Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xicbse-Chemistry Asst 2
Uploaded by
tanishkakannan32530 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Xicbse-chemistry Asst 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesXicbse-Chemistry Asst 2
Uploaded by
tanishkakannan3253Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
GREEN PARK INTERNATIONAL SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOL, NAMAKKAL
XII* (CBSE) – CHEMISTRY – ASSIGNMENT – 2
SOLUTIONS
Topics : Henry law, Raoult’s law, Ideal, Non-ideal & Azeotropic mixture
Choose the correct answer :
1. The vapour pressure of pure liquid A is 70torr a) Vapour pressure of A in the pure state is
at 27oC it forms an ideal solution with another 50mm Hg
liquid B. The mole fraction of B is 0.2 and b) Vapour pressure of B in the pure state is
total vapour pressure of the solution is 84 torr 650mm Hg
at 27oC. The vapour pressure of pure liquid B c) Ratio of final vapour pressure to the initial
at 27oC is vapour pressure is 1 : 0.5
1) 140 torr 2) 50 torr d) Ratio of vapour pressure of pure B to the
3) 14 torr 4) 70 torr vapour pressure of pure A is 13 : 1
2. Equal moles of benzene and toluene are mixed 1) a, b 2) a, b, d
the V.P of benzene and toluene in pure state
3) b, c, d 4) b, c, d
are 700 and 600mm Hg respectively. The
6. An ideal solution was obtained by mixing
mole fraction of benzene in vapour state is
methanol and ethanol. If the partial vapour
1) 0.7 2) 0.47
pressure of methanol and ethanol are 2.619
3) 0.50 4) 0.54
kPa and 4.556 kPa respectively. The
3. The solubility of N2(g) at 593 mm of Hg is composition of vapour (interms of mole
5.3 x 10–4 in water. Its solubility at 860 mm fraction) will be
and at the same temperature in water is
1) 0.635 MeOH, 0.365 EtOH
1) 5.3 x 10–4 2) 7.68 x 10–4
2) 0.365 MeOH, 0.635 EtOH
3) 9.0 x 10–4 4) 1.2 x 10–3
3) 0.574 MeOH, 0.326 EtOH
4. The Henry’s law constant for the solubility of
4) 0.173 MeOH, 0.827 EtOH
N2 gas in water at 298K is 1.0 x 105 atm. The
mole fraction of N2 in air is 0.8. The number 7. Henry’s constant of four gases A, B, C and D
of moles of N2 from air dissolved in 10moles in water are 40.3, 1.67, 0.413 and 0.611 298 K
of water at 298K and 5atm pressure is and 1 atm. The gas which has maximum
solubility in water at 298K and 1 atm is
1) 4.0 x 10–4 2) 4.0 x 10–5
3) 5.0 x 10–4 4) 4.0 x 10–6 1) A 2) B
5. At 300K, the vapour pressure of an ideal 3) C 4) D
solution containing 1mole of A and 3 moles of 8. Henry’s law constant for CO2 in water is
B is 500 mm Hg. At the same temperature, 2 1.67 x 108 pa at 298K. Calculate the quantity
moles of B are added to the solution. The of CO2 in 500mL of soda water when packed
vapour pressure of solution increases by 10% under 2.5 atm CO2 pressure at 298K.
of the original vapour pressure correct 1) 0.0422 moles 2) 0.0822 moles
statements about the vapour pressure are 3) 0.0622 moles 4) 0.0122 moles
2
9. Raoult’s law is not valid in 13. Choose the correct statement
1) Non-ideal solution showing positive 1) Azeotropic mixture can be separated into
deviation their components by fractional distillation
2) Non-ideal solution showing negative 2) For ideal solutions enthalpy of mixing is
deviation always greater than zero
3) Mixture of two immiscible liquid 3) Components of all non-ideal solution
4) All of these showing positive deviation cannot be
10. A mixture of two liquids A and B having separated out by fractional distillation
boiling point of A is 70oC and boiling point of 4) Non-ideal solution showing positive
B is 100oC, distills at 101.2oC as single liquid deviation enthalpy of mixing is greater than
hence the mixture is zero
1) Ideal solution 14. A and B forms non-ideal solution showing
2) Non–ideal solution showing +ve deviation positive deviation. Boiling point of pure A and
3) Non-ideal solution showing –ve deviation B is 350K and 380K respectively. The
solution will boil at (approximate)
4) Immiscible solution
1) 350 K 2) 380 K
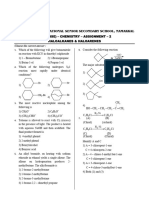
11. Match the following
3) > 380 K 4) < 350 K
Column – I
15. Assertion (A) : Henry’s law and Raoult’s law
A) Ethanol + acetone
are not independent i.e., one can be derived
B) Chloro benzene + bromo benzene
from the other.
C) Ethanol + water
Reason (R) : The partial pressure of
D) Acetone + chloroform component is inversely proportional to the
Column – II mole fraction of that component in an ideal
p) form maximum boiling azeotrope solution.
q) ptotal = PAo + PBo 1) Both (A) and (R) are true and the (R) is a
correct explanation of the (A)
r) form minimum boiling azeotrope
2) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not a
s) does not form azeotrope
correct explanation of the (A)
1) A-p, B-s, C-r, D-r
3) (A) is true but the (R) is false
2) A-r, B-q, s, C-p, D-r
4) Both (A) and (R) are false
3) A-r, B-q, s, C-r, D-p
16. 1kg of water under a nitrogen pressure of
4) A-s, B-p, s, C-p, D-r
1 atmosphere dissolved 0.02 gm of nitrogen at
12. Vapour pressure of mixture of liquid A and 293K. Calculate Henry’s law constant
liquid B at 70oC is given by PT = 180 XB + 90
1) 7.7 x 104 atm 2) 7.7 x 103 atm
(in mm), where XB is the mole fraction of B in
3) 2 x 10–5 atm 4) 2 x 10–2 atm
the liquid mixture. Calculate the vapour
pressure of pure A and pure B 17. Total vapour pressure of mixture of 1 mol X
1) 90, 270 2) 180, 90 ( PXo = 150 torr) and 2 mol Y ( PYo = 300 torr)
3) 120, 360 4) 0, 90 was found to be experimentally 240 torr. In
this case
3
1) There is a negative deviation from Raoult’s 1) 0.549 2) 0.200
law 3) 0.786 4) 0.478
2) There is a positive deviation from Raoult’s 20. Which of the following curve represents the
law Henry’s law? (Units of ‘K’ is gm bar–1 and
3) There is no deviation from Raoult’s law m = mass of gas)
4) Cannot be decided
18. Two liquids A and B have PAo and PBo in the
1) 2)
ratio of 1 : 3 and the ratio of number of moles
of A and B in liquid phase are 1 : 3 then mole
fraction of “A” in vapour phase in equilibrium
with the solution is equal to 3) 4)
1) 0.1 2) 0.2
3) 0.5 4) 1.0
19. A solution has a 1 : 4 mole ratio of pentane to
hexane. The vapour pressure of the pure
hydrocarbons at 20oC are 440mm Hg for
pentane and 120mm Hg for hexane. The mole
fraction of pentane in the vapour phase would
be
You might also like
- Dilute Solution & Colligative Properties-Assignment PDFDocument25 pagesDilute Solution & Colligative Properties-Assignment PDFggk201375% (4)
- KS3 Maths Progress Delta 1 Unit 2 PDFDocument14 pagesKS3 Maths Progress Delta 1 Unit 2 PDFMuhammad AmmarNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Replacing Part of Cement With Waste Material - ReviewDocument7 pagesReplacing Part of Cement With Waste Material - ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Solution Tsd3Document3 pagesSolution Tsd3Mahendra RajpootNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry For JEE AdvDocument8 pagesSurface Chemistry For JEE AdvAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (7.4.2022) - 24921131Document5 pagesAssignment 2 (7.4.2022) - 24921131Harshwardhan Singh Thakur 7No ratings yet
- Solutions - PYQs - Lakshya NEET 2025Document2 pagesSolutions - PYQs - Lakshya NEET 2025mailuseless437No ratings yet
- Printable Mole Concept SheetDocument9 pagesPrintable Mole Concept SheetPratham MoreNo ratings yet
- Aakash Chemistry CPP CH 2 SolutionDocument9 pagesAakash Chemistry CPP CH 2 Solutionthakartanishq07No ratings yet
- Henry and RaoultsDocument2 pagesHenry and Raoultschaitanya goyalNo ratings yet
- Eamcet Part Test-1Document3 pagesEamcet Part Test-1udaysrinivasNo ratings yet
- Guess Paper 3 Isc ChemistryDocument5 pagesGuess Paper 3 Isc ChemistrySanjanaNo ratings yet
- Solutions 1Document7 pagesSolutions 1bibhas_samantaNo ratings yet
- Bcco 2019Document4 pagesBcco 2019lzljackieNo ratings yet
- Blockbuster Problems Chemistry QnsDocument121 pagesBlockbuster Problems Chemistry Qnstrinathreddy3300No ratings yet
- One Markc Combined Board QuestionsDocument19 pagesOne Markc Combined Board Questionssyedasifbasha1990No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jul 02, 2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan Jul 02, 2023VILLAIN EX.No ratings yet
- Solutions - Practice Sheet - Sarthak KCET PDFDocument6 pagesSolutions - Practice Sheet - Sarthak KCET PDFAkanksh KNo ratings yet
- 11th 2Document5 pages11th 2Vaibhava SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MRT MDocument8 pagesMRT MSrijan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument5 pagesSolutionsPranav ShinojNo ratings yet
- Topic:-: SolutionsDocument3 pagesTopic:-: SolutionsGnaneshwarNo ratings yet
- Solutions - DPP 08 (Of Lec 09) - Lakshya JEE 2024Document3 pagesSolutions - DPP 08 (Of Lec 09) - Lakshya JEE 2024Hamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5Document5 pagesTutorial Chapter 5Nur Aqilah Ainaa Binti SahrolNo ratings yet
- Solutions QTSDocument22 pagesSolutions QTSBHADRANo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam November 2011Document4 pagesMid Term Exam November 2011Beatriz IzquierdoNo ratings yet
- Solutions Class 12th Practice Paper 1Document6 pagesSolutions Class 12th Practice Paper 1Liyutsa ZirangeNo ratings yet
- 48 Practice Problems For CH 17Document9 pages48 Practice Problems For CH 17Hasantha PereraNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Revision Test Question Papers EM 221210Document10 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Revision Test Question Papers EM 221210forever gamersNo ratings yet
- 29-Poll - C-29 (Chemistry) SolutionsDocument4 pages29-Poll - C-29 (Chemistry) SolutionsNandish PatelNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument6 pagesSolutionkodigudlaharshavardhanNo ratings yet
- 1 QP SolutionDocument6 pages1 QP Solution27122005adityagargNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 Solution-Properties ExercisesDocument13 pagesChapter-7 Solution-Properties Exercisestran huyNo ratings yet
- Distillation ChEN DLSUDocument2 pagesDistillation ChEN DLSUJelain HumarangNo ratings yet
- DPP - LT - CHE - 08-07-21: SR - Physical Chemistry Revision Work SheetDocument13 pagesDPP - LT - CHE - 08-07-21: SR - Physical Chemistry Revision Work SheetShivakumar SomanapallyNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument47 pagesChemistryAnubhav ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Short Practice Test 01 Test Paper Chemistry Lakshya NEET 2024Document4 pagesShort Practice Test 01 Test Paper Chemistry Lakshya NEET 2024meashishswami2006No ratings yet
- Solutions: WWW - Crackjee.xyzDocument6 pagesSolutions: WWW - Crackjee.xyzRashmi Ranjan DasNo ratings yet
- Solution Test PaperDocument2 pagesSolution Test PaperSAKSHI PANDEYNo ratings yet
- WorksheetXIIPT1202324Document12 pagesWorksheetXIIPT1202324coolpengu47No ratings yet
- Target DPP TestDocument4 pagesTarget DPP TestayusanupamNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xii-Chem-1. SolutionsDocument4 pagesHsslive-Xii-Chem-1. Solutionsnr249488No ratings yet
- 1 MS SolutionDocument11 pages1 MS SolutionsachinNo ratings yet
- The Neutrons and The ProtonsDocument2 pagesThe Neutrons and The ProtonsRhea Mae BiñarNo ratings yet
- 12TH Class Chapter Wise QP 2022-23Document146 pages12TH Class Chapter Wise QP 2022-23Aaghash A SNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Line by Line 2024-25 Ch-1.SolutionsDocument39 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Line by Line 2024-25 Ch-1.SolutionsAbhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 Basic ConceptsDocument2 pagesAssignment-2 Basic ConceptsNilaksh Jha 9DNo ratings yet
- Solutions (MCQ, Assertion & Case Base)Document16 pagesSolutions (MCQ, Assertion & Case Base)ANKUSH HOODANo ratings yet
- Xii Cbse Half Grand Test Question PaperDocument7 pagesXii Cbse Half Grand Test Question PaperSrinivas NakkaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Cet-11Document2 pagesChemistry Cet-11VenomNo ratings yet
- Nsec 2022Document13 pagesNsec 2022Ayushmaan DhanaiNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Important Questions With Solutions 2023Document18 pagesJEE Main Important Questions With Solutions 2023vaibhavsatishpattanashettiNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Liquid Solutions Important QuestionsDocument24 pagesJEE Advanced Liquid Solutions Important QuestionsSuyog AmruNo ratings yet
- 6645646Document2 pages6645646honeylet tayactacNo ratings yet
- Dilute SolutionsDocument21 pagesDilute SolutionsBombay TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesChemistry Review QuestionsEMİRCAN İPEKNo ratings yet
- DiagnosticsDocument8 pagesDiagnosticsNORBERTUS KRISNU PRABOWONo ratings yet
- Final Test CHM271Document5 pagesFinal Test CHM271NURUL AINUN MUHAMMAD NORNo ratings yet
- CH 2 1Document15 pagesCH 2 1Mohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- NEET Sample (Model-5) Question Paper With Answer Keys - Free PDF DownloadDocument40 pagesNEET Sample (Model-5) Question Paper With Answer Keys - Free PDF Downloadt.nishar61258No ratings yet
- Xicbse Electrochemistry Ass 2 QPDocument3 pagesXicbse Electrochemistry Ass 2 QPtanishkakannan3253No ratings yet
- Xicbse Che Haloalkanes Haloarenes 2 QPDocument3 pagesXicbse Che Haloalkanes Haloarenes 2 QPtanishkakannan3253No ratings yet
- Xicbse Che Asst 1 AnsDocument3 pagesXicbse Che Asst 1 Anstanishkakannan3253No ratings yet
- Xicbse Che Asst 2 AnsDocument3 pagesXicbse Che Asst 2 Anstanishkakannan3253No ratings yet
- Analysis in Essential OilDocument23 pagesAnalysis in Essential OilBadtzNo ratings yet
- The Teacher's Guide: To The Corrosion ToolkitDocument42 pagesThe Teacher's Guide: To The Corrosion ToolkitCiceroNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry 10th by ZumdahlDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry 10th by Zumdahlevenehautpas.g0rmkq100% (46)
- Aerodex WB: Interior Cabin CoatingDocument5 pagesAerodex WB: Interior Cabin CoatingАндрей МошкинNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document5 pagesLab Report 1Trịnh Gia HânNo ratings yet
- BORLOGDocument4 pagesBORLOGKaren TrinitaNo ratings yet
- Regeneration of Softener Standard ProcedureDocument2 pagesRegeneration of Softener Standard ProcedureMdrahaman Mithu100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - The Mole CalculationsDocument40 pagesChapter 1 - The Mole Calculationsredifentsemosiane6No ratings yet
- Advanced Chemical Escape Hood: Oil & Gas - Petrochemical and Chemical Processing - Mining - DefenceDocument4 pagesAdvanced Chemical Escape Hood: Oil & Gas - Petrochemical and Chemical Processing - Mining - DefenceJan VenterNo ratings yet
- Predicting The Earthquake Response of Buildings Using Equivalent Single Degree of Freedom SystemDocument9 pagesPredicting The Earthquake Response of Buildings Using Equivalent Single Degree of Freedom SystemElvis GuizadoNo ratings yet
- Technical SpecificationDocument6 pagesTechnical SpecificationAyse ClkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Movement in HumansDocument7 pagesChapter 17 - Movement in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Important Questions On Bioinorganic Chemistry 80Document7 pagesImportant Questions On Bioinorganic Chemistry 80Fahad KhanNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentSunnnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Chapter 1) Answers PDFDocument66 pagesTutorial (Chapter 1) Answers PDFAMIRAH ISHAMI ISHAKNo ratings yet
- Johnsondiversey Acifoam: Acidic Foam Cleaner-DescalerDocument2 pagesJohnsondiversey Acifoam: Acidic Foam Cleaner-DescalerHamzeh AbdelhadiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry WorksheetDocument7 pagesChemistry WorksheetSridevi PisipatiNo ratings yet
- DALUBATAN MIDTERMv2 REACTION PAPERDocument1 pageDALUBATAN MIDTERMv2 REACTION PAPERNeo PorpayasNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Plastic TilesDocument4 pagesBehavior of Plastic TilesJournalNX - a Multidisciplinary Peer Reviewed JournalNo ratings yet
- HPLC Analysis of Mono-And Disaccharides in Food Products: October 2013Document6 pagesHPLC Analysis of Mono-And Disaccharides in Food Products: October 2013Long PhiNo ratings yet
- Fiche Technique Garniture R-MGDocument2 pagesFiche Technique Garniture R-MGongoloNo ratings yet
- Suto S130-S132 en 23-1 PDFDocument5 pagesSuto S130-S132 en 23-1 PDFVikas PatidarNo ratings yet
- Specification For Glycerin, Natural, USP, EP, BP (G1016) : Item NumberDocument2 pagesSpecification For Glycerin, Natural, USP, EP, BP (G1016) : Item NumberPartha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- CSIA Titration Lab June 2022Document5 pagesCSIA Titration Lab June 2022Clumley ClungNo ratings yet
- wch13 01 Que 20230120Document16 pageswch13 01 Que 20230120Rohee TariqNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Formation and Reduction of Copper Oxide NanostructuresDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Formation and Reduction of Copper Oxide NanostructuresEdgar Fabian Pinzon NietoNo ratings yet
- Cheet Sheet For Becker Rotary Vane PartsDocument12 pagesCheet Sheet For Becker Rotary Vane PartsMistysPartsNo ratings yet
- Waves FormulasDocument2 pagesWaves FormulasHshs HshshNo ratings yet