Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1st Day For DLL Week 1
Uploaded by
Razty Tiquez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
344 views14 pagesIt is about the introduction of ICT
Original Title
1st Day for DLL Week 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIt is about the introduction of ICT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
344 views14 pages1st Day For DLL Week 1
Uploaded by
Razty TiquezIt is about the introduction of ICT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
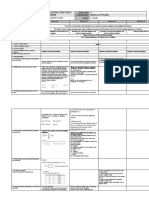
OBJECTIVES:
The learner will be able to…
1.Illustrate random variable
(discrete and continuous)
2. Distinguish between a
discrete and a continuous
variable
A random variable is a variable
whose possible values are
determined by chance. It is
typically represented by an
uppercase letter usually X while
its corresponding lower case
letter in this case, x , is used to
represent one of its values.
In the illustration above, random variable is
represented by upper case X. The lower
case x represents the specific values.
Hence, x=3, x=2, x=2, x=1, x=2, x=1, x=1,
x=0
The sample space for the possible
outcomes is
S={ HHH, HHT,HTH,HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT}
The value of the variable X can be 0, 1, 2 or
3.
Random variables can be either
discrete or continuous
A discrete random variable can only
take a finite (countable) number or
distinct values. Distinct values mean
values that are exact and can be
represented by non negative whole
numbers.
A continuous random variable can
assume an infinite number of values
in an interval between two specific
values. This means they can
assume values that can be
represented not only by nonnegative
whole numbers but also fractions
decimals. These values are often
results of measurement.
ACITIVTY
Base on the given definition, Identify
if the given is discrete or continuous
random variable. Write discrete or
continuous
1. Let X=number of students
randomly selected to be interviewed
by a researcher.
2. Let Y=the weights of randomly
selected students in kilogram.
3. Let Y=number of left-handed
teachers randomly selected in a
faculty room.
4. Let X=the lengths of randomly selected
shoes of senior students in centimeters.
5. Let Z=number of defective light
bulbs among randomly selected light
bulbs.
The following are examples of discrete random
variable.
1.Let X=number of students randomly selected to
be interviewed by a researcher. This is a
discrete random variable because its possible
values are 1,2, 3 and so on.
2.Let Y=number of left-handed teachers
randomly selected in a faculty room.
3.Let Z=number of defective light bulbs among
randomly selected light bulbs.
The following are examples continuous
random variables
1.Let Y=the weights of randomly
selected students in kilogram. The
weight of the student for example can
be 50. 5 kg
2.Let X=the lengths of randomly
selected shoes of senior students in
centimeters.
Think-Pair-Share
1.Let X=number of women randomly
selected in a political rally.
2. Let Z=the hourly temperature last
Sunday.
3. Let Y=the heights of daisy plant in the
backyard.
Evaluating:
Copy and answer in your activity notebook.
Determine if the random variable X or Y is discrete or
continuous. Write Dis if discrete and Con if
continuous
1.X = number of points scored in the last
season by a randomly selected basketball
player in the PBA
2.Y=the height of a randomly selected
student inside the library in centimeter.
3.X=number of birds in the nest
4. Y= the weights in kg or randomly
selected dancers after taking up
aerobics
5. Z=number of words read by
the students in an hour
You might also like
- DLL Statistics Senior High ScoolDocument8 pagesDLL Statistics Senior High ScoolKaren Calooy100% (1)
- Random Variables and Probability Distributions Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesRandom Variables and Probability Distributions Lesson Planloice crisostomoNo ratings yet
- Stat 1Document4 pagesStat 1demrick100% (1)
- CO - Discrete and Continuous VariablesDocument9 pagesCO - Discrete and Continuous VariablesRolly FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Cot 3RD QuarterDocument5 pagesCot 3RD QuarterMildred OrtizNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Q3W3Document3 pagesStatistics and Probability Q3W3Beverly NevadoNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesDay 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4: I. Objectivesariel a. ortizNo ratings yet
- Random SamplingDocument67 pagesRandom SamplingDionisia Rivera Dita100% (1)
- DLL-Estimation of ParametersDocument3 pagesDLL-Estimation of ParametersYmma Bravo Malana100% (1)
- General Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at Depedtambayanph - Blogspot.com) Q1, Week 04Document3 pagesGeneral Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at Depedtambayanph - Blogspot.com) Q1, Week 04Gerry Areola Aquino100% (1)
- Grades 11 Probability Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGrades 11 Probability Lesson PlanMICHAEL ANGELO MAYORDONo ratings yet
- Quarter 1Document64 pagesQuarter 1Val LaborNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 3 - Stat and Proba Q3Document6 pagesDLL Week 3 - Stat and Proba Q3JESSIE GRACE DE LUNANo ratings yet
- Session 1/january 23 Session 2/january 24 Session 3/january 25 Session 4/january 26Document4 pagesSession 1/january 23 Session 2/january 24 Session 3/january 25 Session 4/january 26jun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Thess-DLP-COT 1-Q4-Rejection RegionDocument15 pagesThess-DLP-COT 1-Q4-Rejection RegionThess ValerosoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Grade 11 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Grade 11 Statistics and ProbabilityMichael P. JamisNo ratings yet
- Stat Q3 WK4 Las3Document1 pageStat Q3 WK4 Las3Gladzangel LoricabvNo ratings yet
- DLL - Week - 10 - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument3 pagesDLL - Week - 10 - Statistics and ProbabilityRoboCopyNo ratings yet
- DLL Stat 5th Week For COTDocument5 pagesDLL Stat 5th Week For COTJessa May Marcos100% (1)
- DLL - Week - 9 - Statistics and ProbabilityDocument2 pagesDLL - Week - 9 - Statistics and ProbabilityRoboCopyNo ratings yet
- Name: Score: Grade & Section: DateDocument3 pagesName: Score: Grade & Section: DateJaycelyn Magboo BritaniaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Day 3Document6 pagesWeek 2 Day 3Dindin Oromedlav LoricaNo ratings yet
- 3rd WeekDocument4 pages3rd WeekArtemist FowlNo ratings yet
- Statistics DLP 03-4Document1 pageStatistics DLP 03-4Christine Enderes CastroNo ratings yet
- Cot 2ndDocument2 pagesCot 2ndYmma Bravo Malana100% (1)
- Co DoDocument4 pagesCo DoCristine LawanNo ratings yet
- DLL BudgetedDocument9 pagesDLL BudgetedAbigail Vale?No ratings yet
- Session 1/january 30 Session 2/january 31 Session 3/february 1 Session 4/february 2Document3 pagesSession 1/january 30 Session 2/january 31 Session 3/february 1 Session 4/february 2jun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 2 StatDocument4 pagesDLL Week 2 Statwilhelmina romanNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday ThursdayDocument6 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday ThursdayAnn Manuel BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- LAC Session on Hypothesis TestingDocument22 pagesLAC Session on Hypothesis TestingMauro UbungenNo ratings yet
- Stat Q3 WK3 Las2Document1 pageStat Q3 WK3 Las2Gladzangel Loricabv0% (1)
- Statistics and Probability Lesson 7Document3 pagesStatistics and Probability Lesson 7Pearl Arianne MontealegreNo ratings yet
- SP Iii-2Document10 pagesSP Iii-2DIOMEDIS POLLESCASNo ratings yet
- LP Chapter 4 Lesson 2 Point Estimation of The Population MeanDocument2 pagesLP Chapter 4 Lesson 2 Point Estimation of The Population MeanAldrin Dela Cruz0% (1)
- LP Random VariablesDocument8 pagesLP Random VariablesGary Omar PacanaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability FinalDocument3 pagesStatistics and Probability FinalGerby Godinez100% (2)
- Q4 Week 2 Week 3 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument22 pagesQ4 Week 2 Week 3 Statistics and ProbabilityAngeleehNo ratings yet
- 14 February 13 - 16, 2017Document4 pages14 February 13 - 16, 2017jun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- 1.1 TG For Normal DistributionDocument5 pages1.1 TG For Normal DistributionVincere André AlbayNo ratings yet
- DLL Stat and Probab 1st Quarter RevDocument8 pagesDLL Stat and Probab 1st Quarter RevJoselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Gen Math 1.intro and Real LifeDocument27 pagesGen Math 1.intro and Real LifeLeciram Santiago MasikipNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grading Stat and Prob 2017-2018Document3 pages3rd Grading Stat and Prob 2017-2018Mariel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- GENMATHWEEK9Document1 pageGENMATHWEEK9Pia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Null and Alternative Hypothesis: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesNull and Alternative Hypothesis: I. ObjectivesJohn ClausNo ratings yet
- Detaled Lesson Plan in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument4 pagesDetaled Lesson Plan in Statistics and ProbabilitykarrenNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Statistics and Probability November 5, 2019Document2 pagesLesson Plan in Statistics and Probability November 5, 2019Elmer Piad100% (1)
- School Statistics Lesson on Mean and VarianceDocument17 pagesSchool Statistics Lesson on Mean and VarianceJay Jay h. JantarNo ratings yet
- DLL GenMath Logarithmic2Document3 pagesDLL GenMath Logarithmic2Nicole Mosca100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Statistics and Probability October 29, 2019Document3 pagesLesson Plan in Statistics and Probability October 29, 2019Elmer PiadNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob Q1 W6Document7 pagesStat and Prob Q1 W6Nimrod LadianaNo ratings yet
- CCNHS statistics lessonDocument6 pagesCCNHS statistics lessonjun del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Thess-DLP-COT Q4-Testing HypothesisDocument14 pagesThess-DLP-COT Q4-Testing HypothesisThess ValerosoNo ratings yet
- Stat 5Document20 pagesStat 5denizsaday100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Statistics and Probability November 13, 2019Document2 pagesLesson Plan in Statistics and Probability November 13, 2019Elmer PiadNo ratings yet
- Contextualized LP in General MathematicsDocument6 pagesContextualized LP in General MathematicsSerdnelem Rhodz MacedaNo ratings yet
- Stat Module Q3 Week1Document11 pagesStat Module Q3 Week1Eloisa Jane BituinNo ratings yet
- SP Midterm ReviewerDocument2 pagesSP Midterm ReviewersNo ratings yet
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocument5 pagesStatistics and ProbabilityMario Anacleto0% (2)
- Statistics and ProbabililityDocument6 pagesStatistics and ProbabililityTricia MendozaNo ratings yet
- Peace Corps Facilitator Retreat - Oct 2013 REQUEST FOR PROPOSALDocument2 pagesPeace Corps Facilitator Retreat - Oct 2013 REQUEST FOR PROPOSALAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps DocumentsNo ratings yet
- Roj and Venchu Thesis RevisedDocument30 pagesRoj and Venchu Thesis RevisedMark Robles Salvador87% (15)
- Delyana - English Teaching by Project-Based Learning - Creating Game Made by Microsoft Power PointDocument18 pagesDelyana - English Teaching by Project-Based Learning - Creating Game Made by Microsoft Power PointDelyana EbNo ratings yet
- Science Fairs and ExhibitionsDocument26 pagesScience Fairs and ExhibitionsBincyNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter May 2-4, 2023 3isDocument6 pages4th Quarter May 2-4, 2023 3isSharlene Jane Chavez EleccionNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On GeosyntheticsDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Geosyntheticsvasej0nig1z3100% (1)
- Enhancing English Macro Skills of Vietnamese College StudentsDocument26 pagesEnhancing English Macro Skills of Vietnamese College StudentsBùi Thị Kiều GiangNo ratings yet
- Graham Macphee The Architecture of The Visible Technology and Urban Visual CultureDocument241 pagesGraham Macphee The Architecture of The Visible Technology and Urban Visual Cultureasf-asfNo ratings yet
- Ford Porject CharterDocument12 pagesFord Porject Charterrishabh mehraNo ratings yet
- Stephen CurrentOpinionPsych 101215 PDFDocument16 pagesStephen CurrentOpinionPsych 101215 PDFNeil RamonedaNo ratings yet
- IABSE 1999 - Foundation For Major BridgesDocument365 pagesIABSE 1999 - Foundation For Major BridgesKrzysztof Szewczyk100% (2)
- Director Project Management Pharmaceuticals in Strasbourg France CV Resume Pascale ClementDocument3 pagesDirector Project Management Pharmaceuticals in Strasbourg France CV Resume Pascale ClementPascaleClementNo ratings yet
- Lcup Compre Stat Review EditedDocument44 pagesLcup Compre Stat Review EditedJoseph Cabrera100% (1)
- Traffic Thesis StatementDocument5 pagesTraffic Thesis StatementDustin Pytko100% (2)
- London Mathematical SocietyDocument56 pagesLondon Mathematical SocietyRommel CGNo ratings yet
- Pg. 36 Syllabus 4.58 ME - MECH-MFG SYSTEMDocument49 pagesPg. 36 Syllabus 4.58 ME - MECH-MFG SYSTEMShoaib ShaikNo ratings yet
- 05 N318 30162Document21 pages05 N318 30162Dani PhilipNo ratings yet
- Access at This Point - With Perhaps 15-20 Percent of Research Articles Made FreelyDocument23 pagesAccess at This Point - With Perhaps 15-20 Percent of Research Articles Made FreelyIchlasulNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management MCQDocument9 pagesMarketing Management MCQanuj singhNo ratings yet
- The Latest Advancements in Delayed Coke Drums Inspection Reliability Techniques Harold CIA Mumbai 2016 PDFDocument23 pagesThe Latest Advancements in Delayed Coke Drums Inspection Reliability Techniques Harold CIA Mumbai 2016 PDFFayaz MohammedNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument19 pagesLearning Stylesclarissa renoloNo ratings yet
- Siregar Et Al 2020Document15 pagesSiregar Et Al 2020UtamiNo ratings yet
- Connecting Self-Regulated Learning and Performance With Instruction Across High School Leanring Content AreasDocument468 pagesConnecting Self-Regulated Learning and Performance With Instruction Across High School Leanring Content Areasebrown7100% (1)
- ENGR 100 Bridge ReportDocument6 pagesENGR 100 Bridge ReportPresidaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper MCQ 2Document72 pagesResearch Paper MCQ 2AamirKhanMohmandNo ratings yet
- Health Facilities and Services Regulatory Bureau: Republic of The Philippines Department of HealthDocument60 pagesHealth Facilities and Services Regulatory Bureau: Republic of The Philippines Department of HealthMichael Capuyan JrNo ratings yet
- Work MethodsDocument82 pagesWork MethodsHRUSHIKESH MANENo ratings yet
- Advanced Database Multiple Choice QuestionDocument6 pagesAdvanced Database Multiple Choice QuestionGashaw MekonnenNo ratings yet
- (PDF) Village Road ConstructionDocument25 pages(PDF) Village Road ConstructionpradeepNo ratings yet
- Research Topics UPSLISDocument6 pagesResearch Topics UPSLISChristian Robert NalicaNo ratings yet