Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organelle Study Sheet (Faith)
Uploaded by
qp8jv2nxkfCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organelle Study Sheet (Faith)
Uploaded by
qp8jv2nxkfCopyright:
Available Formats
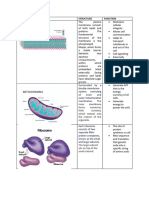
Organelle Structure Function
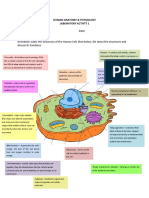
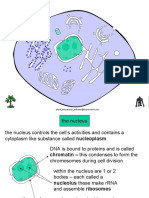
Nucleus -Sphere like shape -Contains the cells
-Placement is in the middle of genetics(control center)
the cell -dna replication is present as
-Stored in a gel like well as the genes mature
substance(nucleoplasm) form
-final gene growth stage is
located in the cytoplasm
- responsible for protein
synthesis, cell division,
growth,.
-control center of the cell
-manages cells reproduction
-acts as a brain of the cell
-allows a selective passage
of different types of
molecules(proteins nucleic
acids) in and out of the
nucleus
-ribosome assembly
-nucleus is present in the cell
and is attached to the nuclear
membrane
Nucleolus -sphere or oblong structure -ribosomal genes are copied
found in nucleus -composed of
-large dark spot RNA(ribonucleic acid) and
proteins
-lacks a membrane
-makes parts to help build the
most important workers of the
cell(the ribosomes)
-nucleolus is a sub organelle
present inside the nucleus
and is not attached to any
membrane
Mitochondrion -surrounded by a double -produces energy through the
membrane system process of oxidative
-consists of an inner and phosphorylation
outer membrane -responsible for
-separated intermembrane managing/regulating
space metabolic activity
-detoxes ammonia in the liver
cells
-promotes cell multiplication
and cell growth
plays an important role in:
oxidative phosphorylation-
a biological mechanism that
uses the reduction of oxygen
to produce adenosine
triphosphate, a high-energy
phosphate bond.
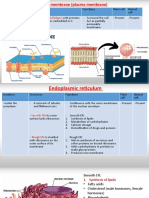
Rough and Smooth -smooth er is a continuous - The ser is typically
Endoplasmic Reticulum extension of the rough er used for the storage
-located more to the far end of liquids and steroids
from the nucleus - rer plays a significant
-rough er shaped like role in the synthesis of
flattened hollow pancakes various proteins
-smooth er is tubular in - Difference of the ser
structure and rer are the
ribosomes
- ribosomes attach to
the surface and gives
a rough appearance
(rough er)
- smooth er does not
have ribosomes on its
surface (possess
ribosomes attached to
its membrane)
Golgi Apparatus -a series of 5-8 cup shaped -helps package proteins and
membrane covered flat sacs lipid molecules
called cisternae -proteins are destined to be
-looks like a stack of deflated exported from the cell
balloons -a series of stacked
membranes
-proteins are transported to
lysosomes, the plasma
membrane, or released after
being processed and sorted
after leaving the ER
-The Golgi is the place where
sphingomyelin and glycolipids
are made
Ribosome - A little like a - made of both RNA
hamburger with a and protein
puffy bun on top - the site of the protein
- Appear flattened and synthesis in the cell
spherical - protein synthesis in
the cell
- the messenger RNA
(mRNA) sequence is
read by the ribosome,
which then converts
the genetic code into
a specific string of
amino acids that
develop into extended
chains and fold to
create proteins.
- use metabolic energy,
accessible
transferable RNAs,
and cellular
supplemental proteins
to carry out the
beginning, extension,
and end of peptide
synthesis
- produces protein by
following the coded
instructions from the
DNA
Lysosome -sphere shaped sacs filled -digestive system of the cell
with hydrolytic enzymes -degrades material taken up
-spherical bodies about 50-70 from outside the cell to digest
in diameter and are bounded -responsible for the digestion
by a single membrane of macromolecules, old cell
parts, and microorganisms
-responsible
-cell membrane repairs
-responses against foreign
substances (bacteria and
viruses)
Vacuole -surrounded by a thin -plant cell(help maintain
membrane and filled with fluid water balance)
and any molecules they take -involved in intracellular
-membrane bound subcellular digestion
structure -animal cell(generally small
and help sequester waste)
-a single vacuole can take up
most of the interior space of
the plant cell
-insulating materials that may
be harmful to the cell
-containing small molecules
Chloroplast -oval shaped -produce energy through
-has two membranes(outer photosynthesis and oxygen
membrane and an inner release processes
membrane) -sustains plant growth and
-intermembrane space crop yield
approx 10-20 nm wide -responsible for biosynthesis
of active compounds (amino
acids, vitamins, lipids,
nucleotides, phytohormones,
etc)
-plant cell
Cell Wall -rigid external layer -specifically designed to
-plasma membrane that provide structural support and
consists of both lipids and rigidity
proteins -keeps all interior
-phospholipid layer(provides components of the cell intact
a stable barrier between two -keeps cell safe from external
aqueous compartments) environment
-plant cell
-protects against infection
and mechanical stress
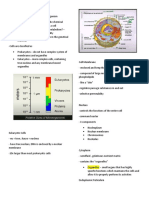
Cytoplasm -thick solution (fills each cell -consists of a nucleus and
and is inclosed by cell organelles such as
membrane) mitochondria and vacuoles
-mainly composed of water,
salt and protein,.
- in eukaryotes cells the
cytoplasm includes all the
materials inside the cell and
outside of the nucleus
-provides a platform in which
other organelles can operate
within the cell
-cell expansion, growth, and
replication is all carried out
Cilia/Flagella Flagella- long wavy -antenna like protrusions
structures(extend from -present on many times of
plasma membrane and are eukaryotic cells
used to move an entire cell) - provides functions such as
CIlia- short hair like structures locomotion, mucus clearance,
(that are used to move entire fluid circulation,
cells or substances along the chemosensation, and
outer surface of the cell) mechanosensation,.
-to move water relative to the
cell in regular
movement(cilia)
-helps organism in movement
and acts as a sensory organ
to detect temp and PH
changes(flagella)
Cell Membrane -consists of lipids and -serves as gatekeepers and
proteins barriers
-plasma membrane -some molecules can diffuse
-two dense lines separated across the lipid bilayer but
by an intervening space others can not
- gases,oxygen, and carbon
dioxide cross membranes
rapidly
-transports materials coming
in and out of the cell
-they contain receptors that
allow specific molecules such
as ions, nutrients, waste that
mediate cellular and
extracellular activities to pass
between organelles and the
outside environment
You might also like
- Cell BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesCell BIOLOGYAria Moon100% (1)
- Cell BiologyDocument306 pagesCell BiologySathish K. Samy100% (2)
- General Biology 1Document38 pagesGeneral Biology 1Kaye Kathlene Basubas90% (10)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- 1GS Cell PPT 2018Document73 pages1GS Cell PPT 2018pixiedustNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure2Document6 pagesCell Structure2CRYSTAL A. ARIETANo ratings yet
- The Human CellDocument1 pageThe Human CellAira Viloria Orbillo100% (1)
- The Process of Cell DivisionDocument42 pagesThe Process of Cell Divisionishimwe kwizera willyNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyDocument6 pagesCells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Test IB BIO HL 123Document7 pagesCell Test IB BIO HL 123AdamNo ratings yet
- Bio F4 Bab 2Document31 pagesBio F4 Bab 2Alwani FarahiNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 (The Cell)Document6 pagesActivity 2 (The Cell)Sophia VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy-lab ACTSDocument5 pagesAnaPhy-lab ACTSCEEJNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocument24 pagesEukaryotic Cell StructureKarolina RyśkiewiczNo ratings yet
- Micropara ReviewerDocument13 pagesMicropara ReviewerEmhnaly Kae AggalutNo ratings yet
- Cell 3Document10 pagesCell 3OscarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - CellDocument9 pagesWorksheet 1 - CellDiva putri DamayantiNo ratings yet
- ORGANELLESDocument3 pagesORGANELLESIya BiancaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Plant Cell and Its FunctionsDocument2 pagesParts of Plant Cell and Its FunctionsThiody Hope Mongas50% (2)
- F4 C2 NotesDocument15 pagesF4 C2 Notesmarisyayasmin050907No ratings yet
- Class 9 Cytoplasm To MitochondriaDocument2 pagesClass 9 Cytoplasm To Mitochondrianivya MariyamnobyNo ratings yet
- Sunlight For Energy. Chloroplast - Is Where Photosynthesis HappenDocument4 pagesSunlight For Energy. Chloroplast - Is Where Photosynthesis HappenSamantha VeraNo ratings yet
- Pro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDocument5 pagesPro Bef Ore Karyotic Nucleus: BloodDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- BIO C2 @notastpm04Document35 pagesBIO C2 @notastpm04Aprillia ChanNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument5 pagesCell StructuresSTEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoNo ratings yet
- A Double Membrane Composed of Lipids and Proteins, Present in Plant and Animal CellDocument2 pagesA Double Membrane Composed of Lipids and Proteins, Present in Plant and Animal CellLerr Real RelleNo ratings yet
- Cells/Organ Elles Structures Functions: NucleusDocument8 pagesCells/Organ Elles Structures Functions: NucleusHazimah MohiddinNo ratings yet
- Asa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaDocument1 pageAsa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaMary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellGalvez Glaiza ElaineNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory: Definition of Cell Plant CellDocument6 pagesCell Structure & Function Cell Theory: Definition of Cell Plant Celljean magallonesNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer Paolo PurisimaDocument7 pagesBiology Reviewer Paolo PurisimaPaolo JoaquinNo ratings yet
- 083 41 Final Biologi T4 DLP-30-60Document31 pages083 41 Final Biologi T4 DLP-30-60Farhan DarwisyNo ratings yet
- Biology: Prokaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesBiology: Prokaryotic CellsVictoria IlaganNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument5 pagesMicrotahashahzad9901No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: NucleusDocument4 pagesCell Organelles: NucleusVeronica AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Histonotes 1Document3 pagesHistonotes 1mayumi takagiNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotesBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Salud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFDocument5 pagesSalud - Lab Activity 3 - The Cell - Biochem - BSN 1-Coc A. PDFFaye SaludNo ratings yet
- H2 BIO Cell Structure NotesDocument15 pagesH2 BIO Cell Structure NotesEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Summary and Model Answers:: 3.2.1 Cell StructureDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Summary and Model Answers:: 3.2.1 Cell Structureteee100% (1)
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraNo ratings yet
- CellDocument15 pagesCellvijayp2No ratings yet
- Module 1 - Cells As The Basis of LifeDocument10 pagesModule 1 - Cells As The Basis of LifeElla RelfNo ratings yet
- BIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Hi StolecDocument4 pagesHi StolecMariana Luccini De LeonNo ratings yet
- Plant Vacuoles Sap Water OsmosisDocument3 pagesPlant Vacuoles Sap Water OsmosisChrister MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument16 pagesReviewer in BiologyAngel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Parts of The CellDocument3 pagesParts of The CellMa Claire TumboconNo ratings yet
- MC3 - Lecture Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMC3 - Lecture Activity 1 PDFFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- CELLS AND TISSUES Notes (Anaphy)Document2 pagesCELLS AND TISSUES Notes (Anaphy)Lanette Liana A. LocaylocayNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument10 pagesCell StructureririNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 FullDocument130 pagesChap 5 Fullgaelle tannous100% (1)
- (Zoolone) Animal CellDocument5 pages(Zoolone) Animal CellRenee Margarette GrapilonNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument32 pagesCell Structure and Functionnaveedalikhoso365100% (1)
- Cell Biology Inventory COMPLETEDocument18 pagesCell Biology Inventory COMPLETEmariam miladNo ratings yet
- Biology: Cell StructureDocument3 pagesBiology: Cell StructureFernanda AntonialliNo ratings yet
- Soriano, Cindy M. (Bio 024) Lab Activity 3 - The Animal CellDocument4 pagesSoriano, Cindy M. (Bio 024) Lab Activity 3 - The Animal CellCindy Macaranas SorianoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Its StucturesDocument7 pagesCell Organelles and Its StucturesHailey Eisleen LazaroNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument12 pagesCell OrganellesVeronica AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- See Figure 7.5 Page 167 of The Book That Shows The Difference in Structure of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument17 pagesSee Figure 7.5 Page 167 of The Book That Shows The Difference in Structure of Prokaryotes and EukaryotesMartin ColicoNo ratings yet
- Biology Cells Microscopy 1Document14 pagesBiology Cells Microscopy 1Andrea Trish NicolasNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and StructureDocument4 pagesCell Theory and StructureKrizhia MacayaonNo ratings yet
- Upload It 1Document5 pagesUpload It 1John Rey Bandong100% (1)
- Bio 1 PDFDocument13 pagesBio 1 PDFjayan sivaNo ratings yet
- L7.8.9.Cell BiologyDocument81 pagesL7.8.9.Cell BiologyGeethanjali SivakumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.3 - Energy Systems: 3.3.1 Draw A Diagram To Show The Ultrastructure of A Generalized Animal CellDocument8 pagesTopic 3.3 - Energy Systems: 3.3.1 Draw A Diagram To Show The Ultrastructure of A Generalized Animal CellTiago José ReisNo ratings yet
- Cell BingoDocument6 pagesCell BingoArcely DavidNo ratings yet
- SLHT Science 7 Q2 WK (4) 4 (Ok)Document6 pagesSLHT Science 7 Q2 WK (4) 4 (Ok)renier calumpangNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument18 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotecj bariasNo ratings yet
- Central VacuoleDocument10 pagesCentral VacuoleBlack manNo ratings yet
- CH 03 CellsDocument62 pagesCH 03 CellsMarylene MontoyaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 ExtraDocument2 pages3.1 ExtraEyad TalaatNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and Functions PDFDocument3 pagesCell - Structure and Functions PDFmaya__scribd100% (1)
- Mitosis Mind MapDocument1 pageMitosis Mind MapMaria alejandra Penagos CeballosNo ratings yet
- MCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First ComDocument74 pagesMCQs & QUs On Fsirst Year First Commaisara10No ratings yet
- Soriano, Cindy M. (Bio 024) Lab Activity 3 - The Animal CellDocument4 pagesSoriano, Cindy M. (Bio 024) Lab Activity 3 - The Animal CellCindy Macaranas SorianoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 2ndqtDocument83 pagesModule 4 2ndqtJanelle RegachoNo ratings yet
- Tingkatan 4 Bab 2Document4 pagesTingkatan 4 Bab 2Wan RoziahNo ratings yet
- Science Tech Class 2 Basic Biology Lyst4385 Lyst7065Document66 pagesScience Tech Class 2 Basic Biology Lyst4385 Lyst7065UdishaSinghNo ratings yet
- HURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-2 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument20 pagesHURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-2 Cell Structure and OrganisationMahin IslamNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions 2Document3 pagesCell Parts and Functions 2Arshelyn Donna NovenoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsjhabNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument2 pagesBiology Notes3raser01No ratings yet
- Magic School Bus EssayDocument5 pagesMagic School Bus Essayapi-305346506No ratings yet
- Science 7 Second Quarter - Module 2 Cells and Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument6 pagesScience 7 Second Quarter - Module 2 Cells and Levels of Biological OrganizationAriel angelioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For First Quarter GENBIO1Document57 pagesReviewer For First Quarter GENBIO1Rshyron Crain GrospeNo ratings yet
- 1ST Sem - Course Outline - BiologyDocument3 pages1ST Sem - Course Outline - BiologyMarielle AlystraNo ratings yet