Digital LiteracyDocument23 pagesThe Media and The Literacies:: Media Literacy, Information Literacy, Digital Literacyalexandra mae doblonNo ratings yet
- The Media and The Literacies:: Media Literacy, Information Literacy, Digital LiteracyDocument23 pagesThe Media and The Literacies:: Media Literacy, Information Literacy, Digital LiteracySai GuyoNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument3 pagesMil ReviewerTravis AmadoNo ratings yet
- Doaa Article Presentation Media LiteracyDocument23 pagesDoaa Article Presentation Media LiteracyRutchelNo ratings yet
- EDUC 108 - Media LiteracyDocument41 pagesEDUC 108 - Media LiteracyLee DuquiatanNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Messages And/or Images: Purposive CommunicationDocument9 pagesEvaluating Messages And/or Images: Purposive CommunicationSteve Francis MendozaNo ratings yet
- MIL Notes-Week 1-10Document24 pagesMIL Notes-Week 1-10Chrystell JaneNo ratings yet
- Unleashing Your Creative Spark: A Comprehensive Guide to Content CreationFrom EverandUnleashing Your Creative Spark: A Comprehensive Guide to Content CreationNo ratings yet
- Request To InspectionDocument4 pagesRequest To Inspectionaldrin josephNo ratings yet
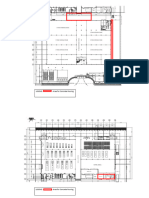
- Legend: - Area For Concrete PouringDocument4 pagesLegend: - Area For Concrete Pouringaldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Information Resource Selection of Undergraduate Student in Academic Search TasksDocument2 pagesInformation Resource Selection of Undergraduate Student in Academic Search Tasksaldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Written Exam Answer Coc 1 and Coc2Document12 pagesWritten Exam Answer Coc 1 and Coc2aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER-9-2nd Quarter-MODULE 2Document5 pagesCOMPUTER-9-2nd Quarter-MODULE 2aldrin joseph100% (1)
- CL ReviewerDocument2 pagesCL Revieweraldrin josephNo ratings yet
- QUALITY STANDARD WEEK 5 and 6Document13 pagesQUALITY STANDARD WEEK 5 and 6aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Construction-Work-Pass-With Hit NbiDocument1 pageConstruction-Work-Pass-With Hit Nbialdrin josephNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Skills (11Document1 pageEnhancing Skills (11aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- RS101 Module 2Document36 pagesRS101 Module 2aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Module Week 2Document13 pages21st Century Module Week 2aldrin joseph67% (3)
- Module 3 - Community Engagement - Week 3 and 4Document9 pagesModule 3 - Community Engagement - Week 3 and 4aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- 4rt Module Week 5 and 6 Nov 2 13Document20 pages4rt Module Week 5 and 6 Nov 2 13aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement, Solidarity and CitizenshipDocument10 pagesCommunity Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenshipaldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Oral Ommunication Preliminary Examination For GRADE 11Document4 pagesOral Ommunication Preliminary Examination For GRADE 11aldrin joseph100% (1)
- Booklet No.2 - Introduction To Computing Final PDFDocument41 pagesBooklet No.2 - Introduction To Computing Final PDFaldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement Week 5 and 6Document8 pagesCommunity Engagement Week 5 and 6aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Community Engagemen Week 7 and 8Document6 pagesCommunity Engagemen Week 7 and 8aldrin josephNo ratings yet
- Annex 1 Draft ESRS Set1 XBRLDocument1,175 pagesAnnex 1 Draft ESRS Set1 XBRLRaghunathNo ratings yet
- Additional Customer - Ids in The Transactions Table' and Customer Address Table' But Not in Customer Master (Customer Demographic) 'Document2 pagesAdditional Customer - Ids in The Transactions Table' and Customer Address Table' But Not in Customer Master (Customer Demographic) 'ranbir singhNo ratings yet
- 1.1 CRM - Definition & ConceptDocument4 pages1.1 CRM - Definition & ConceptPalak JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document25 pagesChapter 10Ngoc Pham BichNo ratings yet
- Certified Rac Win September 2018Document30 pagesCertified Rac Win September 2018BBBTRCACL 2023No ratings yet
- Chillers: Services For Air-Cooled, Water-Cooled, Absorption and Specialty Drive ChillersDocument2 pagesChillers: Services For Air-Cooled, Water-Cooled, Absorption and Specialty Drive ChillersNhật Phong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 8 Criteria's For Selection of Product For ExportDocument5 pages8 Criteria's For Selection of Product For ExportJayagokul SaravananNo ratings yet
- Blocher8e EOC SM Ch05 FinalDocument54 pagesBlocher8e EOC SM Ch05 FinalPhiranat NANGSIKHUNNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - EcommerceDocument20 pagesLesson 1 - EcommerceFranco SanPedroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18-Spoilage, Rework andDocument2 pagesChapter 18-Spoilage, Rework andZeinab MohamadNo ratings yet
- Simulation 5 - Appendix BDocument5 pagesSimulation 5 - Appendix BnelsonquilelliNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Organizational Resources On Customers SatisfactionDocument13 pagesThe Impact of Organizational Resources On Customers SatisfactionGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- Module 09: Requirement Specification: Tutor: Hans MulderDocument12 pagesModule 09: Requirement Specification: Tutor: Hans Mulderdavid artantoNo ratings yet
- FILE 20210820 162411 Nguyen-Thi-Vy-FGW-HN 251699 0Document82 pagesFILE 20210820 162411 Nguyen-Thi-Vy-FGW-HN 251699 0VuPhuong AnhNo ratings yet
- The Stock Market - Cig Anul 2 Sem 1 - Comunicare in Faceri in Limba AnglezaDocument10 pagesThe Stock Market - Cig Anul 2 Sem 1 - Comunicare in Faceri in Limba AnglezaMincu IulianNo ratings yet
- Service MarketingDocument15 pagesService MarketingJenniferdjajaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Analysis of Kotak 1Document91 pagesFundamental Analysis of Kotak 1Abhijith V AshokNo ratings yet
- Talent Acquistion, Engagement and Retention Conclave - From NHRDDocument4 pagesTalent Acquistion, Engagement and Retention Conclave - From NHRDDeepak VinodNo ratings yet
- Data Analytics and VisualizationDocument7 pagesData Analytics and VisualizationZeeshan MallikNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 KTQT PDF - SVDocument15 pagesChapter6 KTQT PDF - SVPhong Phạm NghĩaNo ratings yet
- List Cima P3Document1 pageList Cima P3rinaldi brutusNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 & 4Document12 pagesTopic 3 & 4ChristyNo ratings yet
- On 1 April 20x5 Hardy Entity Acquired 4 Million ofDocument1 pageOn 1 April 20x5 Hardy Entity Acquired 4 Million ofTaimour HassanNo ratings yet
- Penjelasan Absen 08 - 15 Agt So SPPDocument25 pagesPenjelasan Absen 08 - 15 Agt So SPPnampatisembiringNo ratings yet