Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Measure Electricity with Ammeters & Voltmeters
Uploaded by
muhammad zeeshanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Measure Electricity with Ammeters & Voltmeters
Uploaded by
muhammad zeeshanCopyright:
Available Formats
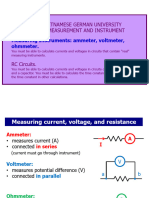
AMMETER-VOLTMETER
AMMETER www.citycollegiate.com
Ammeter is an electrical measuring device, which is used to measure electric current through the
circuit. It is the modified form of galvanometer
CONNECTION OF AMMETER IN CIRCUIT
An ammeter is always connected in series to a circuit.
SYMBOL
For latest information , free computer courses and high impact notes visit www.citycollegiate.com
CONVERSION OF GALVANOMETER
INTO AMMETER
Since Galvanometer is a very sensitive instrument therefore it can’t measure heavy currents. In order to
convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter, a very low resistance known as "shunt" resistance is
connected in parallel to Galvanometer. Value of shunt is so adjusted that most of the current passes
through the shunt. In this way a Galvanometer is converted into Ammeter and can measure heavy
currents without fully deflected.
VALUE OF SHUNT RESISTANCE www.citycollegiate.com
Let resistance of galvanometer = Rg and it gives full-scale deflection when current Ig is passed through
it. Then,
Vg = IgRg -------(i)
Let a shunt of resistance (Rs) is connected in parallel to galvanometer. If total current through the
circuit is I.
Then current through shunt:
Is = (I-Ig)
potential difference across the shunt:
Vs= IsRs
or
Vs = (I – Ig)Rs -------(ii)
But
Vs =Vg
(I - Ig)Rs = IgRg
VOLT METER
Voltmeter is an electrical measuring device, which is used to measure potential difference between two
points in a circuit.
CONNECTION OF VOLTMETER IN CIRCUIT
Voltmeter is always connected in parallel to a circuit.
SYMBOL
CONVERSION OF GALVANOMETER INTO
VOLTMETER www.citycollegiate.com
Since Galvanometer is a very sensitive instrument, therefore it can not measure high potential
difference. In order to convert a Galvanometer into voltmeter, a very high resistance known as "series
resistance" is connected in series with the galvanometer.
VALUE OF SERIES RESISTANCE www.citycollegiate.com
Let resistance of galvanometer = Rg and resistance Rx (high) is connected in series to it. Then
combined resistance = (Rg + Rx).
If potential between the points to be measured = V and if galvanometer gives full-scale deflection,
when current "Ig" passes through it. Then,
V = Ig (Rg + Rx)
V = IgRg + IgRx
V – IgRg = IgRx
Rx = (V – IgRg)/Ig
Thus Rx can be found.
For latest information , free computer courses and high impact notes visit www.citycollegiate.com
|PHOTOSHOP|FLASH|SWISH|FLAX|INTERNET|PHYSICS|CHEMISTRY|HOME|
You might also like
- Tuning spark ignition engines with the ECUMaster EMU BlackDocument230 pagesTuning spark ignition engines with the ECUMaster EMU Blacksxp100% (1)
- Multimeter VIMPDocument61 pagesMultimeter VIMPSysu KumarNo ratings yet
- RJTTDocument98 pagesRJTTA340_600No ratings yet
- 111307149-Dash-8-PHB-a28-1146-041 2 PDFDocument241 pages111307149-Dash-8-PHB-a28-1146-041 2 PDFjul100% (2)
- Shorthand IFR ClearanceDocument3 pagesShorthand IFR ClearanceGabriel Sanchez100% (1)
- The Scanning Electron MicroscopeDocument65 pagesThe Scanning Electron MicroscopeCORE Materials67% (3)
- Adf & NDBDocument20 pagesAdf & NDBNier JavierNo ratings yet
- JFK DP AllDocument14 pagesJFK DP AllH89SANo ratings yet
- Physics Project: ON Moving Coil GalvanometerDocument22 pagesPhysics Project: ON Moving Coil GalvanometerRISHIK100% (5)
- Zamboanga RPMZ Zam PDFDocument25 pagesZamboanga RPMZ Zam PDFochiSultonéNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterDocument19 pagesPhysics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterSHIWANI MOHAN88% (8)
- Saahir PhysicsDocument3 pagesSaahir PhysicsMuhammad QadirNo ratings yet
- Galvanometer's Conversion To Ammeter and VoltmeterDocument1 pageGalvanometer's Conversion To Ammeter and Voltmeteranshvishwakarma2005No ratings yet
- GALVANOMTER DEMONSTRATIONDocument14 pagesGALVANOMTER DEMONSTRATIONRose ytNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterDocument19 pagesPhysics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterAbhi SableNo ratings yet
- Galvanometer ConversionDocument7 pagesGalvanometer Conversionashwin_airNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To AmmeterDocument15 pagesPhysics Project On Convertion of Gslvanometer To Ammeterharshilsapariya501No ratings yet
- Galvanometer To VoltmeterDocument6 pagesGalvanometer To Voltmeterمغیث الحسنNo ratings yet
- Thevininas THMDocument8 pagesThevininas THMaamer_shahbaazNo ratings yet
- Physics KabaDocument24 pagesPhysics KabaPrahlad ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Measurement of ResistanceDocument96 pagesMeasurement of ResistancePraveena BNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Week 1 Electrical MetersDocument14 pages2nd Quarter Week 1 Electrical MetersjNo ratings yet
- Experiment 05Document3 pagesExperiment 05himanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- Instrument MeasurementDocument6 pagesInstrument MeasurementMarlon Desacula IINo ratings yet
- How to Measure Electrical Quantities with MultimetersDocument9 pagesHow to Measure Electrical Quantities with MultimetersTaufiq Fahlifi YfzerobrrNo ratings yet
- Conversion of GalvanometerDocument13 pagesConversion of GalvanometerSimar Kaur100% (1)
- Analog Measuring InstrumentsDocument43 pagesAnalog Measuring Instrumentsmuvvala charithaNo ratings yet
- PMMC Instrument: DC Voltmeter and Ammeter: Abstract-The Permanent-Magnet Moving-CoilDocument5 pagesPMMC Instrument: DC Voltmeter and Ammeter: Abstract-The Permanent-Magnet Moving-CoilCj LlemosNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument1 pageElectricitywakakkaNo ratings yet
- Measuring InstrumentsDocument28 pagesMeasuring InstrumentsRemotsaletswe MoalosiNo ratings yet
- 2 Binoy GalvanometerDocument47 pages2 Binoy GalvanometersujeenNo ratings yet
- Emi Load EffectDocument49 pagesEmi Load Effect12a3.letuananh.05No ratings yet
- Experiment # 5Document7 pagesExperiment # 5Abdullah TahirNo ratings yet
- Analog Electrical Devices and MeasurementsDocument21 pagesAnalog Electrical Devices and MeasurementsGabriel MarzinottoNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Extra High Voltage Long Transmission LinesDocument15 pagesSimulation of Extra High Voltage Long Transmission LinesAshish Tyagi0% (1)
- Conversion of Galvanometer Into VoltmeterDocument1 pageConversion of Galvanometer Into VoltmeterKhadim ShahNo ratings yet
- Phys 212Document39 pagesPhys 212Tilahun TesfayeNo ratings yet
- EMMI Manual 022210224626 6Document29 pagesEMMI Manual 022210224626 6Rudresh AravapalliNo ratings yet
- Static RelayDocument62 pagesStatic Relayannamalaiasmani1551No ratings yet
- NotesDocument11 pagesNotesDILIP KUMAR BairagiNo ratings yet
- VoltmetersDocument35 pagesVoltmetersjunaydNo ratings yet
- Ammeter, Voltmeter, and OhmmeterDocument21 pagesAmmeter, Voltmeter, and OhmmeterKenji XenonNo ratings yet
- Dynamometer Type WattmeterDocument9 pagesDynamometer Type WattmeterChauhan AyushmaanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document49 pagesLecture 13Rafael Mappala DagasaoNo ratings yet
- 1082-LAB 10 Voltmeters and AmmetersDocument9 pages1082-LAB 10 Voltmeters and AmmetersNghi TranNo ratings yet
- Ammeter and VoltmeterDocument29 pagesAmmeter and Voltmeterashutoshmall444No ratings yet
- Series Parallel Circuit Ammeter and VoltmeterDocument32 pagesSeries Parallel Circuit Ammeter and VoltmeterJohn Paulo De LeonNo ratings yet
- Tle Reviewer Pt. 4Document4 pagesTle Reviewer Pt. 4Anonymous lnq6NlgaMNo ratings yet
- Comsat S University Islamabad: Course Title: Course Name: Lab: Group MembersDocument3 pagesComsat S University Islamabad: Course Title: Course Name: Lab: Group MembersMalik ZohaibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Direct Current MetersDocument42 pagesChapter 2 - Direct Current MetersANDREW LEONG CHUN TATT STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Moving Coil GalvanometerDocument13 pagesMoving Coil GalvanometerSaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2-Masterclass Solar - Electrical Fundamentals Batch 29Document40 pages2-Masterclass Solar - Electrical Fundamentals Batch 29Anthony PoldoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 05Document24 pagesLecture Notes 05Abdul Hakeem Semar KamaluddinNo ratings yet
- 2 Pulse CircuitsDocument74 pages2 Pulse CircuitsWaqar Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Connecting Voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter in A Circuit SunilSaharanDocument2 pagesConnecting Voltmeter, Ammeter and Wattmeter in A Circuit SunilSaharanPankaj Kumar Singh100% (1)
- AC & DC MetersDocument2 pagesAC & DC Metersk85yfbwhynNo ratings yet
- BridgectsDocument11 pagesBridgectsAshish ParasharNo ratings yet
- 26 - Direct-Current Circuits - R K Parida.Document11 pages26 - Direct-Current Circuits - R K Parida.MonicaNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits 2Document34 pagesDC Circuits 2safwanz2000No ratings yet
- Slides For CLass 1 EMDDocument49 pagesSlides For CLass 1 EMDKuppan Chetty RamanathanNo ratings yet
- ECE3155 Ex 4 Nonlinear CktsDocument9 pagesECE3155 Ex 4 Nonlinear Cktsअजय ढकालNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument8 pagesElectricitylohitha charyNo ratings yet
- Analog IDocument27 pagesAnalog IAamir Ahmed Ali Salih100% (1)
- MDocument1 pageMmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- A Production Lot Contains Hundred Items Five of Which Are DefectiveDocument2 pagesA Production Lot Contains Hundred Items Five of Which Are Defectivemuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument1 pageAnswermuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Star BurnDocument9 pagesStar BurnnireadaetaNo ratings yet
- Course outline-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesCourse outline-WPS Officemuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Physics Department Date Sheet for Mid-Term ExamsDocument3 pagesPhysics Department Date Sheet for Mid-Term Examsmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Course outline-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesCourse outline-WPS Officemuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Course outline-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesCourse outline-WPS Officemuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- KDocument1 pageKmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- ROLE OF TEACHER AS LEADER IN ISLAMIC PERSPECTIVEDocument20 pagesROLE OF TEACHER AS LEADER IN ISLAMIC PERSPECTIVEmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Anas B-EDocument41 pagesAnas B-Emuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Transverse Standing Waves Resonance and The Overtone Series Mersenne's Laws Longitudinal Standing Waves Other Standing Waves and ApplicationsDocument52 pagesTransverse Standing Waves Resonance and The Overtone Series Mersenne's Laws Longitudinal Standing Waves Other Standing Waves and Applicationsmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Decibel GainDocument17 pagesDecibel Gainmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- (Part 2) : Gain, Attenuation, DecibelsDocument18 pages(Part 2) : Gain, Attenuation, Decibelsmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2muhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Physics Chapter#2, Kinematics Problem #2.1-2.2: By: Muhammad Zeeshan Easy LearningDocument4 pagesClass 9 Physics Chapter#2, Kinematics Problem #2.1-2.2: By: Muhammad Zeeshan Easy Learningmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Role of Teacher As Leader in Islamic PerspectiveDocument4 pagesRole of Teacher As Leader in Islamic Perspectivemuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- KjkoDocument1 pageKjkomuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Wiley BeraDocument24 pagesWiley Beramuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Measure Electricity with Ammeters & VoltmetersDocument2 pagesMeasure Electricity with Ammeters & Voltmetersmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- ThesisGuidelines PDFDocument14 pagesThesisGuidelines PDFPiyushNo ratings yet
- Entry Test M.Phil Physics Spring 2020Document3 pagesEntry Test M.Phil Physics Spring 2020muhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- 3PostNotes PDFDocument6 pages3PostNotes PDFG Nathan JdNo ratings yet
- Abdul Salam Academy Peoples Colony#1 FSDDocument1 pageAbdul Salam Academy Peoples Colony#1 FSDmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- KjkoDocument1 pageKjkomuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- Scalor and Vector DefinitionsDocument28 pagesScalor and Vector Definitionsmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- LLKLDocument1 pageLLKLmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- LLKLDocument1 pageLLKLmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- LLKLDocument1 pageLLKLmuhammad zeeshanNo ratings yet
- CMS HD-1100 - Sensor de Deteccion GLPDocument1 pageCMS HD-1100 - Sensor de Deteccion GLPNestor Raul YamunaqueNo ratings yet
- ClocksDocument1 pageClocksmervetiryakiNo ratings yet
- Vor Dme 1 Rwy 09Document1 pageVor Dme 1 Rwy 09Manuel AscencioNo ratings yet
- RC Dan FLIP FLOP IC 555Document24 pagesRC Dan FLIP FLOP IC 555assaNo ratings yet
- Lemd PDFDocument60 pagesLemd PDFJason GonzalezNo ratings yet
- WADY - BanyuwangiDocument4 pagesWADY - BanyuwangiLandy FebriansyahNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Session 2 of 2019Document4 pagesModule 13 Session 2 of 2019HshsjNo ratings yet
- LSZH App1 Ils14 PDFDocument1 pageLSZH App1 Ils14 PDFManuel KauppNo ratings yet
- SBJVSBGR PDF 24may21Document31 pagesSBJVSBGR PDF 24may21Francisco FortesNo ratings yet
- SBGRSBCF5Document33 pagesSBGRSBCF5SR ZECA URUBUNo ratings yet
- SECU (Mariscal Lamar)Document14 pagesSECU (Mariscal Lamar)GuilhermeVasconcelosNo ratings yet
- ADF and Finisher Paper Jam CodesDocument10 pagesADF and Finisher Paper Jam CodesRicho DeepNo ratings yet
- SKIPPER COMBO TANK PARTS LISTDocument12 pagesSKIPPER COMBO TANK PARTS LISTsonotiumNo ratings yet
- Wsap Payalebar 1122Document8 pagesWsap Payalebar 1122jepriendoNo ratings yet
- Instrument Approach Chart - Icao: WSD34 500ft ALT GND Wsr6 200ft ALT GNDDocument1 pageInstrument Approach Chart - Icao: WSD34 500ft ALT GND Wsr6 200ft ALT GNDabang fayyadNo ratings yet
- Calibrating Precision Measurement ToolsDocument2 pagesCalibrating Precision Measurement ToolselavarasanNo ratings yet
- Explore Zanzibar's Abeid Amani Karume International AirportDocument2 pagesExplore Zanzibar's Abeid Amani Karume International AirportМистермарк МистерклимюкNo ratings yet
- Barometer - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument5 pagesBarometer - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Cal. V195Document25 pagesCal. V195Gianluca ScarselliNo ratings yet
- Introduction Measuring Instruments Ammeter Voltmeter Multimeter OscilloscopeDocument10 pagesIntroduction Measuring Instruments Ammeter Voltmeter Multimeter Oscilloscopekumar_sushil850No ratings yet
- Typical Calibration Procedures For SphygmomanometersDocument1 pageTypical Calibration Procedures For SphygmomanometersHealth Care Without Harm - Asia100% (2)
- Adjustments of The Wye LevelDocument2 pagesAdjustments of The Wye Levelgemma_austria21100% (1)